邻丙氧基苯酚 | 6280-96-2
中文名称
邻丙氧基苯酚
中文别名
2-羟基苯丙醚;邻苯二酚单丙基醚;2-丙氧基苯酚;邻羟基苯丙醚
英文名称
2-propoxyphenol
英文别名
o-propoxyphenol;2-Propyloxy-phenol
CAS
6280-96-2
化学式
C9H12O2
mdl
MFCD06655033
分子量
152.193
InChiKey
JFSVGKRARHIICJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
沸点:227°C (estimate)
-
密度:1.0523
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2.2
-
重原子数:11
-
可旋转键数:3
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.333
-
拓扑面积:29.5
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:2
安全信息
-
海关编码:2909500000
-
危险性防范说明:P273,P301+P312+P330,P302+P352,P305+P351+P338
-
危险性描述:H302,H315,H319,H412
-
储存条件:2-8°C
SDS
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 1-methoxy-2-n-propoxybenzene 29515-39-7 C10H14O2 166.22 2-(烯丙氧基)苯酚 2-allyloxyphenol 1126-20-1 C9H10O2 150.177 木榴油 2-methoxy-phenol 90-05-1 C7H8O2 124.139 胡椒环 Methylenedioxybenzene 274-09-9 C7H6O2 122.123 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 1-methoxy-2-n-propoxybenzene 29515-39-7 C10H14O2 166.22 —— (1-allyloxy-2-propoxybenzene) 1005005-88-8 C12H16O2 192.258 3-(2-丙氧基苯氧基)-1,2-丙烷二醇 rac-3-(2-propoxyphenoxy)-propane-1,2-diol 63991-76-4 C12H18O4 226.273 苯(甲)醛,4-羟基-3-丙氧基- 3-propoxy-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde 110943-74-3 C10H12O3 180.203
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:反对白菜弯角线虫Trichoplusia ni的二烷氧基苯和二烷氧基烯丙基苯的摄食和产卵抑制剂:潜在的昆虫行为控制剂摘要:在实验室生物测定中,针对白菜弯角曲霉Trichoplusia ni评估了各个二烷氧基苯化合物/对以及通过取代的烯丙氧基苯的克莱森重排获得的羟基或烷氧基取代的烯丙基苯的拒食剂,产卵抑制物和毒性作用。大多数化合物/组强烈抑制幼虫摄食,有些还表现出温和的毒性和产卵抑制作用。一些化合物/组比商业驱虫剂DEET(N,N- diethyl- m-甲苯胺),因为进食和产卵都可以阻止白菜弯角。根据获得的产卵数据,提出了有关产卵部位的一般假设:一种与苯环同一侧的烷基和烯丙基结合的方式会产生阻吓作用,另一种与烷基和烯丙基的结合方式相反。苯环导致刺激。结果表明,某些构效关系对提高化合物的功效和设计用于农业的新型无毒昆虫控制剂很有用。DOI:10.1021/jf9045123
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:The Baeyer-Villiger Oxidation of Aromatic Aldehydes and Ketones with Hydrogen Peroxide Catalyzed by Selenium Compounds. A Convenient Method for the Preparation of Phenols摘要:一系列有机硒化合物被研究作为过氧化氢在拜耳-维利格氧化反应中的活化剂。结果发现,这是一种方便且经济的转化具有聚合环系或供电子取代基的芳香醛、乙酰苯的多甲氧基衍生物为酚类的方法。该方法使用由芳硒酸活化的过氧化氢作为氧化剂。DOI:10.1055/s-1989-27183
文献信息
-
BISPHENOL COMPOSITION CONTAINING AROMATIC ALCOHOL SULFONATE AND METHOD FOR PRODUCING SAME, POLYCARBONATE RESIN AND METHOD FOR PRODUCING SAME, AND BISPHENOL PRODUCTION METHOD申请人:MITSUBISHI CHEMICAL CORPORATION公开号:US20200190004A1公开(公告)日:2020-06-18A bisphenol composition including a specific amount of aromatic alcohol sulfonate, and a simple method of producing it are provided. Also provided is a method of producing a polycarbonate resin in which, by using the bisphenol composition including a specific amount of aromatic alcohol sulfonate, melt polymerization reaction can be efficiently allowed to proceed to produce a polycarbonate resin having an excellent color tone. A bisphenol composition including an aromatic alcohol sulfonate at not less than 0.1 ppb by mass with respect to a bisphenol. A method of producing a bisphenol composition, including reacting a ketone or an aldehyde with an aromatic alcohol in the presence of sulfuric acid to produce a bisphenol composition. A method of producing a polycarbonate resin, including producing a polycarbonate resin using the bisphenol composition. A polycarbonate resin including a specific amount of aromatic alcohol sulfonate.
-
Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel azole derivatives as selective potent inhibitors of brassinosteroid biosynthesis作者:Kazuhiro Yamada、Osamu Yajima、Yuko Yoshizawa、Keimei OhDOI:10.1016/j.bmc.2013.03.006日期:2013.5Brassinosteroids (BRs) are phytohormones that control several important agronomic traits, such as flowering, plant architecture, seed yield, and stress tolerance. To manipulate the BR levels in plant tissues using specific inhibitors of BR biosynthesis, a series of novel azole derivatives were synthesized and their inhibitory activity on BR biosynthesis was investigated. Structure–activity relationship油菜素类固醇(BRs)是控制几种重要农艺性状的植物激素,例如开花,植物结构,种子产量和胁迫耐受性。为了利用BR生物合成的特异性抑制剂来控制植物组织中的BR水平,合成了一系列新型的唑衍生物,并研究了它们对BR生物合成的抑制活性。结构-活性关系研究表明,2 RS,4 RS -1- [4-(2-烯丙氧基苯氧基甲基)-2-(4-氯苯基)-[1,3]二氧戊环-2-基甲基] -1 H- [1, 2,4]三唑(G 2)是BR生物合成的高选择性抑制剂,IC 50值约为46±2 nM,这是迄今为止观察到的最有效的BR生物合成抑制剂。使用赤霉素(GA)生物合成突变体和BR信号突变体分析该合成系列的作用机理表明,主要的作用部位是BR生物合成。将BR生物合成中间体喂入经过化学处理的拟南芥幼苗的实验表明,该合成系列的目标位点是CYP90,它们负责菜油甾醇的C-22和/或C-23羟基化作用。
-
无卤阻燃环氧树脂前驱体、组合物、模塑料制品、制法及应用申请人:中国科学院宁波材料技术与工程研究所公开号:CN111793091A公开(公告)日:2020-10-20
-
Direct oxidation of the C(sp<sup>2</sup>)–C(sp<sup>3</sup>) bond from benzyltrimethylsilanes to phenols作者:Wei Li、Guolin Gao、Yuan Gao、Chao Yang、Wujiong XiaDOI:10.1039/c7cc01868a日期:——A novel pathway for direct conversion of benzylsilanes to phenols by oxidation with Na2S2O8 and oxygen is efficiently developed under mild and neutral conditions. The reaction shows good functional group tolerance to afford phenols in moderate yields. The possible mechanism is proposed based on the isotopic labeling trials.
-
Oral care compositions with color changing indicator申请人:Sabnis W. Ram公开号:US20060222601A1公开(公告)日:2006-10-05The invention describes color changing toothpastes and mouthwashes which contains acid-base indicator(s) for interaction with the oral cavity to provide a color change indicative of treatment time.
表征谱图
-
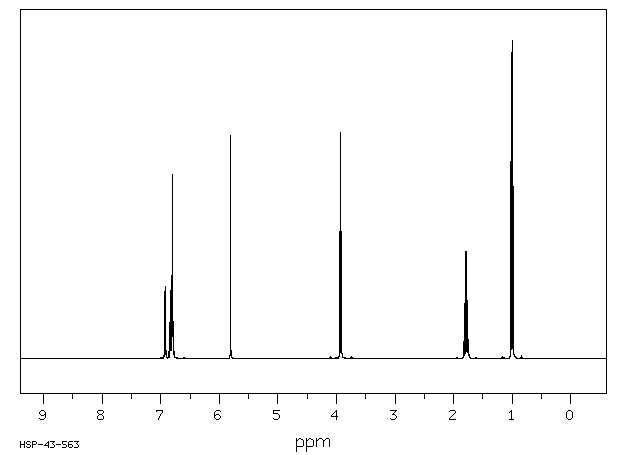
氢谱1HNMR
-
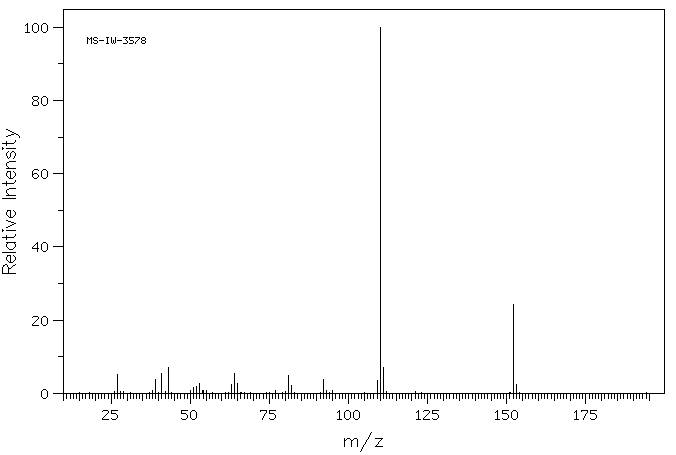
质谱MS
-
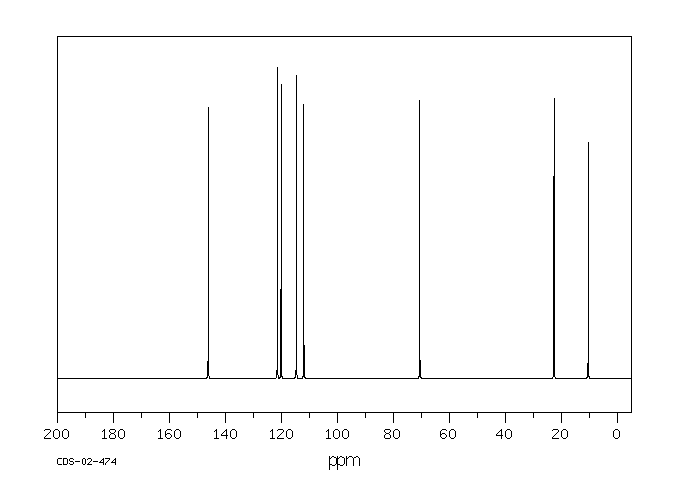
碳谱13CNMR
-
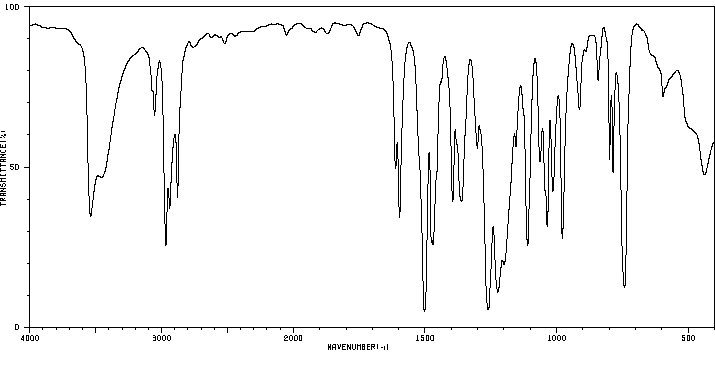
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(R)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二异丙氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂环戊烯
(2S,3R)-3-(叔丁基)-2-(二叔丁基膦基)-4-甲氧基-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂戊环
(2S,2''S,3S,3''S)-3,3''-二叔丁基-4,4''-二甲氧基-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-2,2''-联苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂戊环
(2R,2''R,3R,3''R)-3,3''-二叔丁基-4,4''-二甲氧基-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-2,2''-联苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂戊环
(2-氟-3-异丙氧基苯基)三氟硼酸钾
(+)-6,6'-{[(1R,3R)-1,3-二甲基-1,3基]双(氧)}双[4,8-双(叔丁基)-2,10-二甲氧基-丙二醇
麦角甾烷-6-酮,2,3,22,23-四羟基-,(2a,3a,5a,22S,23S)-
鲁前列醇
顺式6-(对甲氧基苯基)-5-己烯酸
顺式-铂戊脒碘化物
顺式-四氢-2-苯氧基-N,N,N-三甲基-2H-吡喃-3-铵碘化物
顺式-4-甲氧基苯基1-丙烯基醚
顺式-2,4,5-三甲氧基-1-丙烯基苯
顺式-1,3-二甲基-4-苯基-2-氮杂环丁酮
非那西丁杂质7
非那西丁杂质3
非那西丁杂质22
非那西丁杂质18
非那卡因
非布司他杂质37
非布司他杂质30
非布丙醇
雷诺嗪
阿达洛尔
阿达洛尔
阿莫噁酮
阿莫兰特
阿维西利
阿索卡诺
阿米维林
阿立酮
阿曲汀中间体3
阿普洛尔
阿普斯特杂质67
阿普斯特中间体
阿普斯特中间体
阿托西汀EP杂质A
阿托莫西汀杂质24
阿托莫西汀杂质10
阿托莫西汀EP杂质C
阿尼扎芬
阿利克仑中间体3
间苯胺氢氟乙酰氯
间苯二酚二缩水甘油醚
间苯二酚二异丙醇醚
间苯二酚二(2-羟乙基)醚
间苄氧基苯乙醇
间甲苯氧基乙酸肼
间甲苯氧基乙腈
间甲苯异氰酸酯