2-氰基丙烯酸甲酯 | 137-05-3
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:-40 °C
-
沸点:bp 48-49°
-
密度:nD25 1.443. d20 1.1044
-
LogP:0.24 at 25℃ and pH7
-
物理描述:Methyl 2-cyanoacrylate is a clear slightly yellow liquid. (NTP, 1992)
-
颜色/状态:Clear, colorless liquid
-
气味:Strong, acrid odor
-
闪点:82.78 °C (closed cup)
-
溶解度:less than 1 mg/mL at 72° F (NTP, 1992)
-
蒸汽密度:Relative vapor density (air = 1): 3.8
-
蒸汽压力:0.2 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
稳定性/保质期:
Liquid /dries/ within 15-45 seconds without aid of catalysts, heat, or solvent evaporation.
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of /nitrogen oxides and CN-/.
-
粘度:2.2 cP at 25 °C
-
表面张力:37.41 dynes/cm
-
气味阈值:Between 1 & 3 ppm
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.4430 at 25 °C/D
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0.6
-
重原子数:8
-
可旋转键数:2
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.2
-
拓扑面积:50.1
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:3
ADMET
安全信息
-
职业暴露等级:B
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: 2 ppm (8 mg/m3), STEL: 4 ppm (16 mg/m3)
-
危险品标志:Xi
-
危险类别码:R36/37/38
-
RTECS号:AS7000000
-
海关编码:2926909090
-
危险性防范说明:P210,P264,P280,P305+P351+P338,P337+P313
-
危险性描述:H319,H227
-
储存条件:库房应保持低温、通风、干燥,并注意防火,同时要与强氧化剂分开存放。
SDS
制备方法与用途
这是一种无色液体,沸点为47-48℃(0.267kPa),相对密度1.1044(27/4℃),折光率1.443(25℃)。它溶于乙醚、氯仿、甲基氯化碳、苯和二氧六环,但不溶于甲醇或乙醇,在暴露于空气中时会逐渐聚合。
用途该物质具有短暂聚合的特点,并且具有强大的粘着力,用作胶粘剂和聚合物的单体。它可用于皮肤手术切口及新鲜伤口的粘合。
生产方法2-氰基丙烯酸甲酯由氰乙酸甲酯通过聚合、裂解获得。具体步骤为:将氰乙酸甲酯(见24530)和哌啶混合,然后加入预热至80℃的甲醛中,并保温搅拌反应1小时。随后将反应液转移至冰水中进行冷却,经过球磨、粉碎、洗涤及干燥后得到聚2-氰基丙酸甲酯。接着将此产物与对苯二酚、五氧化二磷和磷酸三甲酚加入反应锅中,在微负压条件下通入二氧化硫,并加热到230℃以实现裂解过程。再次加入对苯二酚、五氧化二磷及二氧化硫,减压蒸馏,收集80℃(0.67kPa)的馏分,即得2-氰基丙烯酸甲酯。此物质需在0.01%对苯二酚密封保存。
类别易燃液体
毒性分级高毒
急性毒性口服 - 大鼠 LD50: 1600 毫克/公斤;吸入 - 大鼠 LC50: 101 ppm/6小时
刺激数据皮肤 - 兔子 0.5 毫克/4小时,重度刺激
爆炸物危险特性为可燃性液体,在79℃以上会与空气形成爆炸性混合物。
可燃性危险特性易燃;高温时释放有毒氧化氮气体
储运特性库房低温、通风及干燥环境储存。防火,并将此物质存放在远离强氧化剂的位置。
灭火剂小火使用化学干粉、二氧化碳或普通泡沫,以及洒水设备扑灭。大火情况下则需使用洒水设备、水雾或普通泡沫进行灭火。
职业标准时间加权平均容许浓度(TWA): 8 毫克/立方米;短时接触容许浓度(STEL): 18 毫克/立方米
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 氰乙酸甲酯 Methyl cyanoacetate 105-34-0 C4H5NO2 99.0892 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 1,10-decanediol bis-2-cyanoacrylate 60755-41-1 C18H24N2O4 332.4 癸基2-氰基丙-2-烯酸酯 n-decyl 2-cyanoacrylate 3578-07-2 C14H23NO2 237.342
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:5,6-二氢-4 H -1,3,5-二噻嗪,2,3-二氢-6-thioxo-6 H -1,3-噻嗪和6-氨基-1,3-二硫辛的合成摘要:衍生自含有活性亚甲基或磺酰胺基,二硫化碳和氢氧化钠或氢氧化钾的化合物的二硫醇盐(1)或(2)与甲醛和伯胺进行曼尼斯(Mannish)反应形成5,6-二氢-1, 3,5-二噻嗪(3)或(4)。衍生自乙酰乙酸乙酯的二硫醇盐(12)在上述条件下环化为2,3-二氢-3,4-二甲基-6-硫代氧-6 H -1,3-噻嗪-5-羧酸乙酯(18)。衍生自氰基乙酸酯的二硫醇盐(20)或衍生自苯乙酮的二硫醇盐(10)与甲醛和氰基乙酸酯或2-氰基丙烯酸酯相互作用形成6-氨基-1,3-二硫辛(26)或亚氨基二噻吩(28) 。6-氨基-2-[((1-氰基-1-乙氧基羰基)亚甲基] -1,3-二硫基-5-羧酸甲酯(26; R 1 = Et,R 2= Me)与脂族酰氯形成N-酰基衍生物。在氧化时,二硫精(26; R 1= Et,R 2= Me)收缩成2-氰基-2-(4-氰基-1,3-二硫代噻吩-5-亚烷基)乙酸乙酯(31)。DOI:10.1039/p19800001038
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Derivatives of fatty acids and method of preparing same摘要:公开号:US02391251A1
文献信息
-
Conjugatively Stabilized Bridgehead Olefins: Formation and Reaction of Remarkably Stable Homoadamant-3-enes Substituted with Phenyl and Methoxycarbonyl Groups作者:Masatomi Ohno、Motohiro Itoh、Masami Umeda、Ryoji Furuta、Kazumoto Kondo、Shoji EguchiDOI:10.1021/ja953977q日期:1996.1.1Conjugatively stabilized double bonds were formed at the bridgehead of homoadamantane by way of the 1,2-carbon shift of adamantylcarbene (-carbenoid) intermediates generated from decomposition of the diazo precursors (1-adamantyl)diazophenylmethane (7) and methyl (1-adamantyl)diazoacetate (10). Decomposition to 4-phenyl- and 4-methoxycarbonyl-substituted homoadamant-3-enes 1 and 2 was much more efficient通过重氮前体 (1-金刚烷基) 重氮苯基甲烷 (7) 和甲基 (1-金刚烷基) 分解产生的金刚烷基卡宾 (-carbenoid) 中间体的 1,2- 碳位移,在高金刚烷的桥头处形成了共轭稳定的双键。 )重氮乙酸酯 (10)。在二氯甲烷中用 Rh2(OAc)4 催化分解为 4-苯基-和 4-甲氧基羰基取代的高金刚烷-3-烯 1 和 2 比光解或热解(FVP;在 7 的情况下,茚满-稠合高金刚烷是通过苯基卡宾重排然后插入桥连亚甲基产生的)。在 Rh 催化中,7 和 10 在己烷中和与 Rh2(NHCOCH3)4 的反应没有促进 1 和 2 的形成,这表明 Rh-卡宾配合物的极化结构参与了 1,2-碳位移。
-
Synthesis of adamantane derivatives. LXVIII. Cycloaddition reactions of 2-(1-adamantyl)-1,3-butadiene and -heterodienes.作者:TADASHI SASAKI、KAZUO SHIMIZU、MASATOMI OHNODOI:10.1248/cpb.32.1433日期:——2-(1-Adamantyl)-1, 3-butadiene (1) was prepared by p-toluenesulfonic acid-catalyzed dehydration of the corresponding allyl alcohol 5. The Diels-Alder reactions of 1 with a variety of dienophiles proceeded smoothly to give adamantane-substituted six-membered carbo-and heterocycles. Similarly, [4+2] cycloaddition reactions of adamantane-bearing heterodienes afforded some adamantyl-oxazines.
-
Synthesis and X-ray structural study of 1-adamantylmethyl 2-cyanoacrylate and 1,10-decanediol bis-2-cyanoacrylate作者:V. N. Khrustalev、O. V. Shishkin、S. V. Lindeman、Yu. T. Struchkov、M. A. Galkina、Yu. G. GololobovDOI:10.1007/bf01430733日期:1996.9by the reaction of 2-cyanoacryloyl chloride with 1-adamantylmethanol . 1,10-Decanediol bis-2-cyanoacrylate (2) was synthesized by transesterification of methyl 2-cyanoacrylate with 1,10-decanediol. Esters1 and2 were studied by X-ray structural analysis.
-
6-alkoxy-3,4-dihydro-2h-pyrans from substituted α,β-unsaturated esters作者:H.K. Hall、H.A.A. Rasoul、M. Gillard、M. Abdelkader、P. Nogues、R.C. SentmanDOI:10.1016/s0040-4039(00)86901-4日期:1982.1Cycloaddition reactions of substituted α,β-unsaturated esters with various electronich olefins lead to 6-alkoxy-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyrans.取代的α,β-不饱和酯与各种电子烯烃的环加成反应会生成6-烷氧基-3,4-二氢-2H-吡喃。
-
Rationalization of Dye Uptake on Titania Slides for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells by a Combined Chemometric and Structural Approach作者:Valentina Gianotti、Giada Favaro、Luca Bonandini、Luca Palin、Gianluca Croce、Enrico Boccaleri、Emma Artuso、Wouter van Beek、Claudia Barolo、Marco MilanesioDOI:10.1002/cssc.201402194日期:2014.11model photosensitizer (D5) for application in dye‐sensitized solar cells has been studied by a combination of XRD, theoretical calculations, and spectroscopic/chemometric methods. The conformational stability and flexibility of D5 and molecular interactions between adjacent molecules were characterized to obtain the driving forces that govern D5 uptake and grafting and to infer the most likely arrangement
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
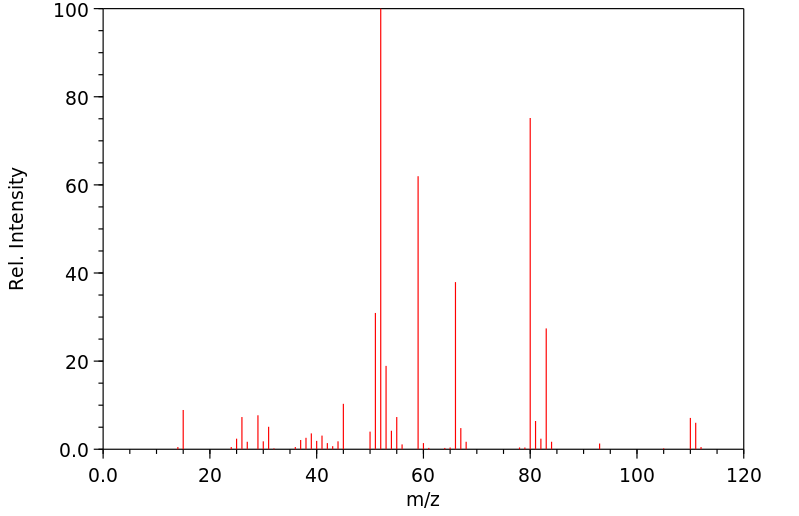
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
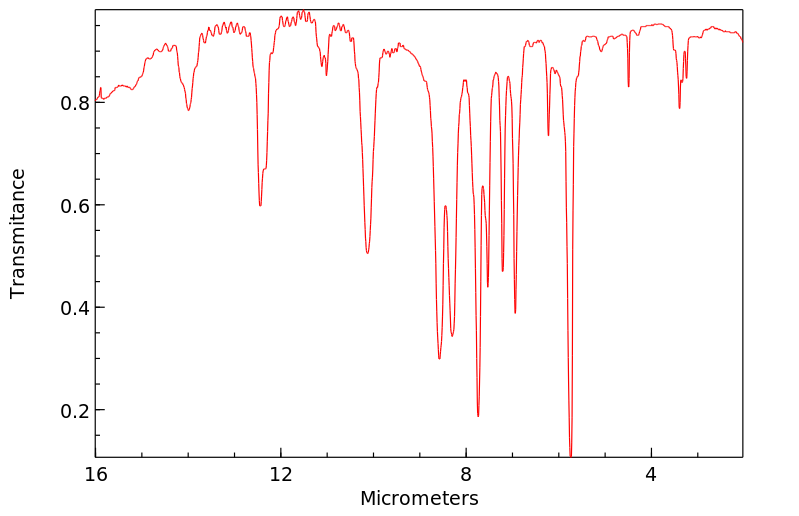
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息