野百合碱 | 315-22-0
中文名称
野百合碱
中文别名
单响尾蛇毒蛋白;响尾蛇毒蛋白;农吉利碱;农吉利甲素;大叶猪尿青碱
英文名称
monocrotaline
英文别名
MCT;Monocrotalin;(1R,4R,5R,6R,16R)-5,6-dihydroxy-4,5,6-trimethyl-2,8-dioxa-13-azatricyclo[8.5.1.013,16]hexadec-10-ene-3,7-dione
CAS
315-22-0
化学式
C16H23NO6
mdl
——
分子量
325.362
InChiKey
QVCMHGGNRFRMAD-XFGHUUIASA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:204 °C (dec.) (lit.)
-
比旋光度:-54.8o (C=5 IN CHLOROFORM)
-
沸点:463.55°C (rough estimate)
-
密度:1.1512 (rough estimate)
-
溶解度:可溶于DMSO(加热时高达50mg/ml)、乙醇(加热时高达10mg/ml)或氯仿等有机溶剂(高达50mg/ml)
-
LogP:-0.370 (est)
-
颜色/状态:Prisms from absolute alcohol
-
味道:Bitter
-
蒸汽压力:7.5X10-13 mm Hg @ 25 °C /Estimated/
-
稳定性/保质期:
VOLATILITY VERY SLIGHT; STABLE FOR LONG PERIODS AT ROOM TEMP IN CLOSED CONTAINERS
-
旋光度:Specific optical rotation (ethanol): -15 deg @ 20 °C/D
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of /nitrogen oxides/.
-
解离常数:pKa = 5.83 /Estimated/
-
碰撞截面:172.9 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: TW, Method: calibrated with polyalanine and drug standards]
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-0.7
-
重原子数:23
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:3.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.75
-
拓扑面积:96.3
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:7
ADMET
代谢
使用毒参碱的研究已经确认,通过大鼠肝微粒体混合功能氧化酶系统形成了吡咯代谢物。去氢毒参碱(毒参碱吡咯)具有高度细胞毒性,能产生与原生物碱类似的心肺、心血管和肝脏病变。它是一种高度反应性的烷基化剂,在细胞内形成后,会立即与细胞成分反应,产生可溶或结合的次级代谢物,或者水解为去氢氨基醇,去氢雷特奈酸。
Studies with monocrotaline have confirmed the formation of pyrrolic metabolites by the mixed-function oxidase system of the microsomal fraction of rat liver. Dehydromonocrotaline (monocrotaline pyrrole) is highly cytotoxic, producing pulmonary, cardiac, vascular and hepatic lesions similar to those produced by the parent alkaloid. It is a highly reactive alkylating agent which, on formation within the cell, reacts immediately with cell constituents to give soluble or bound secondary metabolites or hydrolyzes to the dehydroaminoalcohol, dehydroretronecine.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
使用预先用苯巴比妥处理的大鼠肝脏微粒体,所测试的13种生物碱均被代谢为N-氧化物和吡咯形成。这两条途径似乎是独立的。N-氧化物与吡咯代谢物的比例因酯的类型而异:对于开放式二酯生物碱最高,对于12元大环二酯和单酯最低。夹竹桃碱是其中一种被测试的物质。
Using microsomes from livers of phenobarbital-pretreated male rats, all 13 alkaloids tested were metabolized to n-oxide and pyrrole formation. The 2 pathways appeared to be independent. Ratio of n-oxide to pyrrolic metabolites varied, depending on type of ester: it was highest for open diester alkaloids and lowest for 12-membered macrocyclic diesters and for monoesters. Monocrotaline was one of those tested.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
对吡咯烷生物碱,(14)C 单角花碱的代谢进行了比较研究,使用了大鼠和豚鼠的肝微粒体。 ... 在豚鼠中,酯酶水解占代谢的92%;大鼠没有显示出酯酶活性。这个结果可能解释了豚鼠对吡咯烷生物碱毒性的抵抗。脱氢吡咯被发现在豚鼠中是主要的吡咯代谢物,尽管比色分析表明在大鼠微粒体培养中存在多个吡咯基团。
The comparative metabolism of the pyrrolizidine alkaloid, (14)C monocrotaline, was studied using rat and guinea pig hepatic microsomes. ... Esterase hydrolysis accounted for 92% of the metabolism in the guinea pig; the rat displayed no esterase activity. This result may explain the guinea pig's resistance to pyrrolizidine alkaloid toxicity. Dehydropyrrole was found to be the major pyrrolic metabolite in the guinea pig, although colorimetric analysis indicated multiple pyrrolic moieties in the rat microsomal incubations.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
这份报告表明,雄性大鼠尿液中排出了单叶孕烷和千里光碱的Ehrlich试剂阳性代谢物,这种代谢物是(+/-)-6,7-二氢-7-羟基-1-羟甲基-5H-吡咯里西啶的N-乙酰半胱氨酸结合物……这一发现提示,在肝脏生成的吡咯烷生物碱的反应性代谢物能够以谷胱甘肽结合物或巯基尿酸的形式,在循环系统的水环境中存活。
This report demonstrates that an Ehrlich reagent positive metabolite of monocrotaline and senecionine is excreted in the urine of male rats as an N-acetylcysteine conjugate of (+/-)-6,7-dihydro-7-hydroxy-1-hydroxymethyl-5H-pyrrolizine ... This finding suggests that reactive metabolites of pyrrolizidine alkaloids generated in the liver can survive the aqueous environment of the circulatory system as glutathione conjugates or mercapturic acids.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
没有关于人类的数据。有充分的证据表明对动物具有致癌性。总体评估:2B组:该物质可能对人类具有致癌性。
No data are available in humans. Sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity in animals. OVERALL EVALUATION: Group 2B: The agent is possibly carcinogenic to humans.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
国际癌症研究机构致癌物:野百合碱
IARC Carcinogenic Agent:Monocrotaline
来源:International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC)
毒理性
国际癌症研究机构(IARC)致癌物分类:2B组:可能对人类致癌
IARC Carcinogenic Classes:Group 2B: Possibly carcinogenic to humans
来源:International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC)
毒理性
国际癌症研究机构专著:第10卷:(1976年)一些天然存在的物质
IARC Monographs:Volume 10: (1976) Some Naturally Occurring Substances
来源:International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC)
毒理性
职业性肝毒素 - 第二性肝毒素:在职业环境中的毒性效应潜力是基于人类摄入或动物实验的中毒案例。
Occupational hepatotoxin - Secondary hepatotoxins: the potential for toxic effect in the occupational setting is based on cases of poisoning by human ingestion or animal experimentation.
来源:Haz-Map, Information on Hazardous Chemicals and Occupational Diseases
吸收、分配和排泄
...单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次静脉注射单次
After sc administration of monocrotaline /in rats/, 50-70% of the dose was found in urine as unchanged monocrotaline... monocrotaline (or metabolite) concentration were highest in the liver, kidney and stomach.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
吡咯里西啶生物碱单体rotaline已被证明在大鼠中可引起肝坏死和肺动脉高压。为了更好地理解其作用机制,进行了组织分布和共价结合研究,在给予(14)C标记的单体rotaline(60 mg/kg,200微Ci/kg,sc)后4小时和24小时进行。对于4小时的研究,单体rotaline当量在红细胞、肝脏、肾脏、肺和血浆中的水平分别为85、74、67、36和8 nmol/g组织,而共价结合水平分别为上述组织的125、132、39、64、44 pmol/mg蛋白质。24小时的组织分布水平分别为红细胞、肝脏、肾脏、肺和血浆的49、25、9、10、2 nmol/g组织,而肝脏、肾脏和肺的共价结合分别为74、28和55 pmol/mg蛋白质。我们还研究了(14)C标记的单体rotaline(60 mg/kg,10微Ci/kg,iv)的动力学,结果显示放射性物质迅速消除,约7小时内注入的放射性物质在尿液和胆汁中回收了大约90%。血浆中的放射性水平从113 nmol/g的单体rotaline当量降至7小时的11 nmol/g,而红细胞水平在同一时间点从144降至仅81 nmol/g。红细胞中单体rotaline当量的明显保留表明,这个器官可能充当从肝脏到其他器官(包括肺)的代谢物载体,并可能在肺毒性中发挥作用。
The pyrrolizidine alkaloid monocrotaline has been shown to cause hepatic necrosis and pulmonary hypertension in the rat. To better understand the mechanism of action, tissue distribution and covalent binding studies were conducted at 4 and 24 hr following administration of (14)C monocrotaline (60 mg/kg, 200 microCi/kg, sc). For the 4 hr study, the levels of monocrotaline equivalents were 85, 74, 67, 36, and 8 nmol/g of tissue for RBC, liver, kidney, lung, and plasma, respectively, while the covalent binding levels were 125, 132, 39, 64, 44 pmol/mg of protein for tissues as listed above. The 24 hr tissue distribution levels were 49, 25, 9, 10, 2 nmol/g of tissue for RBC, liver, kidney, lung, and plasma, respectively, while covalent binding was 74, 28, and 55 pmol/mg of protein for liver, kidney, and lung, respectively. We also studied the kinetics of (14)C monocrotaline (60 mg/kg, 10 microCi/kg, iv), which demonstrated rapid elimination of radioactivity with approximately 90% recovery of the injected radioactivity in the urine and bile by 7 hr. The plasma levels of radioactivity dropped from 113 nmol/g of monocrotaline equivalents to 11 nmol/g at 7 hr while RBC levels decreased from 144 to only 81 nmol/g at the same time point. The apparent retention of monocrotaline equivalents in the RBC suggests that this organ may act as the carrier of metabolites from the liver to other organs including the lung and may play a role in the pulmonary toxicity.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
危险等级:6.1(b)
-
危险品标志:T
-
安全说明:S36/37/39,S45
-
危险类别码:R25
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:29399990
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1544 6.1/PG 3
-
包装等级:III
-
危险类别:6.1(b)
-
危险标志:GHS06,GHS08
-
危险性描述:H301,H351
-
危险性防范说明:P281,P301 + P310
SDS
制备方法与用途
野百合碱概述
野百合碱是从豆科植物农吉利及大叶猪屎青中提取的一种生物碱,外观为白色结晶粉末,微有异臭且味苦。它微溶于水,溶于甲醇和无水乙醇,并易溶于氯仿。熔点为196~198℃。这种生物碱是一种具有致突变、致癌作用的肝毒性倒千里光裂碱型吡咯里西啶生物碱,临床常用其枸橼酸盐。野百合碱对多种肿瘤有抑制作用,被认为是一种烷化剂,可通过烃化DNA发挥抗癌效应。
药动学给药后,主要分布于肝、肾、胃等器官组织中。大部分药物在24小时内以原型从尿中排出体外,在肝脏中的存留时间较长。
用途野百合碱主要用于局部或外敷治疗皮肤癌,如皮肤鳞状细胞癌和基底细胞癌疗效较佳,也可用于宫颈癌、阴茎癌的局部注射。但对急性白血病全身应用时肝毒性较大而被废弃。

不良反应全身用药时,其毒性较大,主要表现为肝脏损害,可引起肝肿大、门脉循环障碍和腹水;其他还有消化道反应、骨髓抑制及泌尿道刺激。局部用药的毒性则相对较小。
注意事项再生障碍性贫血、肝损害、肾功能不良者、孕妇禁用本品,哺乳期妇女应慎用。
该概述、不良反应和注意事项由Chemicalbook的侍艳编辑整理(2016-01-13)。
化学性质野百合碱微溶于水,可溶于甲醇和无水乙醇,并易溶于氯仿。它来源于豆科植物大猪屎豆。
用途用于含量测定、鉴定及药理实验等。
野百合碱是一种吡咯里西啶生物碱,常用于诱导大鼠肺部疾病。在临床上主要用于治疗皮肤鳞状细胞癌和基底细胞癌,对急性白血病、子宫颈癌也有一定疗效。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— monocrotaline N-oxide 35337-98-5 C16H23NO7 341.361 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— Spectabilin 520-55-8 C18H25NO7 367.399 —— Crobarbatine 49679-23-4 C15H21NO5 295.335 —— monocrotaline N-oxide 35337-98-5 C16H23NO7 341.361 —— 7,9-di-O-acetylretronecine 25471-78-7 C12H17NO4 239.271
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:野百合碱 在 palladium on activated charcoal barium dihydroxide 、 氢气 作用下, 以 乙醇 、 水 为溶剂, 反应 3.0h, 生成 (1R,7S,8R)-7-(羟基甲基)-2,3,5,6,7,8-六氢-1H-吡咯里嗪-1-醇参考文献:名称:Ipomoea hederifolia 及相关物种的吡咯里西啶生物碱摘要:摘要 最近从番薯中分离得到的新型吡咯里西啶生物碱(ipangulines)的共同碱不是turneforcidine,而是它的1β-差向异构体platynecine。从 I. hederifolia 地上部分分离出三种新型 ipangulines 并鉴定为 9-O -[2-hydroxy-3-(2-acetoxy)-2-methylbutyryl]-7-O-salicyloylplatynecine (ipanguline B 2 ), 9 -O -[2-羟基-3-(2-甲基丁酰氧基)-2-甲基丁酰]-platynecine (ipanguline D 10 ) 和 9-O -salicyloylplatynecine (ipanguline D 11 )。全面的 GC-质谱分析还揭示了种类繁多的 >38 铂金单酯和二酯。它们被分类为 ipangulines A(具有一个苯乙酸部分的二酯)、ipangulinesDOI:10.1016/s0031-9422(97)01082-0
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Synthesis of monocrotaline by nucleophilic macrolactonization摘要:DOI:10.1021/jo00226a045
文献信息
-
N-substituted benzothiophenesulfonamide derivatives申请人:TOA EIYO Ltd.公开号:US20030229126A1公开(公告)日:2003-12-11The present invention relates to an N-substituted benzothiophenesulfonamide derivative or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof and applications thereof. Furthermore, it provides an agent for preventing or treating cardiac or circulatory disease and so on caused by abnormal increase of production of angiotensin II or endothelin I based on chymase activity, or by activation of mast cell, and an agent for preventing adhesion after surgery, wherein the agent has a selective inhibitory action on chymase.
-
PROCESS FOR THE SYNTHESIS OF AMINAPHTONE申请人:LABORATORI BALDACCI SPA公开号:US20140323747A1公开(公告)日:2014-10-30The present invention concerns a new process for the synthesis of aminaphtone, which makes use of non-toxic solvents and reagents, under mild reaction and temperature conditions. The aminaphtone obtained with the method of the present invention also has a purity of at least 98% in weight. The method comprises the following steps: a) epoxidating menadione 1 to provide epoxide 2, b) acidifying epoxide 2 to provide hydroxynaphthoquinone 3, c) esterifying between hydroxynaphthoquinone 3 and 4-aminobenzoyl chloride to obtain compound 4, and d) reducing compound 4 in the presence of a reducing agent in water to obtain aminaphtone.
-
5-Substituted isoquinoline derivatives申请人:Yamada Rintaro公开号:US20050020623A1公开(公告)日:2005-01-27A compound represented by the following formula (1) or a salt thereof: wherein R 1 represents hydrogen atom, a halogen atom and the like; R 2 represents hydrogen atom, a halogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group and the like; and R 3 represents —O—X—C(A 1 )(A 11 )—C(A 2 )(A 2l )—N(A 3l )(A 3 )(X represents propylene group etc., A 11 and A 21 represent hydrogen atom, or a C 1-6 alkyl group, A 31 represents a C 1-6 alkyl group substituted with hydroxyl group, or hydrogen atom, and A 1 , A 2 , and A 3 represent hydrogen atom, a C 1-6 alkyl group and the like) and the like, which has an inhibitory activity on the phosphorylation of myosin regulatory light chain, and is useful for treatment of diseases relating to contraction of various cells and the like.
-
Nitrogen-containing tricyclic compounds申请人:Yamada Rintaro公开号:US20060247266A1公开(公告)日:2006-11-02A novel compound represented by the following formula (1) or a salt thereof [wherein R 1 , R 5 , R 6 , R 7 , and R 8 represent hydrogen atom, a halogen atom, hydroxyl group, an alkyl group, an alkenyl group and the like; X 1 . . . X 2 represents —CH(R 2 )—CH(R 3 )—, —CH(R 2 )—CH(R 3 )—CH(R 4 )—, —C(R 2 )═C(R 3 )—, or —C(R 2 )═C(R 3 )—CH(R 4 )—(R 2 , R 3 , and R 4 represent hydrogen atom, or an alkyl group); A 1 , A 11 , A 2 , and A 21 represent hydrogen atom, or an alkyl group; Y represents —CH(A 3 )-, —CH(A 3 )-C(A 4 )(A 41 )-, —CH(A 3 )-C(A 4 )(A 41 )-C(A 5 )(A 51 )-, or a single bond (A 3 , A 4 , A 41 , A 5 , and A 51 represent hydrogen atom, or an alkyl group), and Z represents hydroxyl group, or —N(A 6 )(A 61 )(A 6 represents hydrogen atom, or an alkyl group, and A 61 represents hydrogen atom, an alkyl group, a substituted alkyl group and the like)], having an action of potently inhibiting phosphorylation of myosin regulatory light chain.以下式(1)表示的新化合物或其盐[其中R1、R5、R6、R7和R8代表氢原子、卤素原子、羟基、烷基、烯基等;X1...X2代表—CH(R2)—CH(R3)—、—CH(R2)—CH(R3)—CH(R4)—、—C(R2)=C(R3)—或—C(R2)=C(R3)—CH(R4)—(R2、R3和R4代表氢原子或烷基);A1、A11、A2和A21代表氢原子或烷基;Y代表—CH(A3)-、—CH(A3)-C(A4)(A41)-、—CH(A3)-C(A4)(A41)-C(A5)(A51)-或单一键(A3、A4、A41、A5和A51代表氢原子或烷基),Z代表羟基或—N(A6)(A61)(A6代表氢原子或烷基,A61代表氢原子、烷基、取代烷基等)]具有强烈抑制肌球蛋白调节轻链磷酸化的作用。
-
NEPRILYSIN INHIBITORS申请人:Hughes Adam D.公开号:US20130330366A1公开(公告)日:2013-12-12In one aspect, the invention relates to compounds having the formula XII: where R a , R b , R 2 , R 7 , and X are as defined in the specification, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. The compounds described herein are prodrugs of compounds having neprilysin inhibition activity. In another aspect, the invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising these compounds; methods of using these compounds; and processes and intermediates for preparing these compounds.在一方面,本发明涉及具有公式XII的化合物: 其中R a ,R b ,R 2 ,R 7 和X如说明书中所定义,或其药用可接受的盐。所述的化合物是具有中性粒细胞弹性蛋白酶抑制活性的化合物的前药。在另一方面,本发明涉及包含这些化合物的药物组合物;使用这些化合物的方法;以及制备这些化合物的过程和中间体。
表征谱图
-
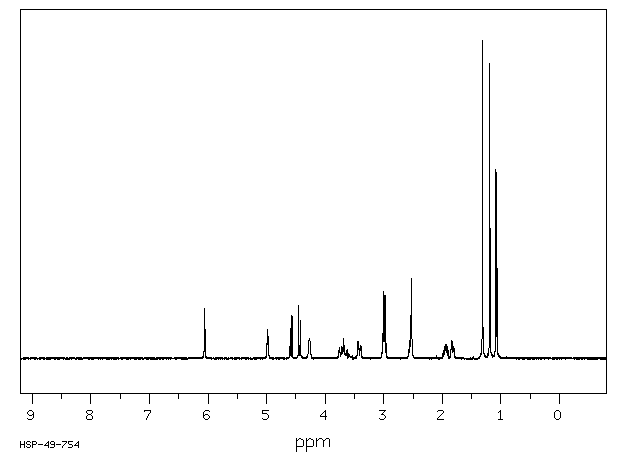
氢谱1HNMR
-
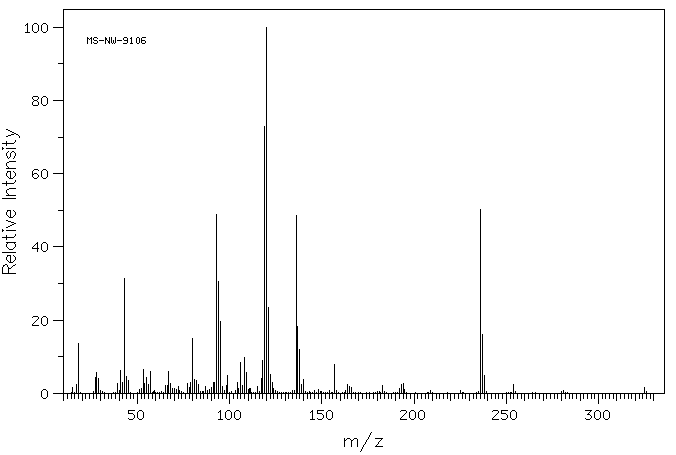
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
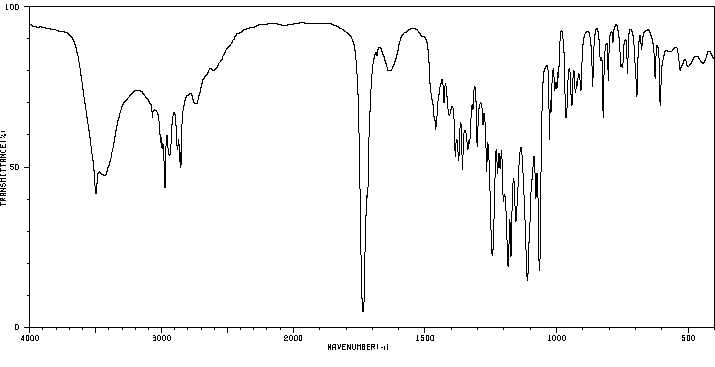
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
野百合碱 N-氧化物
野百合碱
螺[环氧乙烷-2,1'-吡咯里嗪]
脱氢野百合碱
矮陀陀酰胺碱
盐酸西那西林
灰毛束草碱
毛束草碱N-氧化物
毛束草碱
暗黄猪屎豆碱
去氢毛果天芥菜碱
去氢天芥菜碱
去氢倒千里光裂碱
去氢倒千里光裂碱
去氢倒千里光碱
克拉沙霉素B
克拉沙霉素A
N-甲基-N-[(2R,3R,3aS,4S,6alphaS)-2,3,3a,6alpha-四氢-2,4-甲桥-4H-呋喃并[3,2-b]吡咯-3-基]-乙酰胺
N-(3-羟基-2,4-二甲基苯基)乙酰胺
8-氧杂-5-氮杂三环[5.1.1.01,5]壬-2,6-二烯
8-氧杂-2-氮杂三环[5.2.1.02,6]癸-1(9),3,5-三烯
7-羟基-6,7-二氢-5H-吡咯里嗪-1-甲醛
7-(羟基甲基)-3H-吡咯里嗪-3-酮
7-(甲氧基羰基)-6,7-二氢-5H-吡咯啉-1-羧酸
5H-吡咯并[2,1-a]异吲哚,5a,6,7,8-四氢-
3H-吡咯里嗪-3,5(2H)-二硫酮
3-甲酰基-5,6,7,8-四氢中氮茚-2-羧酸
3-氨基-N-[2,5-二氢-5-羰基-1-(2,4,5-三氯苯基)-1H-吡唑-4-基]苯酰胺
3-氧代吡咯里嗪-2-羧酸乙酯
3-氧代-3H-吡咯里嗪-2-甲酰氯
3-氧代-2,3-二氢-1H-吡咯里嗪-5-羧酸
3-氧代-2,3,5,7a-四氢-1H-吡咯里嗪-7-甲醛
3-氧-3氢-吡咯嗪-2-甲酸
3-(2,6-二乙酰基-3,7-二甲基-5H-吡咯里嗪-1-基)丙酸
2H,3H-氧杂环丁烷并[2,3-a]吡咯里嗪
2-(6-乙基-2,3-二氢-1H-吡咯里嗪-1-基)苯胺
2,5-二(叔-壬基二硫代)-1,3,4-噻二唑
2,3-二氢-7-甲基-1H-吡咯里嗪-1-酮
2,3-二氢-7-(羟基甲基)-1H-吡咯里嗪-1-酮
2,3-二氢-1H-吡咯里嗪-7-羧酸
2,3-二氢-1H-吡咯里嗪-7-甲醇
2,3-二氢-1H-吡咯里嗪-7-甲腈
2,3-二氢-1H-吡咯里嗪-1-胺
2,3-二氢-1H-吡咯里嗪-1-甲腈
2,3-二氢-1H-吡咯嗪-5-甲醛
2,3-二氢-1H-吡呤-1,7-二羧酸
2,3-二氢-(6ci,7ci,8ci,9ci)-1H-吡咯里嗪-1-酮
2,3,5,7a-四氢-1H-吡咯烷
2,2-二氯-1-(3H-吡咯里嗪-5-基)乙酮
1H-吡咯里嗪-2(3H)-酮