4-羟基苯甲酸正壬酯 | 38713-56-3
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:44°C
-
沸点:367.59°C (rough estimate)
-
密度:1.0468 (rough estimate)
-
稳定性/保质期:
常规情况下不会分解,也没有任何危险反应。
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):5.9
-
重原子数:19
-
可旋转键数:10
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.562
-
拓扑面积:46.5
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:3
安全信息
-
安全说明:S26,S36/37/39
-
危险类别码:R36/37/38
-
海关编码:2918290000
-
储存条件:密封、阴凉、干燥保存。
SDS
SAFETY DATA SHEET
Section 1. IDENTIFICATION
Product name: Nonyl 4-Hydroxybenzoate
Revision number: 5
Section 2. HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION
GHS classification
PHYSICAL HAZARDS Not classified
HEALTH HAZARDS
Skin corrosion/irritation Category 2
Category 2A
Serious eye damage/eye irritation
Skin sensitization Category 1
Not classified
ENVIRONMENTAL HAZARDS
GHS label elements, including precautionary statements
Pictograms or hazard symbols
Signal word Warning
Hazard statements Causes skin irritation
Causes serious eye irritation
May cause an allergic skin reaction
Precautionary statements:
Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray.
[Prevention]
Contaminated work clothing should not be allowed out of the workplace.
Wash hands thoroughly after handling.
Wear protective gloves/eye protection/face protection.
IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses,
[Response]
if present and easy to do. Continue rinsing.
If eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention.
IF ON SKIN: Gently wash with plenty of soap and water.
If skin irritation or rash occurs: Get medical advice/attention.
Wash contaminated clothing before reuse.
Section 3. COMPOSITION/INFORMATION ON INGREDIENTS
Substance/mixture: Substance
Components: Nonyl 4-Hydroxybenzoate
Percent: >98.0%(LC)(T)
38713-56-3
CAS Number:
Synonyms: 4-Hydroxybenzoic Acid Nonyl Ester , Nonylparaben
Chemical Formula: C16H24O3
Nonyl 4-Hydroxybenzoate
Section 4. FIRST AID MEASURES
Inhalation: Remove victim to fresh air and keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing.
Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell.
Skin contact: Remove/Take off immediately all contaminated clothing. Gently wash with plenty of
soap and water. If skin irritation or rash occurs: Get medical advice/attention.
Eye contact: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present
and easy to do. Continue rinsing. If eye irritation persists: Get medical
advice/attention.
Ingestion: Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell. Rinse mouth.
A rescuer should wear personal protective equipment, such as rubber gloves and air-
Protection of first-aiders:
tight goggles.
Section 5. FIRE-FIGHTING MEASURES
Suitable extinguishing Dry chemical, foam, water spray, carbon dioxide.
media:
Precautions for firefighters: Fire-extinguishing work is done from the windward and the suitable fire-extinguishing
method according to the surrounding situation is used. Uninvolved persons should
evacuate to a safe place. In case of fire in the surroundings: Remove movable
containers if safe to do so.
Special protective When extinguishing fire, be sure to wear personal protective equipment.
equipment for firefighters:
Section 6. ACCIDENTAL RELEASE MEASURES
Personal precautions, Use personal protective equipment. Keep people away from and upwind of spill/leak.
protective equipment and Entry to non-involved personnel should be controlled around the leakage area by
emergency procedures: roping off, etc.
Environmental precautions: Prevent product from entering drains.
Methods and materials for Sweep dust to collect it into an airtight container, taking care not to disperse it.
containment and cleaning Adhered or collected material should be promptly disposed of, in accordance with
up: appropriate laws and regulations.
Section 7. HANDLING AND STORAGE
Precautions for safe handling
Technical measures: Handling is performed in a well ventilated place. Wear suitable protective equipment.
Prevent dispersion of dust. Wash hands and face thoroughly after handling.
Use a local exhaust if dust or aerosol will be generated.
Advice on safe handling: Avoid contact with skin, eyes and clothing.
Conditions for safe storage, including any
incompatibilities
Storage conditions: Keep container tightly closed. Store in a cool and dark place.
Store away from incompatible materials such as oxidizing agents.
Packaging material: Comply with laws.
Section 8. EXPOSURE CONTROLS / PERSONAL PROTECTION
Engineering controls: Install a closed system or local exhaust as possible so that workers should not be
exposed directly. Also install safety shower and eye bath.
Personal protective equipment
Respiratory protection: Dust respirator. Follow local and national regulations.
Hand protection: Protective gloves.
Safety glasses. A face-shield, if the situation requires.
Eye protection:
Skin and body protection: Protective clothing. Protective boots, if the situation requires.
Section 9. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
Physical state (20°C): Solid
Crystal- Powder
Form:
Colour: White
No data available
Odour:
Nonyl 4-Hydroxybenzoate
Section 9. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
pH: No data available
Melting point/freezing point:44°C
Boiling point/range: No data available
Flash point: No data available
Flammability or explosive
limits:
Lower: No data available
Upper: No data available
Relative density: No data available
Solubility(ies):
[Water] No data available
[Other solvents] No data available
Section 10. STABILITY AND REACTIVITY
Chemical stability: Stable under proper conditions.
Possibility of hazardous No special reactivity has been reported.
reactions:
Incompatible materials: Oxidizing agents
Hazardous decomposition Carbon monoxide, Carbon dioxide
products:
Section 11. TOXICOLOGICAL INFORMATION
Acute Toxicity: No data available
Skin corrosion/irritation: No data available
Serious eye No data available
damage/irritation:
Germ cell mutagenicity: No data available
Carcinogenicity:
No data available
IARC =
NTP = No data available
Reproductive toxicity: No data available
Section 12. ECOLOGICAL INFORMATION
Ecotoxicity:
Fish: No data available
Crustacea: No data available
Algae: No data available
Persistence / degradability: No data available
Bioaccumulative No data available
potential(BCF):
Mobility in soil
Log Pow: No data available
Soil adsorption (Koc): No data available
Henry's Law No data available
constant(PaM3/mol):
Section 13. DISPOSAL CONSIDERATIONS
Recycle to process, if possible. Consult your local regional authorities. You may be able to dissolve or mix material
with a combustible solvent and burn in a chemical incinerator equipped with an afterburner and scrubber system.
Observe all federal, state and local regulations when disposing of the substance.
Section 14. TRANSPORT INFORMATION
Hazards Class: Does not correspond to the classification standard of the United Nations
UN-No: Not listed
Nonyl 4-Hydroxybenzoate
Section 15. REGULATORY INFORMATION
Safe management ordinance of dangerous chemical product (State Council announces on January 26, 2002
and revised on February 16,2011): Safe use and production, the storage of a dangerous chemical, transport,
loading and unloading were prescribed.
SECTION 16 - ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
N/A
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 对羟基苯甲酸甲酯 methyl 4-hydroxybenzoate 99-76-3 C8H8O3 152.15 对羟基苯甲酸 4-hydroxy-benzoic acid 99-96-7 C7H6O3 138.123 4-苄氧基苯甲酸甲酯 4-benzyloxy-benzoic acid methyl ester 32122-11-5 C15H14O3 242.274 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— nonyl 4-[(aminosulphonyl)oxy]benzoate —— C16H25NO5S 343.444
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:4-羟基苯甲酸正壬酯 在 sodium hydride 、 氨基磺酰氯 作用下, 以 N,N-二甲基甲酰胺 、 甲苯 为溶剂, 反应 10.5h, 生成 nonyl 4-[(aminosulphonyl)oxy]benzoate参考文献:名称:4-[(氨基磺酰基)氧基]苯甲酸的烷基和环烷基酯衍生物对雌酮硫酸酯酶(ES)的抑制作用。摘要:在寻找有效的雌酮硫酸酯酶(ES)抑制剂的过程中,我们进行了一系列4-[((氨基磺酰基)氧基]苯甲酸的酯的合成和生化评估。研究结果表明,合成的化合物具有有效的抑制活性,实际上环辛基衍生物比目前正在接受临床试验的667-COUMATE更有效。DOI:10.1016/j.bmcl.2003.11.067
-
作为产物:描述:1-壬醇 在 palladium dihydroxide 偶氮二甲酸二异丙酯 、 氢气 、 溶剂黄146 、 三苯基膦 作用下, 以 四氢呋喃 、 乙酸乙酯 为溶剂, 反应 14.0h, 生成 4-羟基苯甲酸正壬酯参考文献:名称:多功能食品添加剂的分子设计:抗氧化抗真菌剂。摘要:合成了一系列的3,4-二羟基苯甲酸烷基酯(原儿茶酸酯),并使用2-倍连续肉汤稀释法测定了它们对酿酒酵母的杀真菌活性。3,4-二羟基苯甲酸壬基酯和辛基酯被认为对这种酵母最有效,其杀真菌剂的最低浓度分别为12.5微克/毫升。发现该活性与疏水性烷基链长相关。时间杀灭曲线研究表明,3,4-二羟基苯甲酸壬酯在任何生长阶段均对啤酒酵母有杀真菌作用,且该活性不受pH值的影响。烷基3的杀菌活性 注意到4-二羟基苯甲酸酯具有非特异性破坏天然膜相关功能作为表面活性剂(表面活性剂)并抑制呼吸电子转运的能力。但是,3,4-二羟基苯甲酸壬酯的主要杀真菌活性可能来自其作为表面活性剂的能力。DOI:10.1021/jf049687n
文献信息
-
[EN] METALOXYPHTHALOCYANINE COMPOUNDS<br/>[FR] COMPOSES DE METALOXYPHTALOCYANINE
-
Synthesis and biochemical evaluation of some novel benzoic acid based esters as potential inhibitors of oestrone sulphatase作者:Caroline Owen、Karen James、Luther Sampson、Sabbir AhmedDOI:10.1211/002235702568日期:2010.2.18
Abstract Oestrone sulphatase is an important target in the fight against hormone-dependent breast cancer. In an effort to investigate the reported definitive pharmacophore for oestrone sulphatase and continue our search for potent inhibitors of this enzyme, we have undertaken extensive synthesis, biochemical evaluation and physicochemical property determination of a range of benzoic acid based esters. Here, we report the initial results of our study into a series of straight chain alkyl esters of 4-sulphonylbenzoic acid. Using these compounds, we have investigated the involvement of two physicochemical properties, namely logP and pKa. The results of this study show that there was a strong correlation between the inhibitory activity and the logP of the parent compound. Within the series of compounds studied, hydrophobicity appears to be a more important factor than pKa in determining the overall inhibitory activity. In a previous report, we showed that pKa plays an important role in stabilizing the phenoxide ion resulting from the hydrolysis of the sulphamate group. Here, we propose that although pKa is an important factor in determining the overall inhibitory activity when a wide range of compounds are considered, both hydrophobicity and pKa need to be considered in the design of potential inhibitors of oestrone sulphatase.
醇酮硫酸酶是对抗激素依赖性乳腺癌的重要靶点。为了研究已报道的醇酮硫酸酶的明确药效团并继续寻找这种酶的有效抑制剂,我们进行了大量的苯甲酸酯类化合物的合成、生化评价和理化性质测定。在这里,我们报告了我们对一系列直链烷基苯磺酸酯的研究初步结果。使用这些化合物,我们研究了两种理化性质,即logP和pKa的参与。这项研究结果显示,抑制活性与母体化合物的logP之间存在强烈相关性。在研究的化合物系列中,疏水性似乎比pKa更重要,决定了整体的抑制活性。在先前的报告中,我们表明pKa在稳定由磺酸酯基水解产生的苯酚根离子中起重要作用。在这里,我们提出,尽管pKa在考虑广泛的化合物时在确定整体抑制活性中起重要作用,但在设计潜在的醇酮硫酸酶抑制剂时,需要同时考虑疏水性和pKa。 -
METHOD OF PROVING AUTHENTICITY, SIGNAL CONVERSION METHOD, POLYMER WELDING METHOD, METHOD OF PRODUCING LITHOGRAPHIC PRINTING PLATE, INK FOR PRINTING, TONER, AND HEAT RAY-SHIELDING MATERIAL, EACH USING NAPHTHALOCYANINE COMPOUND, AND METHOD OF PRODUCING NAPHTHALOCYANINE COMPOUND申请人:Kimura Keizo公开号:US20110311911A1公开(公告)日:2011-12-22Disclosed is a method of proving the authenticity of goods or a support comprising using a compound represented by Formula (I). wherein, in Formula (I), each of R 11 to R 46 independently represents a hydrogen atom or a substituent group, wherein when a benzene ring is substituted with any of R 11 to R 46 , any groups adjacent to each other among R 11 to R 46 may be bonded each other to form a ring; M represents a hydrogen atom, a metal ion, or a group containing a metal ion; and n represents 1 or 2. The infrared absorption efficiency is high and the deterioration in infrared absorption over time is ameliorated. The infrared absorption efficiency is high and the deterioration in infrared absorption over time is ameliorated.
-
Rational design of antimicrobial agents: antifungal activity of alk(en)yl dihydroxybenzoates and dihydroxyphenyl alkanoates作者:Ken-ichi Nihei、Atsuko Nihei、Isao KuboDOI:10.1016/j.bmcl.2003.08.057日期:2003.11similar antifungal activity against Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Their nonyl derivatives exhibit the most potent antifungal activity against this yeast with the minimum fungicidal concentration (MFC) in the range between 12.5 and 50 microg/mL. In addition, various 3,4-dihydroxybenzoates, possessing different side chains, namely unsaturated, branched and alicyclic were synthesized and their activity was compared每个3,4-和3,5-二羟基苯甲酸烷基酯和3,4-和3,5-二羟基苯基链烷酸烷基酯的同源系列(C3-C14)对啤酒酵母具有相似的抗真菌活性。它们的壬基衍生物对这种酵母表现出最有效的抗真菌活性,其最小杀真菌浓度(MFC)在12.5至50微克/毫升之间。此外,合成了具有不同侧链的各种3,4-二羟基苯甲酸酯,即不饱和,支链和脂环族,并比较了它们的活性。
-
Molecular Design of Antifungal Agents作者:Isao Kubo、Ping Xiao、Ken-ichi Nihei、Ken-ichi Fujita、Yoshiro Yamagiwa、Tadao KamikawaDOI:10.1021/jf020088v日期:2002.7.1In a rational approach to the design of antifungal agents against Saccharomyces cerevisiae, a series of alkyl gallates (3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoates) were synthesized and assayed. Nonyl gallate (1) was found to be the most effective with a minimum fungicidal concentration (MFC) of 12.5 microg/mL (42 microM), followed by octyl gallate (2) with an MFC of 25 microg/mL (89 microM). These MFCs are little influenced
表征谱图
-
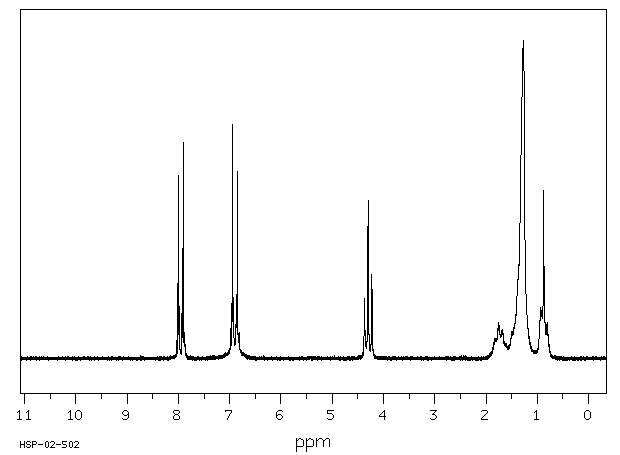
氢谱1HNMR
-
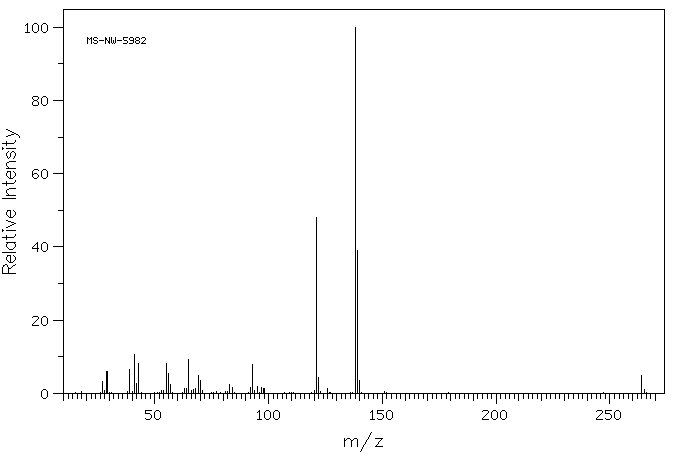
质谱MS
-
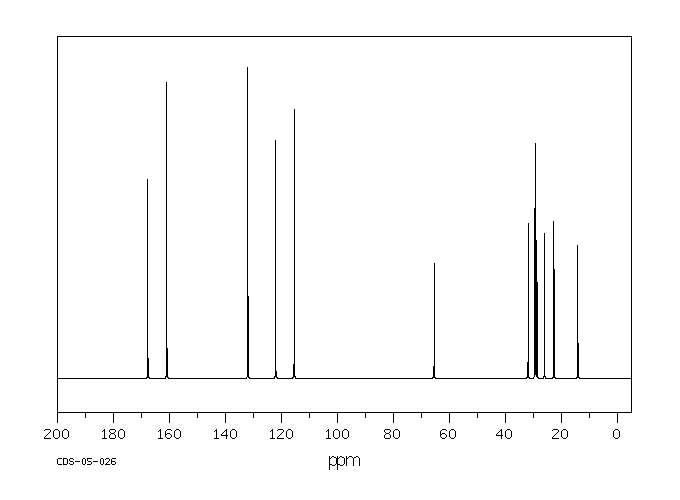
碳谱13CNMR
-
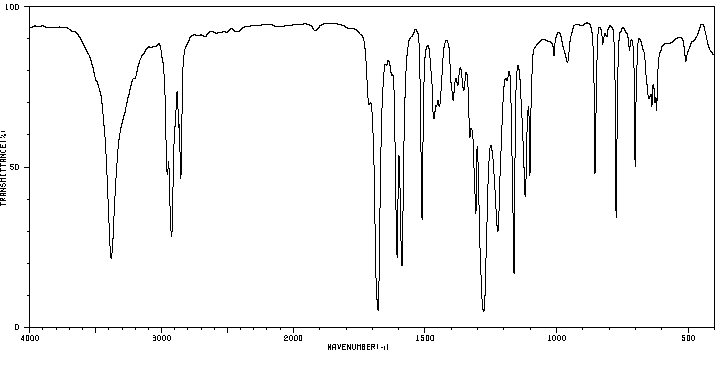
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息