3-氟联苯 | 2367-22-8
中文名称
3-氟联苯
中文别名
——
英文名称
3-fluorobiphenyl
英文别名
3-fluoro-1,1'-biphenyl;3-Fluorbiphenyl;3-fluoro-1,1′-biphenyl;1-fluoro-3-phenylbenzene
CAS
2367-22-8
化学式
C12H9F
mdl
MFCD01740506
分子量
172.202
InChiKey
MRCAAFFMZODJBP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:26-27 °C
-
沸点:153-154 °C(Press: 50 Torr)
-
密度:1.2874 g/cm3(Temp: 18 °C)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):4.1
-
重原子数:13
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:1
安全信息
-
海关编码:2903999090
-
危险性防范说明:P261,P280,P305+P351+P338
-
危险性描述:H302,H315,H319,H332,H335
-
储存条件:储存条件:室温、密封、干燥
SDS
Material Safety Data Sheet
Section 1. Identification of the substance
Product Name: 3-Fluorobiphenyl
Synonyms:
Section 2. Hazards identification
Harmful by inhalation, in contact with skin, and if swallowed.
Section 3. Composition/information on ingredients.
Ingredient name: 3-Fluorobiphenyl
CAS number: 2367-22-8
Section 4. First aid measures
Skin contact: Immediately wash skin with copious amounts of water for at least 15 minutes while removing
contaminated clothing and shoes. If irritation persists, seek medical attention.
Eye contact: Immediately wash skin with copious amounts of water for at least 15 minutes. Assure adequate
flushing of the eyes by separating the eyelids with fingers. If irritation persists, seek medical
attention.
Inhalation: Remove to fresh air. In severe cases or if symptoms persist, seek medical attention.
Ingestion: Wash out mouth with copious amounts of water for at least 15 minutes. Seek medical attention.
Section 5. Fire fighting measures
In the event of a fire involving this material, alone or in combination with other materials, use dry
powder or carbon dioxide extinguishers. Protective clothing and self-contained breathing apparatus
should be worn.
Section 6. Accidental release measures
Personal precautions: Wear suitable personal protective equipment which performs satisfactorily and meets local/state/national
standards.
Respiratory precaution: Wear approved mask/respirator
Hand precaution: Wear suitable gloves/gauntlets
Skin protection: Wear suitable protective clothing
Eye protection: Wear suitable eye protection
Methods for cleaning up: Mix with sand or similar inert absorbent material, sweep up and keep in a tightly closed container
for disposal. See section 12.
Environmental precautions: Do not allow material to enter drains or water courses.
Section 7. Handling and storage
Handling: This product should be handled only by, or under the close supervision of, those properly qualified
in the handling and use of potentially hazardous chemicals, who should take into account the fire,
health and chemical hazard data given on this sheet.
Store in closed vessels.
Storage:
Section 8. Exposure Controls / Personal protection
Engineering Controls: Use only in a chemical fume hood.
Personal protective equipment: Wear laboratory clothing, chemical-resistant gloves and safety goggles.
General hydiene measures: Wash thoroughly after handling. Wash contaminated clothing before reuse.
Section 9. Physical and chemical properties
Appearance: Not specified
Boiling point: No data
No data
Melting point:
Flash point: No data
Density: No data
Molecular formula: C12H9F
Molecular weight: 172.2
Section 10. Stability and reactivity
Conditions to avoid: Heat, flames and sparks.
Materials to avoid: Oxidizing agents.
Possible hazardous combustion products: Carbon monoxide, hydrogen fluoride.
Section 11. Toxicological information
No data.
Section 12. Ecological information
No data.
Section 13. Disposal consideration
Arrange disposal as special waste, by licensed disposal company, in consultation with local waste
disposal authority, in accordance with national and regional regulations.
Section 14. Transportation information
Non-harzardous for air and ground transportation.
Section 15. Regulatory information
No chemicals in this material are subject to the reporting requirements of SARA Title III, Section
302, or have known CAS numbers that exceed the threshold reporting levels established by SARA
Title III, Section 313.
SECTION 16 - ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
N/A
Section 1. Identification of the substance
Product Name: 3-Fluorobiphenyl
Synonyms:
Section 2. Hazards identification
Harmful by inhalation, in contact with skin, and if swallowed.
Section 3. Composition/information on ingredients.
Ingredient name: 3-Fluorobiphenyl
CAS number: 2367-22-8
Section 4. First aid measures
Skin contact: Immediately wash skin with copious amounts of water for at least 15 minutes while removing
contaminated clothing and shoes. If irritation persists, seek medical attention.
Eye contact: Immediately wash skin with copious amounts of water for at least 15 minutes. Assure adequate
flushing of the eyes by separating the eyelids with fingers. If irritation persists, seek medical
attention.
Inhalation: Remove to fresh air. In severe cases or if symptoms persist, seek medical attention.
Ingestion: Wash out mouth with copious amounts of water for at least 15 minutes. Seek medical attention.
Section 5. Fire fighting measures
In the event of a fire involving this material, alone or in combination with other materials, use dry
powder or carbon dioxide extinguishers. Protective clothing and self-contained breathing apparatus
should be worn.
Section 6. Accidental release measures
Personal precautions: Wear suitable personal protective equipment which performs satisfactorily and meets local/state/national
standards.
Respiratory precaution: Wear approved mask/respirator
Hand precaution: Wear suitable gloves/gauntlets
Skin protection: Wear suitable protective clothing
Eye protection: Wear suitable eye protection
Methods for cleaning up: Mix with sand or similar inert absorbent material, sweep up and keep in a tightly closed container
for disposal. See section 12.
Environmental precautions: Do not allow material to enter drains or water courses.
Section 7. Handling and storage
Handling: This product should be handled only by, or under the close supervision of, those properly qualified
in the handling and use of potentially hazardous chemicals, who should take into account the fire,
health and chemical hazard data given on this sheet.
Store in closed vessels.
Storage:
Section 8. Exposure Controls / Personal protection
Engineering Controls: Use only in a chemical fume hood.
Personal protective equipment: Wear laboratory clothing, chemical-resistant gloves and safety goggles.
General hydiene measures: Wash thoroughly after handling. Wash contaminated clothing before reuse.
Section 9. Physical and chemical properties
Appearance: Not specified
Boiling point: No data
No data
Melting point:
Flash point: No data
Density: No data
Molecular formula: C12H9F
Molecular weight: 172.2
Section 10. Stability and reactivity
Conditions to avoid: Heat, flames and sparks.
Materials to avoid: Oxidizing agents.
Possible hazardous combustion products: Carbon monoxide, hydrogen fluoride.
Section 11. Toxicological information
No data.
Section 12. Ecological information
No data.
Section 13. Disposal consideration
Arrange disposal as special waste, by licensed disposal company, in consultation with local waste
disposal authority, in accordance with national and regional regulations.
Section 14. Transportation information
Non-harzardous for air and ground transportation.
Section 15. Regulatory information
No chemicals in this material are subject to the reporting requirements of SARA Title III, Section
302, or have known CAS numbers that exceed the threshold reporting levels established by SARA
Title III, Section 313.
SECTION 16 - ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
N/A
上下游信息
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 3-氟联苯-4-羧酸 3'-Fluor-biphenyl-4-carbonsaeure 1841-58-3 C13H9FO2 216.212 1-(3'-氟-4-联苯基)乙酮 1-(3’-fluorobiphenyl-4-yl)ethanone 5002-42-6 C14H11FO 214.239
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:一些取代的联苯-4-羧酸,4-联苯基乙酸和4-氨基联苯的合成摘要:描述了一系列取代的联苯-4-羧酸和4-氨基联苯的合成。包括母体联苯-4-羧酸,4-联苯基乙酸和三种取代的4-联苯基乙酸的制剂。DOI:10.1039/j39660000840
-
作为产物:描述:3-fluoro-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl diethylcarbamate 在 二氯化双(三环己基膦)镍(II) 、 1,1,3,3-四甲基二硅氧烷 、 K3PO4 作用下, 以 甲苯 为溶剂, 反应 15.0h, 以85%的产率得到3-氟联苯参考文献:名称:Cine Substitution of Arenes Using the Aryl Carbamate as a Removable Directing Group摘要:An efficient and controlled means to achieve a rare cine substitution of arenes is reported. The methodology relies on the strategic use of aryl O-carbamates as readily removable directing groups for arene functionallzation. The removal of aryl carbamates is achieved by employing an airstable Ni(II) precatalyst, along with an inexpensive reducing agent, to give synthetically useful yields across a range of substrates. The net cine substitution process offers a new strategy for analogue synthesis, which complements the well-established logic for achieving arene functionalization by ipso substitution.DOI:10.1021/ol301275u
文献信息
-
[EN] NOVEL AGENTS TARGETING CYP51<br/>[FR] NOUVEAUX AGENTS CIBLANT CYP51申请人:SCRIPPS RESEARCH INST公开号:WO2015048306A1公开(公告)日:2015-04-02The invention provides inhibitors of a sterol C14-demethylase, a new series of 4- aminopyridyl-based lead inhibitors targeting Trypanosoma cruzi CYP51 (TcCYP51) developed using structure-based drug design as well as structure -property relationship (SPR) analyses. The screening hit starting point, LP 10 (KD < 42 nM; EC50 of 0.65 μΜ), has been optimized to give the potential leads that have low nanomolar binding affinity to TcCYP51 and significant activity against T. cruzi amastigotes cultured in human myoblasts. Many of the optimized compounds have improved microsome stability, and most are selective against the T. cruzi CYP51 relative to human CYPs 1A2, 2D6 and 3A4 (<50% inhibition at 1 μΜ). A rationale for the improvement of microsome stability and selectivity of inhibitors against human metabolic CYP enzymes is presented. In addition, the binding mode of several compounds of the invention with the T. brucei CYP51 (TbCYP51) ortholog has been characterized by x-ray structure analysis. Orally active compounds and their cyclodextrin complexes have been shown to be effective against Chagas-infected mice.该发明提供了一种甾醇C14-去甲基酶的抑制剂,这是一种新系列基于4-氨基吡啶的首选抑制剂,通过基于结构的药物设计以及结构-性质关系(SPR)分析来瞄准Trypanosoma cruzi CYP51(TcCYP51)而开发的。筛选起始点LP 10(KD < 42 nM;EC50为0.65 μΜ)已经经过优化,产生了具有低纳摩尔级别结合亲和力和对在人类肌细胞培养的T. cruzi游离体的显著活性的潜在首选抑制剂。许多经过优化的化合物具有改善的微粒体稳定性,大多数相对于人类CYPs 1A2、2D6和3A4对T. cruzi CYP51具有选择性(在1 μΜ下<50%的抑制)。提出了改善微粒体稳定性和抑制剂对人类代谢CYP酶的选择性的理由。此外,通过X射线结构分析表征了该发明的几种化合物与T. brucei CYP51(TbCYP51)同源物的结合方式。口服活性化合物及其环糊精复合物已被证明对克氏病感染的小鼠有效。
-
Synthesis of Amido-N-imidazolium Salts and their Applications as Ligands in Suzuki-Miyaura Reactions: Coupling of Hetero- aromatic Halides and the Synthesis of Milrinone and Irbesartan作者:Manian Rajesh Kumar、Kyungho Park、Sunwoo LeeDOI:10.1002/adsc.201000592日期:2010.12.17catalytic system based on palladium-amido-N-heterocyclic carbenes for Suzuki–Miyaura coupling reactions of heteroaryl bromides is described. A variety of sterically bulky, amido-N-imidazolium salts were synthesized in high yields from the corresponding anilines. This catalytic system effectively promoted Suzuki–Miyaura couplings of heteroaryl bromides and chlorides with a range of boronic acids to描述了基于钯-酰胺基-N-杂环卡宾的Suzuki-Miyaura杂芳基溴化物偶联反应的新催化体系。从相应的苯胺以高收率合成了各种空间庞大的酰胺基-N-咪唑鎓盐。该催化体系有效地促进了杂芳基溴化物和氯化物与一系列硼酸的Suzuki-Miyaura偶联,从而以高收率得到了相应的芳基化合物。随着取代基空间位阻的增加,产率增加。特别是,1-(2,6-二异丙基)-3- ñ - (2,4,6-三-叔-butylphenylacetamido)咪唑鎓溴化物(4BC)在2-溴吡啶和苯基硼酸的偶联反应中显示出850,000 TON。此外,药物化合物如米力农和厄贝沙坦是通过Suzuki-Miyaura偶联,使用体积庞大的酰胺基-N-咪唑鎓盐(4bc)作为配体合成的。
-
The First Suzuki Cross-Couplings of Aryltrimethylammonium Salts作者:Simon B. Blakey、David W. C. MacMillanDOI:10.1021/ja034908b日期:2003.5.1The first Suzuki cross-coupling reaction of aryltrimethylammonium triflates based on the use of an IMes.Ni(0) catalyst system is described. A wide range of electron-withdrawing and electron-donating substituents are tolerated on both the aryltrimethylammonium triflate and the boronic acid components of this reaction. In addition to arylboronic acids, the scope of the reaction is extended to encompass
-
LEUKOTRIENE B4 INHIBITORS申请人:Dominique Romyr公开号:US20100240678A1公开(公告)日:2010-09-23Provided herein are compounds of the formula (I): as well as pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, wherein the substituents are as those disclosed in the specification. These compounds, and the pharmaceutical compositions containing them, are useful for the treatment of diseases such as, for example, COPD本文提供的是式(I)的化合物: 以及其药学上可接受的盐,其中取代基如规范中所披露的那样。这些化合物及含有它们的药物组合物对于治疗诸如COPD等疾病是有用的。
-
Pd-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions of arenediazonium salts with arylsilanes and aryltrifluoroborates in water作者:Kai Cheng、Baoli Zhao、Sai Hu、Xian-Man Zhang、Chenze QiDOI:10.1016/j.tetlet.2013.09.001日期:2013.11Pd-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions of various arenediazonium salts with ArSi(OR)3 and KArBF3 have been achieved in good to excellent yields under simple aerobic conditions in water at room temperature. The functional group tolerance makes these transformations as attractive alternatives to the traditional cross-coupling approaches. Furthermore, the sequence can also be performed in a one-pot domino
表征谱图
-
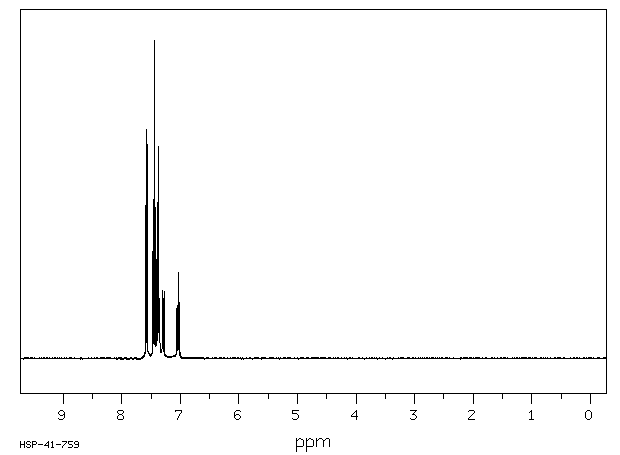
氢谱1HNMR
-
质谱MS
-
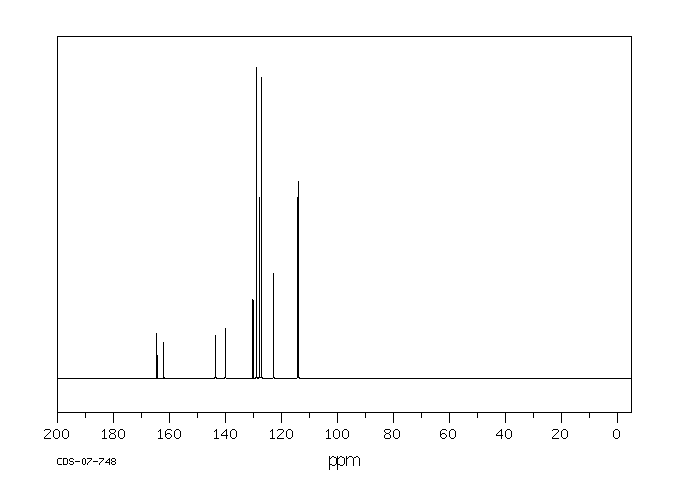
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(βS)-β-氨基-4-(4-羟基苯氧基)-3,5-二碘苯甲丙醇
(S,S)-邻甲苯基-DIPAMP
(S)-(-)-7'-〔4(S)-(苄基)恶唑-2-基]-7-二(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-2,2',3,3'-四氢-1,1-螺二氢茚
(S)-盐酸沙丁胺醇
(S)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧磷杂环戊二烯
(S)-2,2'-双[双(3,5-三氟甲基苯基)膦基]-4,4',6,6'-四甲氧基联苯
(S)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(R)富马酸托特罗定
(R)-(-)-盐酸尼古地平
(R)-(-)-4,12-双(二苯基膦基)[2.2]对环芳烷(1,5环辛二烯)铑(I)四氟硼酸盐
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[((6-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(4-叔丁基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(3-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-4,7-双(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-7“-[(吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2”,3,3'-四氢1,1'-螺二茚满
(R)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二苯氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂环戊烯
(R)-2-[((二苯基膦基)甲基]吡咯烷
(R)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(N-(4-甲氧基苯基)-N-甲基-3-(1-哌啶基)丙-2-烯酰胺)
(5-溴-2-羟基苯基)-4-氯苯甲酮
(5-溴-2-氯苯基)(4-羟基苯基)甲酮
(5-氧代-3-苯基-2,5-二氢-1,2,3,4-oxatriazol-3-鎓)
(4S,5R)-4-甲基-5-苯基-1,2,3-氧代噻唑烷-2,2-二氧化物-3-羧酸叔丁酯
(4S,4''S)-2,2''-亚环戊基双[4,5-二氢-4-(苯甲基)恶唑]
(4-溴苯基)-[2-氟-4-[6-[甲基(丙-2-烯基)氨基]己氧基]苯基]甲酮
(4-丁氧基苯甲基)三苯基溴化磷
(3aR,8aR)-(-)-4,4,8,8-四(3,5-二甲基苯基)四氢-2,2-二甲基-6-苯基-1,3-二氧戊环[4,5-e]二恶唑磷
(3aR,6aS)-5-氧代六氢环戊基[c]吡咯-2(1H)-羧酸酯
(2Z)-3-[[(4-氯苯基)氨基]-2-氰基丙烯酸乙酯
(2S,3S,5S)-5-(叔丁氧基甲酰氨基)-2-(N-5-噻唑基-甲氧羰基)氨基-1,6-二苯基-3-羟基己烷
(2S,2''S,3S,3''S)-3,3''-二叔丁基-4,4''-双(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-2,2''-联苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂戊环
(2S)-(-)-2-{[[[[3,5-双(氟代甲基)苯基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基}-N-(二苯基甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[((1S,2S)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[[((1R,2R)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2-硝基苯基)磷酸三酰胺
(2,6-二氯苯基)乙酰氯
(2,3-二甲氧基-5-甲基苯基)硼酸
(1S,2S,3S,5S)-5-叠氮基-3-(苯基甲氧基)-2-[(苯基甲氧基)甲基]环戊醇
(1S,2S,3R,5R)-2-(苄氧基)甲基-6-氧杂双环[3.1.0]己-3-醇
(1-(4-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(3-溴苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氯苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2,6-二氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(-)-去甲基西布曲明
龙蒿油
龙胆酸钠
龙胆酸叔丁酯
龙胆酸
龙胆紫-d6
龙胆紫