亚甲兰 | 61-73-4
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:190 °C (dec.)(lit.)
-
密度:1.0 g/mL at 20 °C
-
闪点:45 °C
-
溶解度:溶于水、乙醇、乙二醇、甲基溶纤剂
-
最大波长(λmax):661 nm
-
颜色/状态:Dark green crystals or powder from chloroform-ethyl ether
-
气味:Slight odor
-
蒸汽压力:7.0X10-7 mm Hg at 25 °C (est)
-
稳定性/保质期:
Stable under recommended storage conditions.
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of /nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides and chloride/.
-
解离常数:pKa = 3.14 (est)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-0.5
-
重原子数:21
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:3.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.25
-
拓扑面积:43.9
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:4
ADMET
安全信息
-
危险品标志:Xn
-
安全说明:S26,S36,S39
-
危险类别码:R22,R41
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:2934300000
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1993 3/PG 3
-
RTECS号:SP5740000
-
危险性防范说明:P280,P305+P351+P338
-
危险性描述:H302
-
储存条件:本品应密封并在4℃干燥条件下保存。
SDS
模块 1. 化学品
1.1 产品标识符
: Methylene Blue solution
产品名称
1.2 鉴别的其他方法
无数据资料
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途
仅用于研发。不作为药品、家庭或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述
2.1 GHS-分类
眼睛刺激 (类别 2A)
2.2 GHS 标记要素,包括预防性的陈述
象形图
警示词 警告
危险申明
H319 造成严重眼刺激。
警告申明
预防措施
P264 操作后彻底清洁皮肤。
P280 戴护目镜/戴面罩。
事故响应
P305 + P351 + P338 如与眼睛接触,用水缓慢温和地冲洗几分钟。如戴隐形眼镜并可方便地取
出,取出隐形眼镜,然后继续冲洗.
P337 + P313 如仍觉眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
安全技术说明书适用于专业用户。
2.3 其它危害物 - 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
3.2 混合物
组分 分类 浓度或浓度范围
Methylthioninium chloride
1-3%
化学文摘登记号(CA 61-73-4 Acute Tox. 4; Eye Dam. 1;
S No.) 200-515-2 Aquatic Acute 3; H302, H318,
EC-编号 H402
如需在本章节中提及的H类告知和R类描述的全部文字说明,请见第16章节.
模块 4. 急救措施
4.1 必要的急救措施描述
一般的建议
请教医生。 向到现场的医生出示此安全技术说明书。
吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如呼吸停止,进行人工呼吸。 请教医生。
皮肤接触
用肥皂和大量的水冲洗。 请教医生。
眼睛接触
用大量水彻底冲洗至少15分钟并请教医生。
食入
切勿给失去知觉者通过口喂任何东西。 用水漱口。 请教医生。
4.2 主要症状和影响,急性和迟发效应
4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示
无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施
5.1 灭火介质
灭火方法及灭火剂
用水雾,抗乙醇泡沫,干粉或二氧化碳灭火。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害
碳氧化物, 氮氧化物, 硫氧化物, 氯化氢气体
5.3 给消防员的建议
如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步信息
无数据资料
模块 6. 泄露应急处理
6.1 作业人员防护措施、防护装备和应急处置程序
使用个人防护用品。 避免吸入蒸气、烟雾或气体。 保证充分的通风。
6.2 环境保护措施
不要让产品进入下水道。
6.3 泄漏化学品的收容、清除方法及所使用的处置材料
用惰性吸附材料吸收并当作危险废物处理。 放入合适的封闭的容器中待处理。
6.4 参考其他部分
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
7.1 安全操作的注意事项
避免接触皮肤和眼睛。 避免吸入蒸气和烟雾。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性
贮存在阴凉处。 使容器保持密闭,储存在干燥通风处。
7.3 特定用途
无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
8.1 容许浓度
最高容许浓度
没有已知的国家规定的暴露极限。
8.2 暴露控制
适当的技术控制
根据良好的工业卫生和安全规范进行操作。 休息前和工作结束时洗手。
个体防护设备
眼/面保护
带有防护边罩的安全眼镜符合 EN166要求请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟)
检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/EEC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
完全接触
物料: 丁腈橡胶
最小的层厚度 0.11 mm
溶剂渗透时间: 480 min
测试过的物质Dermatril® (KCL 740 / Z677272, 规格 M)
飞溅保护
物料: 丁腈橡胶
最小的层厚度 0.11 mm
溶剂渗透时间: 480 min
测试过的物质Dermatril® (KCL 740 / Z677272, 规格 M)
, 测试方法 EN374
如果以溶剂形式应用或与其它物质混合应用,或在不同于EN
374规定的条件下应用,请与EC批准的手套的供应商联系。
这个推荐只是建议性的,并且务必让熟悉我们客户计划使用的特定情况的工业卫生学专家评估确认才可.
这不应该解释为在提供对任何特定使用情况方法的批准.
身体保护
防渗透的衣服, 防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和数量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
如危险性评测显示需要使用空气净化的防毒面具,请使用全面罩式多功能防毒面具(US)或ABEK型
(EN
14387)防毒面具筒作为工程控制的候补。如果防毒面具是保护的唯一方式,则使用全面罩式送风防
毒面具。 呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息
a) 外观与性状
形状: 液体
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味阈值
无数据资料
d) pH值
无数据资料
e) 熔点/凝固点
无数据资料
f) 沸点、初沸点和沸程
无数据资料
g) 闪点
无数据资料
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 易燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 无数据资料
k) 蒸气压
无数据资料
l) 蒸汽密度
无数据资料
m) 密度/相对密度
无数据资料
n) 水溶性
无数据资料
o) n-辛醇/水分配系数
无数据资料
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性
10.1 反应性
无数据资料
10.2 稳定性
无数据资料
10.3 危险反应
无数据资料
10.4 应避免的条件
无数据资料
10.5 不相容的物质
无数据资料
10.6 危险的分解产物
其它分解产物 - 无数据资料
模块 11. 毒理学资料
11.1 毒理学影响的信息
急性毒性
无数据资料
皮肤刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
眼睛刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
无数据资料
生殖细胞致突变性
无数据资料
致癌性
IARC:
此产品中没有大于或等于 0。1%含量的组分被 IARC鉴别为可能的或肯定的人类致癌物。
生殖毒性
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入可能有害。 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
摄入 如服入是有害的。
皮肤 通过皮肤吸收可能有害。 可能引起皮肤刺激。
眼睛 造成严重眼刺激。
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: 无数据资料
模块 12. 生态学资料
12.1 生态毒性
无数据资料
12.2 持久性和降解性
无数据资料
12.3 潜在的生物累积性
无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移性
无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价
无数据资料
12.6 其它不良影响
无数据资料
模块 13. 废弃处置
13.1 废物处理方法
产品
将剩余的和不可回收的溶液交给有许可证的公司处理。
受污染的容器和包装
按未用产品处置。
模块 14. 运输信息
14.1 联合国危险货物编号
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.2 联合国运输名称
欧洲陆运危规: 非危险货物
国际海运危规: 非危险货物
国际空运危规: 非危险货物
14.3 运输危险类别
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.4 包裹组
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.5 环境危险
欧洲陆运危规: 否 国际海运危规 国际空运危规: 否
海洋污染物(是/否): 否
14.6 对使用者的特别提醒
无数据资料
参见发票或包装条的反面。
模块 15 - 法规信息
N/A
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
亚甲兰(methylene blue,MB)是一种还原剂,易溶于水且能轻易穿过细胞膜。由于其相对无毒的副作用,已被批准用于临床用药。自19世纪进入生物学界以来,亚甲兰的应用范围广泛:作为染料应用于神经解剖学和细菌学的研究;在生物化学研究中,它充当氧化还原反应的指示剂;此外,作为一种解毒剂,亚甲蓝被用于治疗由亚硝酸盐等引起的高铁血红蛋白血症以及氰化物中毒和异环磷酰胺诱导性脑病。
化学性质亚甲兰为金红色闪金黄或闪古铜色粉末。它溶于水后呈蓝色,稍溶于乙醇中。在浓硫酸中的染料会呈现黄光绿色,稀释后变为蓝色。其水溶液加入氢氧化钠后会显紫色,并生成暗紫色沉淀。
用途碱性湖蓝 BB 主要用于棉、腈纶、麻和蚕丝的染色,日晒坚牢度为2-3级。此外,它也适用于纸张染色、竹木着色以及制造墨水和色淀,同时可用于生物细菌组织的染色。
亚甲蓝还可用于麻、蚕丝织物及纸张的染色与竹木着色,并广泛应用于制造墨水和色淀及生物、细菌组织的染色。此外,它可与碱性紫5BN 和黄糊精以78:13:9的比例混合制成碱性品蓝。
亚甲兰是一种无毒染料,在氧化型时呈蓝色,在还原型时不显色。当用于酵母活细胞染色时,由于细胞的新陈代谢作用,细胞内具有较强的还原能力,可以使美蓝由蓝色的氧化型变为无色的还原型;而对于代谢活动微弱或已死的细胞,则不具备这种还原能力,因此被染成蓝色或淡蓝色。这种方法不仅可用于观察酵母细胞形态,还可以用来鉴别活细胞和死细胞。
生产方法亚甲蓝的生产方法如下:首先从N,N-二甲基苯胺进行亚硝化,生成对氨基二甲基苯胺;再经重铬酸钠、硫代硫酸钠氧化、硫化及缩合,然后用氯化锌成盐,经过滤干燥即得成品。原料消耗包括N,N-二甲基苯胺790kg,亚硝酸钠250kg,硫酸760kg,盐酸(31%)500kg,重铬酸钠(95%)1400kg,硫代硫酸钠830kg,精制硫酸铝1060kg,硫酸铜52kg,氯化锌372kg,铁粉650kg。
另一种生产方法为:以N,N-二甲基苯胺为主要原料,首先经亚硝化、还原得到对氨基二甲基苯胺,再经过Na2Cr2O7.Na2S2O3氧化、硫化和缩合生成噻嗪,最后使用ZnCl2成盐,通过盐析、过滤及干燥即可获得成品。
分类亚甲蓝属于有毒物品,毒性分级为中毒。急性口服毒性指标如下:大鼠LD50: 1180毫克/公斤;小鼠LD50: 3500毫克/公斤。该物质可燃性危险特性表现为燃烧时会产生有毒氮氧化物、氯化物和硫氧化物烟雾,同时还伴有药物副作用如紫疳及血液病变。
储运与灭火反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Controlled synthesis of ZnxCd1−xS nanorods and their composite with RGO for high-performance visible-light photocatalysis摘要:Zn0.5Cd0.5S纳米棒具有适当的带隙和纵横比,对可见光显示出最高的光响应。具有线对线界面的Zn0.5Cd0.5S/RGO纳米复合材料表现出增强的光催化活性。DOI:10.1039/c5ra01846c
-
作为产物:描述:2-amino-5-dimethylaminophenylthiosulphonic acid 在 potassium dichromate 、 zinc(II) chloride 作用下, 生成 亚甲兰参考文献:名称:DE46805摘要:公开号:
-
作为试剂:描述:参考文献:名称:一种六氢咪唑并[2,1-a]异喹啉衍生物及其合成方法摘要:本发明提供了一种六氢咪唑并[2,1‑a]异喹啉衍生物及其合成方法,属于化学合成领域,其结构具有独特的咪唑并异喹啉骨架特征,以四氢异喹啉衍生物和苯并噻唑亚胺衍生物为原料,在催化剂、溶剂,在光照条件下混合反应6‑36 h,反应后处理得到六氢咪唑并[2,1‑a]异喹啉衍生物,该类化合物具有潜在的生理和药物活性;本发明具有反应条件温和、操作简单、绿色环保,原料简便易得、产率高、应用易于扩展等优点;产物易分离纯化,避免在后处理过程中冗长的分离过程和中间体化合物的纯化过程,从而节省时间与资源并且提高收率,适用于大规模工业化生产。公开号:CN117700413A
文献信息
-
[EN] COMPOUNDS<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS申请人:GLAXOSMITHKLINE IP DEV LTD公开号:WO2018137593A1公开(公告)日:2018-08-02Provided are novel compounds that inhibit LRRK2 kinase activity, processes for their preparation, compositions containing them and their use in the treatment of or prevention of diseases associated with or characterized by LRRK2 kinase activity, for example Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).提供了抑制LRRK2激酶活性的新化合物,以及它们的制备方法、含有它们的组合物以及它们在治疗或预防与LRRK2激酶活性相关或以其为特征的疾病中的用途,例如帕金森病、阿尔茨海默病和肌萎缩侧索硬化症(ALS)。
-
[EN] PHENOTHIAZINE DERIVATIVES AND USES THEREOF<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS DE PHÉNOTHIAZINE ET LEURS UTILISATIONS申请人:CAMP4 THERAPEUTICS CORP公开号:WO2019195789A1公开(公告)日:2019-10-10The present invention provides phenothiazine compounds, processes for their preparation, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds, and the use of the compounds or the compositions in the treatment of various diseases or conditions, for example ribosomal disorders and ribosomopathies, e.g. Diamond Blackfan anemia (DBA).
-
Benzene Sulfonamide Thiazole and Oxazole Compounds申请人:Adams Jerry Leroy公开号:US20090298815A1公开(公告)日:2009-12-03The present invention provides thiazole sulfonamide and oxazole sulfonamide compounds, compositions containing the same, as well as processes for the preparation and methods for their use as pharmaceutical agents.
-
Macrocyclic Modulators of the Ghrelin Receptor申请人:Ocera Therapeutics, Inc.公开号:US20180110824A1公开(公告)日:2018-04-26The present invention provides novel conformationally-defined macrocyclic compounds that have been demonstrated to be selective modulators of the ghrelin receptor (growth hormone secretagogue receptor, GHS-R1a and subtypes, isoforms and variants thereof). Methods of synthesizing the novel compounds are also described herein. These compounds are useful as agonists of the ghrelin receptor and as medicaments for treatment and prevention of a range of medical conditions including, but not limited to, metabolic and/or endocrine disorders, gastrointestinal disorders, cardiovascular disorders, obesity and obesity-associated disorders, central nervous system disorders, genetic disorders, hyperproliferative disorders and inflammatory disorders.本发明提供了一种新颖的构象定义明确的大环化合物,已经证明是生长激素分泌素受体(GHS-R1a及其亚型、异构体和变体)的选择性调节剂。本文还描述了合成这些新型化合物的方法。这些化合物可用作生长激素分泌素受体的激动剂,用于治疗和预防一系列医疗状况,包括但不限于代谢和/或内分泌紊乱、胃肠道紊乱、心血管疾病、肥胖和与肥胖相关的疾病、中枢神经系统疾病、遗传疾病、过度增殖性疾病和炎症性疾病。
-
COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR DETECTING NERVE AGENTS申请人:Corcoran Robert C.公开号:US20100130757A1公开(公告)日:2010-05-27The present invention provides methods and compositions for detecting, identifying and measuring the abundance of chemical nerve agents. Methods and compositions of the present invention are capable of providing selective detection of phosphorous based nerve agents, such as nerve agents that are esters of methyl phosphonic acid derivatives incorporating a moderately good leaving group at the phosphorus. Selectivity in the present invention is provided by a sensor composition having an alpha (α) effect nucleophile group that undergoes specific nucleophilic substitution and rearrangement reactions with phosphorus based nerve agents having a tetrahederal phosphorous bound to oxygen. The present invention includes embodiments employing a sensor composition further comprising a reporter group covalently linked to the alpha effect nucleophile group allowing rapid optical readout of nerve agent detection events, including direct visual readout and optical readout via spectroscopic analysis.
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
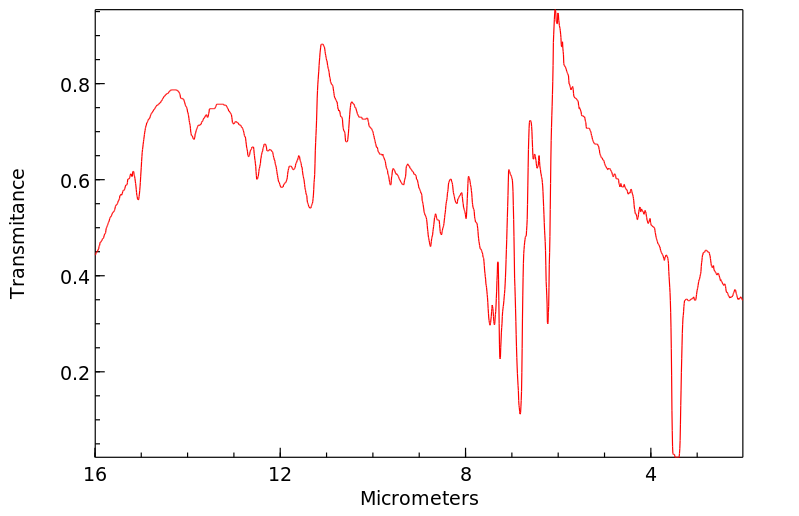
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息