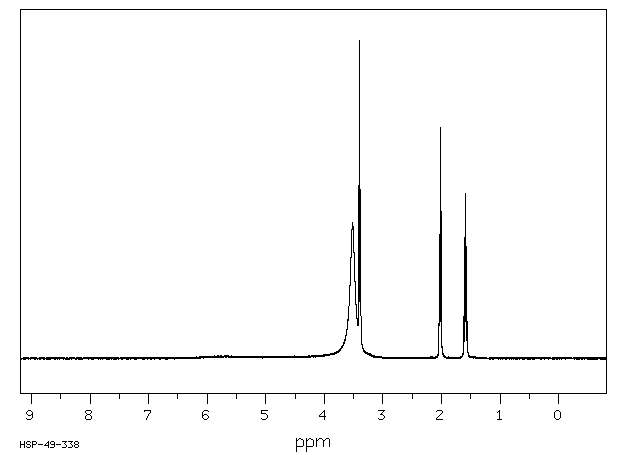
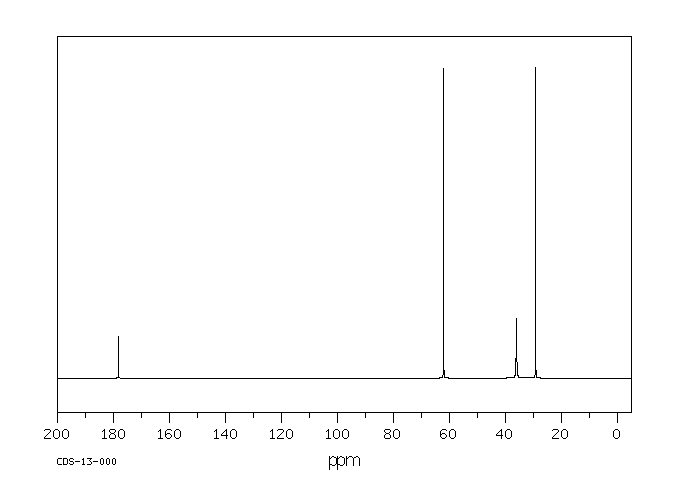
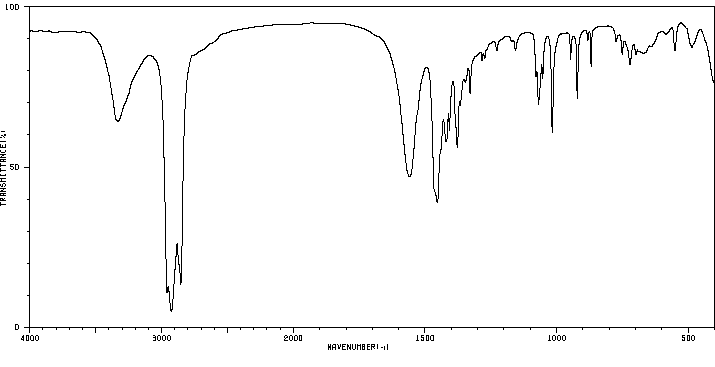
代谢
动物研究表明,主要的消除途径是通过克雷布斯循环产生二氧化碳和水,其次是经过β-氧化。在主要途径中,羟基酸-酮酸转移酶催化了羟丁酸钠转化为琥珀半醛的过程,随后琥珀半醛被琥珀半醛脱氢酶转化为琥珀酸。琥珀酸然后在克雷布斯循环中转变为二氧化碳和水。在α-酮戊二酸存在的情况下,琥珀半醛也可以通过转移酶代谢成二氧化碳和水。
Animal studies indicate that the major elimination pathway is metabolism by the creation of carbon dioxide and water through the Krebs cycle and secondarily by beta-oxidation. In the primary pathway hydroxyacid-oxoacid transhydrogenase catalyzes the conversion of sodium oxybate to succinic semialdehyde which is then transformed to succinic acid by succinic semmialdehyde dehydrogenase. Succinic acid is then turned into carbon dioxide and water in the Krebs cycle. Succinic semialdehyde is also metabolised into carbon dioxide and water by a transhydrofenase in the presence of alpha ketoglutarate.
来源:DrugBank