2-氨基屈 | 789-47-9
中文名称
2-氨基屈
中文别名
——
英文名称
2-Aminochrysene
英文别名
chrysen-2-amine;2-chrysenamine;chrysene-2-amine;Chrysen-amin-(2);2-Amino-chrysen
CAS
789-47-9
化学式
C18H13N
mdl
MFCD00046286
分子量
243.308
InChiKey
KSDIHKMNSYWRFB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):4.8
-
重原子数:19
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:4.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:26
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:1
SDS
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:铜(II)介导的2-氨基萘同系物的氧化偶联。直接二聚化和咔唑形成之间的竞争。摘要:尽管Cu(II)介导的2-氨基萘7a和7b的氧化偶合分别形成了1,1'-联萘13a和13b,但它们的较高同系物和同源物8-12却表现出不同反应模式。因此,2-氨基蒽(8)得到预期的联蒽衍生物15和咔唑16的约1:1混合物,而9-氨基菲(10),3-苯基-1-氨基萘(11)和2-氨基ch (12)几乎分别分别生产了相应的咔唑19、20和21。相反,由于在氮上优先氧化,异构体3-氨基菲(9)产生了偶氮化合物17。咔唑已显示直接来自偶联反应,而不是最初形成的联萘。或者,咔唑19也可以由1b与肼反应制备。另一方面,用肼处理3a导致胺11和芳基肼22形成约2:7的混合物。2,2'-二氨基-1,1'-联蒽(15)已通过拆分为对映体与(-)-N-苄基辛可二鎓氯化物共结晶,并且通过X射线晶体学显示具有(R)-(-)-15构型。DOI:10.1021/jo005691w
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Synthesis of Aminochrysenes by the Oxidative Photocyclization of Acetylaminostilbenes.摘要:在碘和空气存在下,通过乙酰氨基二苯乙烯的氧化光环化反应,然后进行水解,合成了氨基二苯乙烯衍生物。DOI:10.1248/cpb.41.1853
文献信息
-
Polycyclic aromatic compounds as anticancer agents: Synthesis and biological evaluation of some chrysene derivatives
-
[EN] COMPLEXES OF N-HETEROCYCLIC CARBENES FOR TRANSITION METAL CATALYSIS<br/>[FR] COMPLEXES DE CARBÈNES N-HÉTÉROCYCLIQUES POUR LA CATALYSE PAR DES MÉTAUX DE TRANSITION申请人:UNIV RUTGERS公开号:WO2021142289A1公开(公告)日:2021-07-15Described herein is a new class of highly active Pd(II)-NHC complexes bearing anilines as throw-away ligands. These catalysts are well-defined, air- and moisture-stable and can be easily purified by chromatographic techniques. High activity and generality has been exemplified in the Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling by C-N, C-O and C-Cl cleavage. Facile syntheses of these catalysts is also described.
-
[EN] LIGANDS FOR TRANSITION METAL CATALYSTS<br/>[FR] LIGANDS POUR CATALYSEURS À MÉTAL DE TRANSITION申请人:UNIV RUTGERS公开号:WO2021142281A1公开(公告)日:2021-07-15Provided herein are a new class of extremely sterically-bulky, easily prepared N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) ligands of Formula I, or a salt, solvate, geometric isomer, or stereoisomer thereof. The ligands are readily synthetically accessible exploiting the cost-effective, modular alkylation of anilines, an industrial chemical that is available in bulk. The NHC ligands form effective catalysts with transition metals such as Pd.
-
一种钌-二亚胺型配合物、制备方法及其用途申请人:江苏医药职业学院公开号:CN108299509A公开(公告)日:2018-07-20
-
Chromatographic materials for the separation of unsaturated molecules申请人:Waters Technologies Corporation公开号:US10092894B2公开(公告)日:2018-10-09The present disclosure relates to a method of separating a compound of interest, particularly unsaturated compound(s) of interest, from a mixture. The compound is separated using a column having a chromatographic stationary phase material for various different modes of chromatography containing a first substituent and a second substituent. The first substituent minimizes compound retention variation over time under chromatographic conditions. The second substituent chromatographically and selectively retains the compound by incorporating one or more aromatic, polyaromatic, heterocyclic aromatic, or polyheterocyclic aromatic hydrocarbon groups, each group being optionally substituted with an aliphatic group.本公开涉及一种从混合物中分离相关化合物,特别是相关不饱和化合物的方法。使用色谱柱分离化合物,该色谱柱具有用于各种不同色谱模式的色谱固定相材料,其中含有第一取代基和第二取代基。在色谱条件下,第一取代基可最大程度地减少化合物保留时间的变化。第二取代基通过加入一个或多个芳香族、多芳香族、杂环芳香族或多杂环芳香族烃基团(每个基团可选择被脂肪族基团取代),在色谱上选择性地保留化合物。
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
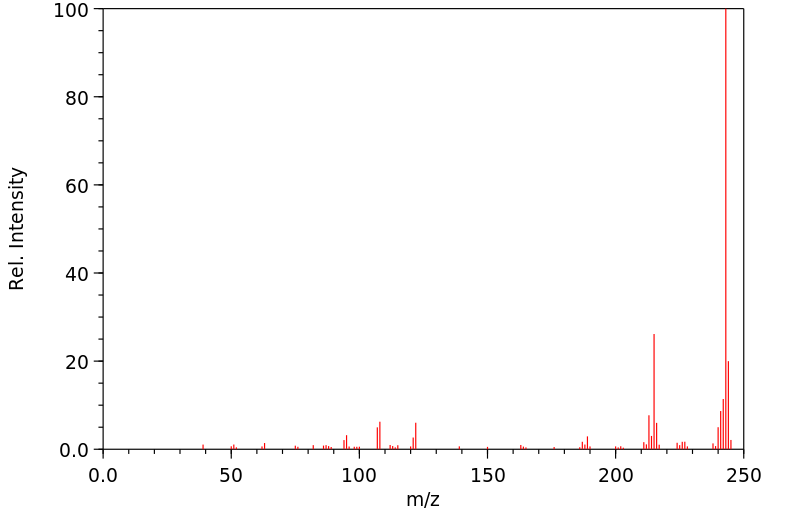
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
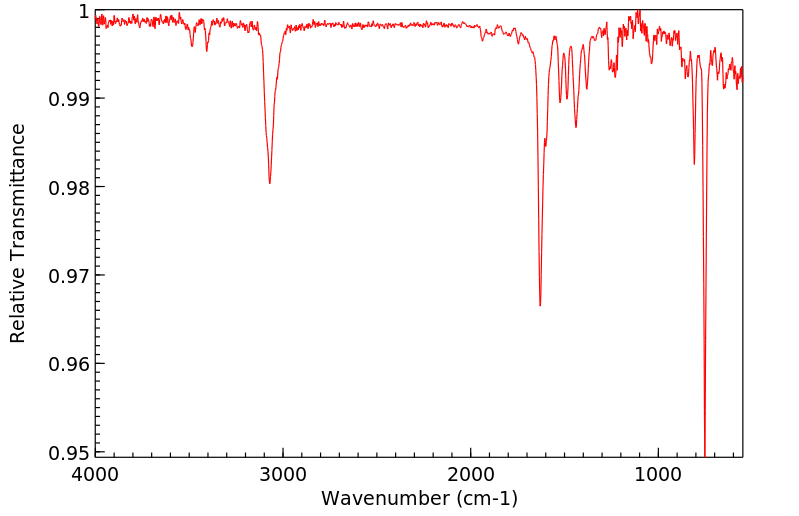
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(R)-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-6,6''-二-9-菲基-1,1''-螺双[1H-茚]-7,7''-二醇
(6,6)-苯基-C61己酸甲酯
高雌二醇
马兜铃酸钠
马兜铃酸盐
马兜铃酸C
马兜铃酸B
马兜铃酸(1:1MIXTUREOFARISTOLOCHICACIDIANDARISTOLOCHICACIDII)
马兜铃酸 Ia
马兜铃酸 IVa
马兜铃酸
颜料黑32
颜料红179
颜料红178
颜料红149
颜料红123
顺式-菲-1,2-二醇-3,4-环氧化物
顺式-苯并(a)屈-11,12-二醇-13,14-环氧化物
雷公藤酚A
镁二(1,4,5,6,7,16,17,18,19,19,20,20-十二氯六环[14.2.1.14,7.02,15.03,8.09,14]二十-5,9,11,13,17-五烯-11-磺酸酯)
钩大青酮
钩大青酮
钙(2+)12-羟基十八烷酸酯
酒石酸布托诺啡
那布扶林
还原红32
足球烯
贝那他汀B
贝母兰素
萘并[2,3-b]荧蒽
萘并[2,1-e][1]苯并二硫杂环戊烷
萘并[2,1-C:7,8-C']二菲
萘并[1,2-e][2]苯并呋喃-1,3-二酮
萘并[1,2-b]屈
萘并[1,2-a]蒽
萘并[1,2-B]菲-6-醇
萘二(六氯环戊二烯)加合物
萘,8-溴-1,2,3-三(1,1-二甲基乙基)-6-甲基-
菲醌单缩氨基硫脲
菲醌
菲并[9,10]呋喃
菲并[9,10-e]醋菲烯
菲并[4,5-bcd]噻吩
菲并[4,5-bcd]呋喃-3-醇
菲并[4,3-d]-1,3-二噁唑-5-羧酸,10-羟基-9-甲氧基-6-硝基-
菲并[3,2-b]噻吩
菲并[2,1-d]噻唑
菲并[2'',1'',10'':4,5,6;7'',8'',9'':4',5',6']二异喹啉并[2,1-a:2',1'-a']二萘嵌间二氮杂苯-8,13-二酮
菲并(3,4-b)噻吩
菲并(1,2-b)噻吩