N,N-二乙醇油酸酰胺 | 93-83-4
中文名称
N,N-二乙醇油酸酰胺
中文别名
油酸二乙醇胺;(Z)-N,N-二(2-羟基乙基)-9-十八烯酸酰胺;(Z(-N,N-二(2-羟基乙基)-9-十八烯酸酰胺
英文名称
oleic acid diethanolamide
英文别名
N,N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)-oleamide;Ninol 90201;Oleic diethanolamide;(Z)-N,N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)octadec-9-enamide
CAS
93-83-4
化学式
C22H43NO3
mdl
——
分子量
369.588
InChiKey
LPMBTLLQQJBUOO-KTKRTIGZSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
沸点:525.6±45.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:0.960±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
-
LogP:6.607 (est)
-
物理描述:Liquid; OtherSolid
-
保留指数:2799.7
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):5.8
-
重原子数:26
-
可旋转键数:19
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.86
-
拓扑面积:60.8
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:3
安全信息
-
危险品运输编号:190kgs
-
海关编码:2924199090
-
储存条件:本品应密封避光保存。
SDS
上下游信息
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 2-[[(Z)-octadec-9-enoyl]-(2-prop-2-enoyloxyethyl)amino]ethyl prop-2-enoate 883743-08-6 C28H47NO5 477.685 —— (Z)-N,N-bis[2-(oxiran-2-ylmethoxy)ethyl]octadec-9-enamide 1421857-93-3 C28H51NO5 481.717 —— N,n-bis(2-trimethylacetoxyethyl)oleamide 63056-97-3 C32H59NO5 537.824
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:脂肪酶催化的脂肪酸二乙醇酰胺的合成。摘要:二乙醇酰胺是非离子型乳化剂,广泛用于化妆品等行业和用作缓蚀剂。南极假丝酵母脂肪酶(Novozym 435)用于催化各种脂肪酸与二乙醇胺的酰胺化反应。脂肪酸,金属离子和水的含量影响二乙醇酰胺的收率。己酸是所有酰基供体中最好的底物。在50摄氏度和250 rpm的脂肪酶催化下,与90 mM脂肪酸和360 mM二乙醇胺在乙腈中进行脂肪酶催化反应24小时后,得到的己酰基二乙醇酰胺(HADEA),月桂酰基二乙醇酰胺(LADEA)和油酰基二乙醇酰胺(OADEA)的产率分别为76.5、49.5和12.1%。添加1 mM金属盐可提高HADEA和LADEA的产量。动力学分析表明,脂肪酶催化反应中HADEA和LADEA的产率主要与正向反应常数k(1)的速率有关。发现无水酶对于酰胺化反应是最好的。对酶操作稳定性的研究表明,南极衣原体脂肪酶分别保留了HADEA和LADEA合成的初始活性的95%和85%(即使重复使用DOI:10.1021/jf0107858
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Nonionic diethanolamide amphiphiles with unsaturated C18 hydrocarbon chains: thermotropic and lyotropic liquid crystalline phase behavior摘要:考察了三种非离子型二乙醇酰胺表面活性剂的纯净状态和溶致液晶相行为,它们含有C18碳氢链,分别带有一个、两个或三个不饱和键。这使得可以探讨不饱和度对二乙醇酰胺表面活性剂相行为的影响。纯净的亚油酰基和亚麻酰基二乙醇酰胺在约−85 °C时发生从玻璃态液晶到液晶的相变,而纯净的油酰基二乙醇酰胺在约−60 °C时发生相变形成液晶材料,然后在−34 °C时再结晶。油酰基二乙醇酰胺随后在约5 °C时发生第三次相变,从晶态相转变为碟状液晶相。在没有水的情况下,从碟状液晶到各向同性液体的转变温度随着不饱和度的增加而降低。加入水会导致所有三种表面活性剂形成层状相(Lα)。层状相在水过量条件下至少在70 °C下稳定。为这三种不饱和C18表面活性剂生成的近似部分二元表面活性剂-水相图表明,每种表面活性剂的过量水点出现在约60%(重量比)表面活性剂。DOI:10.1039/c1cp21808e
文献信息
-
一种阳离子脂质分子及其在核酸递送中的应用申请人:广州市锐博生物科技有限公司公开号:CN110283223B公开(公告)日:2022-01-04本发明公开了一种阳离子脂质分子及其在核酸递送中的应用。所述阳离子脂质分子的结构式如式ⅰ所示,在所述阳离子脂质分子的基础上本发明还提供了阳离子脂质体、脂质复合物、试剂、试剂盒、制剂和药物组合物。本发明提供的阳离子脂质分子的合成工艺简单、稳定性好,其阳离子脂质体兼具高效(可体现为高转染效率)和低毒性;同时稳定均一、易于制备;可用于各种细胞系转染。从而具备优秀的传递性,可将活性物质(如示例的siRNA)高效递送到细胞(如示例的肺癌细胞)、组织、器官中,实现活性物质的高效调控。解决了现有技术中存在的阳离子脂质体的毒性和传递效率不高的问题。
-
Novel Polyphenols That Inhibit Colon Cancer Cell Growth Affecting Cancer Cell Metabolism作者:Marta Gómez de Cedrón、Teodoro Vargas、Andrés Madrona、Aranza Jiménez、María-Jesús Pérez-Pérez、José-Carlos Quintela、Guillermo Reglero、Ana San-Félix、Ana Ramírez de MolinaDOI:10.1124/jpet.118.248278日期:2018.8New series of polyphenols with a hydrophilic galloyl-based head and a hydrophobic N -acyl tail, linked through a serinol moiety, have been synthesized and tested against colon cancer cell growth. Our structure activity relationship studies revealed that galloyl moieties are essential for growth inhibition. Moreover, the length of the N -acyl chain is crucial for the activity. Introduction of a ( Z ) double bond in the acyl chain increased the anticancer properties. Our findings demonstrate that 16 , the most potent compound within this series, has inhibitory effects on colon cancer cell growth and metabolism (glycolysis and mitochondrial respiration) at the same time that it activates 5′AMP-activated kinase (AMPK) and induces apoptotic cell death. Based on these results, we propose that 16 might reprogram colon cancer cell metabolism through AMPK activation. This might lead to alterations on cancer cell bioenergy compromising cancer cell viability. Importantly, these antiproliferative and proapoptotic effects are selective for cancer cells. Accordingly, these results indicate that 16 , with an unsaturated C18 chain, might be a useful prototype for the development of novel colon cancer cell growth inhibitors affecting cell metabolism.一系列具有亲水性鞣酸基头和疏水性N-酰基尾的多酚类化合物,通过酪氨酸基团连接,已被合成并测试其对结肠癌细胞生长的抑制作用。我们的结构活性关系研究表明,鞣酸基团对于生长抑制至关重要。此外,N-酰基链的长度对活性也十分关键。在酰基链中引入(Z)双键增强了抗癌特性。我们的研究发现,化合物16是该系列中最有效的化合物,能够同时抑制结肠癌细胞的生长和代谢(糖酵解和线粒体呼吸),并激活5′AMP激酶(AMPK),诱导细胞凋亡。基于这些结果,我们提出16可能通过AMPK激活重编程结肠癌细胞代谢,这可能导致癌细胞生物能量的变化,从而影响癌细胞的生存能力。重要的是,这些抗增殖和促凋亡的作用对癌细胞具有选择性。因此,这些结果表明,具有不饱和C18链的化合物16可能是开发新型结肠癌细胞生长抑制剂的有用原型,能够影响细胞代谢。
-
Low molecular weight PEI-based biodegradable lipopolymers as gene delivery vectors作者:Miao-Miao Xun、Xue-Chao Zhang、Ji Zhang、Qian-Qian Jiang、Wen-Jing Yi、Wen Zhu、Xiao-Qi YuDOI:10.1039/c2ob27211c日期:——Non-viral gene vectors play an important role in the development of gene therapy. In this report, different hydrophobic chains were introduced into low molecular weight (LMW) PEI-based biodegradable oligomers to form a series of lipopolymers (LPs), and their structure–activity relationships were studied. Results revealed that the nine polymers can condense plasmid DNA well to form nanoparticles with
-
지방산 디알칸올 아미드 제조방법
-
脂肪酸アルカノールアミド誘導体及びそれを含有する化粧料申请人:川研ファインケミカル株式会社公开号:JP2016199479A公开(公告)日:2016-12-01【課題】脂肪酸アルカノールアミドから誘導した、毛髪や皮膚に対して親和性が高い多鎖型高極性油剤の提供。【解決手段】式(1)で示される脂肪酸アルカノールアミド誘導体。[R1はC7〜21の炭化水素鎖;R2は式(2)で表される置換基等;AはH、メチル基、又は−CH2CH2O−R3基;但しR3基は式(2)で表される置換基][R4はC7〜21の炭化水素鎖;それらの混合物でも良い;pは0〜1]【選択図】なし
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
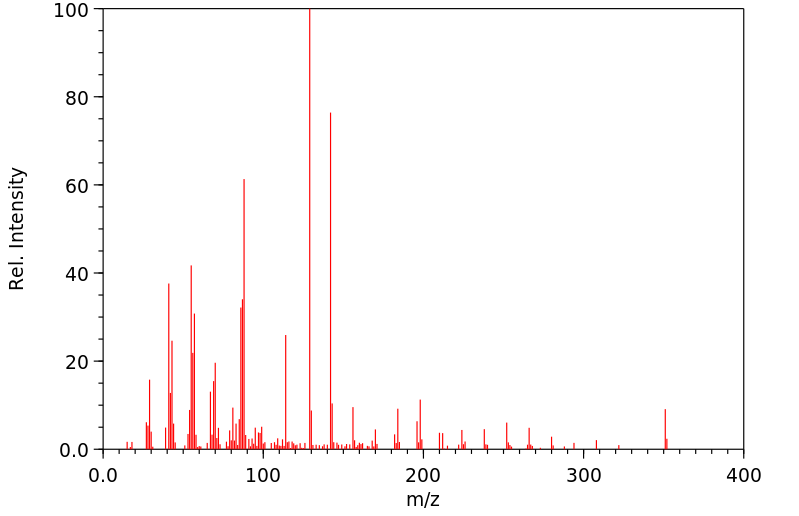
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
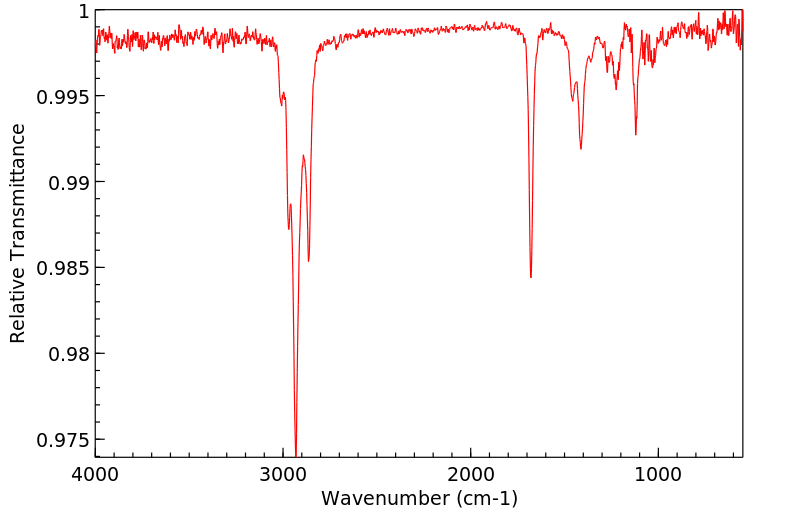
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(±)17,18-二HETE
(±)-辛酰肉碱氯化物
(Z)-5-辛烯甲酯
(Z)-4-辛烯酸
(R)-甲羟戊酸锂盐
(R)-普鲁前列素,游离酸
(R,R)-半乳糖苷
(E)-4-庚烯酸
(E)-4-壬烯酸
(E)-4-十一烯酸
(9Z,12E)-十八烷二烯酸甲酯
(6E)-8-甲基--6-壬烯酸甲基酯-d3
(3R,6S)-rel-8-[2-(3-呋喃基)-1,3-二氧戊环-2-基]-3-羟基-2,6-二甲基-4-辛酮
龙胆二糖
黑曲霉二糖
黄质霉素
麦芽酮糖一水合物
麦芽糖醇
麦芽糖酸
麦芽糖基蔗糖
麦芽糖一水合物
麦芽糖
鳄梨油酸乙酯
鲸蜡醇蓖麻油酸酯
鲸蜡醇油酸酯
鲸蜡硬脂醇硬脂酸酯
鲸蜡烯酸脂
鲸蜡基花生醇
鲫鱼酸
鲁比前列素
鲁比前列素
高级烷基C16-18-醇
高甲羟戊酸
高效氯氰菊酯
高-gamma-亚油酸
马来酸烯丙酯
马来酸氢异丙酯
马来酸氢异丁酯
马来酸氢丙酯
马来酸氢1-[2-(2-羟基乙氧基)乙基]酯
马来酸单乙酯
马来酸单丁酯
马来酸二辛酯
马来酸二癸酯
马来酸二甲酯
马来酸二烯丙酯
马来酸二正丙酯
马来酸二戊基酯
马来酸二异壬酯
马来酸二异丙酯