1,cis-3,trans-5-Trimethylcyclohexane | 1795-26-2
中文名称
——
中文别名
——
英文名称
1,cis-3,trans-5-Trimethylcyclohexane
英文别名
trans,trans-1,3,5-trimethylcyclohexane;1-cis-3-trans-5-trimethylcyclohexane;1r,3t,5t-trimethylcyclohexane;1,3,5-trimethylcyclohexane;1r,3,5t-trimethyl-cyclohexane;trans-1,3,5-trimethyl-cyclohexane
CAS
1795-26-2
化学式
C9H18
mdl
——
分子量
126.242
InChiKey
ODNRTOSCFYDTKF-FBJIGQNJSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:-84.39°C
-
沸点:140.55°C
-
密度:0.7180
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.08
-
重原子数:9.0
-
可旋转键数:0.0
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:0.0
-
氢给体数:0.0
-
氢受体数:0.0
SDS
反应信息
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:硼离子催化芳烃加氢摘要:芳烃的非金属催化氢化代表了一种可持续且环境友好的环己烷衍生物合成方法。在此,我们报告了硼离子催化剂系统的开发,该系统可以氢化多种单环芳烃。此外,这种无金属催化系统允许通过改变反应条件选择性地部分或完全氢化萘和蒽。我们的机理研究表明,硼芳烃介导的 H 2分裂发生在限速步骤之前,生成的中性硼烷和质子化芳烃之间的氢化物转移可能是催化过程中的限速步骤。DOI:10.1039/d3cc01303k
文献信息
-
Polysilane-Immobilized Rh–Pt Bimetallic Nanoparticles as Powerful Arene Hydrogenation Catalysts: Synthesis, Reactions under Batch and Flow Conditions and Reaction Mechanism作者:Hiroyuki Miyamura、Aya Suzuki、Tomohiro Yasukawa、Shu̅ KobayashiDOI:10.1021/jacs.8b06015日期:2018.9.12Hydrogenation of arenes is an important reaction not only for hydrogen storage and transport but also for the synthesis of functional molecules such as pharmaceuticals and biologically active compounds. Here, we describe the development of heterogeneous Rh-Pt bimetallic nanoparticle catalysts for the hydrogenation of arenes with inexpensive polysilane as support. The catalysts could be used in both芳烃的氢化不仅是储氢和运输氢的重要反应,也是合成药物和生物活性化合物等功能性分子的重要反应。在这里,我们描述了非均相 Rh-Pt 双金属纳米颗粒催化剂的开发,用于以廉价的聚硅烷作为载体氢化芳烃。该催化剂可用于间歇和连续流动系统,在温和条件下具有高性能,并显示出广泛的底物通用性。在连续流动系统中,只需将底物和 1 个大气压的 H2 通过装有催化剂的柱子即可获得产物。值得注意的是,在流动系统中观察到比在间歇系统中高得多的催化性能,并且在连续流动条件下表现出极强的耐久性(> 连续运行50天;营业额 >3.4 × 105)。此外,研究了反应机理的细节以及批次和流动中不同动力学的起源,并将获得的知识应用于开发含有两个芳环的化合物的完全选择性芳烃氢化以合成活性药物成分。
-
Catalytic hydrogenation of aromatics under biphasic conditions: isolation and structural characterisation of the cluster intermediate [(η6-C6Me6)2(η6-C6H6)Ru3(μ2-H)2(μ2-OH)(μ3-O)]+作者:Matthieu Faure、Ana Tesouro Vallina、Helen Stoeckli-Evans、Georg Süss-FinkDOI:10.1016/s0022-328x(00)00773-7日期:2001.3the hydrogenation of benzene and benzene derivatives to give the corresponding cyclohexanes under biphasic conditions. The catalytic activity of 2 depends markedly on the substrate, an extremely high activity being observed for ethylbenzene. The cationic species present in the catalytic mixture of the ethylbenzene hydrogenation could be isolated as the tetrafluoroborate salt and characterised as the
-
THE HYDROGENATION OF CERTAIN BRANCHED COMPOUNDS OVER NICKEL作者:Homer. Adkins、Walter H. Zartman、Howard. CramerDOI:10.1021/ja01355a035日期:1931.4
-
Heterogeneous catalysis in organic chemistry. 7. Stereochemistry of the hydrogenation of 1,3,5-trimethylcyclohexene作者:Robert L. Augustine、Farrokh YaghmaieDOI:10.1021/jo00385a040日期:1987.5
-
Chiurdoglu; Bauwens; Doehaerd, Bulletin des Societes Chimiques Belges, 1954, vol. 63, p. 486,490, 491作者:Chiurdoglu、Bauwens、DoehaerdDOI:——日期:——
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
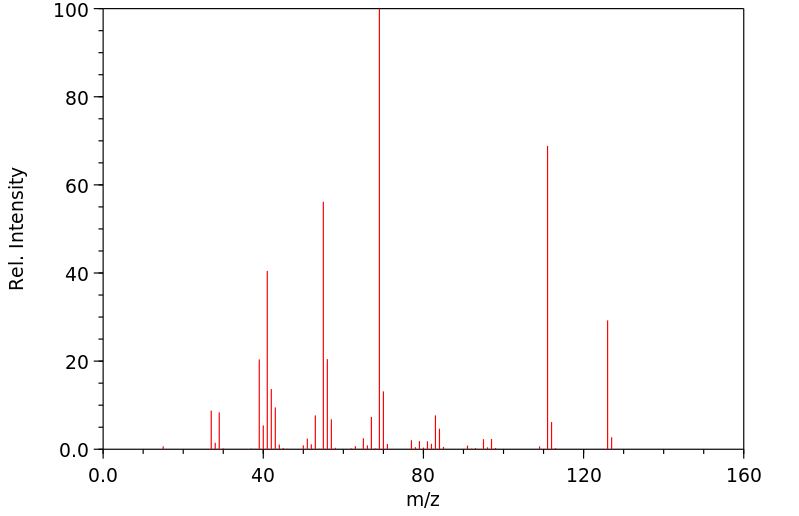
质谱MS
-
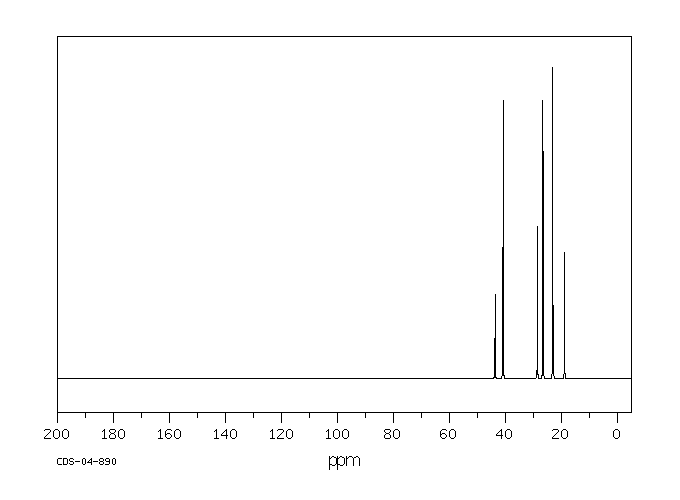
碳谱13CNMR
-
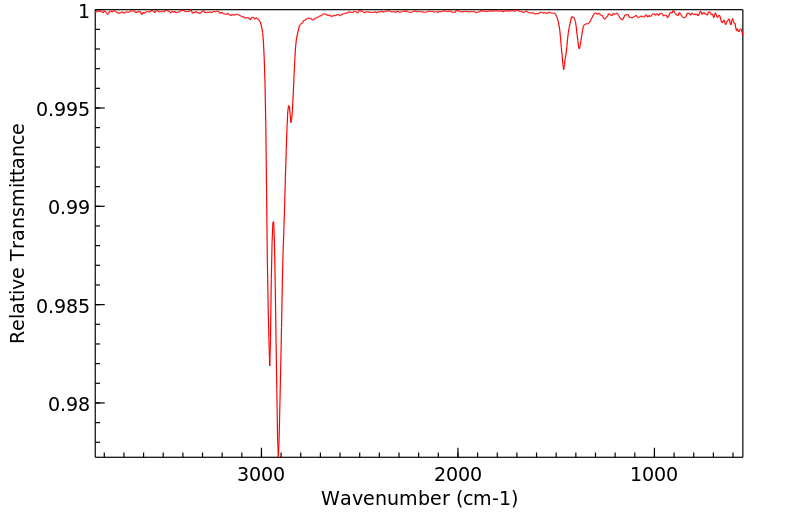
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
顺式-1-乙基-3-甲基环己烷
顺式-1-乙基-2-甲基环丙烷
顺式-1,3-二甲基环庚烷
顺式-1,2-二甲基环丙烷
顺式-1,2-二乙基环戊烷
顺式-1,2-二(1-甲基乙基)环丙烷
顺式-1,2-二(1-甲基乙基)环丙烷
顺式,反式,反式-1,2,4-三甲基环己烷
Copper, ethyl-
辛烷-d18
辛基环戊烷
辛基环丙烷
联苯肼酯
联环戊基
羰基双(环茂二烯基)钛
矿油精
癸烷,2,8-二甲基-
癸烷
decyl radical
癸基环戊烷
異十八烷
甲烷-d3
甲烷-d2
甲烷-d1
甲烷-D4
甲烷-3H
甲烷-13C,d4
甲烷-13C
甲烷
甲基自由基
甲基环辛烷
甲基环癸烷
甲基环戊烷
甲基环己烷-Me-d3
甲基环己烷
甲基环十一烷
甲基环丙烷
甲基环丁烷.
甲基丙烷-2-d
环辛烷-D16
环辛烷
环癸烷
环戊烷-D9
环戊烷-D10
环戊烷-13C1
环戊烷,三(2-辛基十二基)-
环戊烷
环戊基甲基自由基
环戊基环庚烷
环戊基环己烷