氟酰胺 | 66332-96-5
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:108° (Araki, Yabutani); mp 104-105° (Araki, 1985)
-
沸点:339.1±42.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.2463 (estimate)
-
溶解度:可溶于氯仿(少许)、甲醇(少许)
-
LogP:3.700
-
物理描述:COLOURLESS-TO-WHITE CRYSTALS.
-
颜色/状态:White, crystalline solid
-
蒸汽压力:1.33X10-5 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
稳定性/保质期:
Stable under recommended storage conditions.
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits toxic vapors of nitrogen oxides and fluorides.
-
碰撞截面:175.45 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: TW]
-
保留指数:2140.4
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.7
-
重原子数:23
-
可旋转键数:4
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.235
-
拓扑面积:38.3
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:5
ADMET
安全信息
-
RTECS号:CV5581320
-
海关编码:2924299033
SDS
制备方法与用途
大鼠和小鼠急性经口LD₅₀大于10000毫克/公斤,急性经皮在5000毫克/公斤剂量时表现为无毒,对皮肤和黏膜的刺激性很轻微。鲤鱼LC₅₀为2.4毫克/升(48小时)。
化学性质纯品为白色无臭结晶体,熔点108℃(102~103℃),蒸汽压为1.77×10⁻⁹帕斯卡(20℃)。在20℃时的溶解度为:丙酮642克/升,甲醇606克/升(480克/升),氯仿341克/升(238克/升),甲苯56克/升(65克/升),二甲苯29克/升,己烷3克/升,水9.6毫克/升。分配系数为3.7,在pH值3~9的水溶液中稳定,在100℃加热5小时或50℃放置14天无分解。在日光灯(17000勒克斯、96小时)照射下,分解率为1%,说明其对热和光具有较好的稳定性。在土壤中的半衰期为40~60天。
用途氟担菌宁属于苯甲酰胺衍生物,是一种内吸性杀菌剂,用于预防和治疗某些担子菌纲真菌引起的疾病。它能强烈阻碍菌丝的生育和侵入菌丝块的形成。例如,在50毫克/升浓度下进行茎叶处理可以完全防治由丝核菌引起的水稻纹枯病。
用途氟担菌宁是一种内吸杀菌剂,对水稻纹枯病、马铃薯黑痣病等有效。
生产方法邻三氟甲基氯苯经格氏反应、羰基化和水解得到邻三氟甲基苯甲酸。然后进行酰氯化反应,并与间异丙氧基苯胺反应制得氟担菌宁。
制备方法一邻三氟甲基苯甲酰氯可用邻三氟甲基氯苯为原料,经过格氏反应,然后与干冰反应羰基化,再经水解得邻三氟甲基苯甲酸。该酸经酰氯化制得邻三氟甲基苯甲酰氯。在冰冷却下,将邻三氟甲基苯甲酰氯加到四氢呋喃中,在三乙胺存在下及室温条件下与间异丙氧基苯胺反应2小时,得到氟担菌宁。
制备方法二氟担菌宁也可通过3-(2-三氟甲基苯甲酰氨基)苯酚与2-氯代丙烷反应制得。
类别农药
毒性分级低毒
急性毒性口服 - 大鼠 LD₅₀: 10000 毫克/公斤;小鼠 LD₅₀: 10000 毫克/公斤
可燃性危险特性可燃;燃烧会产生有毒的氮氧化物和氯化物气体
储运特性库房应通风、低温干燥,并与食品原料分开储运
灭火剂干粉、泡沫、砂土
上下游信息
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 3'-hydroxy-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzanilide 69392-32-1 C14H10F3NO2 281.234 2-(三氟甲基)苯甲酰胺 2-(trifluoromethyl)benzamide 360-64-5 C8H6F3NO 189.137
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Tsao, Rong; Eto, Morifusa, Agricultural and Biological Chemistry, 1991, vol. 55, # 3, p. 763 - 768摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:描述:3-氨基苯异丙醚 、 2-三氟甲基苯甲酰氯 在 三乙胺盐酸盐 、 三乙胺 作用下, 以 四氢呋喃 、 (2S)-N-methyl-1-phenylpropan-2-amine hydrate 为溶剂, 以91%的产率得到氟酰胺参考文献:名称:Novel benzoic anilide derivative and fungicide containing same摘要:由o-三氟甲基苯甲酸和m-异丙氧基苯胺反应形成的O-三氟甲基苯甲酰m'-异丙氧基苯胺,在控制农业和园艺植物病害方面非常有效。公开号:US04093743A1
-
作为试剂:描述:5-{3-[(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-5-yl)-difluoromethyl]-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazin-6-yl}thiophene-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester 、 sodium hydroxide 、 O-(7-azabenzotriazol-1-yl)-1,1,3,3-tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate 、 1-羟基苯并三唑 、 N,N-二异丙基乙胺 、 N-甲基哌嗪 在 水 、 N,N-二甲基甲酰胺 、 二氯甲烷 、 magnesium sulfate 、 氟酰胺 、 acetonitrile-water 、 final compound 、 HCO3 作用下, 以 tetrahydrofuran methanol 、 二氯甲烷 、 水 为溶剂, 反应 3.5h, 生成 (5-{3-[(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-5-yl)difluoromethyl]-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazin-6-yl}thiophen-2-yl)-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methanone参考文献:名称:TRIAZOLOPYRIDAZINES AS KINASE MODULATORS摘要:本发明涉及式I的三唑并吡嗪化合物:其中R1,R5,R6,R7,R8和A如本文所定义,所述化合物的用途为蛋白酪氨酸激酶调节剂,特别是c-Met的抑制剂,并且所述化合物的用途为减少或抑制细胞或受体中c-Met的激酶活性,并调节细胞或受体中c-Met的表达,以及使用该化合物预防或治疗细胞增殖性疾病和/或与c-Met相关的疾病。本发明还涉及包含本发明化合物的药物组合物,以及治疗肿瘤和其他细胞增殖性疾病的方法。公开号:US20070203136A1
文献信息
-
[EN] ACC INHIBITORS AND USES THEREOF<br/>[FR] INHIBITEURS DE L'ACC ET UTILISATIONS ASSOCIÉES
-
[EN] BICYCLYL-SUBSTITUTED ISOTHIAZOLINE COMPOUNDS<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS ISOTHIAZOLINE SUBSTITUÉS PAR UN BICYCLYLE申请人:BASF SE公开号:WO2014206910A1公开(公告)日:2014-12-31The present invention relates to bicyclyl-substituted isothiazoline compounds of formula (I) wherein the variables are as defined in the claims and description. The compounds are useful for combating or controlling invertebrate pests, in particular arthropod pests and nematodes. The invention also relates to a method for controlling invertebrate pests by using these compounds and to plant propagation material and to an agricultural and a veterinary composition comprising said compounds.本发明涉及公式(I)中变量如索权和说明中所定义的自行车基取代异噻唑啉化合物。这些化合物对抗或控制无脊椎动物害虫,特别是节肢动物害虫和线虫方面具有用途。该发明还涉及一种通过使用这些化合物来控制无脊椎动物害虫的方法,以及包含所述化合物的植物繁殖材料、农业和兽医组合物。
-
[EN] AZOLINE COMPOUNDS<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS AZOLINE申请人:BASF SE公开号:WO2015128358A1公开(公告)日:2015-09-03The present invention relates to azoline compounds of formula (I) wherein A, B1, B2, B3, G1, G2, X1, R1, R3a, R3b, Rg1 and Rg2 are as defined in the claims and the description. The compounds are useful for combating or controlling invertebrate pests, in particular arthropod pests and nematodes. The invention also relates to a method for controlling invertebrate pests by using these compounds and to plant propagation material and to an agricultural and a veterinary composition comprising said compounds.本发明涉及式(I)的噁唑啉化合物,其中A、B1、B2、B3、G1、G2、X1、R1、R3a、R3b、Rg1和Rg2如权利要求和描述中所定义。这些化合物对抗或控制无脊椎动物害虫,特别是节肢动物害虫和线虫方面具有用途。该发明还涉及一种利用这些化合物控制无脊椎动物害虫的方法,以及包括所述化合物的植物繁殖材料、农业和兽医组合物。
-
[EN] SUBSTITUTED QUINAZOLINES AS FUNGICIDES<br/>[FR] QUINAZOLINES SUBSTITUÉES, UTILISÉES EN TANT QUE FONGICIDES申请人:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG公开号:WO2010136475A1公开(公告)日:2010-12-02The present invention relates to a compound of formula (I) wherein wherein the substituents have the definitions as defined in claim 1or a salt or a N-oxide thereof, their use and methods for the control and/or prevention of microbial infection, particularly fungal infection, in plants and to processes for the preparation of these compounds.本发明涉及一种具有如下式(I)的化合物,其中取代基具有权利要求1中定义的定义,或其盐或N-氧化物,它们的用途以及用于控制和/或预防植物中微生物感染,特别是真菌感染的方法,以及制备这些化合物的方法。
-
[EN] MICROBIOCIDAL OXADIAZOLE DERIVATIVES<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS D'OXADIAZOLE MICROBIOCIDES申请人:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG公开号:WO2017157962A1公开(公告)日:2017-09-21Compounds of the formula (I) wherein the substituents are as defined in claim 1, useful as a pesticides, especially fungicides.式(I)的化合物,其中取代基如权利要求1所定义,作为杀虫剂特别是杀菌剂有用。
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
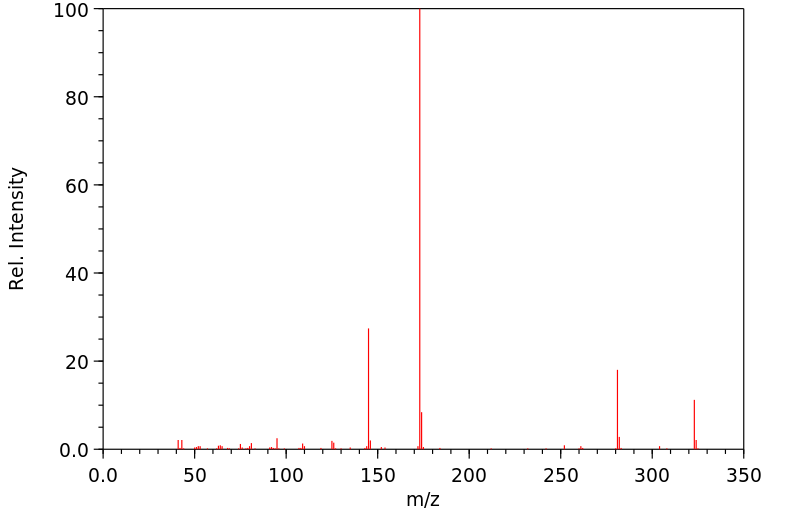
质谱MS
-
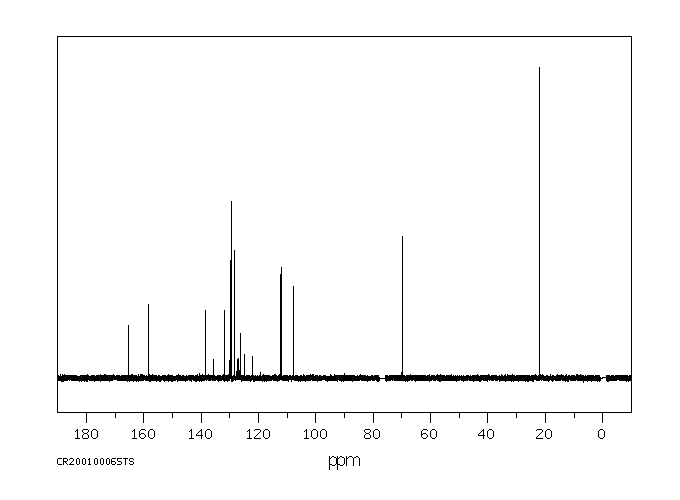
碳谱13CNMR
-
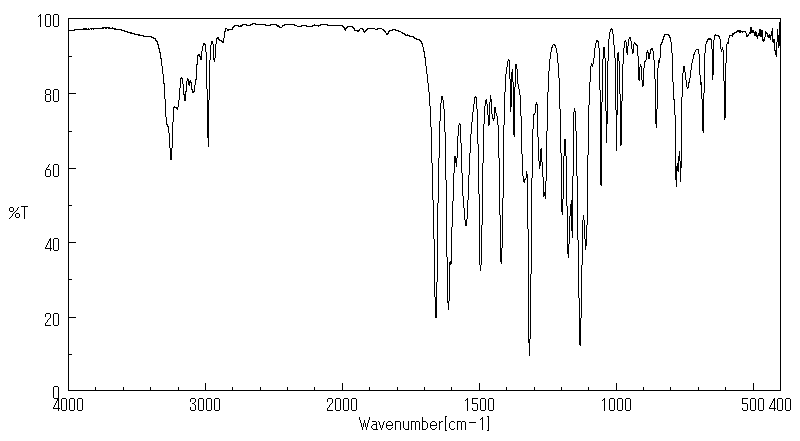
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息