代谢
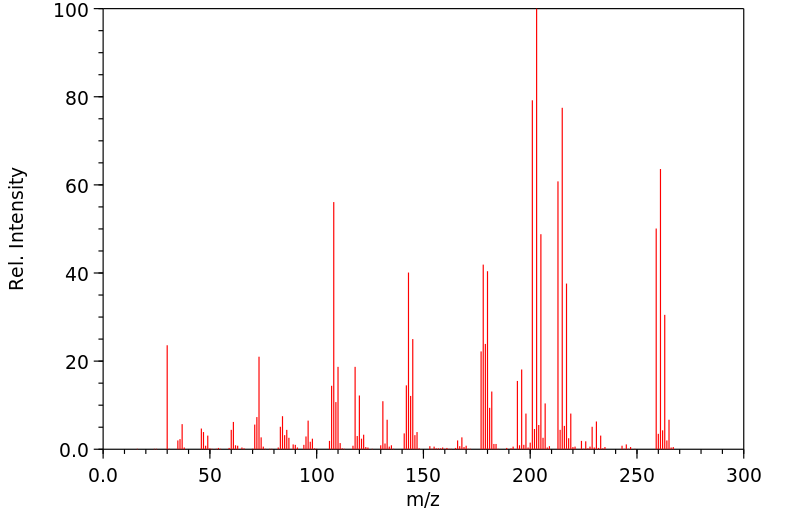
[U-14C]-2,3,5,6-四氯硝基苯(特克纳泽)在雄性和雌性大鼠单次给药1 mg/kg后的代谢命运已经确定,以及在手术准备、胆管插管的雄性大鼠单次口服给药135 mg/kg后的代谢命运。在雌性大鼠中,放射性物质主要随尿液排出(82%)。然而,雄性大鼠在大鼠的尿液和粪便中大约等量排出放射性物质(后者通过胆汁)。主要代谢途径是与谷胱甘肽(GSH)结合并伴随硝基位移。GSH结合物和相关代谢物随胆汁排出,最终以巯基尿酸结合物的形式随尿液排出。半胱氨酸结合物经过β-裂解酶介导的代谢,产生一个硫醇,随后发生甲基化生成硫代苯甲醚,然后发生S-氧化。还形成了一种新型的四氯甲基硫化物代谢物。
The metabolic fate of [U-14C]-2,3,5,6-tetrachloronitrobenzene (tecnazene) has been determined in the male and female rat following a single dose of 1 mg/kg and in surgically prepared, bile-duct-cannulated rats following a single oral dose of 135 mg/kg. Radioactivity in the female rat was excreted mainly in urine (82%). The male rat, however, excreted approximately equal amounts of radioactivity in urine and feces (the latter via bile). The principal metabolic pathway was conjugation with glutathione (GSH) and concomitant nitro-displacement. The GSH-conjugate and related metabolites were excreted in the bile and ultimately in the urine as the mercapturic acid conjugate. The cysteine conjugate underwent beta-lyase-mediated metabolism to yield a thiol that underwent subsequent methylation to the thioanisole followed by S-oxidation. 4. A novel tetrachloromethyldisulphide metabolite was also formed.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)