吡啶-2-甲醛肟氯甲烷盐 | 51-15-0
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:230 °C (lit.)
-
密度:1.3265 (rough estimate)
-
溶解度:少量溶于甲醇和水
-
蒸汽压力:6.74X10-4 mm Hg at 25 °C (est)
-
稳定性/保质期:
No evidence of significant degradation products appears up to 48 hr after pralidoxime autoinjector discharge. Concentration without degradation of the solution was noted over time when the autoinjector needle caused coring of the vial closure ... Mark-1 autoinjectors are not suitable for administering pralidoxime to small children. However, the autoinjectors are a readily available source of concentrated pralidoxime for administering weight-adjusted doses in small children. The pralidoxime solution obtained in this manner remains chemically intact for at least 48 hr.
-
解离常数:pKa = 5.78 (pyridine) (est)
-
碰撞截面:122.6 Ų [M]+ [CCS Type: TW, Method: calibrated with polyalanine and drug standards]
-
亨利常数:Henry's Law constant = 9.98X10-15 atm-cu m/mol at 25 °C (est)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-3.26
-
重原子数:11
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.142
-
拓扑面积:36.5
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:3
ADMET
安全信息
-
危险品标志:Xn
-
安全说明:S26,S36,S37/39
-
危险类别码:R20/22,R36/37/38
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:2933399090
-
RTECS号:UU4200000
-
危险标志:GHS07
-
危险性描述:H302,H312,H332
-
危险性防范说明:P280
-
包装等级:III
-
危险类别:9
-
危险品运输编号:3077
-
储存条件:本品应密封避光保存。
SDS
: Pyridine-2-aldoxime methochloride
化学品俗名或商品名
1.2 鉴别的其他方法
Pralidoxime chloride
2-PAM chloride
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途
仅供科研用途,不作为药物、家庭备用药或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述
2.1 GHS分类
急性毒性, 经口 (类别4)
急性毒性, 吸入 (类别4)
急性毒性, 经皮 (类别4)
2.2 GHS 标记要素,包括预防性的陈述
危害类型象形图
信号词 警告
危险申明
H302 吞咽有害。
H312 皮肤接触有害。
H332 吸入有害。
警告申明
预防
P261 避免吸入粉尘/ 烟/ 气体/ 烟雾/ 蒸汽/ 喷雾。
P264 操作后彻底清洁皮肤。
P270 使用本产品时不要进食、饮水或吸烟。
P271 只能在室外或通风良好之处使用。
P280 穿戴防护手套/ 防护服。
措施
P301 + P312 如果吞下去了: 如感觉不适,呼救解毒中心或看医生。
P302 + P352 如果在皮肤上: 用大量肥皂和水淋洗。
P304 + P340 如果吸入: 将患者移到新鲜空气处休息,并保持呼吸舒畅的姿势。
P312 如感觉不适,呼救解毒中心或医生。
P322 具体措施(见本标签上提供的急救指导)。
P330 漱口。
P363 沾染的衣服清洗后方可重新使用。
处理
P501 将内容物/ 容器处理到得到批准的废物处理厂。
2.3 其它危害物 - 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
3.1 物 质
: Pralidoxime chloride
别名
2-PAM chloride
: C7H9N2O·Cl
分子式
: 172.61 g/mol
分子量
成分 浓度
2-Hydroxyiminomethyl-1-methylpyridinium chloride
-
化学文摘编号(CAS No.) 51-15-0
EC-编号 200-080-9
模块 4. 急救措施
4.1 必要的急救措施描述
一般的建议
请教医生。 出示此安全技术说明书给到现场的医生看。
如果吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如果停止了呼吸,给于人工呼吸。 请教医生。
在皮肤接触的情况下
用肥皂和大量的水冲洗。 请教医生。
在眼睛接触的情况下
用水冲洗眼睛作为预防措施。
如果误服
切勿给失去知觉者从嘴里喂食任何东西。 用水漱口。 请教医生。
4.2 最重要的症状和影响,急性的和滞后的
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示
无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施
5.1 灭火介质
灭火方法及灭火剂
用水雾,耐醇泡沫,干粉或二氧化碳灭火。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害
碳氧化物, 氮氧化物, 氯化氢气体
5.3 救火人员的预防
如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步的信息
无数据资料
模块 6. 泄露应急处理
6.1 人员的预防,防护设备和紧急处理程序
使用个人防护设备。 防止粉尘的生成。 防止吸入蒸汽、气雾或气体。 保证充分的通风。 避免吸入粉尘。
6.2 环境预防措施
不要让产物进入下水道。
6.3 抑制和清除溢出物的方法和材料
收集、处理泄漏物,不要产生灰尘。 扫掉和铲掉。 存放在合适的封闭的处理容器内。
6.4 参考其他部分
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
7.1 安全操作的注意事项
避免接触皮肤和眼睛。 防止粉尘和气溶胶生成。
在有粉尘生成的地方,提供合适的排风设备。一般性的防火保护措施。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性
贮存在阴凉处。 容器保持紧闭,储存在干燥通风处。
7.3 特定用途
无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制/个体防护
8.1 控制参数
最高容许浓度
没有已知的国家规定的暴露极限。
8.2 暴露控制
适当的技术控制
根据工业卫生和安全使用规则来操作。 休息以前和工作结束时洗手。
人身保护设备
眼/面保护
带有防护边罩的安全眼镜符合 EN166要求请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟)
检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/EEC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
身体保护
全套防化学试剂工作服, 防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和含量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
如须暴露于有害环境中,请使用P95型(美国)或P1型(欧盟 英国
143)防微粒呼吸器。如需更高级别防护,请使用OV/AG/P99型(美国)或ABEK-P2型 (欧盟 英国 143)
防毒罐。
呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息
a) 外观与性状
形状: 固体
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味临界值
无数据资料
d) pH值
无数据资料
e) 熔点/凝固点
熔点/熔点范围: 230 °C - lit.
f) 起始沸点和沸程
无数据资料
g) 闪点
无数据资料
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 可燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 无数据资料
k) 蒸气压
无数据资料
l) 相对蒸气密度
无数据资料
m) 相对密度
无数据资料
n) 水溶性
无数据资料
o) 辛醇/水分配系数的对数值
无数据资料
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性
10.1 反应性
无数据资料
10.2 化学稳定性
无数据资料
10.3 危险反应的可能性
无数据资料
10.4 避免接触的条件
无数据资料
10.5 不兼容的材料
强氧化剂, 强碱
10.6 危险的分解产物
其它分解产物 - 无数据资料
模块 11. 毒理学资料
11.1 毒理学影响的信息
急性毒性
半致死剂量(LD50) 静脉内的 - 大鼠 - 96 mg/kg
皮肤腐蚀/刺激
无数据资料
严重眼损伤 / 眼刺激
无数据资料
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
无数据资料
生殖细胞诱变
无数据资料
致癌性
IARC:
此产品中没有大于或等于 0。1%含量的组分被 IARC鉴别为可能的或肯定的人类致癌物。
生殖毒性
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入有害。 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
摄入 误吞对人体有害。
皮肤 如果通过皮肤被吸收是有害的。 可能引起皮肤刺激。
眼睛 可能引起眼睛刺激。
接触后的征兆和症状
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: UU4200000
模块 12. 生态学资料
12.1 毒性
无数据资料
12.2 持久存留性和降解性
无数据资料
12.3 生物积累的潜在可能性
无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移
无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价
无数据资料
12.6 其它不利的影响
无数据资料
模块 13. 废弃处置
13.1 废物处理方法
产品
将剩余的和未回收的溶液交给处理公司。 联系专业的拥有废弃物处理执照的机构来处理此物质。
与易燃溶剂相溶或者相混合,在备有燃烧后处理和洗刷作用的化学焚化炉中燃烧
污染了的包装物
作为未用过的产品弃置。
模块 14. 运输信息
14.1 UN编号
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.2 联合国(UN)规定的名称
欧洲陆运危规: 无危险货物
国际海运危规: 无危险货物
国际空运危规: 无危险货物
14.3 运输危险类别
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.4 包裹组
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.5 环境危险
欧洲陆运危规: 否 国际海运危规 海运污染物: 否 国际空运危规: 否
14.6 对使用者的特别预防
无数据资料
模块 15 - 法规信息
N/A
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
氯解磷定(Pralidoxime Chloride),别名派姆、氯磷定等,是一种有机磷酸酯类解毒药及其他解救药物。作为注射类药物,它主要用于中、重度有机磷中毒的解救,并对如对硫磷、内吸磷、甲拌磷、甲胺磷、特普等有良好疗效。其亲核性基团可以与胆碱酯酶的磷酸化基团结合后共同脱离胆碱酯酶,使其恢复活力,缓解中毒症状。
在轻度有机磷中毒时,可单独应用氯解磷定控制症状;中度、重度中毒时需合并使用阿托品。静脉给药后血中药物迅速达到有效浓度,并且大剂量时还能通过血脑屏障进入脑组织,药物由肾快速排出,无蓄积毒性现象,在国内已有多家公司生产此药物。
作用机理氯解磷定是一种季铵类化合物,其季铵基团能与有机磷杀虫剂结合的已失去活力的磷酰化胆碱酯酶的阳离子部位结合。其亲核性基团可直接与胆碱酯酶的磷酸化基团结合,并共同脱离胆碱酯酶,从而使被抑制的胆碱酯酶恢复活力,但对被有机磷杀虫剂抑制超过36小时的“老化”胆碱酯酶复活效果较差。
此药物主要作用于烟碱样症状,对毒蕈碱样症状作用较弱,且对中枢神经系统症状作用不明显。
适用症状氯解磷定可以取代碘解磷定,对多种有机磷酸酯类杀虫药中毒有不同程度的解救作用。但对氨基甲酸酯类杀虫药引起的中毒效果较差,尤其是马拉硫磷、敌百虫、敌敌畏、乐果、甲氟磷、丙胺氟磷和八甲磷等。
药代动力学氯解磷定为注射类药物,在肌注或静注后血液中药物浓度维持2~3小时,随后逐渐下降。成人轻度中毒者肌肉注射0.5~0.75g,必要时1小时后再重复一次;中度中毒者首次0.75~1.5g,并在1小时内再使用一次;重度中毒者根据情况使用较大剂量。
老年人用药应适当减少用量并减慢静脉注射速度。有机磷杀虫剂中毒患者应用此药物越早越好,且对皮肤吸收引起中毒的患者需脱去被污染的衣服,用肥皂清洗头发和皮肤,口服中毒患者则需要用2.5%碳酸氢钠溶液彻底洗胃。
不良反应使用氯解磷定时可能出现恶心、呕吐、心率增快等现象。注射速度过快可能引发眩晕、视力模糊、复视及动作不协调。严重时可引起头痛、头晕、呼吸抑制甚至癫痫发作和死亡风险增加。
注意事项急性中毒患者需密切观察临床表现,保持呼吸道畅通,并准备好人工呼吸措施。药物使用过程中要随时测定血胆碱酯酶水平,维持在50%~60%以上。氯解磷定过量也会抑制胆碱酯酶活性,加重中毒情况。
化学性质:黄白色结晶性粉末,熔点235-238℃(分解),水中溶解度为640mg/ml。 用途:用于有机磷中毒的解毒剂和作为解毒药。 生产方法:通过将2-甲基吡啶与氯甲烷反应得到2-甲基吡啶氯甲烷盐,然后进行亚硝化反应、中和、结晶等一系列步骤制得。
编辑整理者:鲍泉(Chemicalbook);发布时间:2016-01-24。
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:盐酸吡咯肟肟在浓酸性溶液中的降解途径摘要:使用一种或多种方法鉴定HPLC(1)(X- = Cl-)在浓水溶液(小于或等于50%w / v)中的降解产物:HPLC,极谱法,伏安法,MS和/或核磁共振。发现的产物是2-氰基,2-羧酰胺基和2-羧基-1-甲基-吡啶鎓氯化物,1-甲基吡啶鎓氯化物,氰化物离子,氨和二氧化碳。1-甲基-2-吡啶酮是通过氰化物离子的存在间接鉴定的。降解率随着pH值在1和3.2之间的增加以及浓度在1和50%w / v的氯吡氧肟之间的增加而增加。结果表明1(X- = Cl-)通过腈2的羟基离子催化反应脱水,该腈2水解为吡啶酮6和氰化物离子或水解为2-羧酰胺基-1-甲基吡啶鎓氯化物3。DOI:10.1002/jps.2600750618
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Unnisa, Lateef; Sumakanth; Rao, B. Leelamaheswara, Indian Journal of Chemistry - Section B Organic and Medicinal Chemistry, 2014, vol. 53, # 4, p. 431 - 435摘要:DOI:
-
作为试剂:描述:参考文献:名称:MULTIFUNCTIONAL SMALL MOLECULES摘要:本发明涉及用于治疗和/或预防有机磷酸盐中毒的新型治疗性树状大分子偶联物。特别是,本发明涉及与有机磷酸盐中毒解毒剂(例如,普瑞洛霉素(2-PAM)(4-PAM),奥比多西姆,三甲多西姆,阿索西姆(HI-6),羟基酰胺以及相关的类似物,盐和衍生物)复合的树状大分子,包含这样的树状大分子偶联物的组合物,合成这样的树状大分子偶联物的方法,以及利用这样的树状大分子偶联物(例如,在诊断和/或治疗环境中(例如,用于治疗剂,成像和/或靶向剂(例如,在治疗和/或预防有机磷酸盐中毒)的递送))的系统和方法。公开号:US20150216993A1
文献信息
-
Amino-substituted heterocycles, compositions thereof, and methods of treatment therewith申请人:D'Sidocky Neil R.公开号:US20080242694A1公开(公告)日:2008-10-02Provided herein are Heterocyclic Compounds having the following structure: wherein R 1 , R 2 , X, Y and Z are as defined herein, compositions comprising an effective amount of a Heterocyclic Compound and methods for treating or preventing cancer, inflammatory conditions, immunological conditions, metabolic conditions and conditions treatable or preventable by inhibition of a kinase pathway comprising administering an effective amount of a Heterocyclic Compound to a patient in need thereof.
-
COMPOUNDS AND METHODS TO TREAT ORGANOPHOSPHORUS POISONING申请人:University of Iowa Research Foundation公开号:US20140323473A1公开(公告)日:2014-10-30Organophosphate (OP) nerve agents and pesticides are potent inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase (AChE). Though oxime nucleophiles can reactivate an AChE-phosphyl adduct, the adduct can undergo a reaction called aging, leading to an aged-AChE adduct. The invention provides compounds and methods that can be used to reactivate an aged-AChE adduct. Such compounds and methods are useful to counteract organophosphorus poisoning.
-
ANTHELMINTIC COMPOUNDS AND COMPOSITIONS AND METHOD OF USING THEREOF申请人:Meng Charles Q.公开号:US20140142114A1公开(公告)日:2014-05-22The present invention relates to novel anthelmintic compounds of formula (I) below: wherein Y and Z are independently a bicyclic carbocyclic or a bicyclic heterocyclic group, or one of Y or Z is a bicyclic carbocyclic or a bicyclic heterocyclic group and the other of Y or Z is alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, cycloalkyl, phenyl, heterocyclyl or heteroaryl, and variables X 1 , X 2 , X 3 , X 4 , X 5 , X 6 , X 7 and X 8 are as defined herein. The invention also provides for veterinary compositions comprising the anthelmintic compounds of the invention, and their uses for the treatment and prevention of parasitic infections in animals.本发明涉及以下式(I)的新型驱虫化合物: 其中 Y和Z分别是双环碳环或双环杂环基团,或者Y或Z中的一个是双环碳环或双环杂环基团,另一个是烷基,烯基,炔基,环烷基,苯基,杂环基或杂芳基,以及变量X 1 ,X 2 ,X 3 ,X 4 ,X 5 ,X 6 ,X 7 和X 8 如本文所定义。本发明还提供了包含本发明的驱虫化合物的兽药组合物,以及它们用于治疗和预防动物寄生虫感染的用途。
-
[EN] ANTHELMINTIC DEPSIPEPTIDE COMPOUNDS<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS DEPSIPEPTIDIQUES ANTHELMINTHIQUES申请人:MERIAL INC公开号:WO2018093920A1公开(公告)日:2018-05-24The present invention provides cyclic depsipeptide compounds of formula (I) wherein the stereochemical configuration of at least one carbon atom bearing the groups Cy1, Cy2, R1, R2, R3, R4, Ra and Rb is inverted compared with the naturally occurring cyclic depsipeptide PF1022A. The invention also provides compositions comprising the compounds that are effective against parasites that harm animals. The compounds and compositions may be used for combating parasites in or on mammals and birds. The invention also provides for an improved method for eradicating, controlling and preventing parasite infestation in birds and mammals.
-
Isoindole-imide compounds and compositions comprising and methods of using the same申请人:Muller W. George公开号:US20070049618A1公开(公告)日:2007-03-01This invention relates to isoindole-imide compounds, and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, solvates, stereoisomers, and prodrugs thereof. Methods of use, and pharmaceutical compositions of these compounds are disclosed.
表征谱图
-
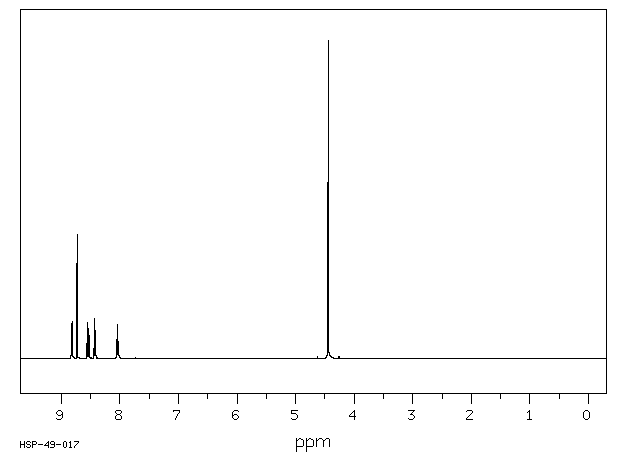
氢谱1HNMR
-
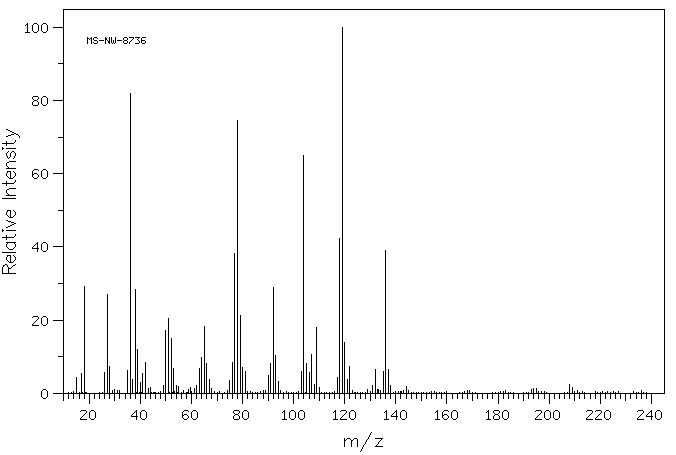
质谱MS
-
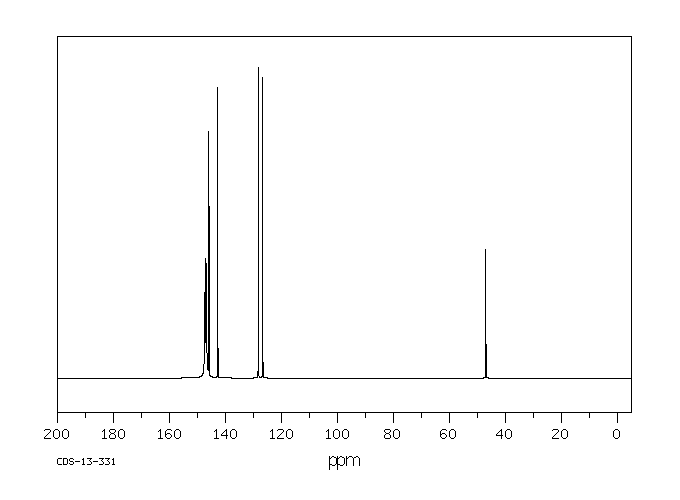
碳谱13CNMR
-
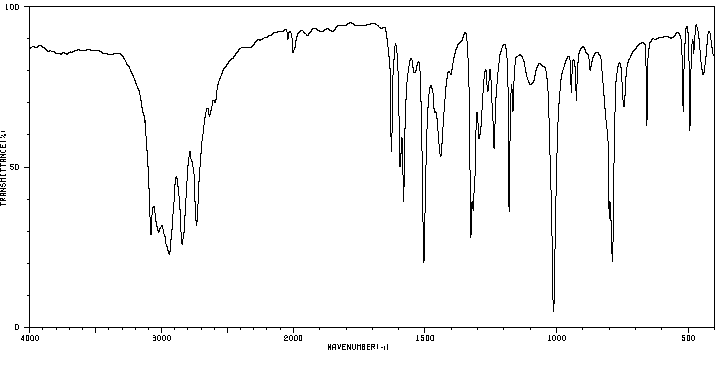
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息