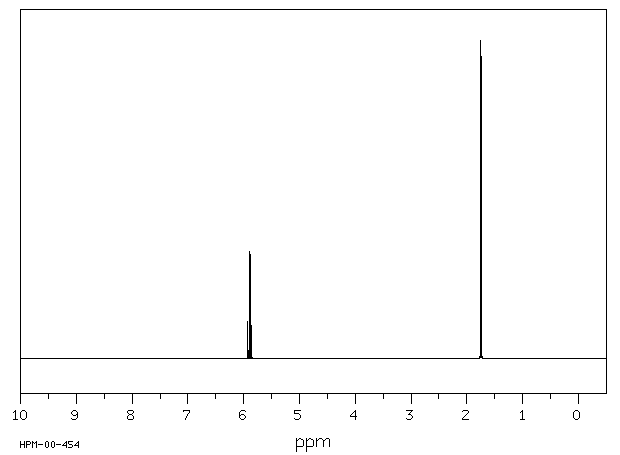
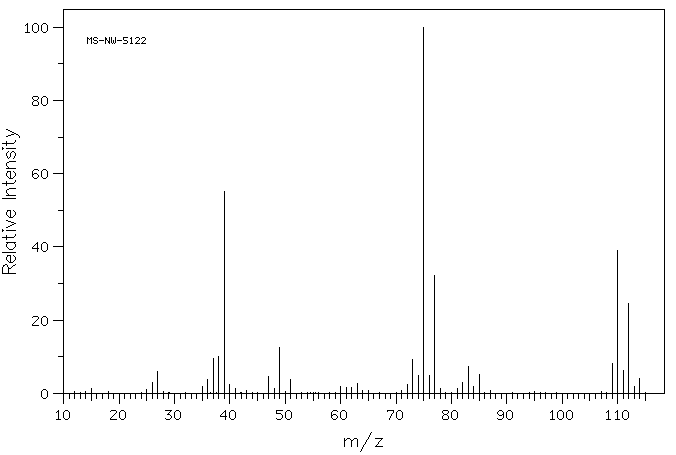
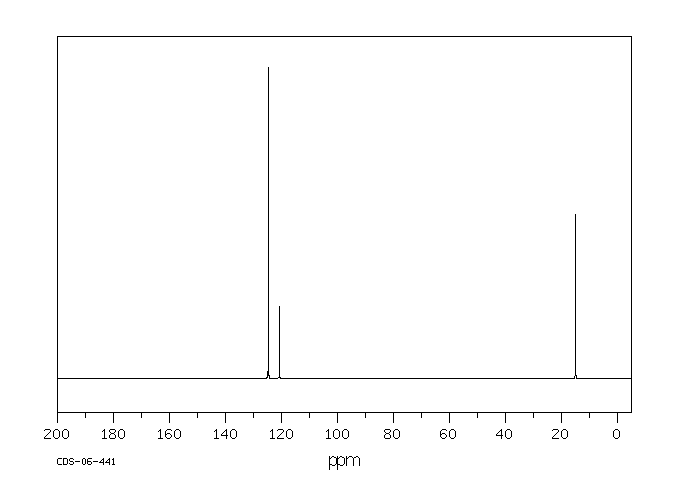
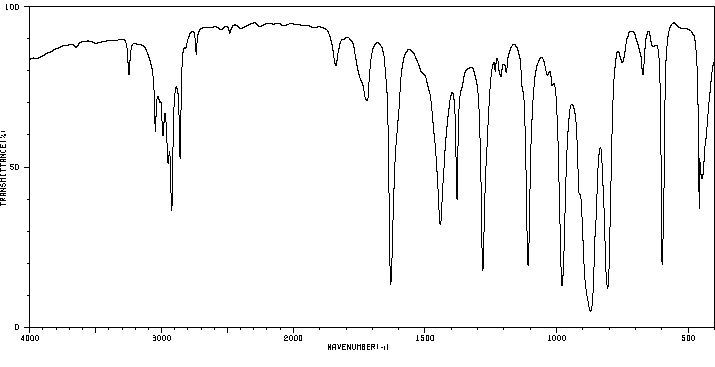
代谢
1,2-D在大鼠体内的代谢会导致形成一种巯基尿酸结合物,主要通过尿液排出。提出的反应中间体包括1,2-环氧丙烷;这个中间体被怀疑是1,2-D致突变效应的原因。谷胱甘肽途径被视为解毒机制,而在高浓度下可能由于这些途径的饱和导致肝脏和肾脏毒性。
Metabolism of 1,2-D in the rat results in the formation of a mercapturic acid conjugate excreted largely in the urine. Proposed reactive intermediates include 1,2-epoxypropane; this intermediate is suspected of being responsible for mutagenic effects of 1,2-D. Glutathione pathways are seen as a detoxification mechanisms, & liver & kidney toxicity at high concns may be due to saturation of these pathways.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)