环己基甲基乙酸酯 | 937-55-3
中文名称
环己基甲基乙酸酯
中文别名
——
英文名称
cyclohexylmethyl acetate
英文别名
——
CAS
937-55-3
化学式
C9H16O2
mdl
MFCD07780584
分子量
156.225
InChiKey
FXKHUBNHBYCRNH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
沸点:183°C(lit.)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2.5
-
重原子数:11
-
可旋转键数:3
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.888
-
拓扑面积:26.3
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:2
安全信息
-
储存条件:室温且干燥
SDS
环己基甲基乙酸酯
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: Cyclohexylmethyl Acetate
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害
易燃液体 第4级
健康危害 未分类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志 无
信号词 警告
危险描述 可燃液体
防范说明
[预防] 远离明火/热表面。
穿戴防护手套/护目镜/防护面具。
[储存] 存放于通风良好处。保持凉爽。
[废弃处置] 根据当地政府规定把物品/容器交与工业废弃处理机构。
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 环己基甲基乙酸酯
百分比: >98.0%(GC)
CAS编码: 937-55-3
俗名: Acetic Acid Cyclohexylmethyl Ester
分子式: C9H16O2
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用水清洗皮肤/淋浴。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
环己基甲基乙酸酯
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,二氧化碳
不适用的灭火剂: 水(有可能扩大灾情。)
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。确保足够通风。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 用合适的吸收剂(如:旧布,干砂,土,锯屑)吸收泄漏物。一旦大量泄漏,筑堤控
制。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的法律法规废弃处置。
副危险性的防护措施 移除所有火源。一旦发生火灾应该准备灭火器。使用防火花工具和防爆设备。
7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止烟雾产生。远离明火和热表面。
采取措施防止静电积累。使用防爆设备。处理后彻底清洗双手和脸。
注意事项: 使用封闭系统,通风。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗、通风良好处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防毒面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
外形(20°C): 液体
外观: 透明
颜色: 无色-极淡的黄色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点: 无资料
沸点/沸程 183 °C
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 0.96
环己基甲基乙酸酯
模块 9. 理化特性
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂] 无资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
避免接触的条件: 明火
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守
国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
环己基甲基乙酸酯
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: Cyclohexylmethyl Acetate
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害
易燃液体 第4级
健康危害 未分类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志 无
信号词 警告
危险描述 可燃液体
防范说明
[预防] 远离明火/热表面。
穿戴防护手套/护目镜/防护面具。
[储存] 存放于通风良好处。保持凉爽。
[废弃处置] 根据当地政府规定把物品/容器交与工业废弃处理机构。
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 环己基甲基乙酸酯
百分比: >98.0%(GC)
CAS编码: 937-55-3
俗名: Acetic Acid Cyclohexylmethyl Ester
分子式: C9H16O2
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用水清洗皮肤/淋浴。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
环己基甲基乙酸酯
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,二氧化碳
不适用的灭火剂: 水(有可能扩大灾情。)
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。确保足够通风。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 用合适的吸收剂(如:旧布,干砂,土,锯屑)吸收泄漏物。一旦大量泄漏,筑堤控
制。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的法律法规废弃处置。
副危险性的防护措施 移除所有火源。一旦发生火灾应该准备灭火器。使用防火花工具和防爆设备。
7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止烟雾产生。远离明火和热表面。
采取措施防止静电积累。使用防爆设备。处理后彻底清洗双手和脸。
注意事项: 使用封闭系统,通风。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗、通风良好处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防毒面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
外形(20°C): 液体
外观: 透明
颜色: 无色-极淡的黄色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点: 无资料
沸点/沸程 183 °C
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 0.96
环己基甲基乙酸酯
模块 9. 理化特性
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂] 无资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
避免接触的条件: 明火
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守
国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
环己基甲基乙酸酯
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:van der Bij; Kooyman, Recueil des Travaux Chimiques des Pays-Bas, 1952, vol. 71, p. 837,843摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:高支化聚苯乙烯铵盐稳定的过渡金属纳米粒子:金属对烯烃和芳烃双相加氢催化的影响摘要:超支化聚苯乙烯轴承铵盐(HPS-NR 3 +氯- )表现为钌,铑,铱,钯和铂纳米粒子的大小极好的稳定剂1〜3纳米均匀地分散在聚合物基质中。所得到的金属-聚合物复合材料的催化性能,[电子邮件保护] 3 +氯- ,取决于金属。通过评估烯烃和芳烃的氢化反应研究了这种依赖性。[电子邮件保护] 3 + Cl的实用程序-如在水/有机两相系统可重复使用的催化剂被证明通过检查含有各种官能团的芳族化合物的氢化的由催化[电子邮件保护] 3 +氯- 。DOI:10.1016/j.tet.2015.04.081
文献信息
-
Esterification of Tertiary Amides by Alcohols Through C−N Bond Cleavage over CeO <sub>2</sub>作者:Takashi Toyao、Md. Nurnobi Rashed、Yoshitsugu Morita、Takashi Kamachi、S. M. A. Hakim Siddiki、Md. A. Ali、A. S. Touchy、Kenichi Kon、Zen Maeno、Kazunari Yoshizawa、Ken‐ichi ShimizuDOI:10.1002/cctc.201801098日期:2019.1.9process proceeds through rate limiting addition of a CeO2 lattice oxygen to the carbonyl group of the adsorbed acetamide species with energy barrier of 17.0 kcal/mol. This value matches well with experimental value (17.9 kcal/mol) obtained from analysis of the Arrhenius plot. Further studies by in situ FT‐IR and temperature programmed desorption using probe molecules demonstrate that both acidic and已经发现CeO 2促进叔酰胺形成酯的醇解反应。本催化体系操作简单,可回收,并且不需要添加剂。酯化过程显示出较宽的底物范围(> 45个实例;分离产率高达93%)。密度泛函理论(DFT)研究与现场FT-IR观察相结合的结果表明,该过程通过速率限制将CeO 2晶格氧加到吸附的乙酰胺类化合物的羰基上进行,能量垒为17.0 kcal / mol 。该值与通过分析Arrhenius图获得的实验值(17.9 kcal / mol)很好地匹配。原位进一步研究FT-IR和使用探针分子的程序升温脱附表明,酸性和碱性性质均很重要,因此,CeO 2对CN键断裂反应表现出最佳性能。
-
Chemoselective Palladium-Catalyzed Oxidation of Vinyl Ether to Acetate Using Hydrogen Peroxide作者:Yoshihiro Kon、Shinji Tanaka、Takuya Nakashima、Kazuhiko Sato、Hiromichi ShimadaDOI:10.1002/jccs.201400058日期:2014.7A practical and environmental‐friendly method was developed to convert vinyl ether into acetate by using a palladium complex with phosphine ligand and hydrogen peroxide. The only by‐product is water.
-
An Amino Alcohol Ligand for Highly Enantioselective Addition of Organozinc Reagents to Aldehydes: Serendipity Rules作者:William A. NugentDOI:10.1021/ol0259488日期:2002.6.1bis(2-bromoethyl) ether. Subsequent hydrogenation over 5% Rh on alumina in the presence of morpholine unexpectedly stops at the hexahydro derivative 4. Amino alcohol 4 promotes the enantioselective addition of diethylzinc to aldehydes at room temperature in up to 99% enantiomeric excess.
-
Mercury-assisted solvolyses of alkyl halides作者:A. McKillop、M.E. FordDOI:10.1016/s0040-4020(01)97118-2日期:1974.1wide variety of alkyl halides with mercury(I) and/or (II) nitrate in 1,2-dimethoxyethane, mercury(II) acetate in acetic acid, aqueous mercury(II) perchlorate, and mercury(II) perchlorate in alcohol solvents have been investigated; as a result, simple high yield procedures for the conversion of alkyl halides into the corresponding nitrate esters, acetate esters, alcohols and ethers have been developed.
-
Me<sub>3</sub>SI-promoted chemoselective deacetylation: a general and mild protocol作者:Aakanksha Gurawa、Manoj Kumar、Sudhir KashyapDOI:10.1039/d1ra03209g日期:——Me3SI-mediated simple and efficient protocol for the chemoselective deprotection of acetyl groups has been developed via employing KMnO4 as an additive. This chemoselective deacetylation is amenable to a wide range of substrates, tolerating diverse and sensitive functional groups in carbohydrates, amino acids, natural products, heterocycles, and general scaffolds. The protocol is attractive because it uses
表征谱图
-
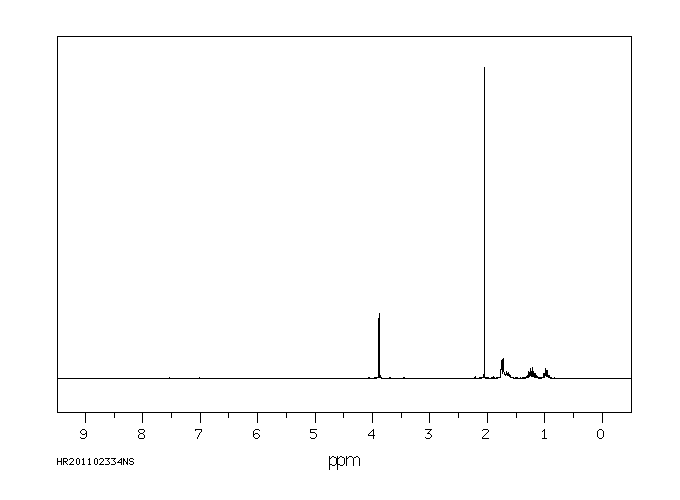
氢谱1HNMR
-
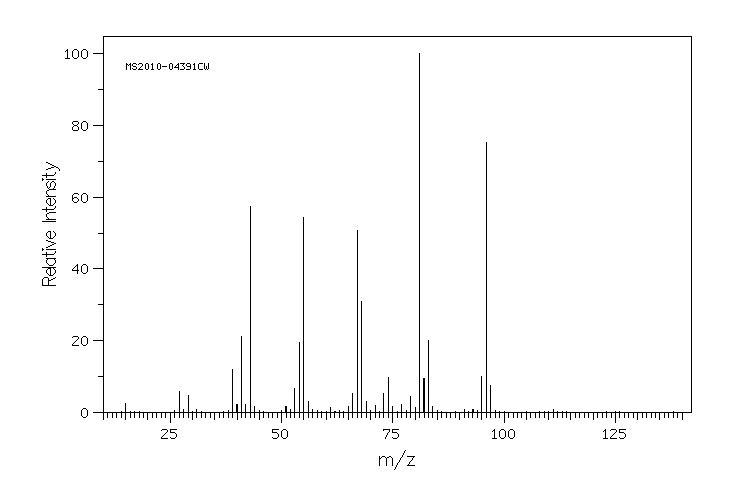
质谱MS
-
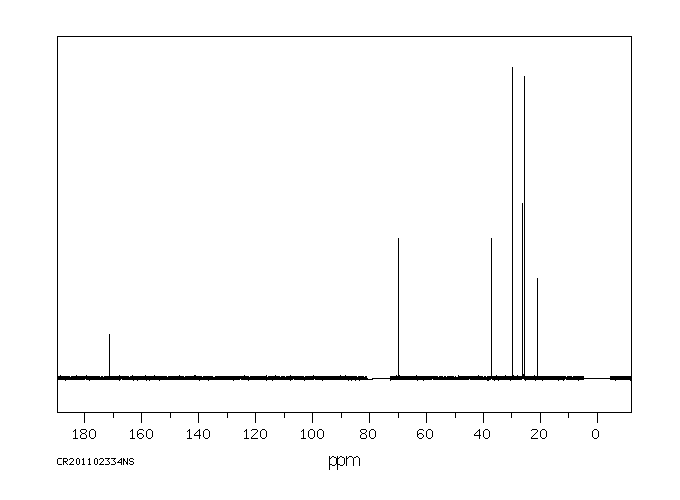
碳谱13CNMR
-
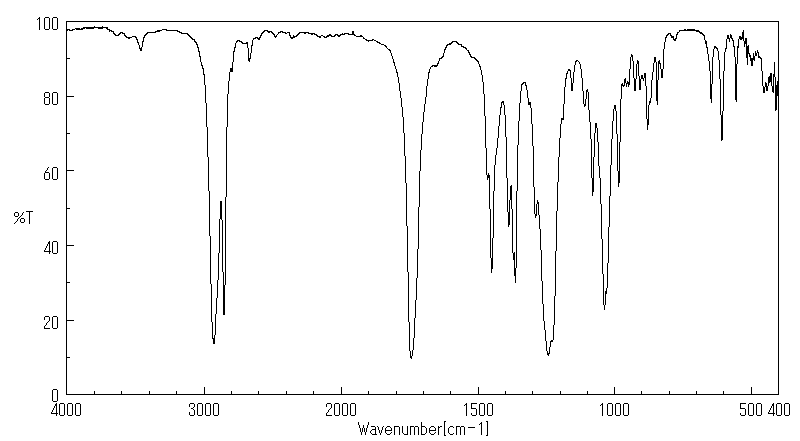
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(甲基3-(二甲基氨基)-2-苯基-2H-azirene-2-羧酸乙酯)
(±)-盐酸氯吡格雷
(±)-丙酰肉碱氯化物
(d(CH2)51,Tyr(Me)2,Arg8)-血管加压素
(S)-(+)-α-氨基-4-羧基-2-甲基苯乙酸
(S)-阿拉考特盐酸盐
(S)-赖诺普利-d5钠
(S)-2-氨基-5-氧代己酸,氢溴酸盐
(S)-2-[[[(1R,2R)-2-[[[3,5-双(叔丁基)-2-羟基苯基]亚甲基]氨基]环己基]硫脲基]-N-苄基-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(S)-2-[3-[(1R,2R)-2-(二丙基氨基)环己基]硫脲基]-N-异丙基-3,3-二甲基丁酰胺
(S)-1-(4-氨基氧基乙酰胺基苄基)乙二胺四乙酸
(S)-1-[N-[3-苯基-1-[(苯基甲氧基)羰基]丙基]-L-丙氨酰基]-L-脯氨酸
(R)-乙基N-甲酰基-N-(1-苯乙基)甘氨酸
(R)-丙酰肉碱-d3氯化物
(R)-4-N-Cbz-哌嗪-2-甲酸甲酯
(R)-3-氨基-2-苄基丙酸盐酸盐
(R)-1-(3-溴-2-甲基-1-氧丙基)-L-脯氨酸
(N-[(苄氧基)羰基]丙氨酰-N〜5〜-(diaminomethylidene)鸟氨酸)
(6-氯-2-吲哚基甲基)乙酰氨基丙二酸二乙酯
(4R)-N-亚硝基噻唑烷-4-羧酸
(3R)-1-噻-4-氮杂螺[4.4]壬烷-3-羧酸
(3-硝基-1H-1,2,4-三唑-1-基)乙酸乙酯
(2S,4R)-Boc-4-环己基-吡咯烷-2-羧酸
(2S,3S,5S)-2-氨基-3-羟基-1,6-二苯己烷-5-N-氨基甲酰基-L-缬氨酸
(2S,3S)-3-((S)-1-((1-(4-氟苯基)-1H-1,2,3-三唑-4-基)-甲基氨基)-1-氧-3-(噻唑-4-基)丙-2-基氨基甲酰基)-环氧乙烷-2-羧酸
(2S)-2,6-二氨基-N-[4-(5-氟-1,3-苯并噻唑-2-基)-2-甲基苯基]己酰胺二盐酸盐
(2S)-2-氨基-N,3,3-三甲基-N-(苯甲基)丁酰胺
(2S)-2-氨基-3-甲基-N-2-吡啶基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-(苯基甲基)丁酰胺,
(2S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-2-吡啶基丁酰胺
(2S,4R)-1-((S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基丁酰基)-4-羟基-N-(4-(4-甲基噻唑-5-基)苄基)吡咯烷-2-甲酰胺盐酸盐
(2R,3'S)苯那普利叔丁基酯d5
(2R)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-(苯甲基)丁酰胺
(2-氯丙烯基)草酰氯
(1S,3S,5S)-2-Boc-2-氮杂双环[3.1.0]己烷-3-羧酸
(1R,5R,6R)-5-(1-乙基丙氧基)-7-氧杂双环[4.1.0]庚-3-烯-3-羧酸乙基酯
(1R,4R,5S,6R)-4-氨基-2-氧杂双环[3.1.0]己烷-4,6-二羧酸
齐特巴坦
齐德巴坦钠盐
齐墩果-12-烯-28-酸,2,3-二羟基-,苯基甲基酯,(2a,3a)-
齐墩果-12-烯-28-酸,2,3-二羟基-,羧基甲基酯,(2a,3b)-(9CI)
黄酮-8-乙酸二甲氨基乙基酯
黄荧菌素
黄体生成激素释放激素(1-6)
黄体生成激素释放激素 (1-5) 酰肼
黄体瑞林
麦醇溶蛋白
麦角硫因
麦芽聚糖六乙酸酯
麦根酸