5-氯水杨酰苯胺 | 4638-48-6
中文名称
5-氯水杨酰苯胺
中文别名
5-氯-2-羟基苯甲酰苯胺;5-氯水杨苯胺;5-氯杨基苯胺
英文名称
5-chlorosalicylanilide
英文别名
5-chloro-2-hydroxy-N-phenylbenzamide;5-chloro-N-(phenyl)-2-hydroxy-benzamide
CAS
4638-48-6
化学式
C13H10ClNO2
mdl
MFCD00002320
分子量
247.681
InChiKey
KGYNGVVNFRUOOZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:210-212 °C(lit.)
-
沸点:336.3±32.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.386±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
-
溶解度:氯仿(微溶)、乙酸乙酯(微溶)
-
稳定性/保质期:
常温常压下稳定,熔点:210-212 °C(文献值)。
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.9
-
重原子数:17
-
可旋转键数:2
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:49.3
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:2
安全信息
-
危险品标志:Xi
-
安全说明:S26,S37/39
-
危险类别码:R36/37/38
-
WGK Germany:3
-
RTECS号:CV2450475
-
海关编码:2924299090
-
储存条件:常温、避光、通风干燥处,密封保存。
SDS
5-氯水杨酰苯胺 修改号码:5
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: 5-Chlorosalicylanilide
修改号码: 5
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害
皮肤腐蚀/刺激 第2级
严重损伤/刺激眼睛 2A类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志
信号词 警告
危险描述 造成皮肤刺激
造成严重眼刺激
防范说明
[预防] 处理后要彻底清洗双手。
穿戴防护手套/护目镜/防护面具。
[急救措施] 眼睛接触:用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续冲洗。
眼睛接触:求医/就诊
皮肤接触:用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激:求医/就诊。
脱掉被污染的衣物,清洗后方可重新使用。
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 5-氯水杨酰苯胺
百分比: >98.0%(N)
CAS编码: 4638-48-6
分子式: C13H10ClNO2
5-氯水杨酰苯胺 修改号码:5
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,雾状水,二氧化碳
特殊危险性: 小心,燃烧或高温下可能分解产生毒烟。
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 清扫收集粉尘,封入密闭容器。注意切勿分散。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的
法律法规处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止粉尘扩散。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果粉尘或浮质产生,使用局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防尘面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
固体
外形(20°C):
外观: 晶体-粉末
颜色: 白色类白色
气味: 无资料
5-氯水杨酰苯胺 修改号码:5
模块 9. 理化特性
pH: 无数据资料
熔点:
206°C
沸点/沸程 无资料
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 无资料
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂] 无资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳, 氮氧化物 (NOx), 氯化氢
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
RTECS 号码: CV2450475
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在可燃溶剂中溶解混合,在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中
焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
5-氯水杨酰苯胺 修改号码:5
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: 5-Chlorosalicylanilide
修改号码: 5
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害
皮肤腐蚀/刺激 第2级
严重损伤/刺激眼睛 2A类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志
信号词 警告
危险描述 造成皮肤刺激
造成严重眼刺激
防范说明
[预防] 处理后要彻底清洗双手。
穿戴防护手套/护目镜/防护面具。
[急救措施] 眼睛接触:用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续冲洗。
眼睛接触:求医/就诊
皮肤接触:用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激:求医/就诊。
脱掉被污染的衣物,清洗后方可重新使用。
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 5-氯水杨酰苯胺
百分比: >98.0%(N)
CAS编码: 4638-48-6
分子式: C13H10ClNO2
5-氯水杨酰苯胺 修改号码:5
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,雾状水,二氧化碳
特殊危险性: 小心,燃烧或高温下可能分解产生毒烟。
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 清扫收集粉尘,封入密闭容器。注意切勿分散。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的
法律法规处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止粉尘扩散。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果粉尘或浮质产生,使用局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防尘面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
固体
外形(20°C):
外观: 晶体-粉末
颜色: 白色类白色
气味: 无资料
5-氯水杨酰苯胺 修改号码:5
模块 9. 理化特性
pH: 无数据资料
熔点:
206°C
沸点/沸程 无资料
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 无资料
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂] 无资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳, 氮氧化物 (NOx), 氯化氢
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
RTECS 号码: CV2450475
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在可燃溶剂中溶解混合,在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中
焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
5-氯水杨酰苯胺 修改号码:5
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 水杨酰苯胺 salicylanilide 87-17-2 C13H11NO2 213.236 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 N-(4-溴苯基)-5-氯-2-羟基苯甲酰胺 N-(4-bromophenyl)-5-chloro-2-hydroxyl benzamide 2627-75-0 C13H9BrClNO2 326.577
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:5-氯水杨酰苯胺 在 盐酸 、 溶剂黄146 、 N,N'-二环己基碳二亚胺 作用下, 以 N,N-二甲基甲酰胺 为溶剂, 反应 4.5h, 生成 [4-chloro-2-(phenylcarbamoyl)phenyl] (2S)-2-amino-3-methylbutanoate;hydrochloride参考文献:名称:New derivatives of salicylamides: Preparation and antimicrobial activity against various bacterial species摘要:Three series of salicylanilides, esters of N-phenylsalicylamides and 2-hydroxy-N-[1-(2-hydroxyphenylamino)-1-oxoalkan-2-yl]benzamides, in total thirty target compounds were synthesized and characterized. The compounds were evaluated against seven bacterial and three mycobacterial strains. The antimicrobial activities of some compounds were comparable or higher than the standards ampicillin, ciprofloxacin or isoniazid. Derivatives 3f demonstrated high biological activity against Staphylococcus aureus (<= 0.03 mu mol/L), Mycobacterium marinum (<= 0.40 mu mol/L) and Mycobacterium kansasii (1.58 mu mol/L), 3g shows activity against Clostridium perfringens (<= 0.03 mu mol/L) and Bacillus cereus (0.09 mu mol/L), 3h against Pasteurella multocida (<= 0.03 mu mol/L) and M. kansasii (<= 0.43 mu mol/L), 3i against methicillin-resistant S. aureus and B. cereus (<= 0.03 mu mol/L). The structure-activity relationships are discussed for all the compounds. (C) 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.DOI:10.1016/j.bmc.2013.08.029
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:针对 SARS-CoV-2 的氯硝柳胺类似物的设计、合成和生物学评价摘要:氯硝柳胺是一种广泛使用的驱虫药,通过TMEM16F抑制和自噬诱导复制来抑制SARS-CoV-2病毒进入,但相对较高的细胞毒性和较差的口服生物利用度限制了其应用。我们合成了 22 种氯硝柳胺类似物,其中发现化合物5具有最佳的抗 SARS-CoV-2 功效(IC 50 = 0.057 μM)和化合物6、10和11(IC 50 = 0.39、0.38 和 0.49 μM,分别)显示出与氯硝柳胺相当的功效。另一方面,化合物5、6、11在人血浆和肝脏S9酶测定中比氯硝柳胺具有更高的稳定性,口服给药时可以提高生物利用度和半衰期。荧光显微镜显示,与氯硝柳胺相比,化合物5在减少磷脂酰丝氨酸外化方面表现出更好的活性,这与 TMEM16F 抑制有关。应用人工智能预测的人TMEM16F蛋白结构进行分子对接,揭示5的4′-NO 2与Arg809形成氢键,而氯硝柳胺则被2′-Cl阻断。DOI:10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114295
文献信息
-
2-HYDROXYARYLAMIDE DERIVATIVE OR PHARMACEUTICALLY ACCEPTABLE SALT THEREOF, PREPARATION METHOD THEREOF, AND PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITION FOR PREVENTING OR TREATING CANCER CONTAINING SAME AS ACTIVE INGREDIENT申请人:Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology公开号:US20140221411A1公开(公告)日:2014-08-07The present invention relates to a 2-hydroxyarylamide derivative or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, a preparation method thereof, and a pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating cancer comprising the same as an active ingredient. The 2-hydroxyarylamide derivative prepared by the present invention is excellent in the inhibition of the activity of TMPRSS4 serine protease and the suppression of the infiltration of TMPRSS4-expressed cancer cells, and thus can be useful as a composition for preventing or treating cancer by inhibiting TMPRSS4 over-expressed in cancer cells, particularly, colorectal cancer, lung cancer, breast cancer, prostate cancer, ovarian cancer, pancreatic cancer, or stomach cancer cells.
-
Bio-evaluation of fluoro and trifluoromethyl-substituted salicylanilides against multidrug-resistant S. aureus作者:Jhajan Lal、Grace Kaul、Abdul Akhir、Shabina B. Ansari、Sidharth Chopra、Damodara N. ReddyDOI:10.1007/s00044-021-02808-4日期:2021.12vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (VRSA) are primary causes of skin and soft tissue infections worldwide. To address the emergency caused due to increasing multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacterial infections, a series of novel fluoro and trifluoromethyl-substituted salicylanilide derivatives were synthesized and their antimicrobial activity was investigated. MIC data reveal that the compounds inhibited S. aureus耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌(MRSA) 和耐万古霉素金黄色葡萄球菌(VRSA) 是全球皮肤和软组织感染的主要原因。为解决由于多重耐药 (MDR) 细菌感染引起的紧急情况,合成了一系列新型氟和三氟甲基取代的水杨酰苯胺衍生物,并对其抗菌活性进行了研究。MIC 数据显示,这些化合物特异性抑制金黄色葡萄球菌(MIC 0.25–64 µg/mL)。MIC < 1 µg/mL的化合物对 Vero 细胞的体外细胞毒性导致鉴定出四种化合物(20、22、24和25 )),选择性指数高于 10。这四种化合物针对 MDR S. aureus小组进行了测试。值得注意的是,5-氯-N- (4'-溴-3'-三氟甲基苯基)-2-羟基苯甲酰胺 ( 22 ) 对 9 种 MRSA 和 3 种 VRSA 菌株表现出优异的活性,MIC 为 0.031–0.062 µg/mL,显着优于对照药物甲氧西林和万古霉素。比较时间-杀灭动力
-
Directing-group-assisted copper-catalyzed oxidative esterification of phenols with aldehydes
-
Structure–activity studies of Wnt/β-catenin inhibition in the Niclosamide chemotype: Identification of derivatives with improved drug exposure作者:Robert A. Mook、Jiangbo Wang、Xiu-Rong Ren、Minyong Chen、Ivan Spasojevic、Larry S. Barak、H. Kim Lyerly、Wei ChenDOI:10.1016/j.bmc.2015.07.001日期:2015.9Non-anilide, N-methyl amides and reverse amide derivatives lost significant potency, while acylated salicylamide derivatives inhibited signaling with potency similar to non-acyl derivatives. Niclosamide’s low systemic exposure when dosed orally may hinder its use to treat systemic disease. To overcome this limitation we identified an acyl derivative of Niclosamide, DK-520 (compound 32), that significantlyWnt信号通路在器官发育和组织稳态的调节中发挥着关键作用。Wnt 活性失调是导致包括癌症在内的许多疾病的主要潜在机制之一。我们之前报道过 FDA 批准的驱虫药 NicloSAmide 可抑制 Wnt/β-catenin 信号传导,并在体外和体内抑制结肠癌细胞的生长。NicloSAmide 是一种多功能药物,除了抑制 Wnt/β-catenin 信号传导外,还具有重要的生物活性。在这里,我们研究了氯硝柳胺的苯胺和水杨酰胺区域中 Wnt 信号传导抑制的 SAR。我们发现4'-硝基取代基可以有效地被三氟甲基或氯取代,并且抑制效力取决于苯胺环中的取代模式。非苯胺、N-甲基酰胺和反向酰胺衍生物失去了显着的效力,而酰化水杨酰胺衍生物抑制信号传导的效力与非酰基衍生物相似。口服氯硝柳胺的全身暴露量较低,可能会阻碍其用于治疗全身性疾病。为了克服这一限制,我们鉴定了氯硝柳胺的酰基衍生物 DK-520(化合物3
-
One-Pot Synthesis of Fused Pyridazino[4,5-b][1,4]oxazepine-diones via Smiles Rearrangement作者:Chen Ma、Yanli Liu、Ying Ma、Chunjing Zhan、Aiping HuangDOI:10.1055/s-0031-1290073日期:2012.1Fused pyridazino[4,5-b][1,4]oxazepine-diones were easily obtained in moderate to excellent yields via Smiles rearrangement. The synthetic approach is supported by a one-pot couplingSmiles rearrangement-cyclization process. This process has potential applications in the synthesis of biologically and medicinally relevant compounds.
表征谱图
-
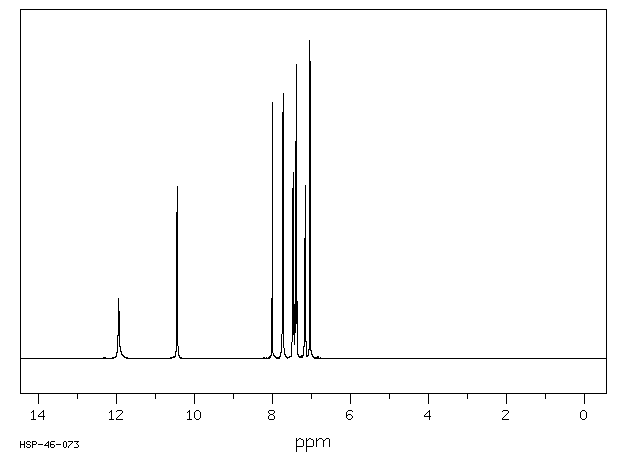
氢谱1HNMR
-
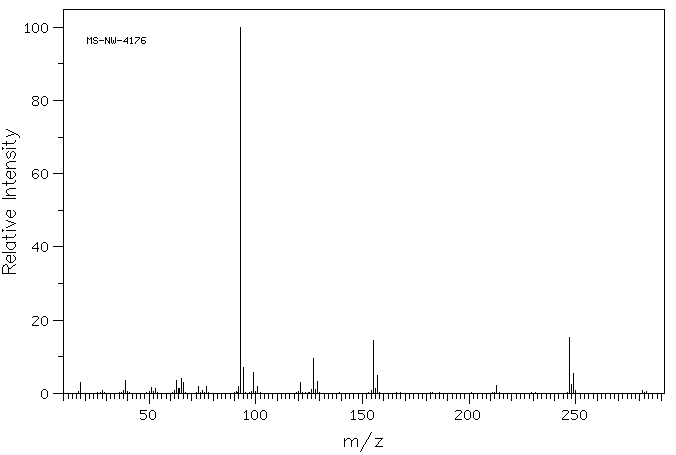
质谱MS
-
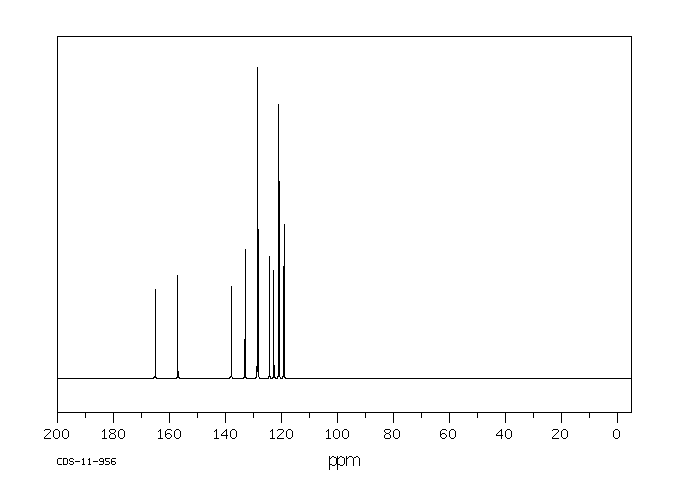
碳谱13CNMR
-
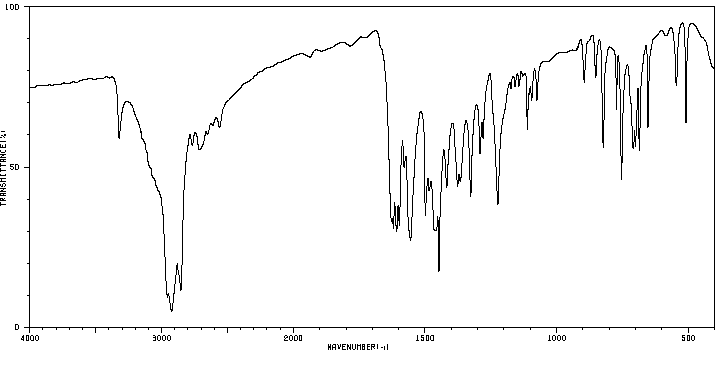
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(βS)-β-氨基-4-(4-羟基苯氧基)-3,5-二碘苯甲丙醇
(S,S)-邻甲苯基-DIPAMP
(S)-(-)-7'-〔4(S)-(苄基)恶唑-2-基]-7-二(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-2,2',3,3'-四氢-1,1-螺二氢茚
(S)-盐酸沙丁胺醇
(S)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧磷杂环戊二烯
(S)-2,2'-双[双(3,5-三氟甲基苯基)膦基]-4,4',6,6'-四甲氧基联苯
(S)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(R)富马酸托特罗定
(R)-(-)-盐酸尼古地平
(R)-(-)-4,12-双(二苯基膦基)[2.2]对环芳烷(1,5环辛二烯)铑(I)四氟硼酸盐
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[((6-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(4-叔丁基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(3-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-4,7-双(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-7“-[(吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2”,3,3'-四氢1,1'-螺二茚满
(R)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二苯氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂环戊烯
(R)-2-[((二苯基膦基)甲基]吡咯烷
(R)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(N-(4-甲氧基苯基)-N-甲基-3-(1-哌啶基)丙-2-烯酰胺)
(5-溴-2-羟基苯基)-4-氯苯甲酮
(5-溴-2-氯苯基)(4-羟基苯基)甲酮
(5-氧代-3-苯基-2,5-二氢-1,2,3,4-oxatriazol-3-鎓)
(4S,5R)-4-甲基-5-苯基-1,2,3-氧代噻唑烷-2,2-二氧化物-3-羧酸叔丁酯
(4S,4''S)-2,2''-亚环戊基双[4,5-二氢-4-(苯甲基)恶唑]
(4-溴苯基)-[2-氟-4-[6-[甲基(丙-2-烯基)氨基]己氧基]苯基]甲酮
(4-丁氧基苯甲基)三苯基溴化磷
(3aR,8aR)-(-)-4,4,8,8-四(3,5-二甲基苯基)四氢-2,2-二甲基-6-苯基-1,3-二氧戊环[4,5-e]二恶唑磷
(3aR,6aS)-5-氧代六氢环戊基[c]吡咯-2(1H)-羧酸酯
(2Z)-3-[[(4-氯苯基)氨基]-2-氰基丙烯酸乙酯
(2S,3S,5S)-5-(叔丁氧基甲酰氨基)-2-(N-5-噻唑基-甲氧羰基)氨基-1,6-二苯基-3-羟基己烷
(2S,2''S,3S,3''S)-3,3''-二叔丁基-4,4''-双(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-2,2''-联苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂戊环
(2S)-(-)-2-{[[[[3,5-双(氟代甲基)苯基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基}-N-(二苯基甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[((1S,2S)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[[((1R,2R)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2-硝基苯基)磷酸三酰胺
(2,6-二氯苯基)乙酰氯
(2,3-二甲氧基-5-甲基苯基)硼酸
(1S,2S,3S,5S)-5-叠氮基-3-(苯基甲氧基)-2-[(苯基甲氧基)甲基]环戊醇
(1S,2S,3R,5R)-2-(苄氧基)甲基-6-氧杂双环[3.1.0]己-3-醇
(1-(4-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(3-溴苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氯苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2,6-二氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(-)-去甲基西布曲明
龙蒿油
龙胆酸钠
龙胆酸叔丁酯
龙胆酸
龙胆紫-d6
龙胆紫