sodium glycocholate | 863-57-0
中文名称
——
中文别名
——
英文名称
sodium glycocholate
英文别名
glycocholic acid sodium salt;sodium glycocholic acid;sodium;(4R)-N-(carboxymethyl)-4-[(3R,5S,7R,8R,9S,10S,12S,13R,14S,17R)-3,7,12-trihydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]pentanimidate
CAS
863-57-0
化学式
C26H42NO6*Na
mdl
——
分子量
487.612
InChiKey
OABYVIYXWMZFFJ-ZUHYDKSRSA-M
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:210-215 °C (subl.)(lit.)
-
溶解度:DMSO(微溶)、乙醇(微溶)、甲醇(微溶)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-1.77
-
重原子数:34
-
可旋转键数:6
-
环数:4.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.92
-
拓扑面积:130
-
氢给体数:4
-
氢受体数:6
安全信息
-
安全说明:S22,S24/25
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:29242990
-
RTECS号:MB9265100
-
储存条件:密封干燥保存。
SDS
Material Safety Data Sheet
Section 1. Identification of the substance
Product Name: Sodium glycocholate
Synonyms:
Section 2. Hazards identification
Harmful by inhalation, in contact with skin, and if swallowed.
Section 3. Composition/information on ingredients.
Ingredient name: Sodium glycocholate
CAS number: 863-57-0
Section 4. First aid measures
Skin contact: Immediately wash skin with copious amounts of water for at least 15 minutes while removing
contaminated clothing and shoes. If irritation persists, seek medical attention.
Eye contact: Immediately wash skin with copious amounts of water for at least 15 minutes. Assure adequate
flushing of the eyes by separating the eyelids with fingers. If irritation persists, seek medical
attention.
Inhalation: Remove to fresh air. In severe cases or if symptoms persist, seek medical attention.
Ingestion: Wash out mouth with copious amounts of water for at least 15 minutes. Seek medical attention.
Section 5. Fire fighting measures
In the event of a fire involving this material, alone or in combination with other materials, use dry
powder or carbon dioxide extinguishers. Protective clothing and self-contained breathing apparatus
should be worn.
Section 6. Accidental release measures
Personal precautions: Wear suitable personal protective equipment which performs satisfactorily and meets local/state/national
standards.
Respiratory precaution: Wear approved mask/respirator
Hand precaution: Wear suitable gloves/gauntlets
Skin protection: Wear suitable protective clothing
Eye protection: Wear suitable eye protection
Methods for cleaning up: Mix with sand or similar inert absorbent material, sweep up and keep in a tightly closed container
for disposal. See section 12.
Environmental precautions: Do not allow material to enter drains or water courses.
Section 7. Handling and storage
Handling: This product should be handled only by, or under the close supervision of, those properly qualified
in the handling and use of potentially hazardous chemicals, who should take into account the fire,
health and chemical hazard data given on this sheet.
Storage: Store in closed vessels, refrigerated.
Section 8. Exposure Controls / Personal protection
Engineering Controls: Use only in a chemical fume hood.
Personal protective equipment: Wear laboratory clothing, chemical-resistant gloves and safety goggles.
General hydiene measures: Wash thoroughly after handling. Wash contaminated clothing before reuse.
Section 9. Physical and chemical properties
Appearance: Not specified
Boiling point: No data
Melting point: No data
Flash point: No data
Density: No data
Molecular formula: C26H42NO6.Na
Molecular weight: 487.6
Section 10. Stability and reactivity
Conditions to avoid: Heat, flames and sparks.
Materials to avoid: Oxidizing agents.
Possible hazardous combustion products: Carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides.
Section 11. Toxicological information
No data.
Section 12. Ecological information
No data.
Section 13. Disposal consideration
Arrange disposal as special waste, by licensed disposal company, in consultation with local waste
disposal authority, in accordance with national and regional regulations.
Section 14. Transportation information
Non-harzardous for air and ground transportation.
Section 15. Regulatory information
No chemicals in this material are subject to the reporting requirements of SARA Title III, Section
302, or have known CAS numbers that exceed the threshold reporting levels established by SARA
Title III, Section 313.
SECTION 16 - ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
N/A
Section 1. Identification of the substance
Product Name: Sodium glycocholate
Synonyms:
Section 2. Hazards identification
Harmful by inhalation, in contact with skin, and if swallowed.
Section 3. Composition/information on ingredients.
Ingredient name: Sodium glycocholate
CAS number: 863-57-0
Section 4. First aid measures
Skin contact: Immediately wash skin with copious amounts of water for at least 15 minutes while removing
contaminated clothing and shoes. If irritation persists, seek medical attention.
Eye contact: Immediately wash skin with copious amounts of water for at least 15 minutes. Assure adequate
flushing of the eyes by separating the eyelids with fingers. If irritation persists, seek medical
attention.
Inhalation: Remove to fresh air. In severe cases or if symptoms persist, seek medical attention.
Ingestion: Wash out mouth with copious amounts of water for at least 15 minutes. Seek medical attention.
Section 5. Fire fighting measures
In the event of a fire involving this material, alone or in combination with other materials, use dry
powder or carbon dioxide extinguishers. Protective clothing and self-contained breathing apparatus
should be worn.
Section 6. Accidental release measures
Personal precautions: Wear suitable personal protective equipment which performs satisfactorily and meets local/state/national
standards.
Respiratory precaution: Wear approved mask/respirator
Hand precaution: Wear suitable gloves/gauntlets
Skin protection: Wear suitable protective clothing
Eye protection: Wear suitable eye protection
Methods for cleaning up: Mix with sand or similar inert absorbent material, sweep up and keep in a tightly closed container
for disposal. See section 12.
Environmental precautions: Do not allow material to enter drains or water courses.
Section 7. Handling and storage
Handling: This product should be handled only by, or under the close supervision of, those properly qualified
in the handling and use of potentially hazardous chemicals, who should take into account the fire,
health and chemical hazard data given on this sheet.
Storage: Store in closed vessels, refrigerated.
Section 8. Exposure Controls / Personal protection
Engineering Controls: Use only in a chemical fume hood.
Personal protective equipment: Wear laboratory clothing, chemical-resistant gloves and safety goggles.
General hydiene measures: Wash thoroughly after handling. Wash contaminated clothing before reuse.
Section 9. Physical and chemical properties
Appearance: Not specified
Boiling point: No data
Melting point: No data
Flash point: No data
Density: No data
Molecular formula: C26H42NO6.Na
Molecular weight: 487.6
Section 10. Stability and reactivity
Conditions to avoid: Heat, flames and sparks.
Materials to avoid: Oxidizing agents.
Possible hazardous combustion products: Carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides.
Section 11. Toxicological information
No data.
Section 12. Ecological information
No data.
Section 13. Disposal consideration
Arrange disposal as special waste, by licensed disposal company, in consultation with local waste
disposal authority, in accordance with national and regional regulations.
Section 14. Transportation information
Non-harzardous for air and ground transportation.
Section 15. Regulatory information
No chemicals in this material are subject to the reporting requirements of SARA Title III, Section
302, or have known CAS numbers that exceed the threshold reporting levels established by SARA
Title III, Section 313.
SECTION 16 - ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
N/A
制备方法与用途
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:sodium glycocholate 在 nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide 乙二胺四乙酸 、 7β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 、 chloylglycine hydrolase 、 Sepharose-CL6B 、 TEA 、 2-巯基乙醇 作用下, 以 phosphate buffer 、 水 为溶剂, 反应 120.33h, 生成 7-酮基-3alpha,12alpha-二羟基胆烷酸参考文献:名称:Xanthomonas maltophilia CBS 897.97 as a source of new 7β- and 7α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases and cholylglycine hydrolase: Improved biotransformations of bile acids摘要:The paper reports the partial purification and characterization of the 7 beta- and 7 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases (HSDH) and cholylglycine hydrolase (CGH), isolated from Xanthomonas maltophilia CBS 897.97. The activity of 7 beta-HSDH and 7 alpha-HSDH in the reduction of the 7-keto bile acids is determined. The affinity of 7 beta-HSDH for bile acids is confirmed by the reduction, on analytical scale, to the corresponding 7 beta-OH derivatives. A crude mixture of 7 alpha- and 7 beta-HSDH, in soluble or immobilized form, is employed in the synthesis, on preparative scale, of ursocholic and ursodeoxycholic acids starting from the corresponding 7 alpha-derivatives. On the other hand, a partially purified 7 beta-HSDH in a double enzyme system, where the couple formate/formate dehydrogenase allows the cofactor recycle, affords 6 alpha-fluoro-3 alpha, 7 beta-dihydroxy-5 beta-cholan-24-oic acid (6-FUDCA) by reduction of the corresponding 7-keto derivative. This compound is not obtainable by microbiological route. The efficient and mild hydrolysis of glycinates and taurinates of bile acids with CGH is also reported. Very promising results are also obtained with bile acid containing raw materials. (c) 2005 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.DOI:10.1016/j.steroids.2005.10.002
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:甘氨酸和牛磺酸缀合的胆汁盐的连续流动合成和放大†摘要:胆汁酸的N-酰基酰胺化的多克规模方案甘氨酸 和 牛磺酸已在连续流处理条件下成功开发。选择中熊去氧胆酸 (UDCA)作为模型化合物, N-乙氧基羰基-2-乙氧基-1,2-二氢喹啉(EEDQ)作为凝结剂,采用了模块化的中反应器辅助流动装置来显着加快反应条件的优化和流动规模的合成。报告并讨论了以收率,在线纯化,分析以及为优化反应和大规模生产而实施的流量设置方面的结果。DOI:10.1039/c2ob25528f
-
作为试剂:描述:参考文献:名称:Vercellone, 1938, vol. 25, p. 207,211摘要:DOI:
文献信息
-
Thermodynamics and structure of inclusion compounds of tauro- and glyco-conjugated bile salts and β-cyclodextrin作者:René Holm、Wei Shi、Rune A. Hartvig、Sune Askjær、Jens Christian Madsen、Peter WesthDOI:10.1039/b820487j日期:——The interaction between natural β-cyclodextrin and bile salts common in rat, dog and man, taurocholate, tauro-β-muricholate, taurodeoxycholate, taurochenodeoxycholate, glycocholate, glycodeoxycholate and glycochenodeoxycholate, was studied using isothermal titration calorimetry, and the structural differences in the interaction were investigated by 1H-ROESY NMR and molecular modeling. The β-cyclodextrin was selected based upon its frequent use in preformulation and drug formulation as oral excipients for the solubilization of drug substances with low aqueous solubility. All the investigated bile salts possessed affinity for the cyclodextrin, though with large variations in the stability constants. The variations in the enthalpic and entropic contributions to the overall Gibbs free energy and consequently the stability constants revealed differences in the binding mode between the investigated bile salts, i.e. the bile salts with a hydroxyl group on C12 interacted differently from the bile salts without this hydroxyl group. These observations were supported by both 1H-ROESY NMR and molecular modeling, which suggested binding on the D-ring in the steroid structure for the former and on the C-ring for the latter bile salts.采用等温滴定量热法研究了天然δ-环糊精与大鼠、狗和人体内常见的胆盐(牛胆酸盐、牛δ-臼胆酸盐、牛脱氧胆酸盐、牛酚脱氧胆酸盐、甘氨胆酸盐、甘氨脱氧胆酸盐和甘氨苯脱氧胆酸盐)之间的相互作用,并通过 1H-ROESY NMR 和分子建模研究了相互作用中的结构差异。之所以选择δ-环糊精,是因为它经常作为口服辅料用于制剂前和药物制剂中,以增溶水溶性较低的药物物质。所有研究的胆汁盐都与环糊精具有亲和性,但稳定性常数差异较大。总体吉布斯自由能的焓贡献和熵贡献的变化以及由此产生的稳定性常数揭示了所研究胆汁盐之间结合模式的差异,即 C12 上带有羟基的胆汁盐与不带羟基的胆汁盐的相互作用方式不同。这些观察结果得到了 1H-ROESY NMR 和分子建模的支持,前者认为与类固醇结构中的 D 环结合,后者认为与 C 环结合。
-
Enzymic .alpha./.beta. inversion of C-3 hydroxyl of bile acids and study of the effects of organic solvents on reaction rates作者:Sergio Riva、Roberto Bovara、Lucia Zetta、Piero Pasta、Gianluca Ottolina、Giacomo CarreaDOI:10.1021/jo00236a018日期:1988.1
-
RIVA, SERGIO;BOVARA, ROBERTO;ZETTA, LUCIA;PASTA, PIERO;OTTOLINA, GIANLUCA+, J. ORG. CHEM., 53,(1988) N 1, 88-92作者:RIVA, SERGIO、BOVARA, ROBERTO、ZETTA, LUCIA、PASTA, PIERO、OTTOLINA, GIANLUCA+DOI:——日期:——
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
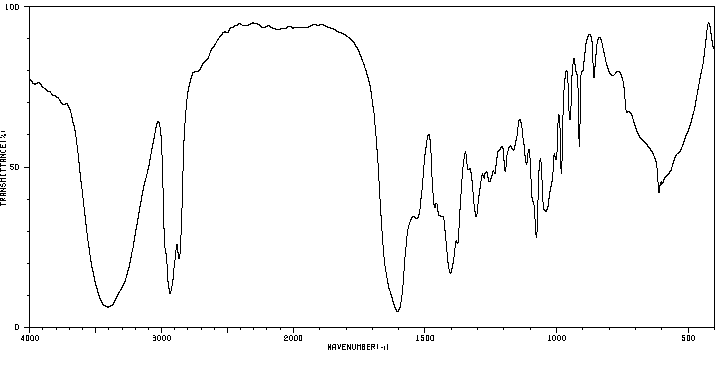
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(5β)-17,20:20,21-双[亚甲基双(氧基)]孕烷-3-酮
(5α)-2′H-雄甾-2-烯并[3,2-c]吡唑-17-酮
(3β,20S)-4,4,20-三甲基-21-[[[三(异丙基)甲硅烷基]氧基]-孕烷-5-烯-3-醇-d6
(25S)-δ7-大发酸
(20R)-孕烯-4-烯-3,17,20-三醇
(11β,17β)-11-[4-({5-[(4,4,5,5,5-五氟戊基)磺酰基]戊基}氧基)苯基]雌二醇-1,3,5(10)-三烯-3,17-二醇
齐墩果酸衍生物1
黄麻属甙
黄芪皂苷III
黄芪皂苷 II
黄芪甲苷 IV
黄芪甲苷
黄肉楠碱
黄果茄甾醇
黄杨醇碱E
黄姜A
黄夹苷B
黄夹苷
黄夹次甙乙
黄夹次甙乙
黄夹次甙丙
黄体酮环20-(乙烯缩醛)
黄体酮杂质EPL
黄体酮杂质1
黄体酮杂质
黄体酮杂质
黄体酮EP杂质M
黄体酮EP杂质G(RRT≈2.53)
黄体酮EP杂质F
黄体酮6-半琥珀酸酯
黄体酮 17alpha-氢过氧化物
黄体酮 11-半琥珀酸酯
黄体酮
麦角甾醇葡萄糖苷
麦角甾醇氢琥珀酸盐
麦角甾烷-6-酮,2,3-环氧-22,23-二羟基-,(2b,3b,5a,22R,23R,24S)-(9CI)
麦角甾烷-3,6,8,15,16-五唑,28-[[2-O-(2,4-二-O-甲基-b-D-吡喃木糖基)-a-L-呋喃阿拉伯糖基]氧代]-,(3b,5a,6a,15b,16b,24x)-(9CI)
麦角甾烷-26-酸,5,6:24,25-二环氧-14,17,22-三羟基-1-羰基-,d-内酯,(5b,6b,14b,17a,22R,24S,25S)-(9CI)
麦角甾-8-烯-3-醇
麦角甾-8,24(28)-二烯-26-酸,7-羟基-4-甲基-3,11-二羰基-,(4a,5a,7b,25S)-
麦角甾-7,22-二烯-3-酮
麦角甾-7,22-二烯-17-醇-3-酮
麦角甾-5,24-二烯-26-酸,3-(b-D-吡喃葡萄糖氧基)-1,22,27-三羟基-,d-内酯,(1a,3b,22R)-
麦角甾-5,22,25-三烯-3-醇
麦角甾-4,6,8(14),22-四烯-3-酮
麦角甾-1,4-二烯-3-酮,7,24-二(乙酰氧基)-17,22-环氧-16,25-二羟基-,(7a,16b,22R)-(9CI)
麦角固醇
麦冬皂苷D
麦冬皂苷D
麦冬皂苷 B