2,2',3,3',5,5'-六甲基-4,4'-二羟基联苯 | 19956-76-4
中文名称
2,2',3,3',5,5'-六甲基-4,4'-二羟基联苯
中文别名
44'-二羟基-22'33'55'-六甲基联苯
英文名称
4,4'-dihydroxy-2,2',3,3',5,5'-hexamethylbiphenyl
英文别名
2,2',3,3',5,5'-hexamethyl-4,4'-dihydroxybiphenyl;2,2',3,3',5,5'-hexamethyl-4,4'-biphenyldiol;2,2',3,3',5,5'-hexamethyl-4,4'-biphenol;2,2',3,3',5,5'-hexamethyl-(1,1'-biphenyl)-4,4'-diol;4-(4-hydroxy-2,3,5-trimethylphenyl)-2,3,6-trimethylphenol
CAS
19956-76-4
化学式
C18H22O2
mdl
——
分子量
270.371
InChiKey
IOJCFCLZQBXCIQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:229 °C
-
沸点:362.6±37.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.084
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):5
-
重原子数:20
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.33
-
拓扑面积:40.5
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:2
安全信息
-
海关编码:2907299090
SDS
上下游信息
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 4-[(4-Ethenylphenyl)methoxy]-1-[4-[(4-ethenylphenyl)methoxy]-2,3,5-trimethylphenyl]-2,3,5-trimethylbenzene —— C36H38O2 502.697
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:2,2',3,3',5,5'-六甲基-4,4'-二羟基联苯 、 氯化偏苯三酸酐 在 吡啶 作用下, 以 四氢呋喃 为溶剂, 生成 4-({4-[4-(3,4-dicarboxyphenylcarbonyloxy)-2,3,5-trimethylphenyl]-2,3,6-trimethylphenyl}oxycarbonyl)benzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid参考文献:名称:[EN] POWDER OF 2,2',3,3',5,5'-HEXAMETHYLBIPHENYL-4,4'-DIOL BIS(TRIMELLITATE ANHYDRIDE)
[FR] POUDRE DE 2,2',3,3',5,5'-HEXAMBIPHÉNYL-4,4'-DIOL BIS(ANHYDRIDE TRIMELLITATE)
[JA] 2,2',3,3',5,5'-ヘキサメチル-ビフェニル-4,4'-ジオール-ビス(トリメリテートアンハイドライド)の粉体摘要:本发明的目标是提供可处理性良好的2,2',3,3',5,5'-六甲基联苯-4,4'-二醇-双(三甲酰基高岭土)的粉末及其制造方法。作为解决方案,提供平均粒径为10μm至40μm的2,2',3,3',5,5'-六甲基联苯-4,4'-二醇-双(三甲酰基高岭土)的粉末。公开号:WO2022176821A1 -
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:过氧化氢的金催化取代酚的氧化摘要:沉积在无机载体上的金纳米颗粒是用过氧化氢水溶液氧化各种取代的苯酚(2,6-二叔丁基苯酚和2,3,6-三甲基苯酚)的有效催化剂。与此相反,以更常规的催化剂,例如含Ti的介孔二氧化硅,其中酚转化成相应的苯醌,金纳米颗粒是非常有选择性的二芳基化合物(3,3',5,5'-四-叔-丁基二苯醌和2,2',3,3',5,5'-六甲基-4,4'-双酚)。产品的收率和选择性取决于所用溶剂,在甲醇中收率> 98%可获得最佳结果。金提供了完全改变取代酚氧化的选择性的可能性,并为清洁合成用于药物应用的联芳基化合物开辟了有趣的前景。DOI:10.1016/j.apcata.2010.08.018
文献信息
-
Oxidation of Phenols and Hydroquinones by Dioxygen Catalyzed by Mixed Addenda Heteropolyoxometalate on Active Carbon (NPV<sub>6</sub>Mo<sub>6</sub>/C)作者:Shinya Fujibayashi、Kouichi Nakayama、Yutaka Nishiyama、Yasutaka IshiiDOI:10.1246/cl.1994.1345日期:1994.7Vanadomolybdophosphate supported on active carbon, NPV6Mo6/C, catalyzed the oxidation and coupling reaction of 2,3,6-trimethylphenol by dioxygen to give trimethyl-p-benzoquinone and 4,4′-dihydroxy-2,2′,3,3′,5,5′-hexamethylbiphenyl, respectively, depending on the solvent used. Hydroquinones and benzyl alcohol were selectively dehydrogenated by the present system, giving the corresponding p-benzoquinones and benzaldehyde, respectively, in good yields.
-
METHOD FOR PRODUCING MULTISUBSTITUTED BIPHENYL COMPOUND AND SOLID CATALYST TO BE USED THEREIN申请人:KYUSHU UNIVERSITY, NATIONAL UNIVERSITY CORPORATION公开号:US20150274689A1公开(公告)日:2015-10-01A method for producing a multisubstituted biphenyl compound is represented by the following formula (2), including a step of coupling a substituted benzene compound represented by the following formula (1) in the presence of a solid catalyst with gold immobilized onto a support.
-
Selective Oxidation of Phenols to Hydroxybenzaldehydes and Benzoquinones with Dioxygen Catalyzed by Polymer-Supported Copper作者:Ken Takaki、Yohei Shimasaki、Tetsuya Shishido、Katsuomi TakehiraDOI:10.1246/bcsj.75.311日期:2002.2Oxidation of 2,6-disubstituted 4-methylphenols with dioxygen by using a CuCl2-poly(4-methyl-4′-vinyl-2,2′-bipyridine) catalyst gave the corresponding 4-hydroxybenzaldehydes in high yields. The activity of the catalyst and the selectivity of the products significantly depended on the reaction conditions and the composition of the catalyst. When the molar ratio of the bipyridine unit of the polymer ligand to Cu was unity, i.e., N/Cu = 2, the best results were obtained. Moreover, the reaction is likely to be promoted by coordination of the products to the catalyst. Similarly, 2,3,6-trimethylphenol and related compounds were converted to p-benzoquinones selectively with a CuCl2-poly(4-vinylpyridine) catalyst. These polymer-supported catalysts were readily recovered and are reusable without noticeable decrease of their activity.
-
A green catalytic method for selective synthesis of iodophenols via aerobic oxyiodination under organic solvent-free conditions作者:Hongchuan Xin、Liangning Hu、Jianqiang Yu、Wenshou Sun、Zengjian AnDOI:10.1016/j.catcom.2017.01.019日期:2017.4A highly efficient catalytic method for aerobic oxyiodination of various phenols catalysed by copper(II) nitrate was achieved under mild conditions using I2 as an iodinating reagent, molecular oxygen as an oxidant, and water as a solvent. The catalyst shows not only high activity for phenols with either electron-donating or electron-withdrawing groups, but also a remarkable selectivity for the formation
-
Choice of Manganese(III) Complexes for the Synthesis of 4,4′-Biphenyldiols and 4,4′-Diphenoquiones作者:Hiroshi Nishino、Nobuyuki Itoh、Makiko Nagashima、Kazu KurosawaDOI:10.1246/bcsj.65.620日期:1992.26-Disubstituted phenols are oxidized with tris(2,4-pentanedionato)manganese(III), [Mn(acac)3], in glacial acetic acid to give the corresponding 4,4′-biphenyldiols in high yields, whereas similar reactions using manganese(III) acetate, [Mn(OAc)3], insted of [Mn(acac)3] quantitatively yield the corresponding 4,4′-diphenoquinones. Cross-coupling reactions of 2,6-di-t-butylphenol and other substituted phenols afford
表征谱图
-
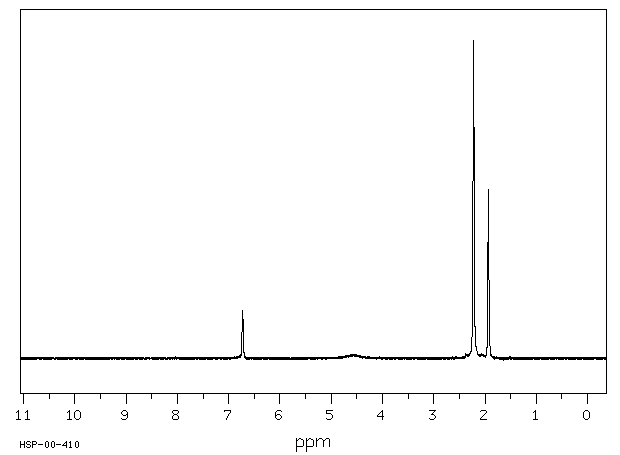
氢谱1HNMR
-
质谱MS
-
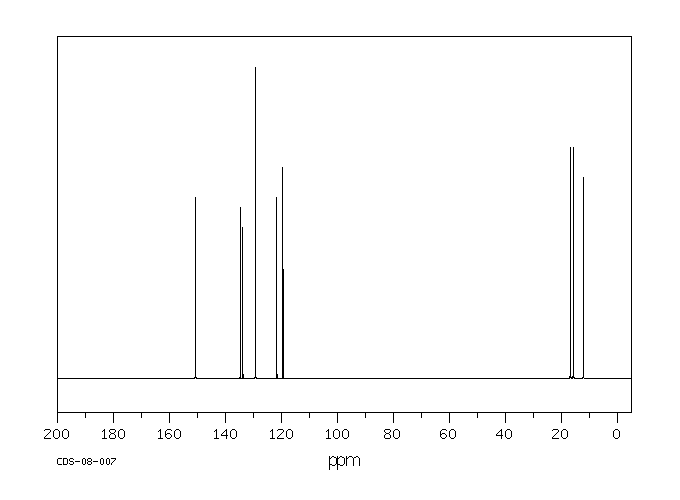
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(βS)-β-氨基-4-(4-羟基苯氧基)-3,5-二碘苯甲丙醇
(S,S)-邻甲苯基-DIPAMP
(S)-(-)-7'-〔4(S)-(苄基)恶唑-2-基]-7-二(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-2,2',3,3'-四氢-1,1-螺二氢茚
(S)-盐酸沙丁胺醇
(S)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧磷杂环戊二烯
(S)-2,2'-双[双(3,5-三氟甲基苯基)膦基]-4,4',6,6'-四甲氧基联苯
(S)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(R)富马酸托特罗定
(R)-(-)-盐酸尼古地平
(R)-(-)-4,12-双(二苯基膦基)[2.2]对环芳烷(1,5环辛二烯)铑(I)四氟硼酸盐
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[((6-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(4-叔丁基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(3-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-4,7-双(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-7“-[(吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2”,3,3'-四氢1,1'-螺二茚满
(R)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二苯氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂环戊烯
(R)-2-[((二苯基膦基)甲基]吡咯烷
(R)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(N-(4-甲氧基苯基)-N-甲基-3-(1-哌啶基)丙-2-烯酰胺)
(5-溴-2-羟基苯基)-4-氯苯甲酮
(5-溴-2-氯苯基)(4-羟基苯基)甲酮
(5-氧代-3-苯基-2,5-二氢-1,2,3,4-oxatriazol-3-鎓)
(4S,5R)-4-甲基-5-苯基-1,2,3-氧代噻唑烷-2,2-二氧化物-3-羧酸叔丁酯
(4S,4''S)-2,2''-亚环戊基双[4,5-二氢-4-(苯甲基)恶唑]
(4-溴苯基)-[2-氟-4-[6-[甲基(丙-2-烯基)氨基]己氧基]苯基]甲酮
(4-丁氧基苯甲基)三苯基溴化磷
(3aR,8aR)-(-)-4,4,8,8-四(3,5-二甲基苯基)四氢-2,2-二甲基-6-苯基-1,3-二氧戊环[4,5-e]二恶唑磷
(3aR,6aS)-5-氧代六氢环戊基[c]吡咯-2(1H)-羧酸酯
(2Z)-3-[[(4-氯苯基)氨基]-2-氰基丙烯酸乙酯
(2S,3S,5S)-5-(叔丁氧基甲酰氨基)-2-(N-5-噻唑基-甲氧羰基)氨基-1,6-二苯基-3-羟基己烷
(2S,2''S,3S,3''S)-3,3''-二叔丁基-4,4''-双(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-2,2''-联苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂戊环
(2S)-(-)-2-{[[[[3,5-双(氟代甲基)苯基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基}-N-(二苯基甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[((1S,2S)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[[((1R,2R)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2-硝基苯基)磷酸三酰胺
(2,6-二氯苯基)乙酰氯
(2,3-二甲氧基-5-甲基苯基)硼酸
(1S,2S,3S,5S)-5-叠氮基-3-(苯基甲氧基)-2-[(苯基甲氧基)甲基]环戊醇
(1S,2S,3R,5R)-2-(苄氧基)甲基-6-氧杂双环[3.1.0]己-3-醇
(1-(4-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(3-溴苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氯苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2,6-二氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(-)-去甲基西布曲明
龙蒿油
龙胆酸钠
龙胆酸叔丁酯
龙胆酸
龙胆紫-d6
龙胆紫