二烯丙基硫醚 | 592-88-1
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:-83 °C
-
沸点:138 °C(lit.)
-
密度:0.887 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
-
蒸气密度:3.9 (vs air)
-
闪点:115 °F
-
溶解度:3mg/mL 乙醇溶液;5mg/mL DMSO 溶液;10mg/mL 二甲基甲酰胺溶液
-
介电常数:4.9(20℃)
-
LogP:2.61
-
物理描述:Liquid
-
颜色/状态:Colorless liquid
-
气味:Garlic odor
-
味道:Garlic
-
蒸汽压力:9.22 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
折光率:Index of refraction = 1.4877 at 27 °C/D
-
保留指数:850;835;850;850;854;854;848;838;872;852;852;849
-
稳定性/保质期:
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2.2
-
重原子数:7
-
可旋转键数:4
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.333
-
拓扑面积:25.3
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:1
ADMET
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险等级:3
-
危险品标志:Xi
-
安全说明:S16,S23,S26,S36,S37/39
-
危险类别码:R10,R36/37/38
-
WGK Germany:2
-
海关编码:2930909090
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1993 3/PG 3
-
RTECS号:BC4900000
-
包装等级:III
-
危险类别:3
-
储存条件:请将物品远离火源,并存放在密封、避光的环境中。
SDS
| 第一部分:化学品名称 |
| 化学品中文名称: | 二烯丙基硫醚;烯丙基硫 |
| 化学品英文名称: | Diallyl thioether;Allyl sulfide |
| 中文俗名或商品名: | |
| Synonyms: | |
| CAS No.: | 592-88-1 |
| 分子式: | C 6 H 10 S |
| 分子量: | 114.21 |
| 第二部分:成分/组成信息 |
| 纯化学品 混合物 | |||
| 化学品名称:二烯丙基硫醚;烯丙基硫 | |||
|
| 第三部分:危险性概述 |
| 危险性类别: | 第6.1类 毒害品 |
| 侵入途径: | 吸入 食入 经皮吸收 |
| 健康危害: | 吸入、摄入或经皮肤吸收对身体有害。本品具有强烈刺激性。高浓度接触严重损害粘膜、上呼吸道、眼和皮肤。接触后引起烧灼感、咳嗽、喘息、喉炎、气短、头痛、恶心和呕吐。 |
| 环境危害: | |
| 燃爆危险: | 本品易燃,有毒,具强刺激性。 |
| 第四部分:急救措施 |
| 皮肤接触: | 脱去污染的衣着,立即用大量流动清水彻底冲洗。如有灼伤,按灼伤处理。 |
| 眼睛接触: | 立即翻开上下眼睑,用流动清水或生理盐水冲洗至少15分钟。就医。 |
| 吸入: | 迅速脱离现场至空气新鲜处。保持呼吸道通畅。呼吸困难时给输氧。呼吸停止时,立即进行人工呼吸。就医。 |
| 食入: | 误服者漱口,饮牛奶或蛋清。就医。 |
| 第五部分:消防措施 |
| 危险特性: | 遇明火、高热易燃。遇水蒸气、酸或酸雾会产生易燃和有毒的硫化氢气体。 |
| 有害燃烧产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳、硫化物。 |
| 灭火方法及灭火剂: | 消防人员必须佩戴过滤式防毒面具(全面罩)或隔离式呼吸器、穿全身防火防毒服,在上风向灭火。尽可能将容器从火场移至空旷处。喷水保持火场容器冷却,直至灭火结束。处在火场中的容器若已变色或从安全泄压装置中产生声音,必须马上撤离。灭火剂:泡沫、干粉、二氧化碳、砂土。 |
| 消防员的个体防护: | |
| 禁止使用的灭火剂: | |
| 闪点(℃): | 46 |
| 自燃温度(℃): | 无资料 |
| 爆炸下限[%(V/V)]: | 无资料 |
| 爆炸上限[%(V/V)]: | 无资料 |
| 最小点火能(mJ): | |
| 爆燃点: | |
| 爆速: | |
| 最大燃爆压力(MPa): | |
| 建规火险分级: |
| 第六部分:泄漏应急处理 |
| 应急处理: | 迅速撤离泄漏污染区人员至安全区,并进行隔离,严格限制出入。切断火源。建议应急处理人员戴自给正压式呼吸器,穿防毒服。尽可能切断泄漏源。防止流入下水道、排洪沟等限制性空间。小量泄漏:用活性炭或其它惰性材料吸收。大量泄漏:构筑围堤或挖坑收容。用泵转移至槽车或专用收集器内,回收或运至废物处理场所处置。 |
| 第七部分:操作处置与储存 |
| 操作注意事项: | 密闭操作,提供充分的局部排风。操作人员必须经过专门培训,严格遵守操作规程。建议操作人员佩戴自吸过滤式防毒面具(全面罩),穿胶布防毒衣,戴橡胶耐油手套。远离火种、热源,工作场所严禁吸烟。使用防爆型的通风系统和设备。防止蒸气泄漏到工作场所空气中。避免与氧化剂、碱类接触。搬运时要轻装轻卸,防止包装及容器损坏。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材及泄漏应急处理设备。倒空的容器可能残留有害物。 |
| 储存注意事项: | 储存于阴凉、通风的库房。远离火种、热源。应与氧化剂、碱类分开存放,切忌混储。不宜大量储存或久存。采用防爆型照明、通风设施。禁止使用易产生火花的机械设备和工具。储区应备有泄漏应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。 |
| 第八部分:接触控制/个体防护 |
| 最高容许浓度: | 中 国 MAC:未制订标准前苏联MAC:未制订标准美国TLV-TWA:未制订标准美国 |
| 监测方法: | |
| 工程控制: | 严加密闭,提供充分的局部排风。 |
| 呼吸系统防护: | 可能接触其蒸气时,必须佩戴防毒面具。紧急事态抢救或撤离时,建议佩戴自给式呼吸器。 |
| 眼睛防护: | 戴化学安全防护眼镜。 |
| 身体防护: | 穿防腐工作服。 |
| 手防护: | 戴防化学品手套。 |
| 其他防护: | 工作现场禁止吸烟、进食和饮水。工作后,淋浴更衣。保持良好的卫生习惯。 |
| 第九部分:理化特性 |
| 外观与性状: | 无色油状液体,有蒜臭味。 |
| pH: | |
| 熔点(℃): | -83 |
| 沸点(℃): | 139 |
| 相对密度(水=1): | 0.89 |
| 相对蒸气密度(空气=1): | 3.90 |
| 饱和蒸气压(kPa): | |
| 燃烧热(kJ/mol): | |
| 临界温度(℃): | |
| 临界压力(MPa): | |
| 辛醇/水分配系数的对数值: | |
| 闪点(℃): | 46 |
| 引燃温度(℃): | 无资料 |
| 爆炸上限%(V/V): | 无资料 |
| 爆炸下限%(V/V): | 无资料 |
| 分子式: | C 6 H 10 S |
| 分子量: | 114.21 |
| 蒸发速率: | |
| 粘性: | |
| 溶解性: | 不溶于水,可混溶于乙醇、乙醚、氯仿、四氯化碳。 |
| 主要用途: | 用于有机合成。 |
| 第十部分:稳定性和反应活性 |
| 稳定性: | 在常温常压下 稳定 |
| 禁配物: | 强氧化剂、强碱。 |
| 避免接触的条件: | |
| 聚合危害: | 能发生 |
| 分解产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳、硫化物。 |
| 第十一部分:毒理学资料 |
| 急性毒性: | |
| 急性中毒: | |
| 慢性中毒: | |
| 亚急性和慢性毒性: | |
| 刺激性: | |
| 致敏性: | |
| 致突变性: | |
| 致畸性: | |
| 致癌性: |
| 第十二部分:生态学资料 |
| 生态毒理毒性: | |
| 生物降解性: | |
| 非生物降解性: | |
| 生物富集或生物积累性: |
| 第十三部分:废弃处置 |
| 废弃物性质: | |
| 废弃处置方法: | 处置前应参阅国家和地方有关法规。建议用焚烧法处置。焚烧炉排出的硫氧化物通过洗涤器除去。 |
| 废弃注意事项: |
| 第十四部分:运输信息 |
| |
| 危险货物编号: | 61595 |
| UN编号: | |
| 包装标志: | |
| 包装类别: | Ⅲ |
| 包装方法: | 小开口钢桶;安瓿瓶外普通木箱;螺纹口玻璃瓶、铁盖压口玻璃瓶、塑料瓶或金属桶(罐)外普通木箱;螺纹口玻璃瓶、塑料瓶或镀锡薄钢板桶(罐)外满底板花格箱、纤维板箱或胶合板箱。 |
| 运输注意事项: | 铁路运输时应严格按照铁道部《危险货物运输规则》中的危险货物配装表进行配装。运输前应先检查包装容器是否完整、密封,运输过程中要确保容器不泄漏、不倒塌、不坠落、不损坏。严禁与酸类、氧化剂、食品及食品添加剂混运。运输时运输车辆应配备相应品种和数量的消防器材及泄漏应急处理设备。运输途中应防曝晒、雨淋,防高温。运输时所用的槽(罐)车应有接地链,槽内可设孔隔板以减少震荡产生静电。中途停留时应远离火种、热源。公路运输时要按规定路线行驶,勿在居民区和人口稠密区停留。 |
| RETCS号: | |
| IMDG规则页码: |
| 第十五部分:法规信息 |
| 国内化学品安全管理法规: | 化学危险物品安全管理条例 (1987年2月17日国务院发布),化学危险物品安全管理条例实施细则 (化劳发[1992] 677号),工作场所安全使用化学品规定 ([1996]劳部发423号)等法规,针对化学危险品的安全使用、生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应规定;常用危险化学品的分类及标志 (GB 13690-92)将该物质划为第6.1 类毒害品。 |
| 国际化学品安全管理法规: |
| 第十六部分:其他信息 |
| 参考文献: | 1.周国泰,化学危险品安全技术全书,化学工业出版社,1997 2.国家环保局有毒化学品管理办公室、北京化工研究院合编,化学品毒性法规环境数据手册,中国环境科学出版社.1992 3.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety,CHEMINFO Database.1998 4.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety, RTECS Database, 1989 |
| 填表时间: | 年月日 |
| 填表部门: | |
| 数据审核单位: | |
| 修改说明: | |
| 其他信息: | 3 |
| MSDS修改日期: | 年月日 |
制备方法与用途
二烯丙基硫醚是指二烯丙基一硫醚、二烯丙基二硫醚、二烯丙基三硫醚和二烯丙基四硫醚等4种成分,存在于蔬菜、葱类腐败物分解体及十字科植物果实中。是大蒜提取液中的主要成分,具有较强的抗癌、抗病毒、抗菌活性,并能较强抑制血小板凝聚、增强机体免疫力。广泛应用在医疗卫生、饲料等行业中。
理化性质二烯丙基硫醚是一种有大蒜气味的油状物,沸点139℃(101.056Pa),相对密度0.8876,折光率1.4877。它溶于乙醚等有机溶剂而不溶于水。可被氧化至二烯丙基砜。

制备方法 生物提取法常见的有水蒸气蒸馏提取法、有机溶剂提取法和超临界CO₂萃取法。在一定压力下加热,利用水作为溶剂可以将天然产物中的可溶性有效成分提取出来,此方法操作简单但对热敏性的有效成分提取损失较大且得率较低,提取物分离较困难。以95%乙醇为提取溶剂,按照1g∶4mL的比例加入提取剂,在温度设定为40℃的条件下酶解0.5h;随后在30℃下萃取1.5h;最后将温度设定在50℃,使用旋蒸仪转速4500r/min减压浓缩提取,提取率可达到0.24%。
化学合成法以Na₂S₂O₃·5H₂O(62g, 0.25mol)与3-溴丙烯(24g, 0.19mol)为原料,在特定条件下进行化学反应,最终得到二烯丙基硫醚。
化学性质无色至淡黄色液体,呈大蒜、洋葱、辣椒气味。沸点138~139℃。不溶于水,混溶于乙醇、乙醚及其他有机溶剂。天然品存在于洋葱、大蒜、芥菜及煮或炸过的牛肉等中。
用途用于日用、食用香精。
生产方法根据GB 2760--2002规定,二烯丙基硫醚为允许使用的食品用香料,主要用于配制洋葱、大蒜、辣椒、小萝卜、芥菜等香精。
性质与分类 主要性质 主要用途- 用于日用、食用香精。
根据GB 2760--2002规定,二烯丙基硫醚为允许使用的食品用香料。主要用于配制洋葱、大蒜、辣椒、小萝卜、芥菜等香精。
分类与毒性- 类别:有毒物品。
- 毒性分级:中毒。
- 急性毒性(口服)-大鼠LD50: 2980毫克/公斤。
- 爆炸物危险特性:与N-溴代丁二酰胺起爆炸反应。
- 可燃性危险特性:明火可燃;燃烧时会放出有毒硫氧化物烟雾;遇热或遇水蒸气会释放出有毒硫化氢气体。
- 储运特性:应库房通风低温干燥,与食品、氧化剂、酸类及含水物分开储运。
泡沫、干粉、二氧化碳、砂土。
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:二烯丙基硫醚 在 phosphotungstic acid 、 [Fe(C5H4P(i-Pr)2)2Rh(C8H12)]BF4 氢气 作用下, 20.0 ℃ 、689.49 kPa 条件下, 反应 16.0h, 生成 二丙硫醚参考文献:名称:固定化的均相催化剂,用于官能化醛,烯烃和炔烃的有效和选择性加氢摘要:带有二膦1,1'-双(二异丙基膦基)二茂铁(DiPFc,1)的固定化阳离子铑(I)催化剂可在温和条件下对一系列官能化醛以及烯烃和炔烃进行有效的化学选择加氢。这种异质催化剂体系易于制备,对空气和湿气在较长时间内稳定,并且易于回收。DOI:10.1021/jo000867f
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Wertheim, Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie, 1845, vol. 55, p. 301摘要:DOI:
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:Effects of the Garlic Components Diallyl Sulfide and Diallyl Disulfide on Arylamine N-Acetyltransferase Activity in Human Colon Tumour Cells摘要:Diallyl sulfide (DAS) and diallyl disulfide (DADS). major components of garlic, were used to determine inhibition of arylamine N-acetyltransferase (NAT) activity in a human colon tumour (adenocarcinoma) cell line. Two assay Systems were performed, one with cellular cytosols (9000 g supernatant), the other with intact bacterial cell suspensions. The NAT activity in a human colon tumour cell line was inhibited by DAS and DADS in a dose-dependent manner in both system: that is, the greater the concentration of DAS and DADS in the reaction, the greater the inhibition of NAT activities in both systems. The data also indicated that DAS and DADS decrease the apparent values of K-m and V-max of NAT enzymes from human colon tumour cells in both systems examined. This is the first report to demonstrate that garlic components do affect human colon tumour cell NAT activity. (C) 1998 Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved.DOI:10.1016/s0278-6915(98)00046-5
文献信息
-
BENZOTHIOPHENE INHIBITORS OF RHO KINASE申请人:Kahraman Mehmet公开号:US20080021026A1公开(公告)日:2008-01-24The present invention relates to compounds and methods which may be useful as inhibitors of Rho kinase for the treatment or prevention of disease.本发明涉及化合物和方法,这些化合物和方法可能作为Rho激酶的抑制剂在治疗或预防疾病方面有用。
-
Chemoselective Rearrangement Reactions of Sulfur Ylide Derived from Diazoquinones and Allyl/Propargyl Sulfides作者:Sijia Yan、Junxin Rao、Cong-Ying ZhouDOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.0c03493日期:2020.11.20three types of rearrangement reactions of sulfur ylide derived from diazoquinones and allyl/propargyl sulfides. With Rh2(esp)2 as the catalyst, diazoquinones react with allyl/propargyl sulfides to form a sulfur ylide, which undergoes a chemoselective tautomerization/[2,3]-sigmatropic rearrangement reaction, a Doyle–Kirmse rearrangement/Cope rearrangement cascade reaction, or a Doyle–Kirmse rearrangement/elimination
-
GLUCAGON-LIKE PROTEIN-1 RECEPTOR (GLP-1R) AGONIST COMPOUNDS申请人:BRADSHAW Curt W.公开号:US20090098130A1公开(公告)日:2009-04-16The present invention provides GA targeting compounds which comprise GA targeting agent-linker conjugates linked to a combining site of an antibody. Various uses of the compounds are provided, including methods to prevent or treat diabetes or diabetes-related conditions.本发明提供了包括连接到抗体结合位点的GA靶向剂-连接剂共轭物的GA靶向化合物。提供了化合物的各种用途,包括预防或治疗糖尿病或与糖尿病相关的疾病的方法。
-
BRM TARGETING COMPOUNDS AND ASSOCIATED METHODS OF USE申请人:Arvinas Operations, Inc.公开号:US20190300521A1公开(公告)日:2019-10-03The present disclosure relates to bifunctional compounds, which find utility as modulators of SMARCA2 or BRM (target protein). In particular, the present disclosure is directed to bifunctional compounds, which contain on one end a ligand that binds to the Von Hippel-Lindau E3 ubiquitin ligase, and on the other end a moiety which binds the target protein, such that the target protein is placed in proximity to the ubiquitin ligase to effect degradation (and inhibition) of target protein. The present disclosure exhibits a broad range of pharmacological activities associated with degradation/inhibition of target protein. Diseases or disorders that result from aggregation or accumulation of the target protein are treated or prevented with compounds and compositions of the present disclosure.本公开涉及双功能化合物,其作为SMARCA2或BRM(靶蛋白)的调节剂具有实用性。具体而言,本公开涉及包含一端结合Von Hippel-Lindau E3泛素连接酶的配体,另一端结合靶蛋白的双功能化合物,使得靶蛋白与泛素连接酶靠近以实现靶蛋白的降解(和抑制)。本公开展示了与靶蛋白降解/抑制相关的广泛药理活性。本公开的化合物和组合物用于治疗或预防由靶蛋白聚集或积累导致的疾病或紊乱。
-
[EN] METHODS AND COMPOUNDS FOR THE TREATMENT OF GENETIC DISEASE<br/>[FR] PROCÉDÉS ET COMPOSÉS POUR LE TRAITEMENT D'UNE MALADIE GÉNÉTIQUE申请人:DESIGN THERAPEUTICS INC公开号:WO2021158707A1公开(公告)日:2021-08-12The present disclosure relates to compounds and methods for modulating the expression of dmpk, and treating diseases and conditions in which dmpk plays an active role. The compound can be a transcription modulator molecule having a first terminus, a second terminus, and oligomeric backbone, wherein: a) the first terminus comprises a DNA-binding moiety capable of noncovalently binding to a nucleotide repeat sequence CAG or CTG; b) the second terminus comprises a protein-binding moiety binding to a regulatory molecule that modulates an expression of a gene comprising the nucleotide repeat sequence CAG or CTG; and c) the oligomeric backbone comprising a linker between the first terminus and the second terminus.本公开涉及化合物和方法,用于调节dmpk的表达,并治疗dmpk发挥积极作用的疾病和病况。该化合物可以是一种转录调节分子,具有第一末端、第二末端和寡聚骨架,其中:a)第一末端包括一种DNA结合基团,能够非共价结合到核苷酸重复序列CAG或CTG;b)第二末端包括结合到调节分子的蛋白结合基团,该调节分子调节包含核苷酸重复序列CAG或CTG的基因的表达;c)寡聚骨架包括连接第一末端和第二末端的连接物。
表征谱图
-
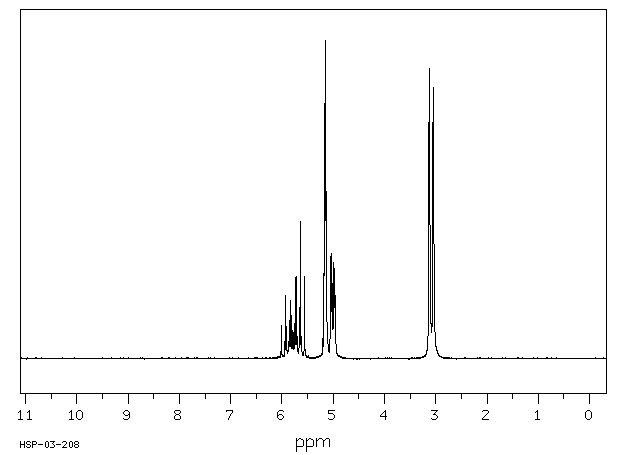
氢谱1HNMR
-
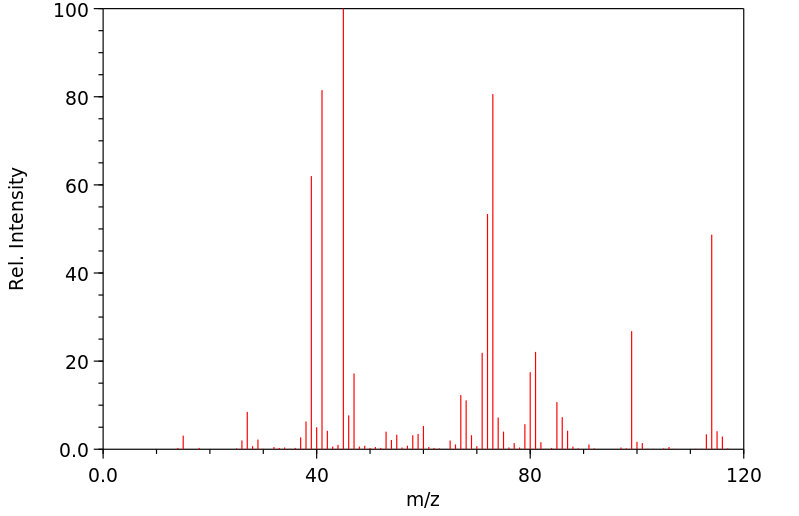
质谱MS
-
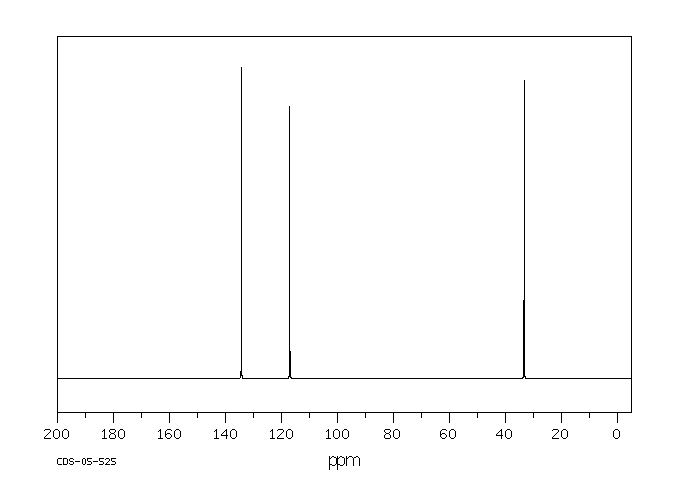
碳谱13CNMR
-
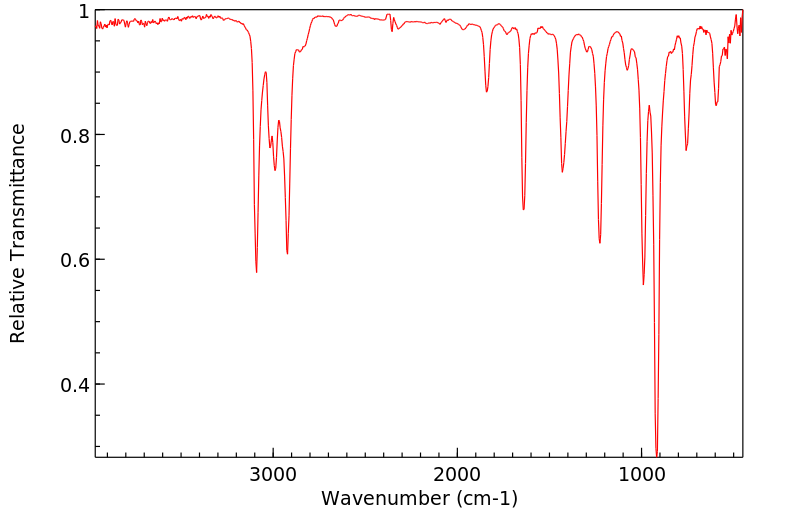
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息