7,12-二甲基苯并[a]蒽 | 57-97-6
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:122-123 °C(lit.)
-
沸点:183-184 °C765 mm Hg(lit.)
-
密度:0.9 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
-
闪点:130 °F
-
物理描述:7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene appears as yellow to greenish-yellow crystals or a yellow solid. Odorless. Maximum fluorescence at 440 nm. Bluish-violet fluorescence in UV light. (NTP, 1992)
-
颜色/状态:Plates, leaflets from acetone-alcohol, faint greenish-yellow tinge
-
气味:Odorless[NOAA; CAMEO Chemicals. Database of Hazardous Materials. 7,12-Dimethylbenz
-
溶解度:In water, 0.061 mg/L water at 25 °C
-
蒸汽压力:6.8X10-7 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
稳定性/保质期:
- 存在于烟气中。
- 具有致癌性。
-
分解:Hazardous decomposition products formed under fire conditions - Carbon oxides.[Sigma-Aldrich; Safety Data Sheet for 7,12-Dimethylbenz
-
保留指数:2711;2713;443.82;443.9;444;442.03;443.38;444.84;443.38
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):5.8
-
重原子数:20
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:4.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.1
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
ADMET
安全信息
-
危险品标志:C,T
-
安全说明:S36/37,S45,S53,S60,S61,S62
-
危险类别码:R22
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:29029090
-
RTECS号:DP4500000
-
包装等级:III
-
危险类别:6.1(b)
-
危险品运输编号:UN 3077 9/PG 3
-
储存条件:本品应密封保存。
SDS
模块 1. 化学品
1.1 产品标识符
: 7,12-二甲基苯并[a]蒽
产品名称
1.2 鉴别的其他方法
1,4-Dimethyl-2,3-benzophenaNThrene
DMBA
9,10-Dimethyl-1,2-benzaNThracene
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途
仅用于研发。不作为药品、家庭或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述
2.1 GHS-分类
急性毒性, 经口 (类别 4)
皮肤刺激 (类别 3)
致癌性 (类别 1B)
2.2 GHS 标记要素,包括预防性的陈述
象形图
警示词 危险
危险申明
H302 吞咽有害。
H316 引起轻微皮肤刺激。
H350 可能致癌。
警告申明
预防措施
P201 在使用前获取特别指示。
P202 在读懂所有安全防范措施之前切勿操作。
P264 操作后彻底清洁皮肤。
P270 使用本产品时不要进食、饮水或吸烟。
P281 使用所需的个人防护设备。
事故响应
P301 + P312 如果吞咽并觉不适: 立即呼叫解毒中心或就医。
P308 + P313 如接触到或有疑虑:求医/ 就诊。
P330 漱口。
P332 + P313 如觉皮肤刺激:求医/就诊。
安全储存
P405 存放处须加锁。
废弃处置
P501 将内容物/ 容器处理到得到批准的废物处理厂。
只限于专业使用者。
2.3 其它危害物 - 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
3.1 物 质
: 1,4-Dimethyl-2,3-benzophenaNThrene
别名
DMBA
9,10-Dimethyl-1,2-benzaNThracene
: C20H16
分子式
: 256.34 g/mol
分子量
组分 浓度或浓度范围
7,12-Dimethylbenz[a]aNThracene
<=100%
化学文摘登记号(CAS 57-97-6
No.) 200-359-5
EC-编号
模块 4. 急救措施
4.1 必要的急救措施描述
一般的建议
请教医生。 向到现场的医生出示此安全技术说明书。
吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如呼吸停止,进行人工呼吸。 请教医生。
皮肤接触
用肥皂和大量的水冲洗。 请教医生。
眼睛接触
用水冲洗眼睛作为预防措施。
食入
切勿给失去知觉者通过口喂任何东西。 用水漱口。 请教医生。
4.2 主要症状和影响,急性和迟发效应
4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示
无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施
5.1 灭火介质
灭火方法及灭火剂
用水雾,抗乙醇泡沫,干粉或二氧化碳灭火。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害
碳氧化物
5.3 给消防员的建议
如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步信息
无数据资料
模块 6. 泄露应急处理
6.1 作业人员防护措施、防护装备和应急处置程序
使用个人防护用品。 避免粉尘生成。 避免吸入蒸气、烟雾或气体。 保证充分的通风。
人员疏散到安全区域。 避免吸入粉尘。
6.2 环境保护措施
如能确保安全,可采取措施防止进一步的泄漏或溢出。 不要让产品进入下水道。
6.3 泄漏化学品的收容、清除方法及所使用的处置材料
收集和处置时不要产生粉尘。 扫掉和铲掉。 放入合适的封闭的容器中待处理。
6.4 参考其他部分
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
7.1 安全操作的注意事项
避免接触皮肤和眼睛。 避免形成粉尘和气溶胶。避免曝露:使用前需要获得专门的指导。
在有粉尘生成的地方,提供合适的排风设备。一般性的防火保护措施。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性
贮存在阴凉处。 使容器保持密闭,储存在干燥通风处。
7.3 特定用途
无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
8.1 容许浓度
最高容许浓度
没有已知的国家规定的暴露极限。
8.2 暴露控制
适当的技术控制
根据良好的工业卫生和安全规范进行操作。 休息前和工作结束时洗手。
个体防护设备
眼/面保护
带有防护边罩的安全眼镜符合 EN166要求请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟)
检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/EEC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
完全接触
物料: 丁腈橡胶
最小的层厚度 0.11 mm
溶剂渗透时间: 480 min
测试过的物质Dermatril® (KCL 740 / Z677272, 规格 M)
飞溅保护
物料: 丁腈橡胶
最小的层厚度 0.11 mm
溶剂渗透时间: 480 min
测试过的物质Dermatril® (KCL 740 / Z677272, 规格 M)
, 测试方法 EN374
如果以溶剂形式应用或与其它物质混合应用,或在不同于EN
374规定的条件下应用,请与EC批准的手套的供应商联系。
这个推荐只是建议性的,并且务必让熟悉我们客户计划使用的特定情况的工业卫生学专家评估确认才可.
这不应该解释为在提供对任何特定使用情况方法的批准.
身体保护
全套防化学试剂工作服, 防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和数量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
如危险性评测显示需要使用空气净化的防毒面具,请使用全面罩式多功能微粒防毒面具N100型(US
)或P3型(EN
143)防毒面具筒作为工程控制的候补。如果防毒面具是保护的唯一方式,则使用全面罩式送风防毒
面具。 呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息
a) 外观与性状
形状: 粉末
颜色: 淡黄
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味阈值
无数据资料
d) pH值
无数据资料
e) 熔点/凝固点
熔点/凝固点: 122 - 123 °C - lit.
f) 沸点、初沸点和沸程
无数据资料
g) 闪点
无数据资料
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 易燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 无数据资料
k) 蒸气压
无数据资料
l) 蒸汽密度
无数据资料
m) 密度/相对密度
无数据资料
n) 水溶性
无数据资料
o) n-辛醇/水分配系数
无数据资料
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性
10.1 反应性
无数据资料
10.2 稳定性
无数据资料
10.3 危险反应
无数据资料
10.4 应避免的条件
无数据资料
10.5 不相容的物质
强氧化剂
10.6 危险的分解产物
其它分解产物 - 无数据资料
模块 11. 毒理学资料
11.1 毒理学影响的信息
急性毒性
半数致死剂量 (LD50) 经口 - 大鼠 - 327 mg/kg
皮肤刺激或腐蚀
皮肤 - 小鼠 - 轻度的皮肤刺激
眼睛刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
无数据资料
生殖细胞致突变性
实验室测试表明由诱变效应
致癌性
该产品是或包含被IARC, ACGIH, EPA, 和 NTP 列为可能是致癌物的组分
可能的人类致癌物
IARC:
此产品中没有大于或等于 0。1%含量的组分被 IARC鉴别为可能的或肯定的人类致癌物。
生殖毒性
实验室试验表明有畸胎生成效应
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入可能有害。 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
摄入 误吞对人体有害。
皮肤 通过皮肤吸收可能有害。 可能引起皮肤刺激。
眼睛 可能引起眼睛刺激。
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: CW3850000
模块 12. 生态学资料
12.1 生态毒性
无数据资料
12.2 持久性和降解性
无数据资料
12.3 潜在的生物累积性
无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移性
无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价
无数据资料
12.6 其它不良影响
无数据资料
模块 13. 废弃处置
13.1 废物处理方法
产品
将剩余的和不可回收的溶液交给有许可证的公司处理。
联系专业的拥有废弃物处理执照的机构来处理此物质。
与易燃溶剂相溶或者相混合,在备有燃烧后处理和洗刷作用的化学焚化炉中燃烧
受污染的容器和包装
按未用产品处置。
模块 14. 运输信息
14.1 联合国危险货物编号
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.2 联合国运输名称
欧洲陆运危规: 非危险货物
国际海运危规: 非危险货物
国际空运危规: 非危险货物
14.3 运输危险类别
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.4 包裹组
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.5 环境危险
欧洲陆运危规: 否 国际海运危规 国际空运危规: 否
海洋污染物(是/否): 否
14.6 对使用者的特别提醒
无数据资料
模块 15 - 法规信息
N/A
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
用途
9,10-二甲基-1,2-苯并蒽是一种蒽类衍生物,可用作生化试剂。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 12-甲基苯并[a]蒽 12-methylbenzo[a]anthracene 2422-79-9 C19H14 242.32 7-(碘甲基)-12-甲基苯并[a]蒽 7-iodomethyl-12-methylbenz[a]anthracene 27018-50-4 C20H15I 382.244 7-氯甲基-12-甲基苯并(a)蒽 7-(Chloromethyl)-12-methylbenzanthracene 13345-62-5 C20H15Cl 290.792 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 3,7,12-trimethylbenzanthracene 35187-23-6 C21H18 270.374 7-羟基甲基-12-甲基苯并(a)蒽 [3H]-7-Hydroxymethyl-12-methylbenz[a]anthracene 568-75-2 C20H16O 272.346 12-羟基甲基-7-甲基苯并(a)蒽 12-hydroxymethyl-7-methylbenz(a)anthracene 568-70-7 C20H16O 272.346 [7-(羟基甲基)苯并[b]菲-12-基]甲醇 7,12-Dihydroxymethylbenzanthracen 2564-65-0 C20H16O2 288.346 12-溴甲基 -7-甲基苯[a]蒽 12-Bromomethyl-7-methyl-benzo[a]anthracene 59230-81-8 C20H15Br 335.243 7,12-双(溴甲基)苯并[a]蒽 7,12-bis(bromomethyl)benz[a]anthracene 34331-98-1 C20H14Br2 414.139 苯并[a]蒽-7,12-二甲醇二乙酸酯 7,12-Diacetoxymethylbenzanthracen 63018-62-2 C24H20O4 372.42
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:170.抑制生长的多环化合物的合成。第一部分摘要:DOI:10.1039/jr9390000802
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Reductive methylation of polycyclic aromatic quinones摘要:DOI:10.1021/jo01295a028
-
作为试剂:描述:N-methyl-N-(3-phenylprop-2-yn-1-yl)prop-2-en-1-amine 在 四(三苯基膦)钯 、 7,12-二甲基苯并[a]蒽 作用下, 以 二氯甲烷 为溶剂, 反应 6.0h, 生成 1-(甲基氨基)-3-苯基-2-丙炔参考文献:名称:仲氨基辅助碳-碳单键裂解进行镧系元素催化的可逆炔交换摘要:据报道,通过仲氨基辅助的CC单键裂解,镧系元素催化的炔基交换。提出了镧系酰胺酰胺配合物作为关键中间体,该中间体经历了前所未有的可逆性β-炔基消除,然后进行炔基交换和亚胺重新插入。释放的炔烃的原位均聚和交叉二聚化可作为将复分解平衡转变为完成反应的另一驱动力。该反应在形式上与常规炔烃复分解反应是互补的,并允许在操作简单的反应条件下,以中等至极好的收率将内部炔丙胺选择性转化为炔烃末端带有不同取代基的那些。DOI:10.1002/anie.201605822
文献信息
-
Pheromone content of azinphosmethyl-susceptible and -resistant obliquebanded leafrollers (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) as a function of time of day and female age作者:Ashraf M. El-Sayed、R.M. TrimbleDOI:10.4039/ent134331-3日期:2002.6
Abstract The effect of time of day and age on the amounts and ratios of four pheromone compounds [(
Z )-11-tetradecenyl acetate (Z 11-14:Ac), (E )-11-tetradecenyl acetate (E 11-14:Ac), (Z )-11-tetradecenol (Z 11-14:OH), and (Z )-11-tetradecenal (Z 11-14:Al)] was compared in azinphosmethyl-susceptible (susceptible) and -resistant (resistant) female obliquebanded leafrollers,Choristoneura rosaceana (Harris). The amounts of all four pheromone compounds varied during the hour before and five hours after the onset of scotophase. The glands of resistant females contained approximately one half the amount ofZ 11-14:Ac andZ 11-14:OH as the glands of susceptible females during the second and third hours of scotophase, and between 50 and 70% as muchZ 11-14:Al as the glands of susceptible females during the hour before and second to fourth hours of scotophase. The glands of susceptible and resistant females contained similar amounts ofE 11-14:Ac. The relative amounts of each of the four pheromone compounds were affected by time of day but not by resistance status. There was a negative linear relationship between the amounts of each of the four compounds and female age in both types of females. The amounts ofZ 11-14:Ac andE 11-14:Ac declined at similar rates with age in susceptible and resistant females; the amounts ofZ 11-14:OH andZ 11-14:Al declined more rapidly with age in susceptible than in resistant females. The relative amounts of the four compounds were not affected by female age. Temporal variation in the relative amounts of pheromone in susceptible and resistantC .rosaceana may be associated with similar variation in the emission of pheromone and corresponding temporal variation in the relative attractiveness of the two types of females.摘要 比较了一天中的时间和年龄对四种信息素化合物[(Z)-11-十四烯基乙酸酯(Z11-14:Ac)、(E)-11-十四烯基乙酸酯(E11-14:Ac)、(Z)-11-十四烯醇(Z11-14:OH)和 (Z)-11-十四烯醛(Z11-14:Al)]进行了比较。所有四种信息素化合物的含量在光照开始前一小时和光照开始后五小时内各不相同。在光斑期的第二和第三小时,抗性雌虫腺体中 Z11-14:Ac 和 Z11-14:OH 的含量约为易感雌虫腺体的一半;在光斑期开始前一小时和第二至第四小时,抗性雌虫腺体中 Z11-14:Al 的含量约为易感雌虫腺体的 50% 至 70%。易感雌虫和抗性雌虫腺体中的 E11-14:Ac 含量相似。四种信息素化合物的相对含量受一天中时间的影响,但不受抗性状态的影响。两种雌虫的四种化合物的含量与雌虫的年龄呈负线性关系。在易感雌性和抗性雌性中,Z11-14:Ac和E11-14:Ac的含量随年龄下降的速度相似;在易感雌性中,Z11-14:OH和Z11-14:Al的含量随年龄下降的速度比抗性雌性快。四种化合物的相对含量不受雌性年龄的影响。易感性和抗性蔷薇雌虫信息素相对含量的时间变化可能与信息素释放量的相似变化以及两种雌虫相对吸引力的相应时间变化有关。 -
Synthesis of Adducts Formed by Iodine Oxidation of Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Presence of Deoxyribonucleosides and Nucleobases作者:Aaron A. Hanson、Eleanor G. Rogan、Ercole L. CavalieriDOI:10.1021/tx980127q日期:1998.10.1hydrocarbons (PAH) undergo two main pathways of metabolic activation related to the initiation of tumors: one-electron oxidation to give radical cations and monooxygenation to yield bay-region diol epoxides. Synthesis of standard adducts is essential for identifying biologically formed adducts. Until recently, radical cation adducts were synthesized by oxidation of the PAH in an electrochemical apparatus多环芳烃(PAH)经历了与肿瘤发生有关的两种主要的代谢活化途径:单电子氧化产生自由基阳离子,单氧化产生海湾区域的二醇环氧化物。标准加合物的合成对于鉴定生物形成的加合物至关重要。直到最近,自由基阳离子加合物是在电化学装置中通过PAH的氧化来合成的,在许多有机化学实验室中尚不容易获得。我们已经开发了一种方便有效的方法,可以使用I2作为氧化剂来合成PAH-核苷加合物。苯并[a] py(BP),二苯并[a],1](DB [a,l] P)和7,12-二甲基苯并[a]蒽的加合物与脱氧鸟苷(dG),脱氧腺苷,鸟嘌呤(瓜)含或不含AgClO4的Me2SO或二甲基甲酰胺(DMF)中的腺嘌呤或腺嘌呤。例如,当在3当量的I2、5当量的dG和1当量的AgClO4存在下,将有效的致癌物BP溶解在DMF中时,45%的BP转化为BP-6-N7Gua。当在没有AgClO4的情况下将BP置于相同的反应条件下时,BP-6-N
-
De Novo Design of Selective Quadruplex–Duplex Junction Ligands and Structural Characterisation of Their Binding Mode: Targeting the G4 Hot‐Spot作者:Laura Díaz‐Casado、Israel Serrano‐Chacón、Laura Montalvillo‐Jiménez、Francisco Corzana、Agatha Bastida、Andrés G. Santana、Carlos González、Juan Luis AsensioDOI:10.1002/chem.202005026日期:2021.4.7Targeting the interface between DNA quadruplex and duplex regions by small molecules holds significant promise in both therapeutics and nanotechnology. Herein, a new pharmacophore is reported, which selectively binds with high affinity to quadruplex–duplex junctions, while presenting a poorer affinity for G‐quadruplex or duplex DNA alone. Ligands complying with the reported pharmacophore exhibit a小分子靶向DNA四链体和双链体区域之间的界面在治疗学和纳米技术中都具有重大前景。本文报道了一种新的药效基团,它以高亲和力选择性结合四链体-双链体连接,而对单独的G-四链体或双链体DNA的亲和力较弱。符合报道的药效基团的配体对四链体-双链体连接具有显着的亲和力和选择性,包括在HIV-1 LTR-III序列中观察到的亲和力和选择性。四联体-双联体连接与该家族的配体之间的复合物的结构已通过NMR方法确定。根据这些数据,通过迄今为止在药物和生物化学中尚未开发的前所未有的相互作用模式,实现了这种结构基序对四链体-双链体连接的显着选择性:将苄基铵部分插入到部分暴露的G-tetrad中心,与双工。所述支架的进一步修饰以及其他片段为基因组G-四链体形成区域的选择性配体的开发开辟了道路。
-
Synthesis and structure determination of the adducts of the potent carcinogen 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene and deoxyribonucleosides formed by electrochemical oxidation: models for metabolic activation by one-electron oxidation作者:N. V. S. RamaKrishna、Ercole L. Cavalieri、E. G. Rogan、G. Dolnikowski、R. L. Cerny、M. L. Gross、H. Jeong、R. Jankowiak、G. J. SmallDOI:10.1021/ja00031a047日期:1992.2Anodic oxidation of 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene (7,12-DMBA) in the presence of dG yields four adducts and one oxygenated derivative of 7,12-DMBA: 7-methylbenz[a]anthracene (MBA)-12-CH 2 -C8dG (13%), 7-MBA-12-CH 2 -N7Gua (55%), 12-MBA-7-CH 2 -N7Gua (12%), 7-MBA-12-CH 2 -C8Gua (10%), and 7,12-(CH 2 OH) 2 -BA (10%). The first three are primary products of the electrochemical reaction, whereas the last
-
Effect of Ultraviolet Light on Polycyclic Hydrocarbons in Sterol Surface Film Systems作者:W. W. Davis、M. E. Krahl、G. H. A. ClowesDOI:10.1126/science.94.2448.519日期:1941.11.282-benzanthracenes and other polycyclic hydrocarbons, when irradiated either in bulk aqueous suspensions or in the comparable excess phase under mixed surface films, were converted rapidly by ultraviolet light to photo-oxides. When held in two-dimensional solution or molecular association with sterols in mixed surface films at the air-water interface, the hydrocarbons were protected from such photodecomposition
表征谱图
-
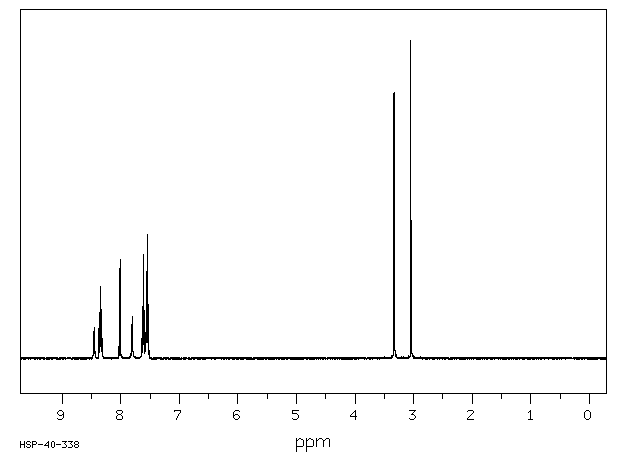
氢谱1HNMR
-
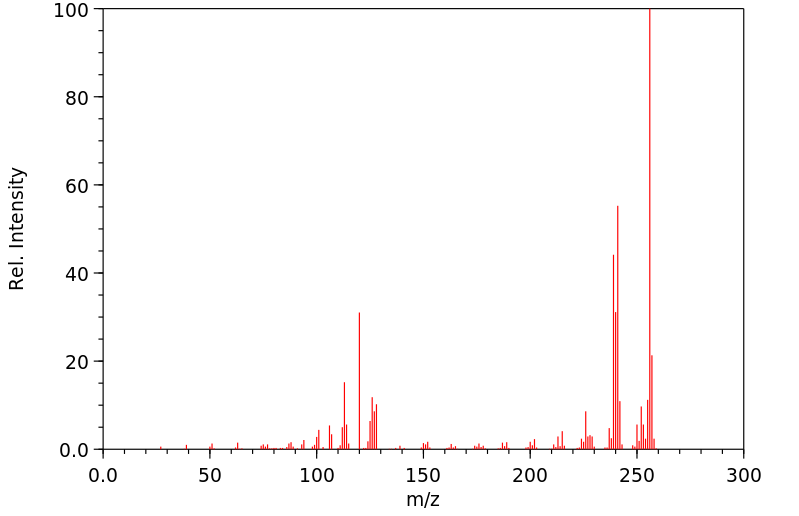
质谱MS
-
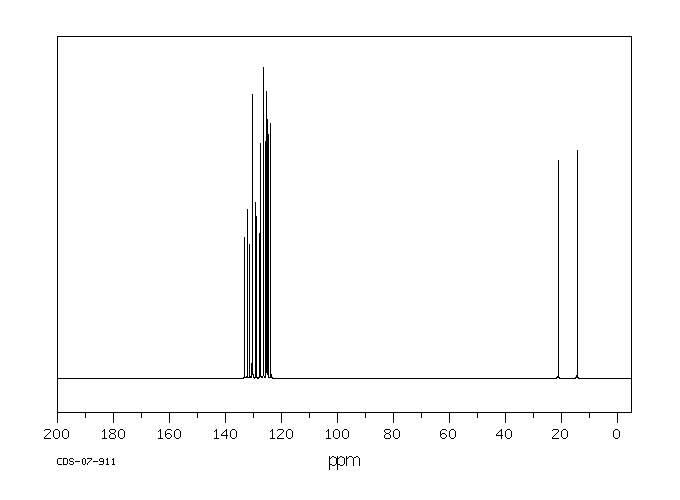
碳谱13CNMR
-
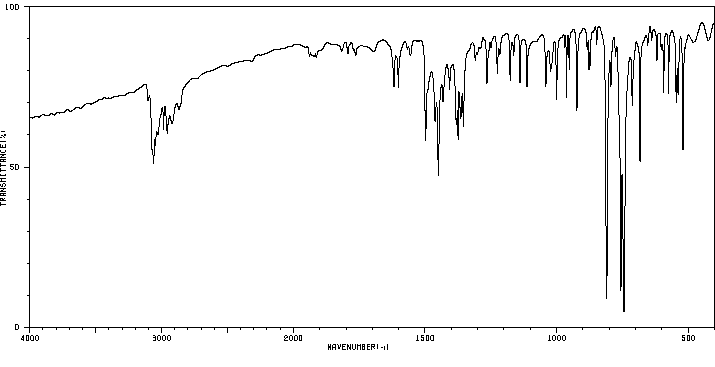
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息