3-四癸炔-1-醇 | 55182-74-6
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:32.5°C (estimate)
-
沸点:155-156°C 0,8mm
-
密度:0.8070 (estimate)
-
闪点:155-156°C/0.8mm
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):5.4
-
重原子数:15
-
可旋转键数:9
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.857
-
拓扑面积:20.2
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:1
安全信息
-
海关编码:2905290000
-
安全说明:S24/25
SDS
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 1-十二炔 1-dodecyne 765-03-7 C12H22 166.307 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 13-十四炔-1-醇 tetradec-13-yn-1-ol 18202-12-5 C14H26O 210.36
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:3-四癸炔-1-醇 在 4-二甲氨基吡啶 、 jones' reagent 、 potassium tert-butylate 、 lithium 、 1,3-丙二胺 、 N,N'-二环己基碳二亚胺 作用下, 以 二氯甲烷 、 丙酮 为溶剂, 反应 2.75h, 生成 2-palmitoyl-3-(4-methoxybenzyl)-sn-glycerol参考文献:名称:A new reagent for the removal of the 4-methoxybenzyl ether: application to the synthesis of unusual macrocyclic and bolaform phosphatidylcholines.摘要:The total synthesis of two novel polymerizable phosphatidylcholines has been accomplished using 3-(4-methoxybenzyl)-sn-glycerol 10 as starting material. Diacylation of 10 with 13-tetradecynoic acid followed by oxidative coupling of the alkynes gives the 32-membered glycerol macrocycle 17. Sequential acylation of 10 with palmitic acid and 15-hexadecynoic acid followed by oxidative coupling gives the bolaform 16, tethered at the 2-position of the glycerol. A new method for the cleavage of 4-methoxybenzyl ethers using dimethylboron bromide at -78-degrees-C in dichloromethane is described. 1,3-Diacetylenes, 1,4-dienes, and esters are stable under the experimental conditions, and the migration of acyl chains from secondary to primary positions is totally suppressed. The diacylglycerols are then efficiently converted into the corresponding phosphatidylcholines by tetrazole-catalyzed phosphitylation with 2-cyanoethyl 2-bromoethyl N,N-diisopropylamino phosphite, oxidation, and treatment with trimethylamine to simultaneously displace the bromide and eliminate the cyanoethyl group.DOI:10.1021/jo00032a033
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:매미나방의 성페로몬인 시스-7,8-에폭시-2-메틸옥타데칸의 합성방법摘要:本发明涉及一种合成缢蛏_WEB construção蛾性信息素顺式-7,8-环氧-2-甲基-1-辛烯的方法,特别是一种以3-丁醇为起始原料,在Ni(OAc)₂催化下通过催化还原反应和格氏反应大量合成缢蛏_WEB construção蛾性信息素顺式-7,8-环氧-2-甲基-1-辛烯的方法。 本发明的合成方法包括以下步骤: (a) 以3-丁醇为原料合成四氢-3-甲基-1-丁醇的步骤; (b) 在Ni(OAc)₂催化下进行部分加氢反应,合成顺式-四氢-3-甲基-1-丁醇的步骤; (c) 以异戊基镁溴为格氏试剂进行格氏反应,合成顺式-2-甲基-7-辛烯的步骤; (d) 进行环氧化反应,合成顺式-7,8-环氧-2-甲基-1-辛烯的步骤。 本发明以3-丁醇为起始原料,使用廉价的Ni(OAc)₂代替昂贵的钯作为催化剂,通过催化还原反应和格氏反应,能够大量合成缢蛏_WEB construção蛾性信息素顺式-7,8-环氧-2-甲基-1-辛烯。根据本发明合成的7,8-环氧-2-甲基-1-辛烯可以用作诱芯,通过利用缢蛏_WEB construção蛾性信息素的诱捕器在户外更容易监测缢蛏_WEB construção蛾的发生情况,并在此基础上向农户等大量提供捕获诱捕器,从而通过不使用化学农药的环保方法防治害虫缢蛏_WEB construção蛾。公开号:KR20240033428A
文献信息
-
Natural Trienoic Acids as Anticancer Agents: First Stereoselective Synthesis, Cell Cycle Analysis, Induction of Apoptosis, Cell Signaling and Mitochondrial Targeting Studies作者:Vladimir A. D’yakonov、Alexey A. Makarov、Lilya U. Dzhemileva、Ilfir R. Ramazanov、Elina Kh. Makarova、Usein M. DzhemilevDOI:10.3390/cancers13081808日期:——
The first Z-stereoselective method was developed for the synthesis of unsaturated acids containing a 1Z,5Z,9Z-triene moiety in 61–64% yields using the new Ti-catalyzed cross-coupling of oxygen-containing and aliphatic 1,2-dienes as the key synthetic step. It was shown for the first time that trienoic acids with non-methylene-interrupted Z-double bonds show moderate cytotoxic activities against tumor cell lines (Jurkat, K562, U937, HL60, HeLa), human embryonic kidney cells (Hek293), normal fibroblasts and human topoisomerase I (hTop1) inhibitory activity in vitro. The synthesized acids efficiently initiate apoptosis of Jurkat tumor cells, with the cell death mechanism being activated by the mitochondrial pathway. A probable mechanism of topoisomerase I inhibition was also hypothesized on the basis of in silico studies resorting to docking. The activation and inhibition of the most versatile intracellular signaling pathways (CREB, JNK, NFkB, p38, ERK1/2, Akt, p70S6K, STAT3 and STAT5 tyrosine kinases) responsible for cell proliferation and for initiation of apoptosis were studied by multiplex assay technology (Luminex xMAP).
第一个Z-立体选择性方法是为合成含有1Z,5Z,9Z-三烯基团的不饱和酸而开发的,利用新的钛催化的含氧和脂肪族1,2-二烯烃的交叉偶联作为关键合成步骤,产率为61-64%。首次表明,具有非亚甲基间断Z-双键的三烯酸对肿瘤细胞系(Jurkat,K562,U937,HL60,HeLa),人类胚胎肾细胞(Hek293),正常成纤维细胞和体外人类拓扑异构酶I(hTop1)具有中等细胞毒活性。合成的酸有效地启动Jurkat肿瘤细胞的凋亡,细胞死亡机制通过线粒体途径被激活。还根据基于对接的体外研究假设了拓扑异构酶I抑制的可能机制。通过多重分析技术(Luminex xMAP)研究了对细胞增殖和凋亡启动负责的最多功能细胞内信号通路(CREB,JNK,NFkB,p38,ERK1/2,Akt,p70S6K,STAT3和STAT5酪氨酸激酶)的激活和抑制。 -
Nitrogen heteroaromatic cations by [2+2+2] cycloaddition作者:Martina Čížková、Viliam Kolivoška、Ivana Císařová、David Šaman、Lubomír Pospíšil、Filip TeplýDOI:10.1039/c0ob00507j日期:——developed capitalizing on a direct pyridine-type nitrogen quaternization followed by metal-catalyzed [2+2+2] cycloaddition with gaseous acetylene. The flexibility of the route is demonstrated on 12 diverse scaffolds based on pyridinium, quinolinium, thiazolium, benzothiazolium, imidazolium, and pyrimidinium. Electrochemical study revealed a quinolinium redox system with two electrochemically distinct forms
-
New bent-core mesogens with carbon–carbon multiple linkages in the terminal chains作者:Gerhard Pelzl、Maria G. Tamba、Sonja Findeisen-Tandel、Martin W. Schröder、Ute Baumeister、Siegmar Diele、Wolfgang WeissflogDOI:10.1039/b803493a日期:——New five-ring bent-core mesogens have been synthesized in which terminal alkynyl chains are connected with the terminal rings of the aromatic core by means of oxycarbonyl groups, cinnamic esters groups or oxyacetic ester moieties. The insertion of CâC triple bonds in different positions of the terminal chains can change the mesophase behaviour and can result in an increase or decrease of the clearing temperatures in comparison to corresponding compounds with saturated chains. In addition, lateral substituents are attached to different positions of the central ring. The mesophase behaviour of the new compounds has been studied by polarizing microscopy, differential scanning calorimetry, X-ray experiments and electro-optical measurements. On the base of the experimental findings new relationships between the molecular structure and the mesomorphic properties have been obtained. Different polar phases (SmCP, Col, B7â²) could be proved, in some of these the polar (ferro- or antiferroelectric) switching takes place through a collective rotation of the molecules around their long axes. Interestingly, three compounds with terminal alkynyl chains form a mesophase with all textural features of a B7 phase although these phases possess obviously a simple layer structure. For the first time it could be observed that helical filaments formed on slow cooling the isotropic liquid are stable to low temperatures. Some of these spirals can serve as nuclei in the growing process of ribbon-like and oval domains. Surprisingly, the helical pitch of the spirals can be exactly recovered in the equidistant stripes of these domains. It is also remarkable that all compounds derived from 2-methylisophthalic acid exhibit unusually high clearing temperatures and that the SmC phases of these compounds show polar switching about 50 K below the SmAâSmC transition temperature.我们合成了新的五环弯曲核中间体,其中的末端炔链通过氧羰基、肉桂酸酯基或氧乙酸酯分子与芳香核的末端环相连。在末端链的不同位置插入 CâC 三键可改变介相行为,与具有饱和链的相应化合物相比,可导致清除温度的升高或降低。此外,横向取代基被连接到中心环的不同位置。我们通过偏振显微镜、差示扫描量热法、X 射线实验和电光测量等方法研究了新化合物的介相行为。在实验结果的基础上,我们获得了分子结构与介观性质之间的新关系。可以证明存在不同的极性相(SmCP、Col、B7â²),其中一些极性相(铁电或反铁电)的切换是通过分子绕其长轴的集体旋转实现的。有趣的是,三种带有末端炔链的化合物形成的介相具有 B7 相的所有纹理特征,尽管这些相明显具有简单的层结构。我们首次观察到,在缓慢冷却各向同性液体时形成的螺旋丝在低温下非常稳定。这些螺旋丝中的一些可以作为带状和椭圆形畴生长过程中的核。令人惊讶的是,螺旋线的螺旋间距可以在这些畴的等距条纹中精确复原。同样值得注意的是,所有由 2-甲基间苯二甲酸衍生的化合物都表现出异常高的清澈温度,而且这些化合物的 SmC 相在 SmAâSmC 转换温度以下约 50 K 处出现极性转换。
-
一种合成顺-3-十四碳烯醇乙酸酯和反-3-十四碳烯醇乙酸酯的方法
-
METHODS FOR THE DETECTION OF FATTY-ACYLATED PROTEIN申请人:Hannoush Rami N.公开号:US20100189660A1公开(公告)日:2010-07-29Sensitive, non-radioactive fatty-acyls of Formula I are useful in in vivo methods for detection and cellular imaging of a fatty-acylated substrate (e.g., protein or polypeptide). In Formula I the symbols X and A, and the subscript n are as described herein. These fatty-acyl compounds are can be used, inter alia, for analyzing the lipid composition of proteins in different biological states under various cellular conditions, and serve as a gateway into global lipidomic analysis of cellular proteins.公式I的敏感、非放射性脂肪酰基(例如蛋白质或多肽)的检测和细胞成像的体内方法中,公式I中的符号X和A,以及下标n如本文所述。这些脂肪酰化化合物可用于分析在不同细胞条件下蛋白质的脂质组成,并作为进入细胞蛋白质全球脂质组学分析的通道。
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
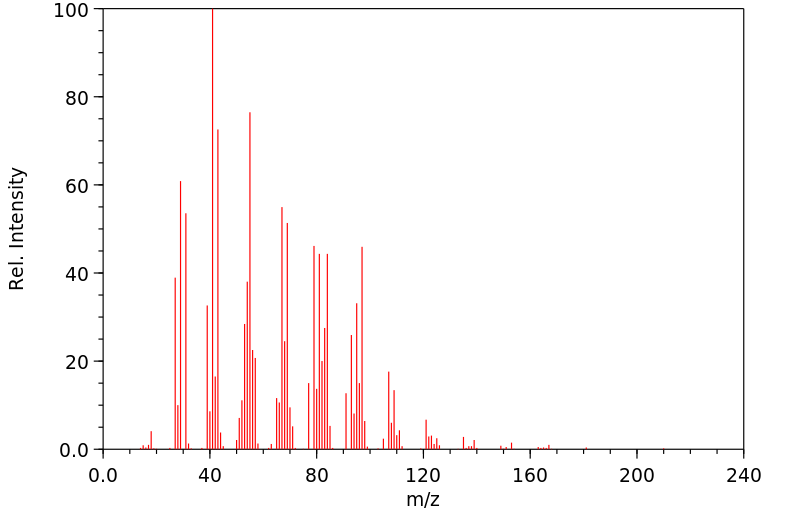
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
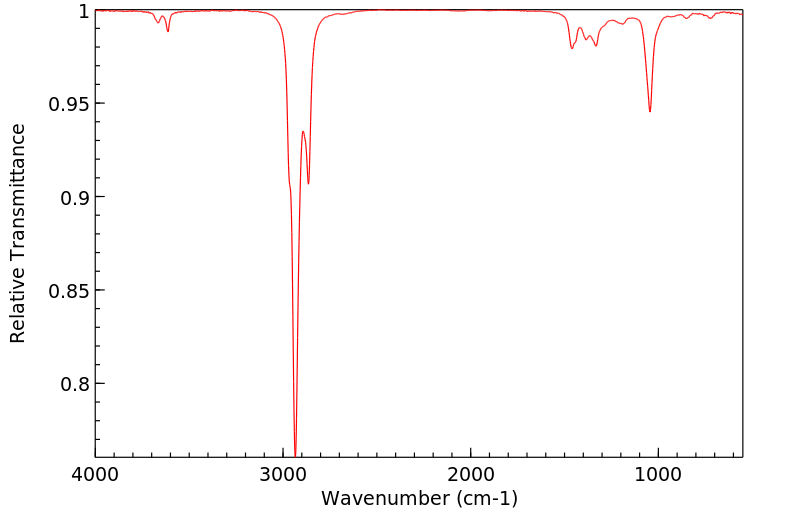
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息