螺[4.5]癸烷 | 176-63-6
中文名称
螺[4.5]癸烷
中文别名
——
英文名称
spiro[4.5]decane
英文别名
spiro[4,5]decane;Spiro[4.5]decan;spiro[4, 5]decane;Spiro-<4,5>-decan;Spiro<4,5>decan;Spiro<4.5>decan
CAS
176-63-6
化学式
C10H18
mdl
——
分子量
138.253
InChiKey
CTDQAGUNKPRERK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
沸点:188.7°C (rough estimate)
-
密度:0.8102 (estimate)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):4.8
-
重原子数:10
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
安全信息
-
海关编码:2902199090
SDS
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:The Preparation and Dehydrogenation of Spirodecane and 3-Methylspirodecane1摘要:DOI:10.1021/ja01855a028
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Chirko,A.I.; Perzashkevich,V.S., Journal of Organic Chemistry USSR (English Translation), 1966, vol. 2, p. 1999 - 2002摘要:DOI:
文献信息
-
Renewable high-density spiro-fuels from lignocellulose-derived cyclic ketones作者:Junjian Xie、Xiangwen Zhang、Lun Pan、Genkuo Nie、Xiu-Tian-Feng E、Qing Liu、Peng Wang、Yafei Li、Ji-Jun ZouDOI:10.1039/c7cc05101h日期:——Renewable high-density spiro-fuels are synthesized from lignocellulose-derived cyclic ketones for the first time, which show higher density, higher neat heat of combustion and lower freezing point compared with other biofuels synthesized from the same feedstock, and thus represent a new type of renewable high-density fuel attractive for practical applications.
-
97.—The Reformatsky reaction with compounds of the ethylene oxide type作者:G. R. Clemo、J. OrmstonDOI:10.1039/jr9330000362日期:——
-
Ring opening of decalin via hydrogenolysis on Ir/- and Pt/silica catalysts作者:Andreas Haas、Sandra Rabl、Marco Ferrari、Vincenzo Calemma、Jens WeitkampDOI:10.1016/j.apcata.2012.03.010日期:2012.5The catalytic conversion of cis-decalin was studied at a hydrogen pressure of 5.2 MPa and temperatures of 250-410 degrees C on iridium and platinum supported on non-acidic silica. The absence of catalytically active Bronsted acid sites was indicated by both FT-IR spectroscopy with pyridine as a probe and the selectivities in a catalytic test reaction, viz, the hydroconversion of n-octane. On iridium/silica, decalin hydroconversion starts at ca. 250-300 degrees C, and no skeletal isomerization occurs. The first step is rather hydrogenolytic opening of one six-membered ring to form the direct ring-opening products butylcyclohexane, 1-methyl-2-propylcyclohexane and 1,2-diethylcyclohexane. These show a consecutive hydrogenolysis, either of an endocyclic carbon-carbon bond into open-chain decanes or of an exocyclic carbon-carbon bond resulting primarily in methane and C-9 naphthenes. The latter can undergo a further endocyclic hydrogenolysis leading to open-chain nonanes. All individual C-10 and C-9 hydrocarbons predicted by this "direct ring-opening mechanism" were identified in the products generated on the iridium/silica catalysts. The carbon-number distributions of the hydrocracked products C-9- show a peculiar shape resembling a hammock and could be readily predicted by simulation of the direct ring-opening mechanism. Platinum on silica was found to require temperatures around 350-400 degrees C at which relatively large amounts of tetralin and naphthalene are formed. The most abundant primary products on Pt/silica are spiro[4.5]decane and butylcyclohexane which can be readily accounted for by the well known platinum-induced mechanisms described in the literature for smaller model hydrocarbons, namely the bond-shift isomerization mechanism and hydrogenolysis of a secondary-tertiary carbon-carbon bond in decalin. (C) 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Alkylidenecarbenes from acyclic vinyl bromides and potassium tert-butoxide作者:Joseph Wolinsky、Gregory W. Clark、Patricia C. ThorstensonDOI:10.1021/jo00867a001日期:1976.3
-
Zelinsky; Schuikin, Chemische Berichte, 1929, vol. 62, p. 2183作者:Zelinsky、SchuikinDOI:——日期:——
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
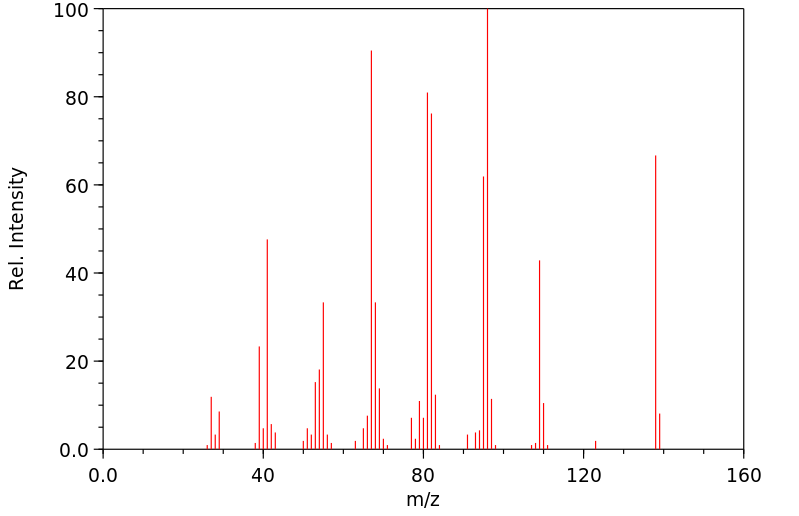
质谱MS
-
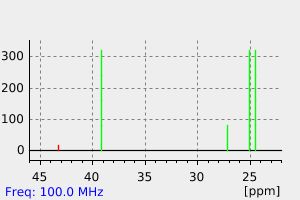
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
降冰片烯
金刚烷-D16
金刚烷
螺戊烷
螺二環己烷
螺[5.6]十二烷
螺[5.5]十一碳-4-烯
螺[5.2]辛-2-烯
螺[4.5]癸烷
螺[4.4]壬-8-烯
螺[3.4]辛烷
螺[3.4]辛-7-烯
螺[3.3]庚-2,5-二烯
螺[2.5]辛烷
螺[2.5]辛-7-烯
螺[2.5]辛-5,7-二烯
螺[2.4]庚-4,6-二烯
螺[2.4]庚-1-烯
螺[2.3]己-1-烯
螺[2.2]戊-1-烯
螺<二环<2.2.2>辛-5-烯-2,1'-环丙烷>
螺<4.4>壬-1,3,7-三烯
螺<4.4>壬-1,3,6,8-四烯
螺(4.4)壬烷
螺(4.4)壬-1,3-二烯
螺(3.4)辛-5,7-二烯
trans-perhydroazulene
萘烷
萘,1,2,3,4,4a,8a-六氢-,顺-
美罗培南中间体F9
篮烷
立方烷
氨基甲硫酸,二甲基-,O,O-(3,3-二甲基1,1-联苯基-2,2-二基)酯
棱晶烷
杜瓦苯
新戊基-1金刚烷
抗氧化剂TH-CPL
庚搭烯
四螺[2.0.2:0.2:0.2:0]十二烷
四螺[2.0.0.0.2.1.1.1]十一烷,顺-
四环己基铅
四环[5.3.0.0<2,6>.0<3,10>]癸-4,8-二烯
四环[5.3.0.0(2,6).0(3,10)]癸烷
四环[4.4.0.02,10.03,7]癸-4,8-二烯
四环[4.2.2.26,5.01,6]十二烷
四环[4.2.0.02,5.03,8]辛烷
四环[3.3.0.02,4.03,6]辛-7-烯
四环<5.3.1.02,6.04,9>十一烷
四环(8.2.2.22,5.26,9)十八碳-1,5,9-三烯
四环(4.1.0.0(2,4).0(3,5))庚烷