methyl 3-(thiophen-2-yl)-1,2-oxazole-5-carboxylate | 22353-87-3
中文名称
——
中文别名
——
英文名称
methyl 3-(thiophen-2-yl)-1,2-oxazole-5-carboxylate
英文别名
3-thiophen-2-yl-isoxazole-5-carboxylic acid methyl ester;Methyl 3-(2-thienyl)-5-isoxazolecarboxylate;methyl 3-thiophen-2-yl-1,2-oxazole-5-carboxylate
CAS
22353-87-3
化学式
C9H7NO3S
mdl
——
分子量
209.225
InChiKey
WPEYZYMKIDHBHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.9
-
重原子数:14
-
可旋转键数:3
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.11
-
拓扑面积:80.6
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:5
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:methyl 3-(thiophen-2-yl)-1,2-oxazole-5-carboxylate 在 水 、 lithium hydroxide 作用下, 以 乙醇 为溶剂, 反应 1.0h, 以64%的产率得到3-(thiophen-2-yl)-1,2-oxazole-5-carboxylic acid参考文献:名称:[EN] METHODS OF TREATING PULMONARY DISEASES AND DISORDERS
[FR] MÉTHODES DE TRAITEMENT DE MALADIES ET TROUBLES PULMONAIRES摘要:本公开涵盖了使用公开化合物治疗慢性阻塞性肺疾病(COPD)、支气管炎和/或哮喘的方法,可选择性地与一个或多个额外活性药剂一起使用。考虑的方法包括口服或吸入给患者一个或多个公开的化合物。公开号:WO2017112853A1 -
作为产物:描述:2-(2-Methoxycarbonyl-ethyl)-3-thiophen-2-yl-isoxazolidine-5-carboxylic acid methyl ester 在 2,3-二氯-5,6-二氰基-1,4-苯醌 作用下, 以 苯 为溶剂, 反应 30.0h, 以85%的产率得到methyl 3-(thiophen-2-yl)-1,2-oxazole-5-carboxylate参考文献:名称:Kusurkar, R. S.; Wadia, M. S.; Bhosale, D. K., Journal of Chemical Research, Miniprint, 1996, # 11, p. 2701 - 2720摘要:DOI:
文献信息
-
[EN] COMPOUNDS, COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS OF INCREASING CFTR ACTIVITY<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS, COMPOSITIONS ET PROCÉDÉS POUR AUGMENTER L'ACTIVITÉ DU CFTR申请人:PROTEOSTASIS THERAPEUTICS INC公开号:WO2017019589A1公开(公告)日:2017-02-02The present disclosure features compounds such as those having the Formulae (I) and (II), which can increase cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) activity as measured in human bronchial epithelial (hBE) cells. The present disclosure also features methods of treating a condition associated with decreased CFTR activity or a condition associated with a dysfunction of proteostasis comprising administering to a subject an effective amount of a disclosed compound, such as a compound of Formula (I) or (II).本公开涉及化合物,例如具有式(I)和(II)的化合物,可以增加在人类支气管上皮细胞(hBE)中测量的囊性纤维化跨膜传导调节蛋白(CFTR)活性。本公开还涉及治疗与CFTR活性降低或蛋白质稳态功能障碍相关的疾病的方法,包括向受试者施用所述化合物的有效量,例如式(I)或(II)的化合物。
-
1,3-Dipolar Cycloaddition Reaction of Thiophenecarbonitrile<i>N</i>-Oxides with Various Dipolarophiles作者:Yoshio Iwakura、Keikichi Uno、Shinsaku Shiraishi、Tatsuhiko HonguDOI:10.1246/bcsj.41.2954日期:1968.12synthesized by the chlorination of corresponding aldoxime with nitrosyl chloride. These compounds gave Δ2-isoxazolines and isoxazoles through 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reaction with compounds having double or triple bond as dipolarophiles. In the cycloaddition reaction, II was less reactive than I. This would be explained by stability of II owing to electron-withdrawing ability of chlorine atom at 5-position
-
Compounds, compositions, and methods for increasing CFTR activity申请人:Proteostasis Therapeutics, Inc.公开号:US10392372B2公开(公告)日:2019-08-27The present disclosure is directed to disclosed compounds that increase cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) activity as measured in human bronchial epithelial (hBE) cells.本公开涉及所公开的能提高囊性纤维化跨膜传导调节因子(CFTR)活性的化合物,这些活性是在人支气管上皮细胞(hBE)中测定的。
-
Compounds, compositions, and methods of increasing CFTR activity申请人:Proteostasis Therapeutics, Inc.公开号:US10548878B2公开(公告)日:2020-02-04The present disclosure features compounds such as those having the Formulae (I) and (II), which can increase cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) activity as measured in human bronchial epithelial (hBE) cells. The present disclosure also features methods of treating a condition associated with decreased CFTR activity or a condition associated with a dysfunction of proteostasis comprising administering to a subject an effective amount of a disclosed compound, such as a compound of Formula (I) or (II).本公开的化合物如具有式(I)和(II)的化合物,可提高在人支气管上皮细胞(hBE)中测定的囊性纤维化跨膜传导调节剂(CFTR)活性。本公开内容还包括治疗与 CFTR 活性降低相关的疾病或与蛋白稳态功能障碍相关的疾病的方法,包括向受试者施用有效量的公开化合物,如式(I)或(II)化合物。
-
[EN] COMPOUNDS, COMPOSITIONS, AND METHODS FOR INCREASING CFTR ACTIVITY<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS, COMPOSITIONS ET PROCÉDÉS POUR AUGMENTER L'ACTIVITÉ DU CFTR申请人:PROTEOSTASIS THERAPEUTICS INC公开号:WO2016105485A3公开(公告)日:2016-09-01
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
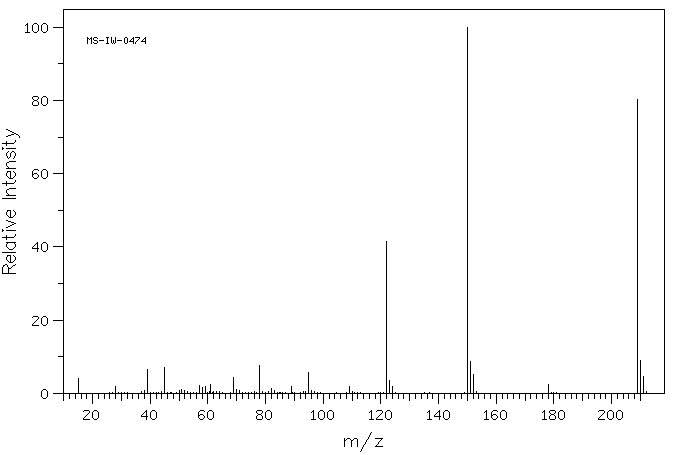
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
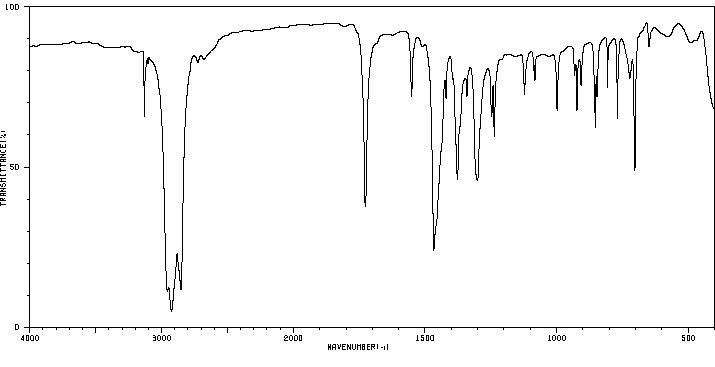
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(SP-4-1)-二氯双(1-苯基-1H-咪唑-κN3)-钯
(5aS,6R,9S,9aR)-5a,6,7,8,9,9a-六氢-6,11,11-三甲基-2-(2,3,4,5,6-五氟苯基)-6,9-甲基-4H-[1,2,4]三唑[3,4-c][1,4]苯并恶嗪四氟硼酸酯
(5-氨基-1,3,4-噻二唑-2-基)甲醇
齐墩果-2,12-二烯[2,3-d]异恶唑-28-酸
黄曲霉毒素H1
高效液相卡套柱
非昔硝唑
非布索坦杂质Z19
非布索坦杂质T
非布索坦杂质K
非布索坦杂质E
非布索坦杂质D
非布索坦杂质67
非布索坦杂质65
非布索坦杂质64
非布索坦杂质61
非布索坦代谢物67M-4
非布索坦代谢物67M-2
非布索坦代谢物 67M-1
非布索坦-D9
非布索坦
非唑拉明
雷非那酮-d7
雷西那德杂质2
雷西纳德杂质L
雷西纳德杂质H
雷西纳德杂质B
雷西纳德
雷西奈德杂质
阿西司特
阿莫奈韦
阿考替胺杂质9
阿米苯唑
阿米特罗13C2,15N2
阿瑞匹坦杂质
阿格列扎
阿扎司特
阿尔吡登
阿塔鲁伦中间体
阿培利司N-1
阿哌沙班杂质26
阿哌沙班杂质15
阿可替尼
阿作莫兰
阿佐塞米
镁(2+)(Z)-4'-羟基-3'-甲氧基肉桂酸酯
锌1,2-二甲基咪唑二氯化物
锌(II)(苯甲醇)(四苯基卟啉)
锌(II)(正丁醇)(四苯基卟啉)
锌(II)(异丁醇)(四苯基卟啉)