代谢
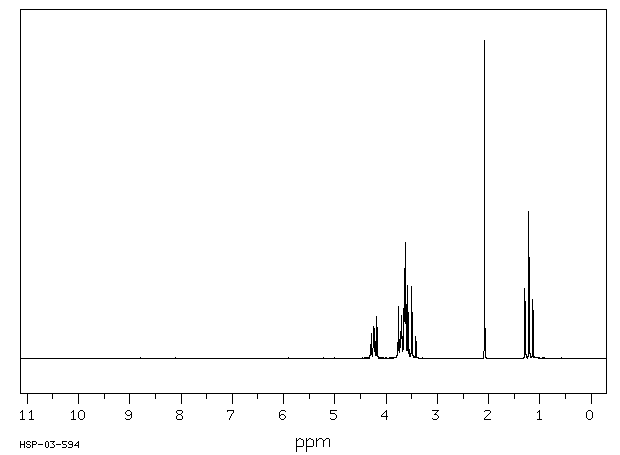
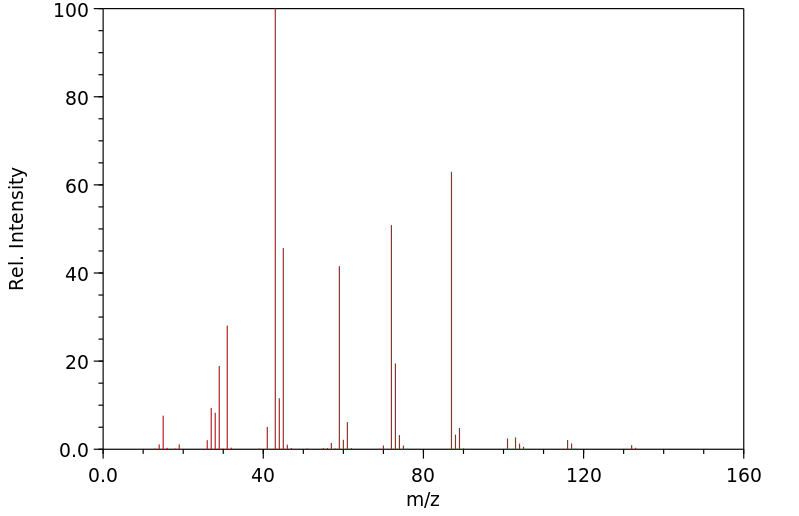
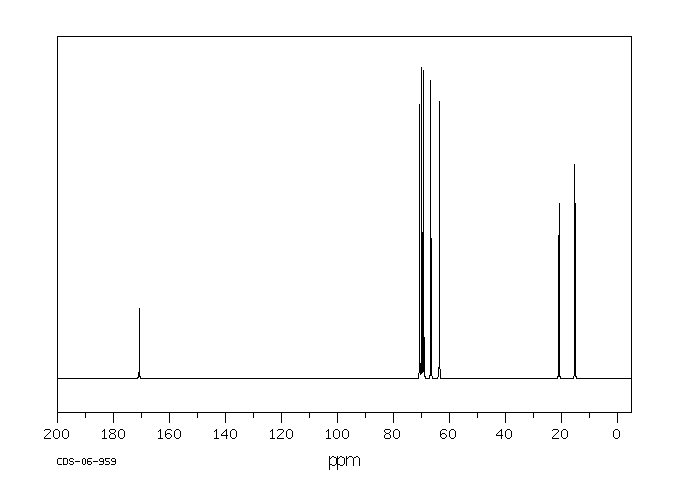
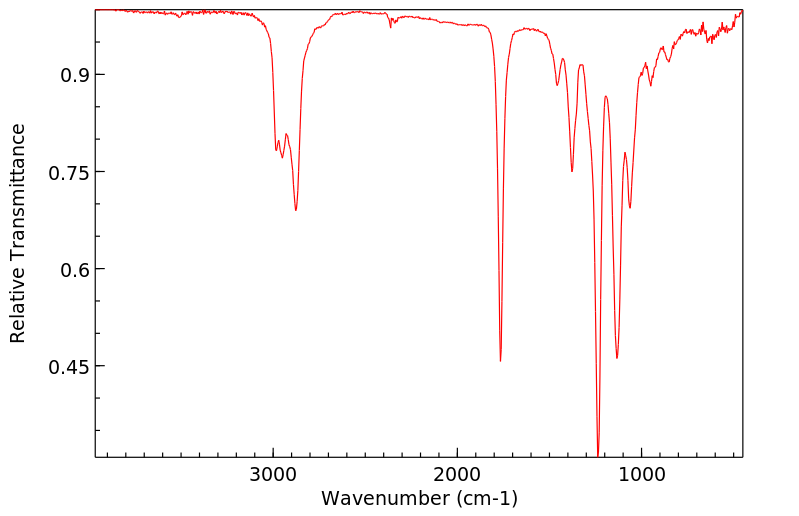
三(2-氯乙基)磷酸盐(TRCP) ... 在亚慢性口服给药后,以剂量、性别和物种依赖性的方式在大脑的海马区域产生损伤。这种损伤在雌性F344大鼠中比雄性F344大鼠更为常见和严重,而在B6C3F1小鼠中并未观察到。当前的调查旨在研究TRCP的代谢,以检测可能导致毒性差异的性别和物种变异。TRCP衍生放射性的消除在 mice 中更快,在8小时内,小鼠通过尿液排出了175 mg/kg口服剂量的70%以上,而大鼠(无论雌雄)则排出了大约40%。然而,尿液中TRCP衍生放射性的代谢轮廓对于两个物种来说是相似的。雌性大鼠尿液中的主要代谢物被鉴定为双(2-氯乙基)羧甲基磷酸。这个代谢物与在雄性大鼠和小鼠尿液中发现的主要代谢物共同层析。在雌性大鼠尿液中还鉴定出另外两种代谢物,即双(2-氯乙基)氢磷酸和双(2-氯乙基)2-羟乙基磷酸的葡萄糖苷酸。这些代谢物也与在雄性大鼠和小鼠尿液中发现的代谢物共同层析。大鼠对TRCP的代谢不受连续九天每天175 mg/kg剂量的诱导或抑制。毒性,如抽搐所证明的,在预先用乙醛脱氢酶抑制剂处理的雄性大鼠中得到了增强。
Tris(2-chloroethyl) phosphate (TRCP) ... produces a dose-, sex-, and species-dependent lesion in the hippocampal region of the brain following subchronic oral administration. This lesion is more common and more severe in female F344 rats than in male F344 rats, and is not observed in B6C3F1 mice. The present investigation of the metabolism of TRCP was designed to detect sex and species variations that might account for differences in toxicity. Elimination of TRCP-derived radioactivity was more rapid in mice, which excreted greater than 70% of an oral dose of 175 mg/kg in urine in 8 hr vs approximately 40% for male or female rats. However, the metabolic profile of TRCP-derived radioactivity in urine was similar for both species. The major metabolite in female rat urine was identified as bis(2-chloroethyl) carboxymethyl phosphate. This metabolite co-chromatographed with the major metabolite found in both male rat and mouse urine. Two additional metabolites identified in female rat urine were bis(2-chloroethyl) hydrogen phosphate and the glucuronide of bis(2-chloroethyl) 2-hydroxyethyl phosphate. These metabolites also cochromatographed with metabolites found in male rat and mouse urine. TRCP metabolism in rats was not induced or inhibited by nine daily 175 mg/kg doses. Toxicity, as evidenced by seizures, was potentiated in male rats pretreated with inhibitors of aldehyde dehydrogenase.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)