(3β,5α,8α,9β,10α,13α,14β,17α)-3-hydroxypregnan-20-one | 210692-32-3
分子结构分类
中文名称
——
中文别名
——
英文名称
(3β,5α,8α,9β,10α,13α,14β,17α)-3-hydroxypregnan-20-one
英文别名
ent-pregnanolone;ent-(3α,5β)-3-hydroxypregnan-20-one;ent-3α-hydroxy-5β-pregnan-20-one;1-[(3S,5S,8S,9R,10R,13R,14R,17R)-3-hydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]ethanone
CAS
210692-32-3
化学式
C21H34O2
mdl
——
分子量
318.5
InChiKey
AURFZBICLPNKBZ-ZGLJFNAKSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):4.9
-
重原子数:23
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:4.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.95
-
拓扑面积:37.3
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:2
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 1-[(3S,5S,8S,9R,10R,13R,14R,17R)-3-(tert-Butyl-dimethyl-silanyloxy)-10,13-dimethyl-hexadecahydro-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-ethanone 210692-31-2 C27H48O2Si 432.762
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:(3β,5α,8α,9β,10α,13α,14β,17α)-3-hydroxypregnan-20-one 在 吡啶 、 三甲基氨基磺酸 、 氨 作用下, 反应 432.0h, 以89%的产率得到(3β,5α,8α,9β,10α,13α,14β,17α)-3-(sulfooxy)pregnan-20-one ammonium salt参考文献:名称:Neurosteroid Analogues. 6. The Synthesis and GABAA Receptor Pharmacology of Enantiomers of Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulfate, Pregnenolone Sulfate, and (3α,5β)-3-Hydroxypregnan-20-one Sulfate摘要:The unnatural enantiomers of dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (1), pregnenolone sulfate (2), and (3 alpha,5 beta)-3-hydroxypregnan-20-one sulfate (3), compounds 4-6, respectively, were prepared by total steroid synthesis. The enantioselectivity of the compounds as negative modulators of the GABA(A) receptors present in cultured rat hippocampal neurons was examined using electrophysiological methods. Enantioselectivity was found for the inhibitory actions of the dehydroepiandrosterone enantiomers, The IC(50)s for compounds 1 and 4 were 11 +/- 1 and 80 +/- 14 mu M, respectively. Little, if any, enantioselectivity was found for the other two pairs of steroid sulfate inhibitors. The IC(50)s for compounds 2 and 5 were 82 +/- 12 and 76 +/- 27 mu M, respectively. The IC(50)s for compounds 3 and 6 were 39 +/- 7 and 46 +/- 2 mu M, respectively. The results suggest that the sites of action for the androstane and pregnane series of steroid sulfate blockers of GABA-mediated current are different. The observed enantioselectivity for the actions of dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate indicates that its inhibitory actions are mediated via a chiral recognition site and provides new evidence in support of the earlier hypothesis that there is a binding site for this compound on GABA(A) receptors. Conversely, the failure to observe enantioselectivity for the actions of pregnenolone sulfate and steroid sulfate 3 indicates that a chiral recognition site far these steroids does not exist on GABA(A) receptors and suggests that the effects of these compounds on this receptor's function may arise indirectly as a consequence of steroid-induced membrane perturbation.DOI:10.1021/jm980148h
-
作为产物:描述:dl-Δ4-androstene-3,17-dione 在 4-二甲氨基吡啶 、 sodium hydroxide 、 硼烷四氢呋喃络合物 、 dimsylsodium 、 potassium tert-butylate 、 四丁基氟化铵 、 双氧水 、 sodium acetate 、 lithium tri-t-butoxyaluminum hydride 、 三乙胺 、 pyridinium chlorochromate 作用下, 以 四氢呋喃 、 二氯甲烷 、 叔丁醇 为溶剂, 反应 67.0h, 生成 (3β,5α,8α,9β,10α,13α,14β,17α)-3-hydroxypregnan-20-one参考文献:名称:Neurosteroid Analogues. 6. The Synthesis and GABAA Receptor Pharmacology of Enantiomers of Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulfate, Pregnenolone Sulfate, and (3α,5β)-3-Hydroxypregnan-20-one Sulfate摘要:The unnatural enantiomers of dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (1), pregnenolone sulfate (2), and (3 alpha,5 beta)-3-hydroxypregnan-20-one sulfate (3), compounds 4-6, respectively, were prepared by total steroid synthesis. The enantioselectivity of the compounds as negative modulators of the GABA(A) receptors present in cultured rat hippocampal neurons was examined using electrophysiological methods. Enantioselectivity was found for the inhibitory actions of the dehydroepiandrosterone enantiomers, The IC(50)s for compounds 1 and 4 were 11 +/- 1 and 80 +/- 14 mu M, respectively. Little, if any, enantioselectivity was found for the other two pairs of steroid sulfate inhibitors. The IC(50)s for compounds 2 and 5 were 82 +/- 12 and 76 +/- 27 mu M, respectively. The IC(50)s for compounds 3 and 6 were 39 +/- 7 and 46 +/- 2 mu M, respectively. The results suggest that the sites of action for the androstane and pregnane series of steroid sulfate blockers of GABA-mediated current are different. The observed enantioselectivity for the actions of dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate indicates that its inhibitory actions are mediated via a chiral recognition site and provides new evidence in support of the earlier hypothesis that there is a binding site for this compound on GABA(A) receptors. Conversely, the failure to observe enantioselectivity for the actions of pregnenolone sulfate and steroid sulfate 3 indicates that a chiral recognition site far these steroids does not exist on GABA(A) receptors and suggests that the effects of these compounds on this receptor's function may arise indirectly as a consequence of steroid-induced membrane perturbation.DOI:10.1021/jm980148h
文献信息
-
Total Synthesis of <i>ent</i>-Pregnanolone Sulfate and Its Biological Investigation at the NMDA Receptor作者:Vojtech Kapras、Vojtech Vyklicky、Milos Budesinsky、Ivana Cisarova、Ladislav Vyklicky、Hana Chodounska、Ullrich JahnDOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.7b03838日期:2018.2.16A unique asymmetric total synthesis of the unnatural enantiomer of pregnanolone, as well as a study of its biological activity at the NMDA receptor, is reported. The asymmetry is introduced by a highly atom-economic organocatalytic Robinson annulation. A new method for the construction of the cyclopentane D-ring consisting of CuI-catalyzed conjugate addition and oxygenation followed by thermal cyclization
-
NEUROACTIVE ENANTIOMERIC 15-, 16- AND 17-SUBSTITUTED STEROIDS AS MODULATORS FOR GABA TYPE-A RECEPTORS申请人:WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY公开号:US20150361125A1公开(公告)日:2015-12-17The present disclosure is generally directed to neuroactive enantiomeric 15-, 16- and 17-substituted steroids with additional optional substituents at carbons 3, 4, 6, 7, 10 and 13, and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, for use as, for example, modulators for GABA type-A receptors. The present disclosure is further directed to pharmaceutical compositions comprising such compounds.
-
Neuroactive enantiomeric 15-, 16- and 17-substituted steroids as modulators for GABA type-A receptors申请人:Washington University公开号:US10202413B2公开(公告)日:2019-02-12The present disclosure is generally directed to neuroactive enantiomeric 15-, 16- and 17-substituted steroids with additional optional substituents at carbons 3, 4, 6, 7, 10 and 13, and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, for use as, for example, modulators for GABA type-A receptors. The present disclosure is further directed to pharmaceutical compositions comprising such compounds.
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
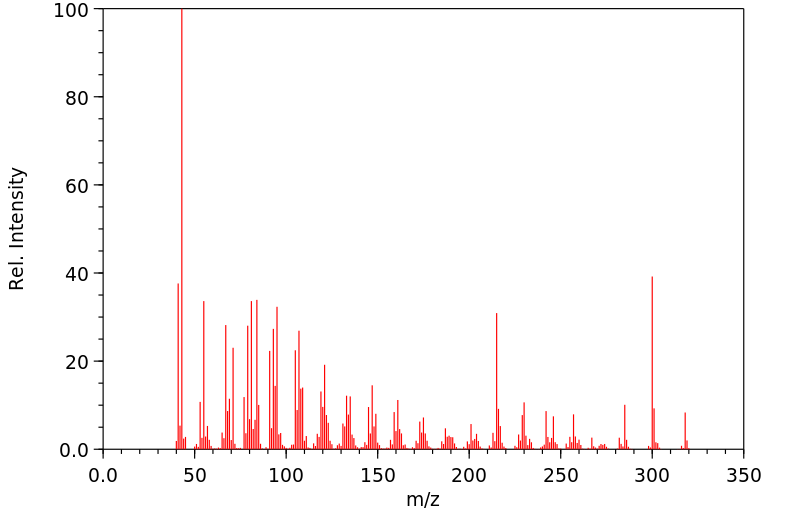
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
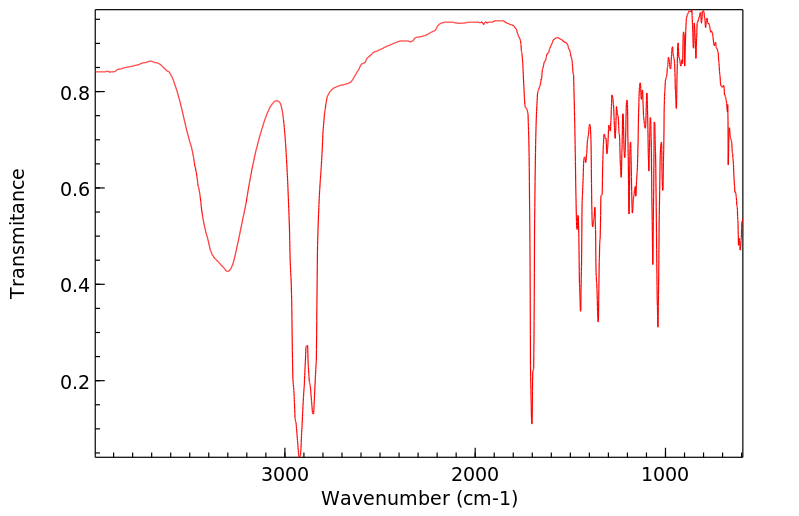
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(5β)-17,20:20,21-双[亚甲基双(氧基)]孕烷-3-酮
(5α)-2′H-雄甾-2-烯并[3,2-c]吡唑-17-酮
(3β,20S)-4,4,20-三甲基-21-[[[三(异丙基)甲硅烷基]氧基]-孕烷-5-烯-3-醇-d6
(25S)-δ7-大发酸
(20R)-孕烯-4-烯-3,17,20-三醇
(11β,17β)-11-[4-({5-[(4,4,5,5,5-五氟戊基)磺酰基]戊基}氧基)苯基]雌二醇-1,3,5(10)-三烯-3,17-二醇
齐墩果酸衍生物1
黄麻属甙
黄芪皂苷III
黄芪皂苷 II
黄芪甲苷 IV
黄芪甲苷
黄肉楠碱
黄果茄甾醇
黄杨醇碱E
黄姜A
黄夹苷B
黄夹苷
黄夹次甙乙
黄夹次甙乙
黄夹次甙丙
黄体酮环20-(乙烯缩醛)
黄体酮杂质EPL
黄体酮杂质1
黄体酮杂质
黄体酮杂质
黄体酮EP杂质M
黄体酮EP杂质G(RRT≈2.53)
黄体酮EP杂质F
黄体酮6-半琥珀酸酯
黄体酮 17alpha-氢过氧化物
黄体酮 11-半琥珀酸酯
黄体酮
麦角甾醇葡萄糖苷
麦角甾醇氢琥珀酸盐
麦角甾烷-6-酮,2,3-环氧-22,23-二羟基-,(2b,3b,5a,22R,23R,24S)-(9CI)
麦角甾烷-3,6,8,15,16-五唑,28-[[2-O-(2,4-二-O-甲基-b-D-吡喃木糖基)-a-L-呋喃阿拉伯糖基]氧代]-,(3b,5a,6a,15b,16b,24x)-(9CI)
麦角甾烷-26-酸,5,6:24,25-二环氧-14,17,22-三羟基-1-羰基-,d-内酯,(5b,6b,14b,17a,22R,24S,25S)-(9CI)
麦角甾-8-烯-3-醇
麦角甾-8,24(28)-二烯-26-酸,7-羟基-4-甲基-3,11-二羰基-,(4a,5a,7b,25S)-
麦角甾-7,22-二烯-3-酮
麦角甾-7,22-二烯-17-醇-3-酮
麦角甾-5,24-二烯-26-酸,3-(b-D-吡喃葡萄糖氧基)-1,22,27-三羟基-,d-内酯,(1a,3b,22R)-
麦角甾-5,22,25-三烯-3-醇
麦角甾-4,6,8(14),22-四烯-3-酮
麦角甾-1,4-二烯-3-酮,7,24-二(乙酰氧基)-17,22-环氧-16,25-二羟基-,(7a,16b,22R)-(9CI)
麦角固醇
麦冬皂苷D
麦冬皂苷D
麦冬皂苷 B