1,5-二氨基戊烷 | 462-94-2
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:9 °C
-
沸点:178-180 °C(lit.)
-
密度:0.873 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
-
闪点:145 °F
-
溶解度:1M HCl:可溶 0.5g/10 mL,澄清,无色
-
LogP:-0.3--0.15 at 21℃
-
物理描述:Liquid
-
颜色/状态:Syrupy, colorless liquid
-
气味:Characeteristic odor
-
蒸汽压力:1.01 mm Hg at 25 °C (est)
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits highly toxic fumes of /nitroxides/.
-
折光率:Index of refraction = 1.463 at 20 °C/D
-
解离常数:pKa1 = 10.25; pKa2 = 9.13
-
保留指数:1035;1035
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-0.6
-
重原子数:7
-
可旋转键数:4
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:52
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:2
ADMET
安全信息
-
危险等级:8
-
危险品标志:C
-
安全说明:S25,S26,S36/37/39,S45
-
危险类别码:R34
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:2921290000
-
危险品运输编号:UN 2735 8/PG 3
-
危险类别:8
-
RTECS号:SA0200000
-
包装等级:III
-
危险标志:GHS02,GHS07
-
危险性描述:H225,H319,H336
-
危险性防范说明:P210,P305 + P351 + P338,P370 + P378,P403 + P235
-
储存条件:储存注意事项:应将储存于阴凉、通风的库房中,并远离火种与热源。保持容器密封完好。需与其他化学物质分开存放,特别是要与氧化剂、酸类及食用化学品分开,严禁混储。配备相应种类和数量的消防器材。储区还应备有泄漏应急处理设备以及合适的收容材料。
制备方法与用途
简介 1,5-二氨基戊烷是一种无色黏稠的发烟液体,带有特殊气味。它主要用于有机合成中间体和环氧树脂固化剂,并广泛应用于高聚物制备以及生物研究。
应用 该化合物可通过基因工程改造的大肠杆菌或谷氨酸棒状杆菌发酵生产。发酵过程中获得的1,5-二氨基戊烷可以用于制造新型生物聚酰胺。
制备 实验室条件下,可以从戊二腈出发合成1,5-二氨基戊烷。具体步骤包括:将戊二腈溶解于无水乙醇中并煮沸,随后迅速加入金属钠;反应完全后加水并蒸除乙醇,剩余物通过过热蒸汽蒸馏处理。所得馏出液经稀盐酸中和、干燥以及冷无水乙醇洗涤后,再用少量固体氢氧化钾分解其生成的盐酸盐,并进行减压蒸馏得到1,5-二氨基戊烷。
化学性质 1,5-二氨基戊烷是一种浆状液体。其沸点为178-180℃(1.6kPa),密度约为0.873(25/4℃),折射率为1.463。易溶于水和乙醇,难溶于乙醚,在低温条件下可结晶化但在常温下又变为液体。该物质具有类似六氢吡啶的气味,并能在空气中发烟,能形成二水化合物。
用途 主要用作有机合成中的中间体。
生产方法 通过赖氨酸脱羧制得1,5-二氨基戊烷;实验室条件下可从戊二腈出发进行制备过程:将戊二腈溶解于无水乙醇中并煮沸,迅速加入金属钠完成反应后加水蒸出乙醇,并用过热蒸汽蒸馏处理剩余物。经稀盐酸中和、干燥以及冷无水乙醇洗涤后,再利用少量固体氢氧化钾分解生成的盐酸盐进行减压蒸馏以获得目标产物。
类别 有毒物品
毒性分级 中毒
急性毒性 皮下注射-大鼠:LD₅₀: 1250 毫克/公斤;口服-小鼠:LD₅₀: 1600 毫克/公斤
可燃性危险特性 明火下易燃;高温分解时释放氮氧化物气体。
储运特性 需在库房中保持通风、低温及干燥条件,并与其他氧化剂、酸类和食品化工添加剂分开存放。
灭火剂 使用干粉、泡沫、二氧化碳或砂土进行灭火。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 正己胺 hexan-1-amine 111-26-2 C6H15N 101.192 5-氨基戊腈盐酸盐 5-Aminopentanenitrile 6066-83-7 C5H10N2 98.1478 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 正己胺 hexan-1-amine 111-26-2 C6H15N 101.192 —— N,N'-dimethylpentane-1,5-diamine 56992-95-1 C7H18N2 130.233 1-(N-甲基)-1,5-戊二胺 N-methylcadaverine 32752-52-6 C6H16N2 116.206 (S)-2-己基胺 (S)-hexan-2-amine 70492-67-0 C6H15N 101.192 5-氨基戊醛 δ-aminopentanal 14049-15-1 C5H11NO 101.148 哌啶 piperidine 110-89-4 C5H11N 85.149
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Demjanow, Zhurnal Russkago Fiziko-Khimicheskago Obshchestva, 1890, vol. 22, p. 389摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:底物选择性超分子串联测定:通过杯芳烃和葫芦脲大环化合物的荧光染料置换监测精氨酸酶和二胺氧化酶的酶抑制作用摘要:适度选择性的主客体结合与令人印象深刻的酶转化特异性相结合,可以实时监测均相溶液中的酶反应。所得酶测定(“超分子串联测定”)利用荧光染料与大环宿主的动态结合,与底物和产物的结合竞争。研究了两个酶促反应的例子:精氨酸酶催化的精氨酸水解为鸟氨酸和二胺氧化酶将尸胺氧化为 5-氨基戊醛,其中底物对大环化合物的亲和力高于产物(“底物选择性测定法” ”)。底物的消耗使荧光染料在酶促反应过程中进入大环,这导致所需的荧光响应。对于精氨酸酶,使用对磺化杯[4]芳烃作为大环化合物,其与精氨酸的结合常数为 6400 M(-1),与鸟氨酸的结合常数为 550 M(-1),与选定的荧光结合常数为 60,000 M(-1)染料(1-氨基甲基-2,3-二氮杂双环[2.2.2]辛-2-烯);该染料在其络合状态下显示出较弱的荧光,这导致在酶促反应过程中关闭荧光响应。对于二胺氧化酶,葫芦[7] uril (CB7) 用作大环,显示结合常数为DOI:10.1021/ja904165c
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:谷氨酸棒杆菌用于自给自足转氨酶反应的生物工厂的开发摘要:非常需要开发从非手性构件开始合成手性胺的生物催化途径。在这里,我们报告了一个自足的全细胞系统,可将模型酮转化为相应的环状亚胺,分离产率高(42%),对映选择性极好(ee > 99%)。在谷氨酸棒杆菌宿主产生的生物催化剂转氨酶,辅因子和“智能”的胺供体(尸胺或腐胺)在体内,并强调了从容易获得的构件中生产高价值化学品的潜力。该报告代表了将代谢工程改造的生物体用于生产智能二胺供体的应用及其在转氨酶生物转化中的应用的第一个实例。DOI:10.1039/d0gc01432j
文献信息
-
Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of the First Dual Tyrosyl-DNA Phosphodiesterase I (Tdp1)–Topoisomerase I (Top1) Inhibitors作者:Trung Xuan Nguyen、Andrew Morrell、Martin Conda-Sheridan、Christophe Marchand、Keli Agama、Alun Bermingam、Andrew G. Stephen、Adel Chergui、Alena Naumova、Robert Fisher、Barry R. O’Keefe、Yves Pommier、Mark CushmanDOI:10.1021/jm300335n日期:2012.5.10Substances with dual tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase I–topoisomerase I inhibitory activity in one low molecular weight compound would constitute a unique class of anticancer agents that could potentially have significant advantages over drugs that work against the individual enzymes. The present study demonstrates the successful synthesis and evaluation of the first dual Top1–Tdp1 inhibitors, which are based在一种低分子量化合物中具有双重酪氨酰-DNA 磷酸二酯酶 I-拓扑异构酶 I 抑制活性的物质将构成一类独特的抗癌剂,可能比针对单个酶的药物具有显着的优势。本研究证明了基于茚并异喹啉化学型的第一个双 Top1-Tdp1 抑制剂的成功合成和评估。一种双(茚并异喹啉)对人 Tdp1 具有显着活性(IC 50= 1.52 ± 0.05 μM),并且作为 Top1 抑制剂与喜树碱等效。通过该系列的结构-活性关系研究,获得了对酶-药物相互作用的重要见解。目前的结果还证明了先前报道的磺酰酯药效团未能在这种茚并异喹啉类抑制剂中赋予 Tdp1 抑制作用,尽管它被证明对类固醇 NSC 88915 有效 ( 7 )。目前的研究将促进未来优化双 Top1-Tdp1 抑制剂的努力。
-
[EN] MACROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS FOR MODULATING IL-17<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS MACROCYCLIQUES POUR UNE MODULATION D'IL-17申请人:ENSEMBLE THERAPEUTICS CORP公开号:WO2013116682A1公开(公告)日:2013-08-08The invention relates generally to macrocyclic compounds of formula I and their therapeutic use. More particularly, the invention relates to macrocyclic compounds that modulate the activity of IL-17 and/or are useful in the treatment of medical conditions, such as inflammatory diseases and other IL-17-associated disorders.这项发明通常涉及公式I的大环化合物及其治疗用途。更具体地,该发明涉及调节IL-17活性的大环化合物,或者用于治疗炎症性疾病和其他与IL-17相关的疾病的大环化合物。
-
Synthesis and Aggregation Properties of Two- and Three-Armed Nitrogen-Rich Chelate Ligands: Novel Bis(N-acylamidines), Tris(N-acylamidines) and Bis(triazapentadienes) with Flexible or Rigid Spacers作者:Juliana Isabel Clodt、Christof Wigbers、Ralph Reiermann、Roland Fröhlich、Ernst-Ulrich WürthweinDOI:10.1002/ejoc.201100218日期:2011.6and three-armed ligands, like bis(N-acylamidines) 7 and 9, tris(N-acylamidines) 8 and bis(1,3,5-triazapenta-1,3-dienes) 10 with different spacers between the ligand moieties, have been easily prepared in moderate-to-good yields starting from diamines, triamines or dicarboxylic acid derivatives. Thus, the reaction of diamines and triamines with N-acylimidates 3 led to bis(N-acylamidines) 7 and tris(N-acylamidines)
-
Design and Synthesis of Peptides Passing through the Blood-Brain Barrier作者:Tateaki Wakamiya、Makoto Kamata、Shoichi Kusumoto、Hiroyuki Kobayashi、Yoshimichi Sai、Ikumi Tamai、Akira TsujiDOI:10.1246/bcsj.71.699日期:1998.3The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective membranous barrier regulating the transport of substances in blood into the brain parenchyma. At present, delivery of biologically active peptides or peptide drugs into the brain is quite an important subject from the standpoint of chemotherapy for brain diseases. H–MeTyr–Arg–MeArg–d-Leu–NH(CH2)8NH2 termed 001-C8 was first synthesized to elucidate the structural specificity of peptides for passing through the BBB. The Nα-methylamino acid and d-amino acid residues were appropriately situated in this peptide to protect against the digestion by peptidase. Furthermore, a number of basic peptides were prepared as 001-C8 analogs for studying the relationship between structure and BBB permeability of peptides.
-
Iodoaminopotentidine and related compounds: a new class of ligands with high affinity and selectivity for the histamine H2 receptor作者:Juergen Hirschfeld、Armin Buschauer、Sigurd Elz、Walter Schunack、Martial Ruat、Elisabeth Traiffort、Jean Charles SchwartzDOI:10.1021/jm00090a013日期:1992.6The synthesis and biological evaluation of a new class of histamine H2 antagonists with N-cyano-N'-[omega-[3-(1-piperidinylmethyl)phenoxy] alkyl]guanidine partial structure are described as part of an extensive research program to find model compounds for the development of new radioligands with high H2 affinity and specific activity. High receptor affinity is achieved by an additional (substituted)描述了一种新型的具有N-氰基-N'-[ω-[3-(1-(哌啶基甲基)苯氧基]烷基]胍部分结构的组胺H2拮抗剂的合成和生物学评估,作为广泛研究计划的一部分,以寻找用于开发具有高H2亲和力和比活性的新型放射性配体的模型化合物。高的受体亲和力是通过一个附加的(取代的)芳环实现的,该芳环通过碳链间隔基和一个胺,羧酰胺,酯或磺酰胺键(“极性基团”)与第三胍N连接。在针对豚鼠心房和回肠以及大鼠主动脉和尾动脉的H2拮抗活性和其他药理作用(例如H1抗组胺药,抗毒蕈碱,抗肾上腺素(α1,β1),5-HT2阻断活性)的功能研究中,该化合物被证明是高效和选择性的组胺H2受体拮抗剂。H2拮抗活性主要取决于N'-烷基链(链A)和N“-间隔基(链B)的长度。具有C3链A和C2链B的化合物最有效。一类物质,即羧酰胺系列,在芳香环上具有广泛的取代基,其中包括碘,氨基和叠氮基,这些化合物在分离的豚鼠右心房中的效能比西咪替丁
表征谱图
-
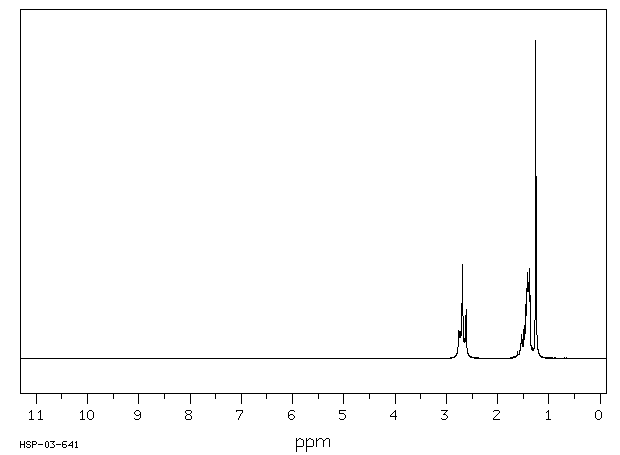
氢谱1HNMR
-
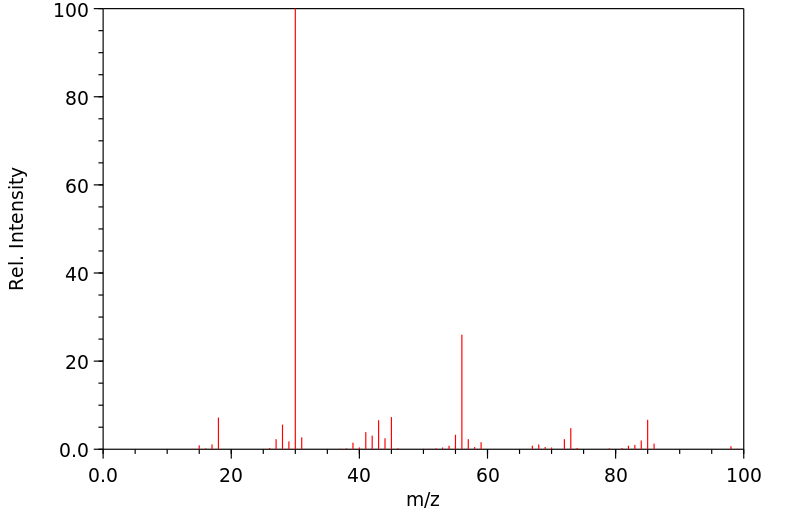
质谱MS
-
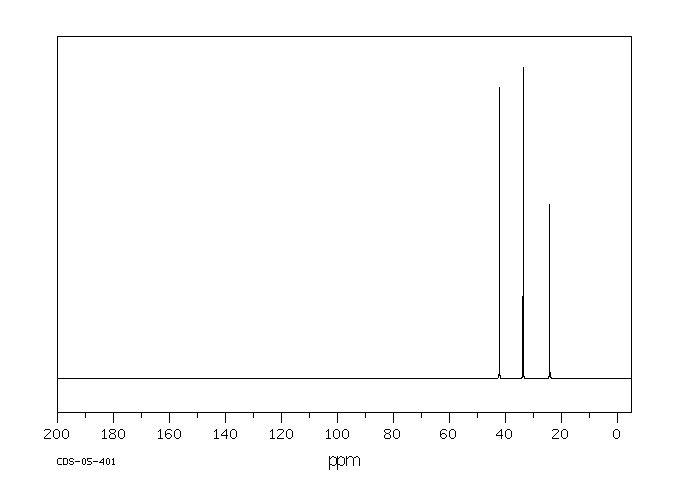
碳谱13CNMR
-
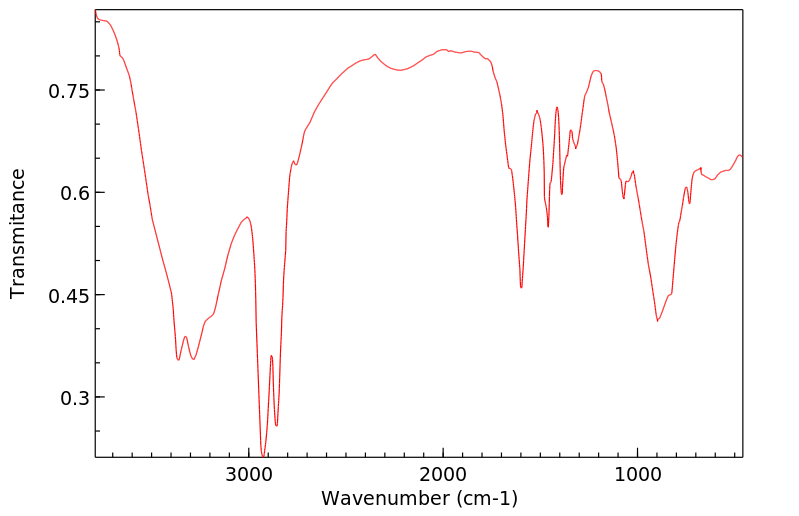
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息