12-甲基苯并[a]蒽 | 2422-79-9
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):5.4
-
重原子数:19
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:4.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.05
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
ADMET
上下游信息
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 7,12-二甲基苯并[a]蒽 7,12-Dimethylbenz[a]anthracene 57-97-6 C20H16 256.347 —— BENZ(a)ANTHRACENE, 12-BROMOMETHYL- 78533-30-9 C19H13Br 321.216 7-甲酰基-12-甲基苯并(a)蒽 12-methyl-benz[a]anthracene-7-carbaldehyde 13345-61-4 C20H14O 270.331 7-(碘甲基)-12-甲基苯并[a]蒽 7-iodomethyl-12-methylbenz[a]anthracene 27018-50-4 C20H15I 382.244 12-甲基苯并[a]蒽-7-甲腈 12-methyl-benz[a]anthracene-7-carbonitrile 63020-25-7 C20H13N 267.33 7-甲氧基甲基-12-甲基苯并[a]蒽 methyl-(12-methyl-benz[a]anthracen-7-ylmethyl)-ether 13345-60-3 C21H18O 286.373 —— ethyl-(12-methyl-benz[a]anthracen-7-ylmethyl)-ether 63020-27-9 C22H20O 300.4
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:207.多环芳烃。第二十四部分摘要:DOI:10.1039/jr9400001125
-
作为产物:描述:alkaline earth salt of/the/ methylsulfuric acid 在 zinc(II) chloride 作用下, 生成 12-甲基苯并[a]蒽参考文献:名称:82.多环芳烃。第十五部分。1:2-苯并蒽的新同源物摘要:DOI:10.1039/jr9370000393
文献信息
-
Substituent Effects in Benz[<i>a</i>]anthracene Carbocations: A Stable Ion, Electrophilic Substitution (Nitration, Bromination), and DFT Study作者:Kenneth K. Laali、Maria A. Arrica、Takao Okazaki、Ronald G. HarveyDOI:10.1021/jo070936r日期:2007.8.31computed relative energies by DFT. Charge delocalization paths in the resulting carbocations were deduced based on the magnitude of Δδ13C values. For the thermodynamically more stable C-12 protonated carbocations, the charge delocalization path is analogous to those derived based on computed NPA charges for the benzylic carbocations formed by 1,2-epoxide (bay-region) and 5,6-epoxide (K-region) ring opening在FSO 3 H / SO 2 ClF中通过低温质子化作用,由异构的单烷基化和二烷基化的苯并[ a ]蒽(BAs)生成了一系列新型的碳正离子化反应。C-7具有单烷基衍生物(5-甲基,6-甲基,7-甲基和7-乙基)以及D环甲基化类似物(9-甲基,10-甲基和11-甲基),或在所有情况下均观察到C-12质子化的碳正离子(作为唯一或主要的碳正离子)。12-甲基衍生物的质子化(9)得到C-7质子化的碳正离子(9H +)作为动能种类和本位-protonated碳阳离子(9AH +)作为热力学阳离子。与12-乙基衍生物(10),在箱式区域空间张力的浮雕大大有利于本位-protonation(10AH +)。具有3,9-二甲基(14),C-7质子化(14H +)(C-12质子化<10%)受到强烈青睐,在1,12-二甲基(15)的情况下,观察到的唯一物质是C-7质子化的碳正离子化(15H +)。对于7-甲
-
Influence of diet on development and oviposition of <i>Forficula auricularia</i> (Dermaptera: Forficulidae)作者:Ghislain Berleur、Jean Gingras、Jean-Claude TourneurDOI:10.4039/ent133705-5日期:2001.10
In North America, the life cycle of the European earwig (
Forficula auricularia L.) can be divided into a nesting phase (hypogean phase) and a free-foraging phase (epigean phase) (Crumbet al. 1941; Behura 1956; Lamb and Wellington 1975). Adults spend the nesting phase in the soil; females burrow into the ground at the onset of the cold weather, lay eggs, and then care for the eggs. Hatching occurs in spring; first- or second-instar nymphs move to the soil surface for the free-foraging period. The earwig, a nocturnal insect, spends the entire daylight period of hiding under trash or in dark crevices. Where two broods occur, females reenter the ground a second time (Lamb and Wellington 1975). Stomach content analyses (Crumbet al. 1941; Sunderland and Vickerman 1980) and food preference tests (McLeod and Chant 1952; Buxton and Madge 1976) revealed that the European earwig is omnivorous. Under laboratory conditions, nymphs fed freshly frozen aphids,Rhopalosiphum padi (L.) (Hemiptera: Aphididae), survive better than those fed green algae or carrots, develop faster, and produce heavier females (Phillips 1981; Carrillo 1985).在北美洲,欧洲蠼(Forficula auricularia L.)的生命周期可分为筑巢期(hypogean phase)和自由觅食期(epigean phase)(Crumb 等人,1941 年;Behura,1956 年;Lamb 和 Wellington,1975 年)。成虫在土壤中度过筑巢阶段;雌虫在寒冷天气开始时钻入地下产卵,然后照料卵。孵化发生在春季;一龄或二龄若虫移到土壤表面自由觅食。蠼是一种夜行性昆虫,整个白天都躲在垃圾堆下或黑暗的缝隙中。当出现两窝幼虫时,雌虫会再次进入地下(Lamb 和 Wellington,1975 年)。胃内容物分析(Crumb 等,1941 年;Sunderland 和 Vickerman,1980 年)和食物偏好测试(McLeod 和 Chant,1952 年;Buxton 和 Madge,1976 年)显示,欧洲蠼是杂食性的。在实验室条件下,喂食新鲜冷冻蚜虫 Rhopalosiphum padi (L.)(半翅目:蚜科)的若虫比喂食绿藻或胡萝卜的若虫存活率更高,发育更快,雌虫体重更大(Phillips,1981 年;Carrillo,1985 年)。 -
Synthesis of Phenol and Quinone Metabolites of Benzo[<i>a</i>]pyrene, a Carcinogenic Component of Tobacco Smoke Implicated in Lung Cancer作者:Daiwang Xu、Trevor M. Penning、Ian A. Blair、Ronald G. HarveyDOI:10.1021/jo801864m日期:2009.1.1612-BP phenols and the BP 1,6-, 3,6-, 6,12-, and 9,10-quinones are now reported. The syntheses of the BP phenols (except 6-HO-BP) involve the key steps of Pd-catalyzed Suzuki−Miyaura cross-coupling of a naphthalene boronate ester with a substituted aryl bromide or triflate ester. The BP quinones were synthesized from the corresponding BP phenols by direct oxidation with the hypervalent iodine reagents多环芳烃(PAH)是有机物燃烧时产生的广泛环境污染物。 PAHs存在于汽车尾气和烟草烟雾中,最近被指定为人类致癌物。目前的证据表明,PAH 被酶促激活,产生与 DNA 相互作用的诱变代谢物。有证据表明存在三种激活途径:二醇环氧化物途径、自由基-阳离子途径和醌途径。这些途径对人类肺癌的相对重要性尚未确定。我们现在报道了原型 PAH 致癌物苯并[ a ]芘 (BP) 的主要苯酚和醌异构体的合成,已知或怀疑这些异构体是人支气管肺泡细胞中 BP 的代谢产物。合成方法被设计为适用于BP代谢物的13 C标记类似物的制备。这些化合物需要作为敏感 LC−MS/MS 方法的标准品,用于分析肺细胞中形成的 BP 代谢物。目前已报道了 1-、3-、6-、9- 和 12-BP 苯酚以及 BP 1,6-、3,6-、6,12- 和 9,10-醌的高效新型合成方法。 BP 苯酚(6-HO-BP 除外)的合成涉及萘硼酸酯与取代的芳基溴或三氟甲磺酸酯的
-
Synthesis of 9,10-Dimethyl-1,2-benzanthracene and of a Thiophene Isolog作者:Reuben B. Sandin、Louis F. FieserDOI:10.1021/ja01868a055日期:1940.11
-
Coördination of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons with Silver Ion; Correlation of Equilibrium Constants with Relative Carcinogenic Potencies<sup>1</sup>作者:Robert E. Kofahl、Howard J. LucasDOI:10.1021/ja01644a020日期:1954.8
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
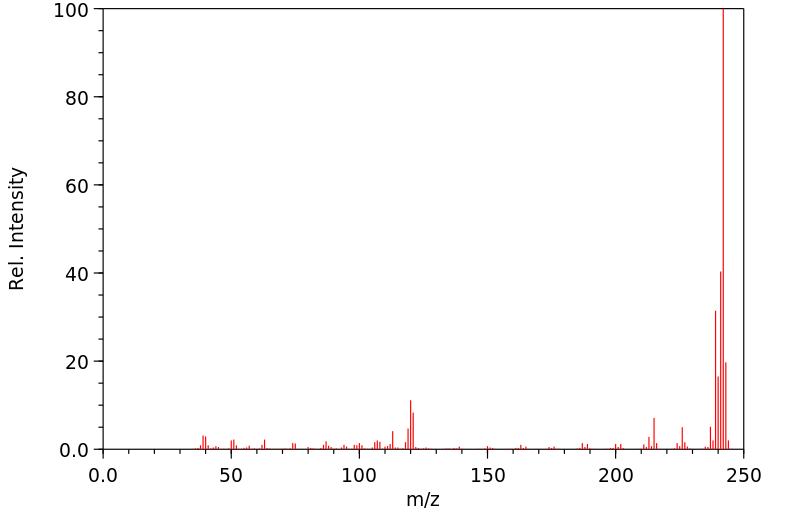
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息