4,5-二溴哒嗪-3-酮 | 5788-58-9
中文名称
4,5-二溴哒嗪-3-酮
中文别名
4,5-二溴-3[2H]-哒嗪酮;4,5-二溴哒嗪-3[2H]-酮;4,5-二溴-3-哒嗪酮
英文名称
4,5-dibromo-3(2H)pyridazinone
英文别名
4,5-dibromopyridazin-3(2H)-one;4,5-dibromo-2,3-dihydropyridazin-3-one;4,5-dibromopyridazin-3-one;4,5-dibromo-2H-pyridazin-3-one;4,5-dibromo-1H-pyridazin-6-one
CAS
5788-58-9
化学式
C4H2Br2N2O
mdl
MFCD00023641
分子量
253.881
InChiKey
AGLQURQNVJVJNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:231-233°C
-
密度:2.53±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted)
-
稳定性/保质期:
在常温常压下保持稳定
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.1
-
重原子数:9
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:41.5
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:2
安全信息
-
危险等级:IRRITANT
-
安全说明:S26,S36
-
危险类别码:R36/37/38
-
海关编码:2933990090
-
危险性防范说明:P261,P305+P351+P338
-
危险性描述:H315,H319,H335
-
储存条件:常温、避光、存放在阴凉干燥处,并密封保存。
SDS
制备方法与用途
用途
4,5-二溴哒嗪-3-酮是一种有机中间体,可用于合成2-(2-四氢吡喃)-4,5-二溴哒嗪-3-酮。该化合物可通过溴化氢、二盐酸肼和乙酸钠反应制备而得。
上下游信息
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 4,5-二溴-2-甲基-2H-吡嗪-3-酮 4,5-dibromo-2-methyl-2H-pyridazin-3-one 13645-74-4 C5H4Br2N2O 267.908
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:一种一锅法合成氟代哒嗪酮的方法摘要:本发明公开了一种一锅法合成氟代哒嗪酮的新方法,将结构如式(I)所示的卤代哒嗪酮,结构如式(III)所示的三取代叔胺,加入反应容器中,于20~130℃温度下直接通入由三氟甲烷高温分解产生的二氧化碳和氟化氢气体,并在所述温度下搅拌反应,用薄层色谱跟踪反应结束后,冷却,反应液中加入适量二氯甲烷稀释,用柱层析分离纯化得到结构如式(II)所示的氟代哒嗪酮,其中,式(I)、(II)中的R及式(III)中的R1、R2、R3表示含碳原子数为1‑10的烷基,X为氯原子或溴原子。本发明不仅提供了一种一锅法合成氟代哒嗪酮的新方法,而且利用了可再生能源。公开号:CN106083731B
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:轻松合成4,5-二取代-3(2 H)-哒嗪酮摘要:最初通过将醇钠加成到高级溴化物中间体中来合成4,5-二取代-3(2 H)-哒嗪酮。少量的平行化学反应会导致成功率降低,因此我们通过进行铜催化的Finkelstein反应来提高反应伙伴的反应性。铜催化的各种醇与生成的碘化物的偶联导致更成功的努力。还描述了该系列化合物的许多替代合成,并且这些方法被证明是通用的,有效的并且适合于平行合成。DOI:10.1016/j.tetlet.2009.03.144
文献信息
-
スルホンアミド誘導体及びその医薬用途申请人:味の素株式会社公开号:JP2016037467A公开(公告)日:2016-03-22【課題】優れたα4インテグリン阻害作用を有する新規化合物を提供する。【解決手段】下記一般式(I)で示されるスルホンアミド誘導体、その医薬的に許容しうる塩又はそのプロドラッグ。(式中、a,b,c,d,D,E,R11,B,e,f,g,h及びWは、明細書中で定義されるとおりである。)【選択図】なし提供具有优良α4整合素抑制作用的新化合物。通过下述通式(I)所示的磺酰胺衍生物,其医药上可接受的盐或其前药。(式中,a,b,c,d,D,E,R11,B,e,f,g,h和W如本说明书中所定义。)【选择图】无
-
MACROCYCLIC, PYRIDAZINONE-CONTAINING HEPATITIS C SERINE PROTEASE INHIBITORS申请人:Moore Joel D.公开号:US20090123425A1公开(公告)日:2009-05-14The present invention relates to compounds of Formula I, II, or III, or pharmaceutically acceptable salts, esters, or prodrugs thereof: which inhibit serine protease activity, particularly the activity of hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS3-NS4A protease. Consequently, the compounds of the present invention interfere with the life cycle of the hepatitis C virus and are also useful as antiviral agents. The present invention further relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising the aforementioned compounds for administration to a subject suffering from HCV infection. The invention also relates to methods of treating an HCV infection in a subject by administering a pharmaceutical composition comprising a compound of the present invention.
-
[EN] PYRIDAZINONE DERIVATIVES AND USE THEREOF AS P2X7 RECEPTOR INHIBITORS<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS DE PYRIDAZINONE ET LEUR UTILISATION COMME INHIBITEURS DU RÉCEPTEUR P2X7申请人:NISSAN CHEMICAL IND LTD公开号:WO2009057827A1公开(公告)日:2009-05-07Novel pyridazinone compounds of formula (I), which inhibit the purinergic P2X7 receptor and are useful for prevention, therapy and improvement of inflammatory and immunological diseases.
-
[EN] COMPOUNDS AND METHODS FOR CD73 MODULATION AND INDICATIONS THEREFOR<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS ET PROCÉDÉS DE MODULATION DE CD73 ET LEURS INDICATIONS申请人:PLEXXIKON INC公开号:WO2021216898A1公开(公告)日:2021-10-28Disclosed are compounds of Formula (I): or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, a solvate, a tautomer, a stereoisomer or a deuterated analog thereof, wherein R1, R2, R3, A, E, L, and G are as described in any of the embodiments described in this disclosure; compositions thereof; and uses thereof.披露了公式(I)的化合物:或其药用盐、溶剂化物、互变异构体、立体异构体或氘代类似物,其中R1、R2、R3、A、E、L和G如本公开的任何实施方案所述;其组合物;及其用途。
-
Discovery of a Potent and Selective TRPC5 Inhibitor, Efficacious in a Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis Model作者:Maolin Yu、Mark W. Ledeboer、Matthew Daniels、Goran Malojcic、Thomas T. Tibbitts、Marie Coeffet-Le Gal、Xin-Ru Pan-Zhou、Amy Westerling-Bui、Maria Beconi、John F. Reilly、Peter Mundel、Jean-Christophe HarmangeDOI:10.1021/acsmedchemlett.9b00430日期:2019.11.14member 5 (TRPC5) helps regulate a tight balance of cytoskeletal dynamics in podocytes and is suggested to be involved in the pathogenesis of proteinuric kidney diseases, such as focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS). As such, protection of podocytes by inhibition of TRPC5 mediated Ca2+ signaling may provide a novel therapeutic approach for the treatment of proteinuric kidney diseases. Herein, we非选择性的Ca 2+渗透性瞬时受体电势(TRP)通道在多种细胞过程中发挥重要作用,包括肌动蛋白重塑和细胞迁移。TRP通道亚家族C,成员5(TRPC5)有助于调节足细胞中细胞骨架动态的紧密平衡,并建议其参与蛋白尿性肾脏疾病(如局灶性节段性肾小球硬化(FSGS))的发病机理。这样,通过抑制TRPC5介导的Ca 2+信号传导来保护足细胞可能为蛋白尿性肾脏疾病的治疗提供一种新颖的治疗方法。在这里,我们描述了通过高通量筛选命中的哒嗪酮1的系统优化对新型TRPC5抑制剂GFB-8438的鉴定。 。GFB-8438在体外保护小鼠足细胞免受硫酸鱼精蛋白(PS)诱导的伤害。它对FSGS的高血压醋酸脱氧皮质酮(DOCA)-盐大鼠模型也有效,可显着降低尿液中的总蛋白和白蛋白浓度。
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
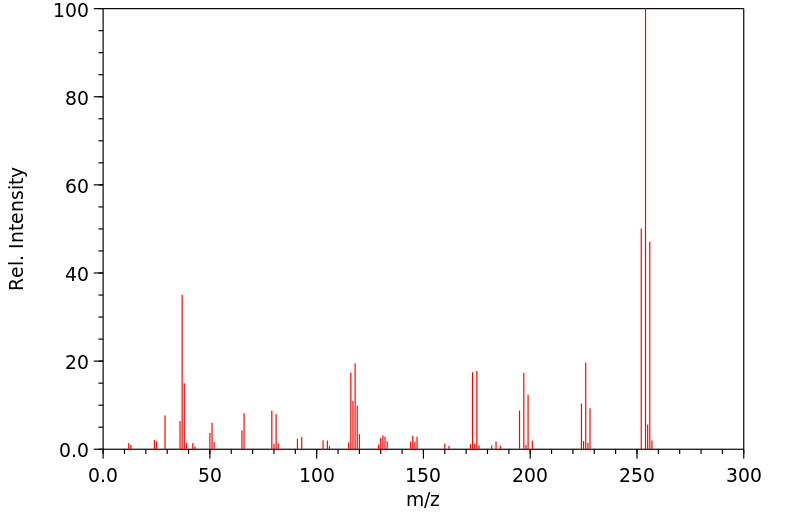
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
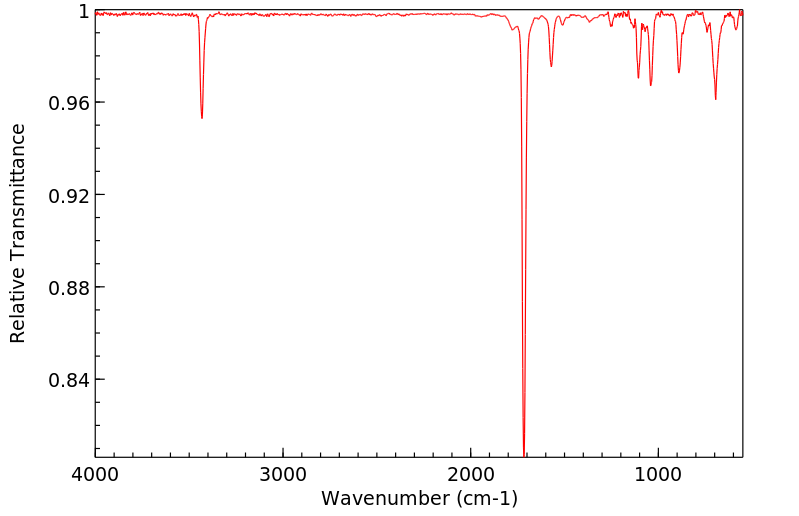
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(S)-3-(2-(二氟甲基)吡啶-4-基)-7-氟-3-(3-(嘧啶-5-基)苯基)-3H-异吲哚-1-胺
(6-羟基嘧啶-4-基)乙酸
(4,5-二甲氧基-1,2,3,6-四氢哒嗪)
鲁匹替丁
马西替坦杂质7
马西替坦杂质4
马西替坦杂质
马西替坦原料药杂质D
马西替坦原料药杂质B
马西替坦
顺式-4-{[5-溴-2-(2,5-二甲基-1H-吡咯-1-基)-6-甲基嘧啶-4-基]氨基}环己醇
非沙比妥
非巴氨酯
非尼啶醇
青鲜素钾盐
雷特格韦钾盐
雷特格韦相关化合物E(USP)
雷特格韦杂质8
雷特格韦EP杂质H
雷特格韦-RT9
雷特格韦
阿西莫司杂质3
阿西莫司
阿脲四水合物
阿脲一水合物
阿维霉素
阿米美啶
阿米洛利
阿米妥钠
阿洛巴比妥
阿普瑞西他滨
阿普比妥
阿巴卡韦相关化合物B(USP)
阿卡明
阿伐那非杂质V
阿伐那非杂质1
阿伐那非杂质
阿伐那非中间体
阿伐那非
铂(2+)二氯化6-甲基-1,3-二{2-[(2-甲基丙基)硫烷基]乙基}嘧啶-2,4(1H,3H)-二酮(1:1)
钴1,2,3,6-四氢-2,6-二氧代嘧啶-4-羧酸酯(1:2)
钠5-烯丙基-4,6-二氧代-1,4,5,6-四氢-2-嘧啶醇酸酯
钠5-乙基-4,6-二氧代-1,4,5,6-四氢-2-嘧啶醇酸酯
钠5-(2-溴丙-2-烯基)-5-丁烷-2-基-4,6-二氧代-1H-嘧啶-2-醇
醌肟腙
酒石酸噻吩嘧啶
那可比妥
辛基2,6-二氧代-1,2,3,6-四氢-4-嘧啶羧酸酯
赛乐西帕杂质3
赛乐西帕KSM3