(Z)-1,3-dichloro-5-(prop-1-en-1-yloxy)benzene
中文名称
——
中文别名
——
英文名称
(Z)-1,3-dichloro-5-(prop-1-en-1-yloxy)benzene
英文别名
(3,5-Dichlorophenyl) (1-propenyl) ether;1,3-dichloro-5-[(Z)-prop-1-enoxy]benzene
CAS
——
化学式
C9H8Cl2O
mdl
——
分子量
203.068
InChiKey
USPMANDNJBFYMJ-IHWYPQMZSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.9
-
重原子数:12
-
可旋转键数:2
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.11
-
拓扑面积:9.2
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:1
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Thermodynamic, spectroscopic, and density functional theory studies of allyl aryl and prop-1-enyl aryl ethers. Part 1. Thermodynamic data of isomerization摘要:通过对70对异构化的烯丙基苯基醚(a)和(Z)-丙-1-烯基苯基醚(b)在DMSO溶液中的化学平衡研究,考察了它们相对热力学稳定性的变化。从平衡常数随温度的变化中,评估了在298.15 K下的异构化吉布斯自由能、焓和熵。由于其低焓值,(Z)-丙-1-烯基苯基醚在平衡状态下具有显著优势,a→b异构化的吉布斯自由能范围从-12至-23 kJ/mol。在大多数反应中,熵的贡献可以忽略不计,但偶尔会发现小于+10 J/K·mol的正值。平衡研究还扩展到涉及两对在烯键C(2)位置带有甲基取代基的相关异构化醚。甲基取代基可以增加烯丙基醚的相对热力学稳定性约3.4 kJ/mol。DOI:10.1039/b101837j
-
作为产物:描述:1-(allyloxy)-3,5-dichlorobenzene 在 (1R,2R)-(-)-N,N'-bis(3,5-di-tert-butylsalicydene)-1,2-cyclohexanediaminocobalt(II) 、 1,1,3,3-四甲基二硅氧烷 、 1-氟-2,4,6-三甲基吡啶三氟甲烷磺酸盐 作用下, 反应 5.0h, 以74%的产率得到(Z)-1,3-dichloro-5-(prop-1-en-1-yloxy)benzene参考文献:名称:使用钴(II)(salen)配合物催化剂在烯丙基醚的氧化异构化中生成特定的Z-烯醇醚的Z选择性。摘要:烯醇醚的结构基序存在于许多高度氧化的生物活性天然产物和药物中。几何上不稳定的Z-烯醇醚的合成具有挑战性。已经开发出一种有效的Z-烯丙基醚(Zalen)配合物使用N-氟-2,4,6-三甲基吡啶三氟甲磺酸盐(Me3NFPY•OTf)作为氧化剂催化的烯丙基醚的Z选择氧化异构化方法。热力学稳定性较低的Z-烯醇醚以高收率和高几何控制制备。该方法还证明了在室温下控制二烯丙基醚的Z-选择性异构化反应的有效性。该催化体系提供了另一种途径来扩展烯丙基醚的传统还原异构化。DOI:10.1021/acs.joc.0c00004
表征谱图
-
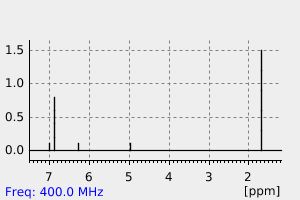
氢谱1HNMR
-
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(βS)-β-氨基-4-(4-羟基苯氧基)-3,5-二碘苯甲丙醇
(S,S)-邻甲苯基-DIPAMP
(S)-(-)-7'-〔4(S)-(苄基)恶唑-2-基]-7-二(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-2,2',3,3'-四氢-1,1-螺二氢茚
(S)-盐酸沙丁胺醇
(S)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧磷杂环戊二烯
(S)-2,2'-双[双(3,5-三氟甲基苯基)膦基]-4,4',6,6'-四甲氧基联苯
(S)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(R)富马酸托特罗定
(R)-(-)-盐酸尼古地平
(R)-(-)-4,12-双(二苯基膦基)[2.2]对环芳烷(1,5环辛二烯)铑(I)四氟硼酸盐
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[((6-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(4-叔丁基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(3-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-4,7-双(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-7“-[(吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2”,3,3'-四氢1,1'-螺二茚满
(R)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二苯氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂环戊烯
(R)-2-[((二苯基膦基)甲基]吡咯烷
(R)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(N-(4-甲氧基苯基)-N-甲基-3-(1-哌啶基)丙-2-烯酰胺)
(5-溴-2-羟基苯基)-4-氯苯甲酮
(5-溴-2-氯苯基)(4-羟基苯基)甲酮
(5-氧代-3-苯基-2,5-二氢-1,2,3,4-oxatriazol-3-鎓)
(4S,5R)-4-甲基-5-苯基-1,2,3-氧代噻唑烷-2,2-二氧化物-3-羧酸叔丁酯
(4S,4''S)-2,2''-亚环戊基双[4,5-二氢-4-(苯甲基)恶唑]
(4-溴苯基)-[2-氟-4-[6-[甲基(丙-2-烯基)氨基]己氧基]苯基]甲酮
(4-丁氧基苯甲基)三苯基溴化磷
(3aR,8aR)-(-)-4,4,8,8-四(3,5-二甲基苯基)四氢-2,2-二甲基-6-苯基-1,3-二氧戊环[4,5-e]二恶唑磷
(3aR,6aS)-5-氧代六氢环戊基[c]吡咯-2(1H)-羧酸酯
(2Z)-3-[[(4-氯苯基)氨基]-2-氰基丙烯酸乙酯
(2S,3S,5S)-5-(叔丁氧基甲酰氨基)-2-(N-5-噻唑基-甲氧羰基)氨基-1,6-二苯基-3-羟基己烷
(2S,2''S,3S,3''S)-3,3''-二叔丁基-4,4''-双(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-2,2''-联苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂戊环
(2S)-(-)-2-{[[[[3,5-双(氟代甲基)苯基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基}-N-(二苯基甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[((1S,2S)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[[((1R,2R)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2-硝基苯基)磷酸三酰胺
(2,6-二氯苯基)乙酰氯
(2,3-二甲氧基-5-甲基苯基)硼酸
(1S,2S,3S,5S)-5-叠氮基-3-(苯基甲氧基)-2-[(苯基甲氧基)甲基]环戊醇
(1S,2S,3R,5R)-2-(苄氧基)甲基-6-氧杂双环[3.1.0]己-3-醇
(1-(4-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(3-溴苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氯苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2,6-二氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(-)-去甲基西布曲明
龙蒿油
龙胆酸钠
龙胆酸叔丁酯
龙胆酸
龙胆紫-d6
龙胆紫