吡哆醇磷酸盐 | 447-05-2
中文名称
吡哆醇磷酸盐
中文别名
磷酸吡哆素维生素B6磷酸盐2-甲基-3-羟基-4,5-双(羟甲基)吡啶二氢磷酸盐;5-磷酸吡哆醇;磷酸吡哆素;维生素B6磷酸盐;2-甲基-3-羟基-4,5-双(羟甲基)吡啶二氢磷酸盐
英文名称
5-hydroxy-4-(hydroxymethyl)-6-methyl-3-pyridylmethyl dihydrogen phosphate
英文别名
Pyridoxin-5'-phosphat;Pyridoxine 5-phosphate;pyridoxine-5′-phosphate;Pyridoxin-phosphat;Pyridoxine phosphate;[5-hydroxy-4-(hydroxymethyl)-6-methylpyridin-3-yl]methyl dihydrogen phosphate
CAS
447-05-2
化学式
C8H12NO6P
mdl
——
分子量
249.16
InChiKey
WHOMFKWHIQZTHY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:210-211 °C
-
沸点:638.5±65.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.628±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
-
溶解度:可微溶于水
-
物理描述:Solid
-
碰撞截面:150.5 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: DT, Method: single field calibrated with Agilent tune mix (Agilent)]
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-1.9
-
重原子数:16
-
可旋转键数:4
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.38
-
拓扑面积:120
-
氢给体数:4
-
氢受体数:7
安全信息
-
海关编码:2933399090
-
储存条件:温度:20°C,环境气体:惰性气体
SDS
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:合理设计伤寒沙门氏菌酸性磷酸酶高效生产5′-磷酸吡哆醛摘要:5′-磷酸吡哆醛(PLP)在食品和医药方面具有很高的价值。然而,实现 PLP 的有效生物合成仍然具有挑战性。在此,首次建立了利用伤寒沙门氏菌酸性磷酸酶( St APase)和大肠杆菌吡哆醇氧化酶( Ec PNPO)作为途径酶从吡哆醇(PN)和焦磷酸盐(PPi)合成PLP的挽救途径。 St APase 被鉴定为限速酶。基于PN磷酸化机制开发了两种蛋白质修饰策略:(1)改善PN与St APase的结合;(2)增强St APase底物结合袋的疏水性。最优突变体M7的k cat / K m是野生型的4.9倍。分析了性能提升的具体机制。在M7和Ec PNPO的催化下,构建了14.5±0.55 g/L的PLP高产菌株,其生产力为1.0±0.02 g/(L·h)(迄今为止最高)。该研究提出了一种有前途的工业规模 PLP 生产方法。DOI:10.1021/acs.jafc.4c00596
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:人吡哆 (am)ine 5'-磷酸氧化酶中吡哆醛 5′-磷酸变构位点的鉴定摘要:足够水平的吡哆醛 5′-磷酸盐 (PLP)(维生素 B6 的催化活性形式)及其在体内的适当分布对人类健康至关重要。PLP 回收途径在这些过程中起着至关重要的作用,其缺陷会导致严重的神经系统疾病。吡哆 (am) 嘧啶 5′-磷酸氧化酶 (PNPO) 的催化作用产生 PLP,是该途径的关键参与者之一。编码 PNPO 的基因突变是导致严重新生儿癫痫的原因。最近,PNPO 也被描述为化疗药物的潜在靶点。我们的实验室强调了 PNPO 在细胞中 PLP 水平调节中的关键作用,这是通过酶的反馈抑制机制发生的,通过在变构位点结合 PLP 来发挥。通过对接分析和定点诱变实验,我们在这里确定了人 PNPO 的变构 PLP 结合位点。该位点与我们之前在大肠杆菌酶同源物中鉴定的变构位点位于同一蛋白质区域。然而,参与 PLP 结合的氨基酸残基的身份和排列完全不同,类似于 PLP 依赖性酶的活性位点的身份和排列。人 PNPODOI:10.1002/pro.4900
文献信息
-
[EN] NOVEL SYNTHETIC OPTIONS TOWARDS THE MANUFACTURE OF (6R,10S)-10- {4-[5-CHLORO-2-(4-CHLORO-1H-1,2,3-TRIAZOL-1-YL)PHENYL]-6-OXO-1(6H)- PYRIMIDINYL}- 1-(DIFLUOROMETHYL)-6-METHYL-1,4,7,8,9,10-HEXAHYDRO-11,15 -(METHENO)PYRAZOLO [4,3-B] [1,7] DIAZACYCLOTETRADECIN-5(6H)-ONE<br/>[FR] NOUVELLES OPTIONS SYNTHÉTIQUES POUR LA FABRICATION DE (6R,10S)-10-{4-[5-CHLORO-2-(4-CHLORO-1H-1,2,3-TRIAZOL-1-YL) PHÉNYL]-6-OXO-1(6H)-PYRIMIDINYL}1-(DIFLUOROMÉTHYL)-6-MÉTHYL-1,4,7,8,9,10-HEXAHYDRO-11,15- (METHENO)PYRAZOLO [4,3-B] [1,7] DIAZACYCLOTÉTRADECIN-5 (6H)-ONE申请人:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO公开号:WO2020210613A1公开(公告)日:2020-10-15Highly efficient methods are provided for preparing key intermediates in the synthesis of Compound (I), which are broadly applicable and can provide selected components having a variety of substituents groups.为合成化合物(I)的关键中间体提供了高效的方法,这些方法具有广泛的适用性,并且可以提供具有各种取代基团的选定组分。
-
METHODS AND COMPOSITIONS FOR IDENTIFYING PROSTATE CANCER OR A HUMORAL IMMUNE RESPONSE AGAINST PROSTATE CANCER申请人:Jooss Karin公开号:US20080279831A1公开(公告)日:2008-11-13The present invention relates to prostate cancer markers, compositions comprising such markers, immunoglobulins specific for such markers, and methods of using such markers and/or immunoglobulins to assess an immune response against prostate cancer. An immune response against the markers correlates with an immune response, in particular a humoral immune response, against prostate cancer cells which immune response is preferably associated with prophylaxis of prostate cancer, treatment of prostate cancer, and/or amelioration of at least one symptom associated with prostate cancer.本发明涉及前列腺癌标志物、包含此类标志物的组合物、针对此类标志物的特异性免疫球蛋白,以及使用此类标志物和/或免疫球蛋白评估针对前列腺癌的免疫反应的方法。针对这些标志物的免疫反应与针对前列腺癌细胞的免疫反应(特别是体液免疫反应)相关联,该免疫反应最好与前列腺癌的预防、治疗和/或至少一种与前列腺癌相关的症状的缓解相关联。
-
Transaminase reactions
-
[EN] NEW PROCESS FOR EARLY SACUBITRIL INTERMEDIATES<br/>[FR] NOUVEAU PROCÉDÉ POUR DES INTERMÉDIAIRES DE SACUBITRIL PRÉCOCES申请人:NOVARTIS AG公开号:WO2018116203A1公开(公告)日:2018-06-28The invention relates to a new enantioselective process for producing useful intermediates for the manufacture of NEP inhibitors or prodrugs thereof, in particular NEP inhibitors comprising a γ-amino-δ-biphenyl-α-methylalkanoic acid, or acid ester, backbone.
-
Interconversions of different forms of vitamin B6 in tobacco plants作者:ShuoHao Huang、HaiBin Zeng、JianYun Zhang、Shu Wei、LongQuan HuangDOI:10.1016/j.phytochem.2011.07.019日期:2011.12are six different vitamin B(6) (VB(6)) forms, pyridoxal (PL), pyridoxamine (PM), pyridoxine (PN), pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP), pyridoxamine 5'-phosphate (PMP), and pyridoxine 5'-phosphate (PNP), of which PLP is the active form. Although plants are a major source of VB(6) in the human diet, and VB(6) plays an important role in plants, the mechanisms underlying the interconversions of different VB(6)有六种不同的维生素 B(6) (VB(6)),吡哆醛 (PL)、吡哆胺 (PM)、吡哆醇 (PN)、5'-磷酸吡哆醛 (PLP)、5'-磷酸吡哆胺 (PMP)、和 5'-磷酸吡哆醇 (PNP),其中 PLP 是活性形式。尽管植物是人类饮食中 VB(6) 的主要来源,并且 VB(6) 在植物中起着重要作用,但不同 VB(6) 形式相互转换的潜在机制尚不清楚。在这项研究中,体外烟草植物在 Murashige 和 Skoog (MS) 基础培养基上生长,并辅以 100mg/L PM、PL 或 PN,并且叶组织中不同 B(6) 维生素的丰度通过高性能液体进行量化色谱法 (HPLC)。VB(6)总量约为3.9 μg/g鲜重,其中PL、PM、PN、PLP和PMP分别占23%、14%、37%、20%和6%。烟草植物含有微量的 PNP。用任何非磷酸化维生素补充培养基导致总 VB(6) 增加约 10 倍,但
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
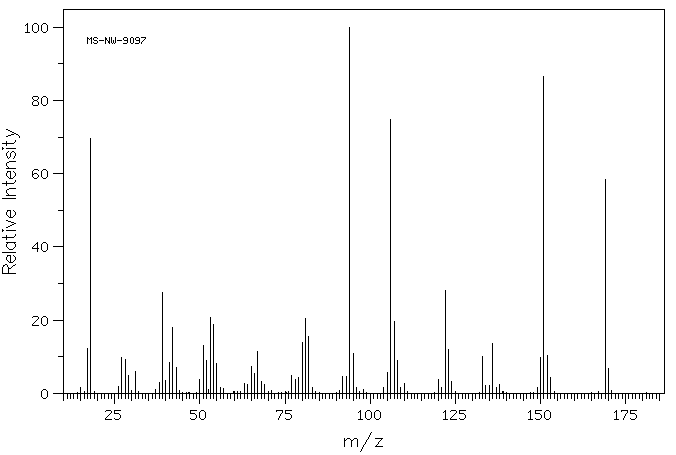
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
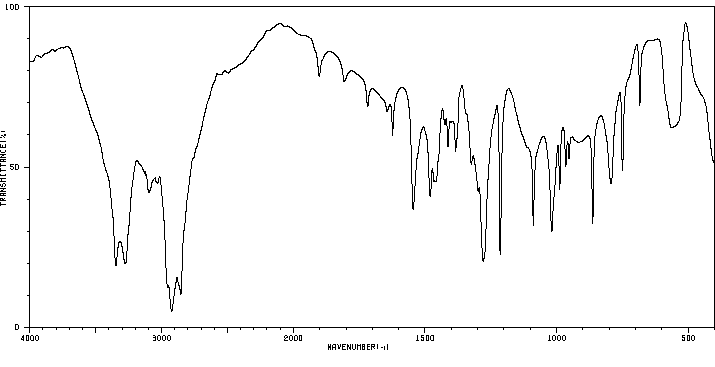
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(S)-氨氯地平-d4
(R,S)-可替宁N-氧化物-甲基-d3
(R)-(+)-2,2'',6,6''-四甲氧基-4,4''-双(二苯基膦基)-3,3''-联吡啶(1,5-环辛二烯)铑(I)四氟硼酸盐
(R)-N'-亚硝基尼古丁
(R)-DRF053二盐酸盐
(5E)-5-[(2,5-二甲基-1-吡啶-3-基-吡咯-3-基)亚甲基]-2-亚磺酰基-1,3-噻唑烷-4-酮
(5-溴-3-吡啶基)[4-(1-吡咯烷基)-1-哌啶基]甲酮
(5-氨基-6-氰基-7-甲基[1,2]噻唑并[4,5-b]吡啶-3-甲酰胺)
(2S,2'S)-(-)-[N,N'-双(2-吡啶基甲基]-2,2'-联吡咯烷双(乙腈)铁(II)六氟锑酸盐
(2S)-2-[[[9-丙-2-基-6-[(4-吡啶-2-基苯基)甲基氨基]嘌呤-2-基]氨基]丁-1-醇
(2R,2''R)-(+)-[N,N''-双(2-吡啶基甲基)]-2,2''-联吡咯烷四盐酸盐
(1'R,2'S)-尼古丁1,1'-Di-N-氧化物
黄色素-37
麦斯明-D4
麦司明
麝香吡啶
鲁非罗尼
鲁卡他胺
高氯酸N-甲基甲基吡啶正离子
高氯酸,吡啶
高奎宁酸
马来酸溴苯那敏
马来酸氯苯那敏-D6
马来酸左氨氯地平
顺式-双(异硫氰基)(2,2'-联吡啶基-4,4'-二羧基)(4,4'-二-壬基-2'-联吡啶基)钌(II)
顺式-二氯二(4-氯吡啶)铂
顺式-二(2,2'-联吡啶)二氯铬氯化物
顺式-1-(4-甲氧基苄基)-3-羟基-5-(3-吡啶)-2-吡咯烷酮
顺-双(2,2-二吡啶)二氯化钌(II) 水合物
顺-双(2,2'-二吡啶基)二氯化钌(II)二水合物
顺-二氯二(吡啶)铂(II)
顺-二(2,2'-联吡啶)二氯化钌(II)二水合物
韦德伊斯试剂
非那吡啶
非洛地平杂质C
非洛地平
非戈替尼
非布索坦杂质66
非尼拉朵
非尼拉敏
雷索替丁
阿雷地平
阿瑞洛莫
阿扎那韦中间体
阿培利司N-6
阿伐曲波帕杂质40
间硝苯地平
间-硝苯地平
镉,二碘四(4-甲基吡啶)-
锌,二溴二[4-吡啶羧硫代酸(2-吡啶基亚甲基)酰肼]-