三甲基-丙基硅烷 | 3510-70-1
中文名称
三甲基-丙基硅烷
中文别名
——
英文名称
trimethylpropylsilane
英文别名
Trimethyl-propyl-silan;Trimethyl-n-propyl-silan;propyltrimethylsilane;n-propyltrimethylsilane;Propyl-trimethylsilan;Trimethyl(propyl)silane
CAS
3510-70-1
化学式
C6H16Si
mdl
——
分子量
116.279
InChiKey
WNWMJFBAIXMNOF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
沸点:89°C
-
密度:0.720
-
保留指数:669;645.6
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2.73
-
重原子数:7
-
可旋转键数:2
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
安全信息
-
海关编码:2931900090
SDS
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 1,1-二甲基硅杂环丁烷 二甲基三亚甲基硅烷 1,1-dimethylsilacyclobutane 2295-12-7 C5H12Si 100.236 丁基三甲基矽烷 n-butyltrimethylsilane 1000-49-3 C7H18Si 130.305 乙基三甲基硅烷 trimethylsilylethane 3439-38-1 C5H14Si 102.252
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Dolgov,B.N. et al., Journal of general chemistry of the USSR, 1960, vol. 30, p. 2960 - 2966摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Effect of a neighboring trimethylsilyl group on the photochemical and mass spectral fragmentation pathways of S-alkyl thioacetates摘要:DOI:10.1021/jo00925a021
-
作为试剂:描述:苯并噻唑 、 反式-查耳酮 在 三甲基-丙基硅烷 、 1-叔丁基-4,4,4-三(二甲氨基)-2,2-二[三(二甲氨基)-正膦亚基氨基]-2Λ5,4Λ5-连二(磷氮基化合物) 作用下, 以 甲苯 为溶剂, 反应 24.0h, 以43%的产率得到(E)-1-(2-benzothiazolyl)-1,3-diphenyl-2-propen-1-ol参考文献:名称:Metal-free deprotonative functionalization of heteroaromatics using organic superbase catalyst摘要:无金属条件下的杂芳香化合物去质子化功能化是通过使用有机超碱性催化剂实现的;一种有机硅添加剂,如三甲基硅基丙炔,被用于激活对羰基化合物进行1,2-加成的催化循环。DOI:10.1039/c0cc03106b
文献信息
-
Single-Site Cobalt Catalysts at New Zr<sub>8</sub>(μ<sub>2</sub>-O)<sub>8</sub>(μ<sub>2</sub>-OH)<sub>4</sub> Metal-Organic Framework Nodes for Highly Active Hydrogenation of Alkenes, Imines, Carbonyls, and Heterocycles作者:Pengfei Ji、Kuntal Manna、Zekai Lin、Ania Urban、Francis X. Greene、Guangxu Lan、Wenbin LinDOI:10.1021/jacs.6b06759日期:2016.9.21We report here the synthesis of robust and porous metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), M-MTBC (M = Zr or Hf), constructed from the tetrahedral linker methane-tetrakis(p-biphenylcarboxylate) (MTBC) and two types of secondary building units (SBUs): cubic M8(μ2-O)8(μ2-OH)4 and octahedral M6(μ3-O)4(μ3-OH)4. While the M6-SBU is isostructural with the 12-connected octahedral SBUs of UiO-type MOFs, the M8-SBU我们在此报告了由四面体连接子甲烷-四(对联苯羧酸盐) (MTBC) 和两种类型的二次构建构成的坚固且多孔的金属有机框架 (MOF)、M-MTBC (M = Zr 或 Hf) 的合成单位 (SBU):立方 M8(μ2-O)8(μ2-OH)4 和八面体 M6(μ3-O)4(μ3-OH)4。虽然 M6-SBU 与 UiO 型 MOF 的 12 个连接八面体 SBU 具有同构,但 M8-SBU 由八个 M(IV) 离子以立方方式由八个 μ2-氧代和四个 μ2-OH 基团连接而成。Zr-MTBC SBU 用 CoCl2 金属化,然后用 NaBEt3H 处理,提供了高活性和可重复使用的固体 Zr-MTBC-CoH 催化剂,用于烯烃、亚胺、羰基和杂环的氢化。Zr-MTBC-CoH 对一系列官能团的耐受性令人印象深刻,并且在三取代和四取代烯烃的氢化中显示出高活性,TON > 8000 用于氢化 2,3-二
-
STABILIZATION OF ACTIVE METAL CATALYSTS AT METAL-ORGANIC FRAMEWORK NODES FOR HIGHLY EFFICIENT ORGANIC TRANSFORMATIONS申请人:The University of Chicago公开号:US20180361370A1公开(公告)日:2018-12-20Metal-organic framework (MOFs) compositions based on post¬synthetic metalation of secondary building unit (SBU) terminal or bridging OH or OH 2 groups with metal precursors or other post-synthetic manipulations are described. The MOFs provide a versatile family of recyclable and reusable single-site solid catalysts for catalyzing a variety of asymmetric organic transformations, including the regioselective boryiation and siiylation of benzyiic C—H bonds, the hydrogenation of aikenes, imines, carbonyls, nitroarenes, and heterocycles, hydroboration, hydrophosphination, and cyclization reactions. The solid catalysts can also be integrated into a flow reactor or a supercritical fluid reactor.
-
Rhenium Hydride/Boron Lewis Acid Cocatalysis of Alkene Hydrogenations: Activities Comparable to Those of Precious Metal Systems作者:Yanfeng Jiang、Jeannine Hess、Thomas Fox、Heinz BerkeDOI:10.1021/ja107187r日期:2010.12.29found to be B(C(6)F(5))(3) > BEt(3) ≈ BH(3)·THF > BPh(3) ≫ BF(3)·OEt(2) > B(OMe)(3) ≫ BCl(3). The stability of the catalytic systems was checked via TON vs time plots, which revealed the boron Lewis acids to cause an approximate inverse order with the Lewis acid strength: BPh(3) > BEt(3) ≈ BH(3)·THF > B(C(6)F(5))(3). For the 2a/BPh(3) system a maximum TON of 3.1 × 10(4) and for the 2a/B(C(6)F(5))(3) system二溴亚硝酰基(二氢)铼(I)络合物 [ReBr(2)(NO)(PR(3))(2)(η(2)-H(2))] (1; R = iPr, a; Cy, b ) 和 Me(2)NH·BH(3) (DMAB) 在 90 °C 或环境温度和 10 bar H(2) 下催化各种末端和环状烯烃(1-己烯、1-辛烯、环辛烯)的氢化、苯乙烯、1,5-环辛二烯、1,7-辛二烯、α-甲基苯乙烯)。在 1-己烯的氢化中实现了 3.6 × 10(4) h(-1) 在 90 °C 和 1.7 × 10(4) h(-1) 在 23 °C 的最大转换频率 (TOF) 值。1/DMAB 系统非凡的催化性能归因于五配位铼 (I) 氢化物复合物 [Re(Br)(H)(NO)(PR(3))(2)] (2; R = iPr, a; Cy, b) 和源自 DMAB 的路易斯酸 BH(3) 的作用。相关的 2/BH(3)·THF 催化体
-
Bis(imino)pyridine Cobalt-Catalyzed Dehydrogenative Silylation of Alkenes: Scope, Mechanism, and Origins of Selective Allylsilane Formation作者:Crisita Carmen Hojilla Atienza、Tianning Diao、Keith J. Weller、Susan A. Nye、Kenrick M. Lewis、Johannes G. P. Delis、Julie L. Boyer、Aroop K. Roy、Paul J. ChirikDOI:10.1021/ja5060884日期:2014.8.27aryl-substituted bis(imino)pyridine cobalt methyl complex, ((Mes)PDI)CoCH3 ((Mes)PDI = 2,6-(2,4,6-Me3C6H2-N═CMe)2C5H3N), promotes the catalytic dehydrogenative silylation of linear α-olefins to selectively form the corresponding allylsilanes with commercially relevant tertiary silanes such as (Me3SiO)2MeSiH and (EtO)3SiH. Dehydrogenative silylation of internal olefins such as cis- and trans-4-octene芳基取代的双(亚氨基)吡啶钴甲基配合物((Mes)PDI)CoCH3((Mes)PDI = 2,6-(2,4,6-Me3C6H2-N=CMe)2C5H3N)促进催化脱氢反应线性α-烯烃的甲硅烷基化以选择性地与商业相关的叔硅烷如 (Me3SiO)2MeSiH 和 (EtO)3SiH 形成相应的烯丙基硅烷。内烯烃(如顺式和反式 4-辛烯)的脱氢硅烷化也仅产生烯丙基硅烷,硅位于烃链的末端,从而形成一种高选择性贱金属催化的 CH 键远程官能化方法保留不饱和度。钴催化反应还使廉价的 α-烯烃能够作为更有价值的 α-烯烃的功能等价物,ω-二烯,并提供了一种独特的方法,用于将硅油与明确定义的碳间隔物进行交联。化学计量实验和氘标记研究支持活化钴烷基前体以形成推定的钴甲硅烷基,其经历烯烃的 2,1-插入,然后从大叔甲硅烷基团的远端碳选择性消除 β-氢,并解释观察到的烯丙基硅烷形成选择性。
-
Decamethyltitanocene hydride intermediates in the hydrogenation of the corresponding titanocene-(η<sup>2</sup>-ethene) or (η<sup>2</sup>-alkyne) complexes and the effects of bulkier auxiliary ligands作者:Jiří Pinkas、Róbert Gyepes、Ivana Císařová、Jiří Kubišta、Michal Horáček、Karel MachDOI:10.1039/c7dt01545c日期:——reactions of titanocene [Cp*2Ti] (Cp* = η5-C5Me5) and its derivatives [Cp*(η5:η1-C5Me4CH2)TiMe] and [Cp*2Ti(η2-CH2=CH2)] with excess dihydrogen at room temperature and pressures lower than 1 bar revealed the formation of dihydride [Cp*2TiH2] (1) and the concurrent liberation of either methane or ethane, depending on the organometallic reactant. The subsequent slow decay of 1 yielding [Cp*2TiH] (2) was mediated钛茂[Cp * 2Ti](Cp * =η5-C5Me5)及其衍生物[Cp *(η5:η1-C5Me4 )TiMe]和[Cp * 2Ti(η2-CH2= )]反应的1H NMR研究在室温和低于1 bar的压力下使用二氢,发现形成了二氢化物[Cp * 2TiH2](1),并同时释放了甲烷或乙烷,具体取决于有机金属反应物。随后产生的缓慢生成1 [Cp * 2TiH](2)(2)的缓慢衰变是由原位形成的并经氢气压力控制的钛茂介导的。通过在氢气存在下蒸发新鲜[Cp * 2Ti]的己烷溶液而获得的晶体产物,其晶体要么在晶胞的不对称部分具有两个独立的分子1,要么在晶体中由1和[Cp * 2Ti]组成的共晶体。 2:1的比例。在室温下进行炔烃配合物[Cp * 2Ti(η2-R1C≡CR2)]的氢化(R1 = R2 = Me或Et),得到烷烃R1 R2,除去氢后,定量地形成2。对于包含较大取代基的炔烃配合物,R1
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
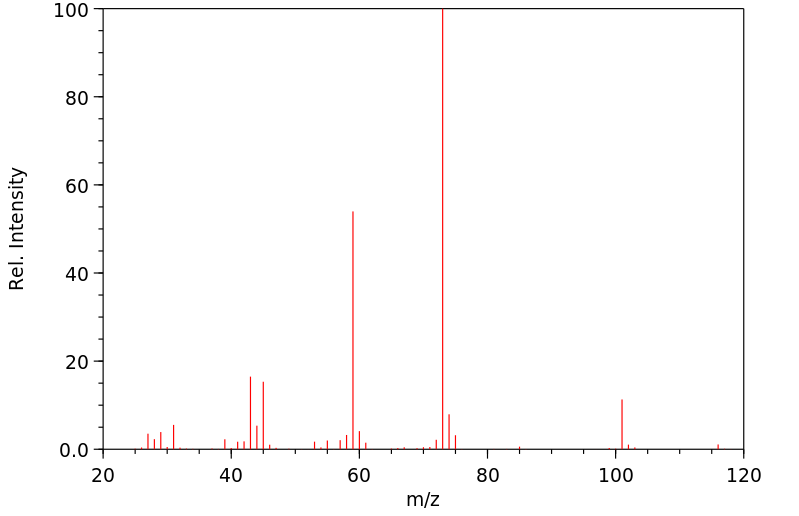
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
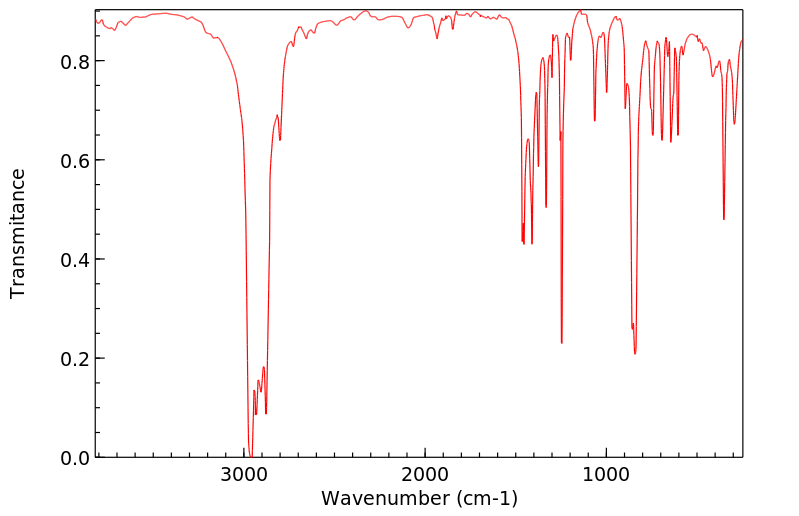
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
镁己烷
锌,二环己基-
锂,3-辛炔基-
锂,(1-苯基乙基)-
铜(I)己基乙炔化物
铜(1+),2-甲基丙烷
铅杂鎓,二乙基甲基-
钠,(1,2,3,4-四甲基-2,4-环戊二烯-1-基)-
钛(4+)四(2,2-二甲基丙烷-1-I去)
邻苯二甲酰基
邻甲基二苯甲酮自由基阳离子
辛烷钠
苄基铜
苄基钠
脱羰秋水仙碱
胂,二(2,2-二甲基丙基)-
纳米碳化钛
红陪酚四甲基醚
红倍酚
秋水仙碱甲硫代磺酸盐
秋水仙碱
碳化锆
碳化铪
碳化铌
碳化铀
碳化钽
碳化钒
碘二氟甲基(1+)
硼化二铬
硫代秋水仙碱
硅烷,二甲基丙基-
硅烷,乙基二甲基-2-丙烯基-
硅烷,乙基二(3-甲基丁基)-
石墨溴化物
甲烷,钼
甲基锡烷
甲基铍氢化物
甲基辛基硅烷
甲基硅烷基阳离子
甲基硅烷
甲基二乙烯基硅烷
甲基丙烯酸7-氧代-4-(苯基偶氮)-1,3,5-环庚三烯-1-基酯
甲基三烯丙基硅烷
甲基三正辛基硅烷
甲基三正己基硅烷
甲基三乙基硅烷
甲基三-N-癸基硅烷
甲基6-肼基-7-氧代-1,3,5-环庚三烯-1-羧酸酯
甲基-三-n-丁基硅烷
甲基(三丙基)硅烷