苯噻硫氰 | 21564-17-0
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
沸点:>120 °C
-
密度:d25 1.05 (c = 0.30)
-
闪点:(open cup): 66°C
-
溶解度:溶于氯仿、乙酸乙酯
-
物理描述:REDDISH VISCOUS LIQUID WITH PUNGENT ODOUR.
-
颜色/状态:Oil
-
气味:Pungent
-
熔点:<-10 °C
-
蒸汽压力:9.0X10-6 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of ... /sulfur oxides & nitrogen oxides/.
-
表面张力:70.39 mN/m at 25 °C
-
保留指数:2162;2118.9
-
稳定性/保质期:
原药为棕红色液体,相对密度1.38,闪点大于120.7℃,蒸气压小于1.33帕。在正常条件下可稳定存放一年,在强碱性环境下易分解。热分解时会排出有毒的氮氧化物和硫氧化物烟雾。
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.1
-
重原子数:14
-
可旋转键数:3
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.11
-
拓扑面积:116
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:5
ADMET
安全信息
-
危险品标志:Xn,T+,N
-
安全说明:S26,S28,S36,S36/37,S38,S45,S60,S61
-
危险类别码:R22
-
海关编码:29342000
-
危险品运输编号:61895
-
RTECS号:XK8150900
SDS
| 第一部分:化学品名称 |
| 化学品中文名称: | 苯噻氰;2-(硫氰基甲基硫代)苯并噻唑 |
| 化学品英文名称: | TCMTB;Thiocyanic acid,2-(benzothiazolylthio)methyl ester |
| 中文俗名或商品名: | |
| Synonyms: | |
| CAS No.: | 21564-17-0 |
| 分子式: | C 9 H 6 N 2 S 3 |
| 分子量: | 238.35 |
| 第二部分:成分/组成信息 |
| 纯化学品 混合物 | ||||||
| 化学品名称:苯噻氰;2-(硫氰基甲基硫代)苯并噻唑 | ||||||
|
| 第三部分:危险性概述 |
| 危险性类别: | 第6.1类 毒害品 |
| 侵入途径: | 吸入 食入 经皮吸收 |
| 健康危害: | 本品属低毒杀菌剂。对眼睛、皮肤有刺激性。误服可中毒。受热分解释出氧化硫和氮氧化物烟雾。 |
| 环境危害: | 对环境可能有危害。 |
| 燃爆危险: | 本品可燃,具刺激性。 |
| 第四部分:急救措施 |
| 皮肤接触: | 用肥皂水及清水彻底冲洗。就医。 |
| 眼睛接触: | 拉开眼睑,用流动清水冲洗15分钟。就医。 |
| 吸入: | 脱离现场至空气新鲜处。就医。 |
| 食入: | 误服者,饮适量温水,催吐。就医。 |
| 第五部分:消防措施 |
| 危险特性: | 遇明火、高热可燃。受高热分解,放出有毒的烟气。 |
| 有害燃烧产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳、氮氧化物、氧化硫。 |
| 灭火方法及灭火剂: | 泡沫、干粉、砂土。 |
| 消防员的个体防护: | 消防人员须佩戴防毒面具、穿全身消防服,在上风向灭火。 |
| 禁止使用的灭火剂: | |
| 闪点(℃): | 120.7 |
| 自燃温度(℃): | |
| 爆炸下限[%(V/V)]: | |
| 爆炸上限[%(V/V)]: | |
| 最小点火能(mJ): | |
| 爆燃点: | |
| 爆速: | |
| 最大燃爆压力(MPa): | |
| 建规火险分级: |
| 第六部分:泄漏应急处理 |
| 应急处理: | 疏散泄漏污染区人员至安全区,禁止无关人员进入污染区,建议应急处理人员戴好防毒面具,穿化学防护服。用砂土吸收,铲入提桶,运至废物处理场所。用水刷洗泄漏污染区,经稀释的污水放入废水系统。如大量泄漏,利用围堤收容,然后收集、转移、回收或无害处理后废弃。 |
| 第七部分:操作处置与储存 |
| 操作注意事项: | 密闭操作,局部排风。防止蒸气泄漏到工作场所空气中。操作人员必须经过专门培训,严格遵守操作规程。建议操作人员佩戴自吸过滤式防毒面具(半面罩),戴化学安全防护眼镜,穿防毒物渗透工作服,戴橡胶手套。远离火种、热源,工作场所严禁吸烟。使用防爆型的通风系统和设备。在清除液体和蒸气前不能进行焊接、切割等作业。避免产生烟雾。避免与氧化剂、碱类接触。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材及泄漏应急处理设备。倒空的容器可能残留有害物。 |
| 储存注意事项: | 储存于阴凉、通风的库房。远离火种、热源。防止阳光直射。保持容器密封。应与氧化剂、碱类分开存放,切忌混储。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材。储区应备有泄漏应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。 |
| 第八部分:接触控制/个体防护 |
| 最高容许浓度: | 中 国 MAC:未制订标准前苏联 MAC:未制订标准美国TLV—TWA:未制订标准 |
| 监测方法: | |
| 工程控制: | 密闭操作,局部排风。 |
| 呼吸系统防护: | 可能接触其蒸气时,佩戴防毒口罩。 |
| 眼睛防护: | 高浓度环境中,戴化学安全防护眼镜。 |
| 身体防护: | 穿紧袖工作服,长筒胶鞋。 |
| 手防护: | 戴防护手套。 |
| 其他防护: | 工作后,淋浴更衣。注意个人清洁卫生。 |
| 第九部分:理化特性 |
| 外观与性状: | 棕色红色液体。 |
| pH: | |
| 熔点(℃): | |
| 沸点(℃): | |
| 相对密度(水=1): | 1.38 |
| 相对蒸气密度(空气=1): | |
| 饱和蒸气压(kPa): | <0.00133 |
| 燃烧热(kJ/mol): | |
| 临界温度(℃): | |
| 临界压力(MPa): | |
| 辛醇/水分配系数的对数值: | |
| 闪点(℃): | 120.7 |
| 引燃温度(℃): | |
| 爆炸上限%(V/V): | |
| 爆炸下限%(V/V): | |
| 分子式: | C 9 H 6 N 2 S 3 |
| 分子量: | 238.35 |
| 蒸发速率: | |
| 粘性: | |
| 溶解性: | 溶于部分有机溶剂。 |
| 主要用途: | 用作农用杀菌剂。 |
| 第十部分:稳定性和反应活性 |
| 稳定性: | 在常温常压下 稳定 |
| 禁配物: | 强氧化剂、强碱。 |
| 避免接触的条件: | |
| 聚合危害: | 不能出现 |
| 分解产物: | 氮氧化物、氧化硫、一氧化碳、二氧化碳。 |
| 第十一部分:毒理学资料 |
| 急性毒性: | LD50:2664mg/kg(大鼠经口);2000mg/kg(兔经皮) LC50: |
| 急性中毒: | |
| 慢性中毒: | |
| 亚急性和慢性毒性: | |
| 刺激性: | |
| 致敏性: | |
| 致突变性: | |
| 致畸性: | |
| 致癌性: |
| 第十二部分:生态学资料 |
| 生态毒理毒性: | |
| 生物降解性: | |
| 非生物降解性: | |
| 生物富集或生物积累性: |
| 第十三部分:废弃处置 |
| 废弃物性质: | |
| 废弃处置方法: | 建议用焚烧法处置。在能利用的地方重复使用容器或在规定场所掩埋。 |
| 废弃注意事项: |
| 第十四部分:运输信息 |
| |
| 危险货物编号: | 61895 |
| UN编号: | 3026 |
| 包装标志: | |
| 包装类别: | |
| 包装方法: | 小开口钢桶;螺纹口玻璃瓶、塑料瓶、复合塑料瓶或铝瓶外普通木箱。 |
| 运输注意事项: | 铁路运输时,可以使用钙塑瓦楞箱作外包装。但须包装试验合格,并经铁路局批准。运输前应先检查包装容器是否完整、密封,运输过程中要确保容器不泄漏、不倒塌、不坠落、不损坏。严禁与酸类、氧化剂、食品及食品添加剂混运。运输时运输车辆应配备相应品种和数量的消防器材及泄漏应急处理设备。运输途中应防曝晒、雨淋,防高温。公路运输时要按规定路线行驶,勿在居民区和人口稠密区停留。 |
| RETCS号: | |
| IMDG规则页码: |
| 第十五部分:法规信息 |
| 国内化学品安全管理法规: | 化学危险物品安全管理条例 (1987年2月17日国务院发布),化学危险物品安全管理条例实施细则 (化劳发[1992] 677号),工作场所安全使用化学品规定 ([1996]劳部发423号)等法规,针对化学危险品的安全使用、生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应规定;常用危险化学品的分类及标志 (GB 13690-92)将该物质划为第6.1 类毒害品。 |
| 国际化学品安全管理法规: |
| 第十六部分:其他信息 |
| 参考文献: | 1.周国泰,化学危险品安全技术全书,化学工业出版社,1997 2.国家环保局有毒化学品管理办公室、北京化工研究院合编,化学品毒性法规环境数据手册,中国环境科学出版社.1992 3.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety,CHEMINFO Database.1998 4.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety, RTECS Database, 1989 |
| 填表时间: | 年月日 |
| 填表部门: | |
| 数据审核单位: | |
| 修改说明: | |
| 其他信息: | 5 |
| MSDS修改日期: | 年月日 |
制备方法与用途
苯噻氰(苯噻硫氰),又称倍生或佳生,化学名为2-(thiocyanomethylthio)benzothiazole。这是一种广谱性的种子保护剂,对由土壤和种子传播的真菌或细菌性病害具有显著防效。它可用于拌种、浸种、灌根或叶面喷雾,防治多种植物病害,如水稻稻瘟病、胡麻叶斑病、白叶枯病、纹枯病、甘蔗风梨病、蔬菜炭疽病、瓜类炭疽病、猝倒病、立枯病、蔓割病以及柑橘溃疡病等。国外市场商品名为TCMTB。作为一款性能优良的杀菌剂,TCMTB具有广谱、高效、低毒的特点,尽管目前生产成本较高,但在国内外市场的使用量正在迅速增加。
应用苯噻氰(苯噻硫氰)是一种经济高效的绿色杀菌剂。它与美国Buckmam公司的BUSAN30L和法国Progiven公司的BIOCIDEMT30属同一类产品。这种化合物可以用于种子处理,对细菌、真菌和藻类具有极强的灭杀和控制作用。在植物和土壤中,其代谢产物残留量较大。该杀菌剂特别适用于防治炭疽病、稻瘟病、猝倒病、立枯病及柑橘溃疡病等。
作用特点苯噻硫氰是一种广谱性种子保护剂,能够预防及治疗经由土壤及种子传播的真菌或细菌性病害,并且可用于防止木材变色和保护皮革。作为一种化学试剂,它在植物与土壤中都有一定的残留效果。
制备以2-巯基苯并噻唑为原料,通过氯甲基化反应生成2-氯甲基硫代苯并噻唑,然后按照特定方法进行合成,最终得到苯噻氰(苯噻硫氰)。该过程包括将干燥的苯和2-巯基苯并噻唑加入带有气体导入管的装置中,在40℃下搅拌溶解后,再加入多聚甲醛,并在回流条件下通入干燥HCl气体1~2小时。反应结束后冷却至室温,用饱和NaCl洗涤有机层直至中性,然后使用无水Na2SO4进行干燥、过滤并旋转蒸馏除去溶剂以得到粗品。通过硅胶G柱层析精制可获得精品化合物2-氯甲基硫代苯并噻唑。根据第一种合成方法的步骤,进一步合成即可得到苯噻氰(苯噻硫氰)。
毒性原油对大鼠急性经口LD50为2664mg/kg(1590mg/kg),兔急性经皮LD50为2000mg/kg,大鼠急性吸入LC50为0.17mg/L。动物试验未见致癌、致畸、致突变作用。虹鳟鱼LC50为0.029mg/L (96h)。对家禽低毒。
适用范围 适宜作物- 水稻
- 小麦
- 瓜类
- 甜菜
- 棉花等
- 蔬菜炭疽病、立枯病
- 柑橘溃疡病
- 稻瘟病
- 白叶枯病
- 纹枯病
广谱性种子保护剂,用于棉花、玉米、水稻、麦类、高粱、甜菜等作物的种子保护。预防和治疗由土壤及种子传播的真菌或细菌性病害。
性质上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 2-甲硫基苯并噻唑 2-methylmercaptobenzothiazole 615-22-5 C8H7NS2 181.282 2-[(氯甲基)硫代]苯并噻唑 (2-chloromethylthio)benzothiazole 28908-00-1 C8H6ClNS2 215.727 2-(甲基亚磺酰)-1,3-苯并噻唑 2-(methylsulfinyl)benzothiazole 3507-54-8 C8H7NOS2 197.282
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Willems,A.G.M. et al., Recueil des Travaux Chimiques des Pays-Bas, 1971, vol. 90, p. 97 - 104摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Muthusubramanian, Lakshmi; Mitra, Rajat B.; Sundara Rao, Indian Journal of Chemistry - Section B Organic and Medicinal Chemistry, 1996, vol. 35, # 12, p. 1331 - 1334摘要:DOI:
文献信息
-
[EN] SUBSTITUTED QUINAZOLINES AS FUNGICIDES<br/>[FR] QUINAZOLINES SUBSTITUÉES, UTILISÉES EN TANT QUE FONGICIDES申请人:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG公开号:WO2010136475A1公开(公告)日:2010-12-02The present invention relates to a compound of formula (I) wherein wherein the substituents have the definitions as defined in claim 1or a salt or a N-oxide thereof, their use and methods for the control and/or prevention of microbial infection, particularly fungal infection, in plants and to processes for the preparation of these compounds.本发明涉及一种具有如下式(I)的化合物,其中取代基具有权利要求1中定义的定义,或其盐或N-氧化物,它们的用途以及用于控制和/或预防植物中微生物感染,特别是真菌感染的方法,以及制备这些化合物的方法。
-
[EN] MICROBIOCIDAL OXADIAZOLE DERIVATIVES<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS D'OXADIAZOLE MICROBIOCIDES申请人:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG公开号:WO2017157962A1公开(公告)日:2017-09-21Compounds of the formula (I) wherein the substituents are as defined in claim 1, useful as a pesticides, especially fungicides.式(I)的化合物,其中取代基如权利要求1所定义,作为杀虫剂特别是杀菌剂有用。
-
Thieno-pyrimidine compounds having fungicidal activity
-
[EN] INSECTICIDAL TRIAZINONE DERIVATIVES<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS DE TRIAZINONE INSECTICIDES申请人:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG公开号:WO2013079350A1公开(公告)日:2013-06-06Compounds of the formula (I) or (I'), wherein the substituents are as defined in claim 1, are useful as pesticides.式(I)或(I')的化合物,其中取代基如权利要求1所定义的那样,可用作杀虫剂。
-
THIENYLPYRIDYLCARBOXAMIDES申请人:Dunkel Ralf公开号:US20110105564A1公开(公告)日:2011-05-05Novel thienylpyridylcarboxamides of the formula (I) The present application is also directed to a plurality of processes for preparing these compounds and their use for controlling unwanted microorganisms, and also novel intermediates and their preparation.
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
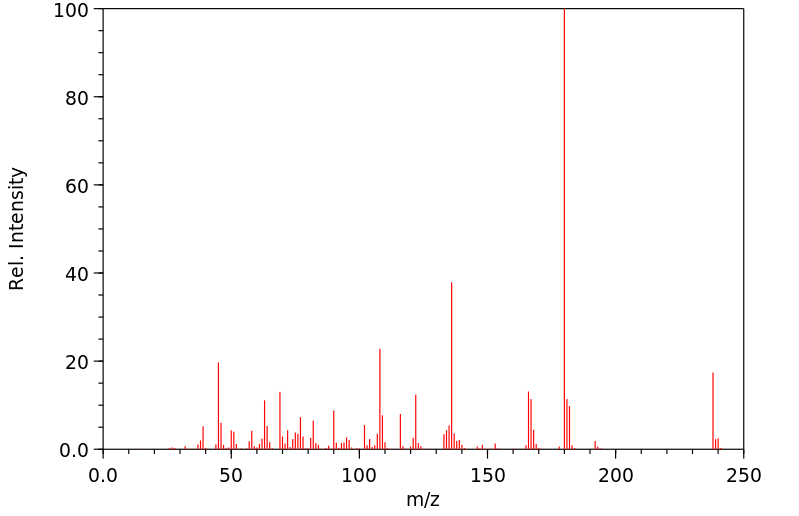
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
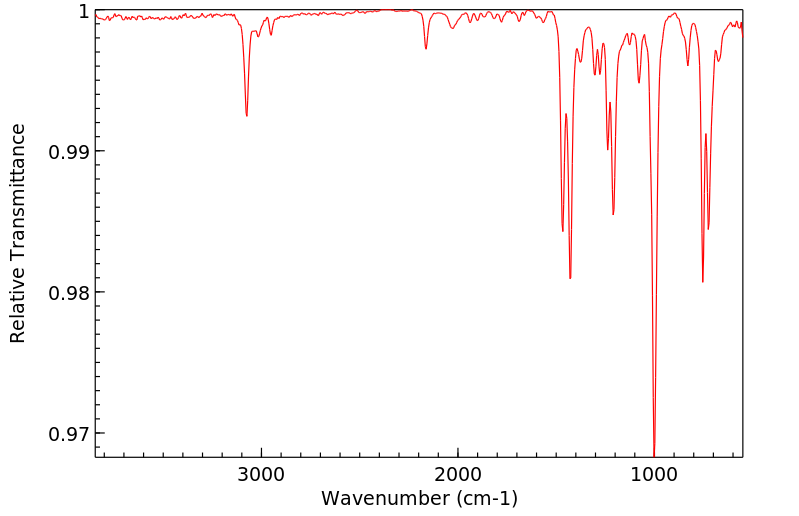
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息