2,3,4,5-四氢吡啶 | 505-18-0
中文名称
2,3,4,5-四氢吡啶
中文别名
哌啶三聚体
英文名称
2,3,4,5-tetrahydropyridine
英文别名
Δ1-piperideine;3,4,5,6-tetrahydropyridine;1-piperideine
CAS
505-18-0
化学式
C5H9N
mdl
MFCD18839151
分子量
83.1332
InChiKey
DWKUKQRKVCMOLP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:60.50 °C
-
沸点:139.2±13.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:0.93±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted)
-
溶解度:可溶于氯仿(少许)
-
保留指数:796
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0.1
-
重原子数:6
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.8
-
拓扑面积:12.4
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:1
安全信息
-
海关编码:2933399090
SDS
上下游信息
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 3-bromo-1-piperideine —— C5H8BrN 162.029
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:半乳糖氧化酶变异体用于酶联反应合成中的氨基醇氧化摘要:据报道,在温和的条件下,在水性系统中,使用选定的工程化半乳糖氧化酶(GOase)变体将氨基醇氧化为醛。GOase变体F 2催化N-羰基苄氧基(Cbz)保护的3-氨基-1,2-丙二醇向相应的α-羟醛的区域选择性氧化,然后将其用于醛缩酶反应。发现另一个变体M 3-5对游离的和N -Cbz保护的脂族和芳族氨基醇表现出活性,从而可以合成内酰胺,例如3,4-二氢萘-1(2 H)-one,2-吡咯烷酮和黄嘌呤内酰胺与黄嘌呤脱氢酶(XDH)或醛氧化酶(PaoABC)进行串联反应。DOI:10.1002/cctc.201500218
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:通过CH键官能化未保护的脂环胺的多样化:瞬时亚胺的脱羧烷基化。摘要:尽管该领域的许多从业者做出了广泛的努力,但未受保护的脂环胺直接 α-C-H 键功能化的方法仍然很少。该领域的一项新进展是利用 N-锂化脂环胺。这些易于获得的中间体通过简单的酮氧化剂的作用转化为瞬时亚胺,然后在温和条件下用β-酮酸进行烷基化,以前所未有的轻松方式提供有价值的β-氨基酮。具有现有 α-取代基的底物可实现区域选择性 α'-烷基化。该方法还适用于通过加入SN Ar步骤方便地一锅合成多环二氢喹诺酮类药物。DOI:10.1002/anie.202011641
-
作为试剂:描述:4-溴-2-乙酰基噻吩 在 2,3,4,5-四氢吡啶 、 盐酸 、 titanium(IV) tetraethanolate 、 碘 、 三甲基铝 、 potassium carbonate 作用下, 以 四氢呋喃 、 1,4-二氧六环 、 甲醇 、 二氯甲烷 、 水 、 甲苯 为溶剂, 反应 30.25h, 生成 8-(4-bromothiophen-2-yl)-8-methyl-2-oxa-5-thia-7-azaspiro[3.5]non-6-en-6-amine参考文献:名称:[EN] SPIROCYCLIC DIHYDRO-THIAZINE AND DIHYDRO-OXAZINE BACE INHIBITORS, AND COMPOSITIONS AND USES THEREOF
[FR] DIHYDRO-THIAZINE SPIROCYCLIQUES ET INHIBITEURS DE BACE DIHYDRO-OXAZINE ET COMPOSITIONS ET UTILISATIONS DE CEUX-CI摘要:提供具有如下式(I)所示结构的化合物:其中A1、A2、A3、Y、R1、R2、R3、R4、R5、R6、m、n和p在此处定义。还提供包括所提供的化合物的药物组合物以及制备和使用所提供的化合物和组合物的方法,例如用于治疗和预防各种疾病,如阿尔茨海默病。公开号:WO2013142613A1
文献信息
-
Heteroaliphatic Dimethylphosphine Oxide Building Blocks: Synthesis and Physico‐Chemical Properties作者:Andrii Fedyk、Evgeniy Y. Slobodyanyuk、Olha Stotska、Bohdan V. Vashchenko、Dmitriy M. Volochnyuk、Dmitriy A. Sibgatulin、Andrey A. Tolmachev、Oleksandr O. GrygorenkoDOI:10.1002/ejoc.202100581日期:2021.12.21Multigram synthesis of saturated heterocyclic dimethylphosphine oxides (derivatives of azetidine, pyrrolidine, piperidine, and morpholine) – advanced building blocks for medicinal chemistry – as well as their physico-chemical properties (pKa, logP, and Sw) are disclosed.
-
A Highly Active System for the Metal-Free Aerobic Photocyanation of Tertiary Amines with Visible Light: Application to the Synthesis of Tetraponerines and Crispine A作者:Julio Cesar Orejarena Pacheco、Alexander Lipp、Alexander M. Nauth、Fabian Acke、Jule-Philipp Dietz、Till OpatzDOI:10.1002/chem.201504845日期:2016.4.4A highly efficient metal‐free catalytic system for the aerobic photocyanation of tertiary amines with visible light is reported. The use of air as terminal oxidant offers an improved safety profile compared with pure oxygen, the used compact fluorescent lamp (CFL) light sources are highly economical, and no halogenated solvents are required. This system not only proves to be effective for a wide variety
-
Diversity-oriented synthesis of cyclic acyldepsipeptides leads to the discovery of a potent antibacterial agent作者:Aaron M. Socha、Nicholas Y. Tan、Kerry L. LaPlante、Jason K. SelloDOI:10.1016/j.bmc.2010.08.032日期:2010.10.15structure, featuring the Joullié-Ugi three-component reaction, was developed. This multicomponent reaction and a related multicomponent reaction, the Ugi four-component reaction, were used to prepare analogs that were designed using the principles of conformational analysis. These cyclic acyldepsipeptides were tested for their activity against drug-resistant, clinical isolates of Staphylococci and Enterococci一类被称为Enepteptins的环状环肽肽抗生素最近因其对多种耐药性细菌的活性而引起了广泛关注,其中包括耐甲氧西林的金黄色葡萄球菌和耐万古霉素的粪肠球菌。这些抗生素通过其新颖的作用机制进一步区别于其中,它们结合并解除了对细胞质蛋白酶ClpP的严格控制的活性。尽管天然产物的药理学性能较差,但一种合成的衍生物,名为acylDEPsipeptide 4(ADEP 4),在体外和小鼠细菌感染模型中均显示出显着的抗菌活性。开发了以Joullié-Ugi三组分反应为特征的ADEP 4肽内酯核心结构的新途径。该多组分反应和相关的多组分反应Ugi四组分反应被用来制备类似物,所述类似物是利用构象分析原理设计的。测试了这些环状酰基肽肽对抗药性,临床分离株的活性。葡萄球菌和肠球菌。一种用四甲基哌酸酯代替哌酸酯的ADEP 4类似物,其对肠球菌的体外抗菌活性比母体化合物高四倍。
-
Tandem Nucleophilic Addition/Oxy-2-azonia-Cope Rearrangement for the Formation of Homoallylic Amides and Lactams: Total Synthesis and Structural Verification of Motuporamine G作者:Lijun Zhou、Zhiming Li、Yue Zou、Quanrui Wang、Italo A. Sanhueza、Franziska Schoenebeck、Andreas GoekeDOI:10.1021/ja310002m日期:2012.12.12oxy-2-azonia-Cope rearrangements give homoallylic amides. In the case of 2-vinylcycloalkanones, the process results in ring enlargement, providing a novel route to 9- to 16-membered lactams. The preparative significance of this protocol was evidenced by a short synthesis of macrocyclic alkaloid motuporamine G. The stereochemistry-defining step of this oxy-azonia-Cope rearrangement was further studied
-
Thermal Activation of Solid-State Molybdenum Halide Clusters with an Octahedral Cluster Framework and Their Application to Catalytic Synthesis of 3-Methylpyridine from Piperidine and Methanol作者:Satoshi Kamiguchi、Ryu Kajio、Hitomi Yamada、Hidetaka Yuge、Kazu Okumura、Hajime Iida、Sayoko Nagashima、Teiji ChiharaDOI:10.1246/bcsj.20150055日期:2015.8.15Solid-state molybdenum halide clusters with an octahedral metal framework MoX2 (or [Mo6X8]X2X4/2) (X = Cl, Br, I) are applied to catalysis. When these clusters are thermally activated in a hydrogen stream above 300 °C, they exhibit catalytic activity for the dehydrogenative C-methylation of piperidine with methanol, to yield 3-methylpyridine. At 400 °C, the selectivity is as high as 74%. This catalytic behavior is different from that of the molecular clusters [(M6Cl12)Cl2(H2O)4]·4H2O (M = Nb, Ta) and (H3O)2[(M6Cl8)Cl6]·6H2O (M = Mo, W), which exhibit Brønsted acidity after thermal activation; piperidine is N-methylated to yield N-methylpiperidine selectively. Elemental analysis and thermogravimetric analysis demonstrate that the solid-state clusters partially eliminate halogen ligands during the activation. Infrared analysis of adsorbed pyridine on the activated clusters shows the presence of a Lewis acid site. This coordinatively unsaturated site of the molybdenum is catalytically active for dehydrogenative C-methylation. The formation of an η3-1-azaallyl species on the molybdenum facilitates the methylation at the 3-position of piperidine, followed by dehydrogenation to yield 3-methylpyridine.固态钼卤代簇合物,具有八面体金属骨架MoX2(或[Mo6X8]X2X4/2)(X = Cl, Br, I),应用于催化领域。当这些簇合物在300°C以上的氢气流中热活化时,它们显示出对哌啶与甲醇进行脱氢化C甲基化反应的催化活性,生成3-甲基吡啶。在400°C时,选择性高达74%。这种催化行为与分子簇合物[(M6Cl12)Cl2(H2O)4]·4 (M = Nb, Ta)和(H3O)2[(M6Cl8)Cl6]·6 (M = Mo, W)不同,后者在热活化后显示出Brønsted酸性;哌啶被N-甲基化,选择性地生成N-甲基哌啶。元素分析和热重分析表明,固态簇合物在活化过程中部分消除了卤素配体。吸附在活化簇合物上的吡啶的红外分析显示存在Lewis酸位点。这种配位不饱和的钼位点对脱氢化C甲基化具有催化活性。在钼上形成η3-1-氮杂烯丙基物种有助于在哌啶的3-位进行甲基化,随后脱氢生成3-甲基吡啶。
表征谱图
-
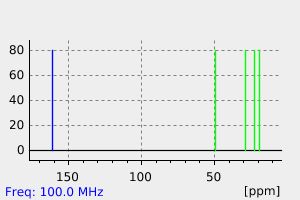
氢谱1HNMR
-
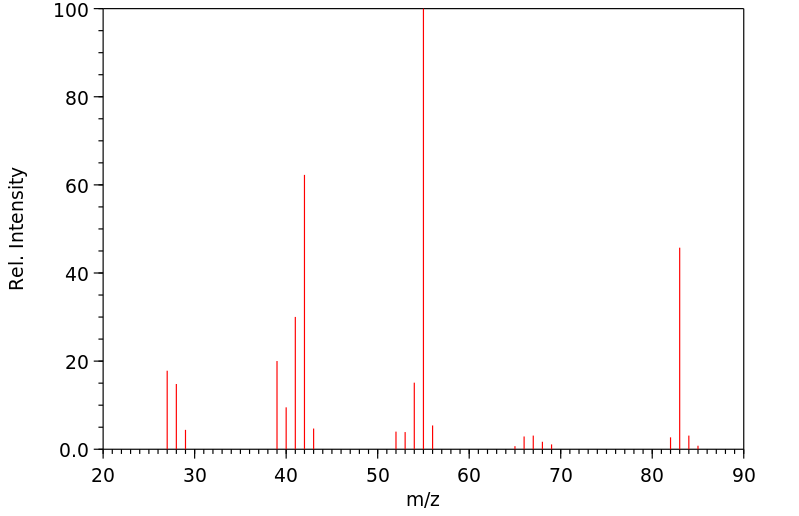
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(S)-氨氯地平-d4
(R,S)-可替宁N-氧化物-甲基-d3
(R)-(+)-2,2'',6,6''-四甲氧基-4,4''-双(二苯基膦基)-3,3''-联吡啶(1,5-环辛二烯)铑(I)四氟硼酸盐
(R)-N'-亚硝基尼古丁
(R)-DRF053二盐酸盐
(5E)-5-[(2,5-二甲基-1-吡啶-3-基-吡咯-3-基)亚甲基]-2-亚磺酰基-1,3-噻唑烷-4-酮
(5-溴-3-吡啶基)[4-(1-吡咯烷基)-1-哌啶基]甲酮
(5-氨基-6-氰基-7-甲基[1,2]噻唑并[4,5-b]吡啶-3-甲酰胺)
(2S,2'S)-(-)-[N,N'-双(2-吡啶基甲基]-2,2'-联吡咯烷双(乙腈)铁(II)六氟锑酸盐
(2S)-2-[[[9-丙-2-基-6-[(4-吡啶-2-基苯基)甲基氨基]嘌呤-2-基]氨基]丁-1-醇
(2R,2''R)-(+)-[N,N''-双(2-吡啶基甲基)]-2,2''-联吡咯烷四盐酸盐
(1'R,2'S)-尼古丁1,1'-Di-N-氧化物
黄色素-37
麦斯明-D4
麦司明
麝香吡啶
鲁非罗尼
鲁卡他胺
高氯酸N-甲基甲基吡啶正离子
高氯酸,吡啶
高奎宁酸
马来酸溴苯那敏
马来酸氯苯那敏-D6
马来酸左氨氯地平
顺式-双(异硫氰基)(2,2'-联吡啶基-4,4'-二羧基)(4,4'-二-壬基-2'-联吡啶基)钌(II)
顺式-二氯二(4-氯吡啶)铂
顺式-二(2,2'-联吡啶)二氯铬氯化物
顺式-1-(4-甲氧基苄基)-3-羟基-5-(3-吡啶)-2-吡咯烷酮
顺-双(2,2-二吡啶)二氯化钌(II) 水合物
顺-双(2,2'-二吡啶基)二氯化钌(II)二水合物
顺-二氯二(吡啶)铂(II)
顺-二(2,2'-联吡啶)二氯化钌(II)二水合物
韦德伊斯试剂
非那吡啶
非洛地平杂质C
非洛地平
非戈替尼
非布索坦杂质66
非尼拉朵
非尼拉敏
雷索替丁
阿雷地平
阿瑞洛莫
阿扎那韦中间体
阿培利司N-6
阿伐曲波帕杂质40
间硝苯地平
间-硝苯地平
镉,二碘四(4-甲基吡啶)-
锌,二溴二[4-吡啶羧硫代酸(2-吡啶基亚甲基)酰肼]-