吡虫啉 | 138261-41-3
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:136-144°C
-
密度:1.542
-
物理描述:Solid
-
颜色/状态:Colorless crystals
-
气味:Slight characteristic odor
-
溶解度:In water, 6.1X10+2 mg/L at 20 °C
-
蒸汽压力:4X10-7 mPa (3X10-12 mm Hg) at 20 °C; 9X10-7 mPa (7X10-12 mm Hg) at 25 °C
-
亨利常数:Henry's Law constant = 1.65X10-15 atm-cu m/mol at 25 °C (est)
-
稳定性/保质期:
Stable under recommended storage conditions.
-
分解:On combustion, forms toxic gases. Decomposes on heating.
-
解离常数:pKa1 = 1.56; pKa2 = 11.12
-
碰撞截面:149.62 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: TW]
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0.8
-
重原子数:17
-
可旋转键数:3
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.33
-
拓扑面积:86.3
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:4
ADMET
安全信息
-
危险品标志:Xn,F,N
-
安全说明:S22,S26,S36
-
危险类别码:R11
-
WGK Germany:2
-
海关编码:2933399026
-
危险品运输编号:UN 2588
-
危险类别:6.1(b)
-
RTECS号:NJ0560000
-
包装等级:III
-
储存条件:0-6°C
SDS
SECTION 1: Identification of the substance/mixture and of the company/undertaking
Product identifiers
Product name : Imidacloprid
: Fluka
REACH No. : A registration number is not available for this substance as the substance
or its uses are exempted from registration, the annual tonnage does not
require a registration or the registration is envisaged for a later
registration deadline.
CAS-No. : 138261-41-3
SECTION 2: Hazards identification
Classification of the substance or mixture
Classification according to Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008
Acute toxicity, Oral (Category 4), H302
Acute aquatic toxicity (Category 1), H400
Chronic aquatic toxicity (Category 1), H410
For the full text of the H-Statements mentioned in this Section, see Section 16.
Classification according to EU Directives 67/548/EEC or 1999/45/EC
Xn Harmful R22
For the full text of the R-phrases mentioned in this Section, see Section 16.
Label elements
Labelling according Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008
Pictogram
Signal word Warning
Hazard statement(s)
Harmful if swallowed.
Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Precautionary statement(s)
Avoid release to the environment.
Dispose of contents/ container to an approved waste disposal plant.
Supplemental Hazard none
Statements
Other hazards - none
SECTION 3: Composition/information on ingredients
Substances
Formula : C9H10ClN5O2
Molecular Weight : 255,66 g/mol
CAS-No. : 138261-41-3
Hazardous ingredients according to Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008
Component Classification Concentration
Imidacloprid
CAS-No. 138261-41-3 Acute Tox. 4; Aquatic Acute 1; <= 100 %
Aquatic Chronic 1; H302,
For the full text of the H-Statements and R-Phrases mentioned in this Section, see Section 16
SECTION 4: First aid measures
Description of first aid measures
General advice
Consult a physician. Show this safety data sheet to the doctor in attendance.
If inhaled
If breathed in, move person into fresh air. If not breathing, give artificial respiration. Consult a physician.
In case of skin contact
Wash off with soap and plenty of water. Consult a physician.
In case of eye contact
Flush eyes with water as a precaution.
If swallowed
Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. Rinse mouth with water. Consult a physician.
Most important symptoms and effects, both acute and delayed
The most important known symptoms and effects are described in the labelling (see section 2.2) and/or in
section 11
Indication of any immediate medical attention and special treatment needed
no data available
SECTION 5: Firefighting measures
Extinguishing media
Suitable extinguishing media
Use water spray, alcohol-resistant foam, dry chemical or carbon dioxide.
Special hazards arising from the substance or mixture
Carbon oxides, Hydrogen chloride gas, nitrogen oxides (NOx)
Carbon oxides, nitrogen oxides (NOx), Hydrogen chloride gas
Advice for firefighters
Wear self contained breathing apparatus for fire fighting if necessary.
Further information
no data available
SECTION 6: Accidental release measures
Personal precautions, protective equipment and emergency procedures
Use personal protective equipment. Avoid dust formation. Avoid breathing vapours, mist or gas. Ensure
adequate ventilation. Avoid breathing dust.
For personal protection see section 8.
Environmental precautions
Do not let product enter drains.
Methods and materials for containment and cleaning up
Pick up and arrange disposal without creating dust. Sweep up and shovel. Keep in suitable, closed
containers for disposal.
Reference to other sections
For disposal see section 13.
SECTION 7: Handling and storage
Precautions for safe handling
Avoid contact with skin and eyes. Avoid formation of dust and aerosols.
Provide appropriate exhaust ventilation at places where dust is formed.
For precautions see section 2.2.
Conditions for safe storage, including any incompatibilities
Store in cool place. Keep container tightly closed in a dry and well-ventilated place.
Specific end use(s)
A part from the uses mentioned in section 1.2 no other specific uses are stipulated
SECTION 8: Exposure controls/personal protection
Control parameters
Components with workplace control parameters
Exposure controls
Appropriate engineering controls
Handle in accordance with good industrial hygiene and safety practice. Wash hands before breaks and
at the end of workday.
Personal protective equipment
Eye/face protection
Safety glasses with side-shields conforming to EN166 Use equipment for eye protection tested
and approved under appropriate government standards such as NIOSH (US) or EN 166(EU).
Skin protection
Handle with gloves. Gloves must be inspected prior to use. Use proper glove removal technique
(without touching glove's outer surface) to avoid skin contact with this product. Dispose of
contaminated gloves after use in accordance with applicable laws and good laboratory practices.
Wash and dry hands.
The selected protective gloves have to satisfy the specifications of EU Directive 89/686/EEC and
the standard EN 374 derived from it.
Body Protection
Complete suit protecting against chemicals, The type of protective equipment must be selected
according to the concentration and amount of the dangerous substance at the specific workplace.
Respiratory protection
For nuisance exposures use type P95 (US) or type P1 (EU EN 143) particle respirator.For higher
level protection use type OV/AG/P99 (US) or type ABEK-P2 (EU EN 143) respirator cartridges.
Use respirators and components tested and approved under appropriate government standards
such as NIOSH (US) or CEN (EU).
Control of environmental exposure
Do not let product enter drains.
SECTION 9: Physical and chemical properties
Information on basic physical and chemical properties
a) Appearance Form: solid
b) Odour no data available
c) Odour Threshold no data available
d) pH no data available
e) Melting point/freezing no data available
point
f) Initial boiling point and no data available
boiling range
g) Flash point no data available
h) Evapouration rate no data available
i) Flammability (solid, gas) no data available
j) Upper/lower no data available
flammability or
explosive limits
k) Vapour pressure no data available
l) Vapour density no data available
m) Relative density no data available
n) Water solubility no data available
o) Partition coefficient: n- no data available
octanol/water
p) Auto-ignition no data available
temperature
q) Decomposition no data available
temperature
r) Viscosity no data available
s) Explosive properties no data available
t) Oxidizing properties no data available
Other safety information
no data available
SECTION 10: Stability and reactivity
Reactivity
no data available
Chemical stability
Stable under recommended storage conditions.
Possibility of hazardous reactions
no data available
Conditions to avoid
no data available
Incompatible materials
Strong oxidizing agents
Hazardous decomposition products
Other decomposition products - no data available
In the event of fire: see section 5
SECTION 11: Toxicological information
Information on toxicological effects
Acute toxicity
no data available
LD50 Oral - rat - 410 mg/kg
LC50 Inhalation - rat - > 5.323 mg/m3
LD50 Dermal - rat - > 5.000 mg/kg
Skin corrosion/irritation
no data available
Serious eye damage/eye irritation
no data available
Respiratory or skin sensitisation
no data available
Germ cell mutagenicity
no data available
Carcinogenicity
IARC: No component of this product present at levels greater than or equal to 0.1% is identified as
probable, possible or confirmed human carcinogen by IARC.
Reproductive toxicity
no data available
Specific target organ toxicity - single exposure
no data available
Specific target organ toxicity - repeated exposure
no data available
Aspiration hazard
no data available
Additional Information
RTECS: NJ0560000
To the best of our knowledge, the chemical, physical, and toxicological properties have not been
thoroughly investigated.
SECTION 12: Ecological information
Toxicity
no data available
Toxicity to fish LC50 - Oncorhynchus mykiss (rainbow trout) - 211 mg/l - 96 h
Persistence and degradability
no data available
Bioaccumulative potential
no data available
Mobility in soil
no data available
Results of PBT and vPvB assessment
PBT/vPvB assessment not available as chemical safety assessment not required/not conducted
Other adverse effects
no data available
SECTION 13: Disposal considerations
Waste treatment methods
Product
Offer surplus and non-recyclable solutions to a licensed disposal company. Dissolve or mix the material
with a combustible solvent and burn in a chemical incinerator equipped with an afterburner and scrubber.
Contaminated packaging
Dispose of as unused product.
SECTION 14: Transport information
UN number
ADR/RID: 3077 IMDG: 3077 IATA: 3077
UN proper shipping name
ADR/RID: ENVIRONMENTALLY HAZARDOUS SUBSTANCE, SOLID, N.O.S. (Imidacloprid)
IMDG: ENVIRONMENTALLY HAZARDOUS SUBSTANCE, SOLID, N.O.S. (Imidacloprid)
IATA: Environmentally hazardous substance, solid, n.o.s. (Imidacloprid)
Transport hazard class(es)
ADR/RID: 9 IMDG: 9 IATA: 9
Packaging group
ADR/RID: III IMDG: III IATA: III
Environmental hazards
ADR/RID: yes IMDG Marine pollutant: yes IATA: yes
Special precautions for user
Further information
EHS-Mark required (ADR 2.2.9.1.10, IMDG code 2.10.3) for single packagings and combination
packagings containing inner packagings with Dangerous Goods > 5L for liquids or > 5kg for solids.
SECTION 15: Regulatory information
This safety datasheet complies with the requirements of Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006.
Safety, health and environmental regulations/legislation specific for the substance or mixture
no data available
Chemical Safety Assessment
Further information
only.
The above information is believed to be correct but does not purport to be all inclusive and shall be
used only as a guide. The information in this document is based on the present state of our knowledge
and is applicable to the product with regard to appropriate safety precautions. It does not represent any
SECTION 16 - ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
N/A
制备方法与用途
吡虫啉是一种烟碱类超高效杀虫剂,具有广谱、高效、低毒、低残留的特点,害虫不易产生抗性,并对人、畜、植物和天敌安全。它不仅有触杀作用,还有胃毒和内吸等多重功效。
毒性吡虫啉原药对雄性大鼠急性经口的LD₅₀为424 mg/kg,雌性大鼠为450~475 mg/kg;雄性、雌性大鼠急性经皮的LD₅₀大于5000 mg/kg;大鼠急性吸入LC₅₀大于0.5 mg/L。对兔眼睛和皮肤无刺激作用。对大鼠蓄积系数K大于5,未见长期或繁殖影响,并且运行试验未发现致癌或诱变作用。
鹌鹑急性经口的LD₅₀为31 mg/kg;水蚤LC₅₀大于32 mg/L;蚯蚓在干土壤中的LC₅₀为10.7 mg/kg。
化学性质纯品吡虫啉是一种白色结晶,熔点分别为143.8℃(A)和136.4℃(B),蒸气压为2×10⁻⁷ Pa (20℃)。在20℃时的溶解度分别为己烷小于0.1 g/L、异丙醇1~2 g/L、水0.5 g/L。其在土壤中的稳定性较高,半衰期为150天。
用途吡虫啉是一种氯化烟酰杀虫剂,具有内吸、胃毒和拒食等作用,主要针对刺吸式口器害虫如蚜虫、叶蝉、飞虱、蓟马等。此外,也可用于防治鞘翅目、双翅目和鳞翅目害虫。
吡虫啉已广泛应用于禾谷类作物、玉米、马铃薯、棉花、蔬菜、柑橘等作物中,还被开发为新的杀白蚊剂,在稻田里可以有效防治重要的跳虫和甲虫类。施用于育苗箱的颗粒剂剂量为0.2~0.3 kg/ha m²;防治甜菜潜叶甲虫和细胸金针虫及各种蚜虫,施药量为117 g/ha m²;防治柑橘白蝇(西班牙)和介壳虫(希腊),建议使用0.01%~0.025%有效成分进行叶面喷洒。
国内对吡虫啉的应用研究十分活跃,相关文献包括《农药》1997年No. 7期的文章。
吡虫啉合成吡虫啉的合成可采用以下步骤:
-
制备2-氯-5-甲基吡啶(2):将0.25 mol的化合物(1)、0.37 mol三乙胺及250 mL CH₂Cl₂均匀混合,氮气保护下滴加邻苯二甲酰氯。滴毕后保温反应2小时,抽滤,CH₂Cl₂洗涤,冷却调pH值至6。馏出物分出油层,水层萃取合并,干燥脱溶得无色至浅黄色油状液体。
-
制备2-氯-5-氯甲基吡啶(3):将上步产物0.15 mol、苯8 mL混合,滴加含0.1 mol SO₂Cl₂的苯溶液。加热回流4小时后脱溶。
-
合成吡虫啉(4):将乙腈10 mL、N-硝基亚米唑烷-2-基胺0.15 mol、碳酸钾7.2 g混合,滴加溶有2-氯-5-氯甲基吡啶0.1 mol的乙腈溶液。加热回流反应5小时后过滤,用乙腈洗滤渣,合并滤液脱溶得褐色固体。
另外一种合成方法是:以甲苯为溶剂,在室温下N-(2-氯-5-吡啶甲基)亚乙基二胺与溴化氰作用生成环合产物。低温条件下加入浓硫酸中,并滴加发烟硝酸,于0℃反应2小时后得到吡虫啉。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 1H-咪唑-2-胺,1-[(6-氯-3-吡啶基)甲基]-4,5-二氢- Desnitro-imidacloprid 115970-17-7 C9H11ClN4 210.666 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 1-[(6-chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl]-N-nitroimidazolin-2-one oxohydrazone 131206-85-4 C9H10ClN5O 239.664 —— 1-(6-chloro-3-pyridylmethyl)-N-aminoimidazolidin-2-ylideneamine —— C9H12ClN5 225.681 1H-咪唑-5-醇,1-[(6-氯-3-吡啶基)甲基]-4,5-二氢-2-(硝基氨基)- 5-Hydroxy-Imidacloprid —— C9H10ClN5O3 271.663 —— N-[1-[(6-chloro-3-pyridyl)methyl]-4,5-dihydro-5-oxoimidazol-2-ylidene]nitramide —— C9H8ClN5O3 269.647 1H-咪唑-2-胺,1-[(6-氯-3-吡啶基)甲基]-4,5-二氢- Desnitro-imidacloprid 115970-17-7 C9H11ClN4 210.666 1-[2-(2,2,2-三氟乙氧基)-5-吡啶基甲基]-2-(硝基亚氨基)咪唑烷 1-[2-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)-5-pyridylmethyl]-2-(nitroimino)imidazolidine 105827-79-0 C11H12F3N5O3 319.243 —— 1-[(6-carboxylethylthio-3-pyridinyl)methyl]-N-nitro-2-imidazolidinimine —— C12H15N5O4S 325.348 —— 4,5-dihydroxyimidacloprid —— C9H10ClN5O4 287.662 —— 1-(6-chloro-3-pyridinylmethyl)-N-nitroimidazolidin-2-ylideneamine 138261-41-3 C9H10ClN5O2 255.664 —— 1-(2-chloro-pyridin-5-yl-methyl)-2-nitroimino-3-nitro-imidazolidine —— C9H9ClN6O4 300.661 —— N-methylimidacloprid 117906-15-7 C10H12ClN5O2 269.691 —— 1,2-bis[(6-chloronicotinyl)-2-nitroiminoimidazolidin-3-yl]ethane 117906-11-3 C20H22Cl2N10O4 537.365 —— N-ethenylimidacloprid —— C12H14ClN5O2 295.728 —— 1,3-bis[(6-chloronicotinyl)-2-nitroiminoimidazolidin-3-yl]propane —— C21H24Cl2N10O4 551.392 —— N-isopropylimidacloprid 105828-07-7 C12H16ClN5O2 297.744 —— N-(6-chloropyridin-3-ylmethyl)-N'-nitroguanidine 131748-56-6 C7H8ClN5O2 229.626 —— N-ethynylimidacloprid —— C12H12ClN5O2 293.713 —— 1,4-bis[(6-chloronicotinyl)-2-nitroiminoimidazolidin-3-yl]-2-butene —— C22H24Cl2N10O4 563.403 —— 4-hydroxy-imidacloprid —— C9H10ClN5O3 271.663 - 1
- 2
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Pesticidal 3-substituted 1-nitro-2-imino-1,3-diazacycloalkanes摘要:化学式为##STR1##的杀虫3-取代1-硝基-2-亚硝基-1,3-二氮杂环烷化合物,其中n代表数字0或1,R.sup.1代表含有1、2、3或4个氮原子和/或一个或两个氧原子或硫原子作为杂原子环成员的五元或六元杂环基团--杂原子的数量为1、2、3或4--并且该基团可以通过卤素、氰基、硝基、烷基、卤代烷基、烯基、卤代烯基、炔基、烷氧基、卤代烷氧基、烯氧基、卤代烯氧基、炔氧基、烷硫基、卤代烷硫基、烯硫基、卤代烯硫基、炔硫基、烷基亚砜基、卤代烷基亚砜基、烷基砜基、卤代烷基砜基、氨基、烷基氨基、二烷基氨基、芳基、芳氧基、芳硫基、芳基氨基、芳基烷基、甲酰氨基、烷基羰基氨基、甲酰基、氨基甲酰基、烷基羰基和/或烷氧羰基取代的五元或六元杂环基团,R.sup.2代表氢或烷基,R.sup.3代表氢或硝基。公开号:US04956356A1
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:一种高收率合成吡虫啉的方法摘要:本发明提供了一种高收率合成吡虫啉的方法,以2‑氯‑5‑氯甲基吡啶、乙二胺和卤化氰为原料,经胺化、环化、硝化等步骤合成吡虫啉。该方法生产过程安全性高、产品纯度好、收率高,易于实现工业化。公开号:CN110746397B
文献信息
-
[EN] ACC INHIBITORS AND USES THEREOF<br/>[FR] INHIBITEURS DE L'ACC ET UTILISATIONS ASSOCIÉES
-
[EN] BICYCLYL-SUBSTITUTED ISOTHIAZOLINE COMPOUNDS<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS ISOTHIAZOLINE SUBSTITUÉS PAR UN BICYCLYLE申请人:BASF SE公开号:WO2014206910A1公开(公告)日:2014-12-31The present invention relates to bicyclyl-substituted isothiazoline compounds of formula (I) wherein the variables are as defined in the claims and description. The compounds are useful for combating or controlling invertebrate pests, in particular arthropod pests and nematodes. The invention also relates to a method for controlling invertebrate pests by using these compounds and to plant propagation material and to an agricultural and a veterinary composition comprising said compounds.本发明涉及公式(I)中变量如索权和说明中所定义的自行车基取代异噻唑啉化合物。这些化合物对抗或控制无脊椎动物害虫,特别是节肢动物害虫和线虫方面具有用途。该发明还涉及一种通过使用这些化合物来控制无脊椎动物害虫的方法,以及包含所述化合物的植物繁殖材料、农业和兽医组合物。
-
[EN] AZOLINE COMPOUNDS<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS AZOLINE申请人:BASF SE公开号:WO2015128358A1公开(公告)日:2015-09-03The present invention relates to azoline compounds of formula (I) wherein A, B1, B2, B3, G1, G2, X1, R1, R3a, R3b, Rg1 and Rg2 are as defined in the claims and the description. The compounds are useful for combating or controlling invertebrate pests, in particular arthropod pests and nematodes. The invention also relates to a method for controlling invertebrate pests by using these compounds and to plant propagation material and to an agricultural and a veterinary composition comprising said compounds.本发明涉及式(I)的噁唑啉化合物,其中A、B1、B2、B3、G1、G2、X1、R1、R3a、R3b、Rg1和Rg2如权利要求和描述中所定义。这些化合物对抗或控制无脊椎动物害虫,特别是节肢动物害虫和线虫方面具有用途。该发明还涉及一种利用这些化合物控制无脊椎动物害虫的方法,以及包括所述化合物的植物繁殖材料、农业和兽医组合物。
-
[EN] MICROBIOCIDAL OXADIAZOLE DERIVATIVES<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS D'OXADIAZOLE MICROBIOCIDES申请人:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG公开号:WO2017157962A1公开(公告)日:2017-09-21Compounds of the formula (I) wherein the substituents are as defined in claim 1, useful as a pesticides, especially fungicides.式(I)的化合物,其中取代基如权利要求1所定义,作为杀虫剂特别是杀菌剂有用。
-
Thieno-pyrimidine compounds having fungicidal activity
表征谱图
-
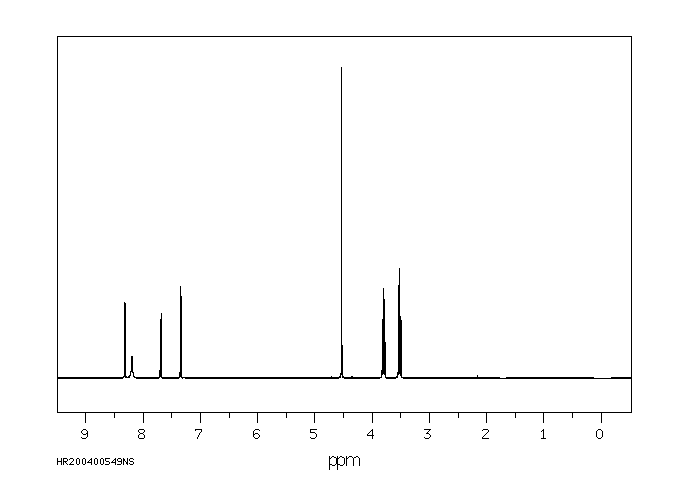
氢谱1HNMR
-
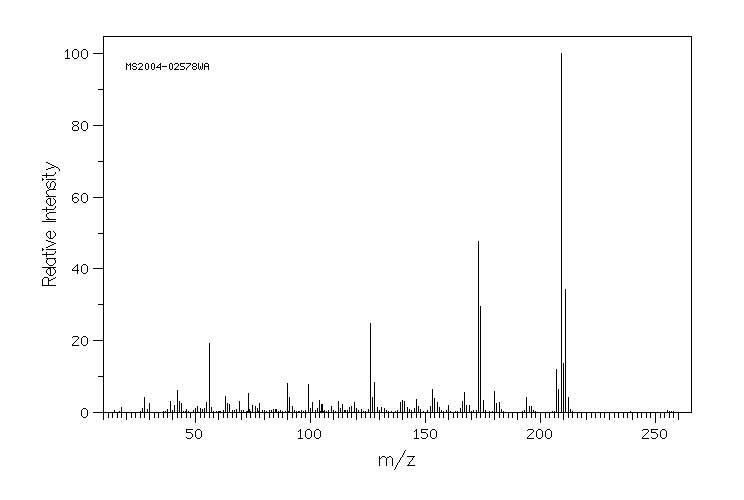
质谱MS
-
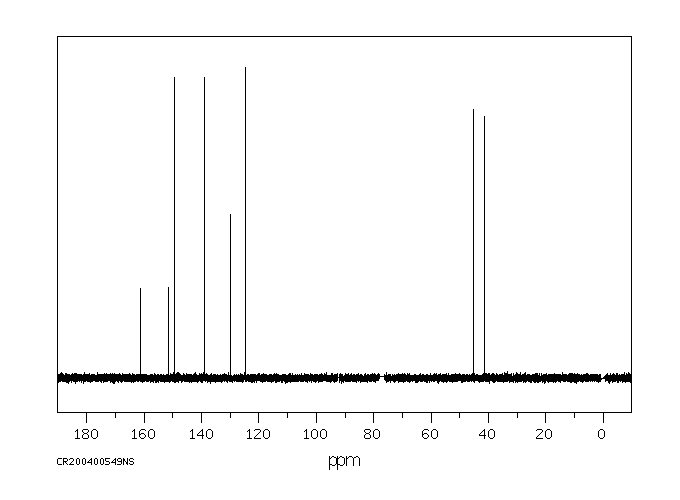
碳谱13CNMR
-
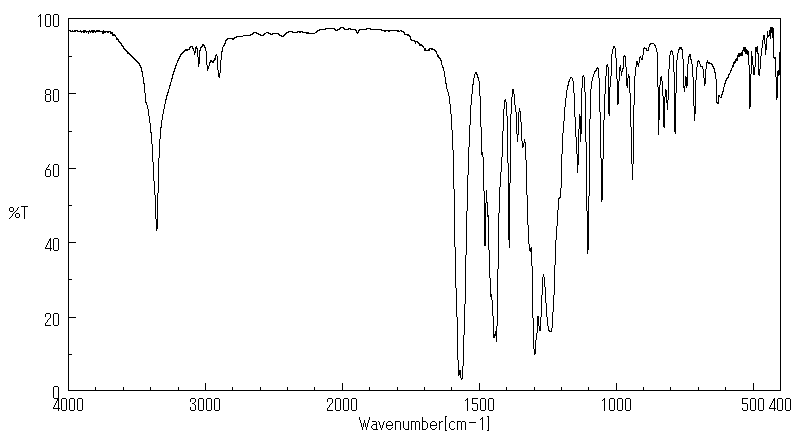
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息