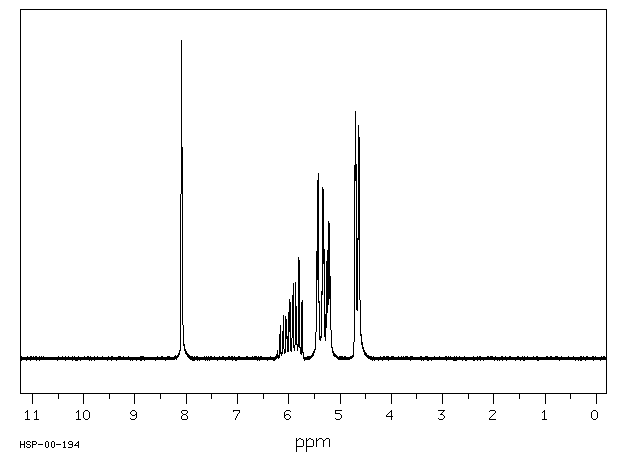
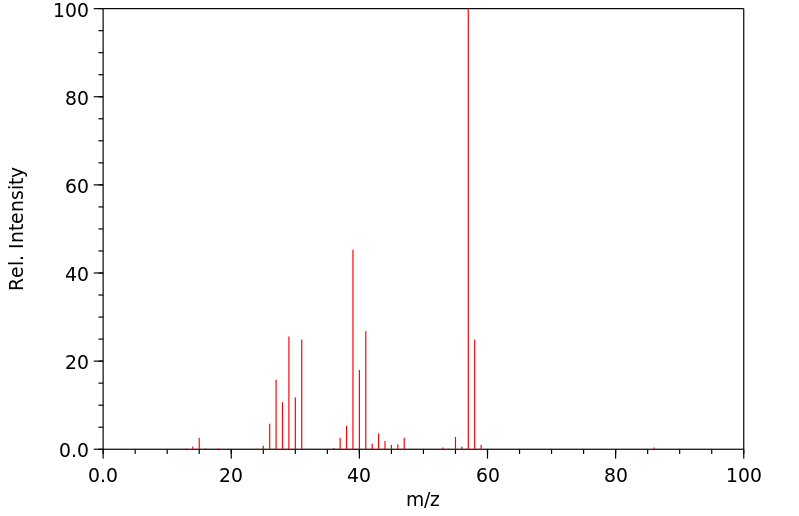
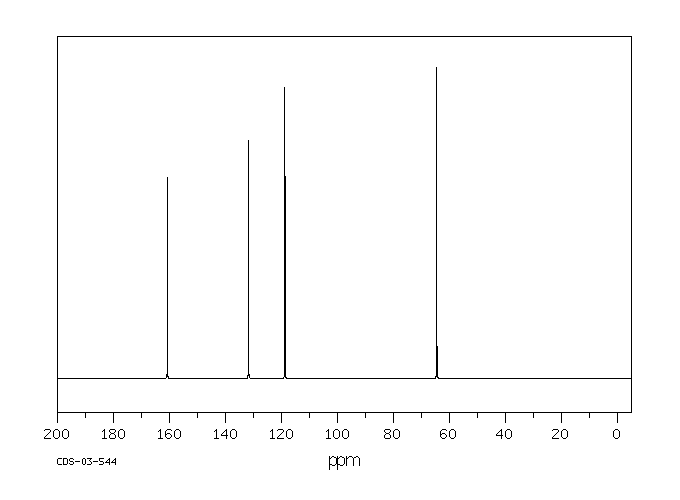
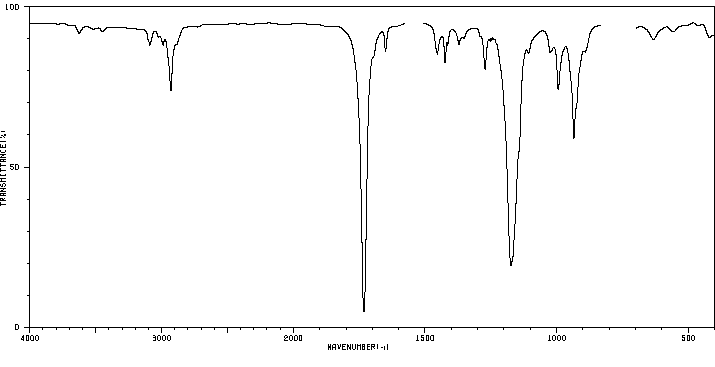
After a brief discussion of the mechanism of radical additions to olefins and of possibilities for initiating the radical chain, the reaction is described as a synthetic method for the preparation of carboxylic acid derivatives. Selected preparative procedures and tables with preparative data indicate the breadth of applicability of the method. The unsaturated compounds: open-chain, cyclic, or bicyclic unsubstituted and substituted olefins, and also dienes and alkynes, can be subjected to free-radical reaction under various conditions with simple and substituted mono- and dicarboxylic acid derivatives as well as with tricarboxylic acid esters. Free acids, esters, lactones, amides, lactams, anhydrides, nitriles, and acid chlorides, and also α-amino-acid derivatives as well as α-halo acids undergo addition reactions with olefins if at least one hydrogen or halogen atom is located on the α- atom of the acid or acid derivative. The dependence of the yields of 1:1 adduct on the reaction parameters in noted and possibilites of an addition which is selective for α-olefins are described.
在简要讨论了自由基加成到烯烃的机制以及引发自由基链的可能途径之后,该反应被描述为一种制备
羧酸衍
生物的合成方法。选取的制备程序和包含制备数据的表格显示了该方法广泛的适用性。不饱和化合物——开链、环状或双环的未取代和取代的烯烃,以及二烯烃和
炔烃,可以在各种条件下与简单和取代的单
羧酸和二
羧酸衍
生物以及
三羧酸酯进行自由基反应。自由酸、酯、内酯、酰胺、内酰胺、酐、腈和酰
氯,以及
α-氨基酸衍
生物和α-卤代酸,在与烯烃发生加成反应时,如果至少有一个氢或卤素原子位于酸或酸衍
生物的α原子上。注意到1:1加合物的产率对反应参数的依赖性,并描述了对α-烯烃具有选择性的加成反应的可能性。