三氟胺氧化物 | 13847-65-9
中文名称
三氟胺氧化物
中文别名
——
英文名称
trifluoroamine oxide
英文别名
Nitrogen fluoride oxide
CAS
13847-65-9
化学式
F3NO
mdl
——
分子量
87.0013
InChiKey
UDOZVPVDQKQJAP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:-161°C
-
沸点:-87.5°C
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.3
-
重原子数:5
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:18.1
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:4
SDS
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Gupta; Kirchmeier, Robert L.; Shreeve, Jean'ne M., Inorganic Chemistry, 1990, vol. 29, # 3, p. 573 - 574摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Oxidative Chemical Oxygenation of NF3 and Novel Synthesis of NF3O摘要:DOI:10.1021/ja00127a033
-
作为试剂:描述:2,2,6,6-四甲基哌啶 在 三氟胺氧化物 、 五氟化磷 作用下, 以 二氯甲烷 为溶剂, 反应 24.0h, 生成 1,1-dimethyl-2-(propan-2-ylidene)cyclopentane compound with 2,2,2,2-tetramethyl-2l7-propane (1:1)参考文献:名称:三氟胺氧化物的反应:无环和环状氟胺和 N-亚硝胺的途径摘要:制备去氟胺和去亚硝基胺二类无环R 2 NF 和R 2 NNO (R=CH 3 ,C 2 H 5 ,nC 3 H 7 ,iC 3 H 7 ,nC 4 H 9 ,iC 4 H 9 ,cC 6 H 11 ) et de fluoroamines et nitrosoamines 杂环饱和 RNF et RNNO (R=cC 4 H 8 ,cC 5 H 10 ,(CH 3 ) 2 -2,6-cC 5 H 8 ,(CH 3 ) 4 -2,2,6 ,6-cC 5 H 6 ) par 反应脱胺对应物 avec NF 3 ODOI:10.1021/ja00162a045
文献信息
-
Evaluation of FNO and F[sub 3]NO as Substitute Gases for Semiconductor CVD Chamber Cleaning作者:T. Yonemura、K. Fukae、Y. Ohira、Y. Mitsui、T. Takaichi、A. Sekiya、T. BeppuDOI:10.1149/1.1616000日期:——Two types of FNO compounds (FNO and F 3 NO) were evaluated as candidates for new chemical vapor deposition (CVD) chamber cleaning gases. NF 3 and C 2 F 6 were measured as the reference. Like NF 3 , as these gases have no carbon in their molecules, no perfluoro carbon (PFC) is thought to be emitted. FNO is a compound highly susceptible to hydrolysis. F 3 ND is expected to decompose more easily than两种类型的 FNO 化合物(FNO 和 F 3 NO)被评估为新化学气相沉积 (CVD) 室清洁气体的候选气体。测量NF 3 和C 2 F 6 作为参考。与 NF 3 一样,由于这些气体的分子中不含碳,因此认为不会排放全氟化碳 (PFC)。FNO 是一种极易水解的化合物。预计 F 3 ND 在大气中比 NF 3 更容易分解,因为它的 NF 键已通过将 N=O 键引入分子中而减弱。因此,预计这些化合物对全球变暖的贡献很小。这些气体的性能是通过测量它们的蚀刻速率和它们的废气来评估的。结果表明,F 3 NO 的蚀刻速率实际上与NF 3 的蚀刻速率相同,而FNO 的蚀刻速率约为NF 3 的1/2。然而,
-
Synthesis and Properties of N<sub>7</sub>O<sup>+</sup>作者:Karl O. Christe、Ralf Haiges、William W. Wilson、Jerry A. BoatzDOI:10.1021/ic9022213日期:2010.2.1The reaction of NOF2+SbF6− with an equimolar amount of HN3 in an anhydrous HF solution at −45 °C produces N3NOF+SbF6−. When an excess of HN3 is used in this reaction, N7O+SbF6− is formed. However, this compound could not be isolated as a solid and rapidly decomposed in a quantitative manner with N2O evolution to N5+SbF6−. This reaction represents a novel and more convenient synthesis for N5+SbF6− becauseNOF的反应2 +的SbF 6 -与HN等摩尔量3在无水HF溶液中在-45℃下产生N个3 NOF +的SbF 6 - 。当过量的HN 3在该反应中使用,N 7 ö +的SbF 6 -形成。然而,这种化合物不能被分离为固体和在具有N个定量的方式迅速分解2 ö进化至N 5 +的SbF 6 - 。该反应代表了一种新颖且更方便的N 5 +合成方法的SbF 6 -因为NOF 2 +的SbF 6 -是更容易地大于N接近2 ˚F +的SbF 6 -和N 5 +可以与所有五个位置进行标记15 N乘的简单使用的末端单标记Ñ 3 - 。N 7 O +的形成通过同位素标记实验和理论计算确定阳离子。结果表明,将第二叠氮基配体添加到同一中心原子上,可使一个配体的带负电的Nα原子受到第二个配体的带正电的Nγ原子的攻击,从而大大降低了分解的活化能垒。为什么双叠氮化物比单叠氮化物或连二叠氮化物的稳定性差得多。
-
Gmelin Handbuch der Anorganischen Chemie, Gmelin Handbook: F: PerFHalOrg.9, 5, page 1 - 38作者:DOI:——日期:——
-
Metcalf, Steven G.; Shreeve, Jean'ne M., Inorganic Chemistry, 1972, vol. 11, # 7, p. 1631 - 1634作者:Metcalf, Steven G.、Shreeve, Jean'ne M.DOI:——日期:——
-
Endothermic Formation of a Chemical Bond by Entropic Stabilization: Difluoronitroxide Radical in Solid Argon作者:Eugenii Ya. Misochko、Alexander V. Akimov、Ilya U. Goldschleger、Alexander I. Boldyrev、Charles A. WightDOI:10.1021/ja982222r日期:1999.1.1Difluoronitroxide radical (F2NO) has been formed in solid argon matrices by successive addition of two diffusing F atoms to NO. This radical exists in dynamic equilibrium with a van der Waals complex (F-FNO). Measurements of the equilibrium concentrations as a function of temperature show that the changes in enthalpy and the entropy associated with formation of the F2NO radical are Delta H = 1240 +/- 180 J/mol and Delta S = 62 +/- 10 J/(mol K). Because both these quantities are positive, the equilibrium favors F2NO only at elevated temperatures. This situation is a rare case in which formation of a chemical bond is stabilized only by an increase in the entropy of the system.
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
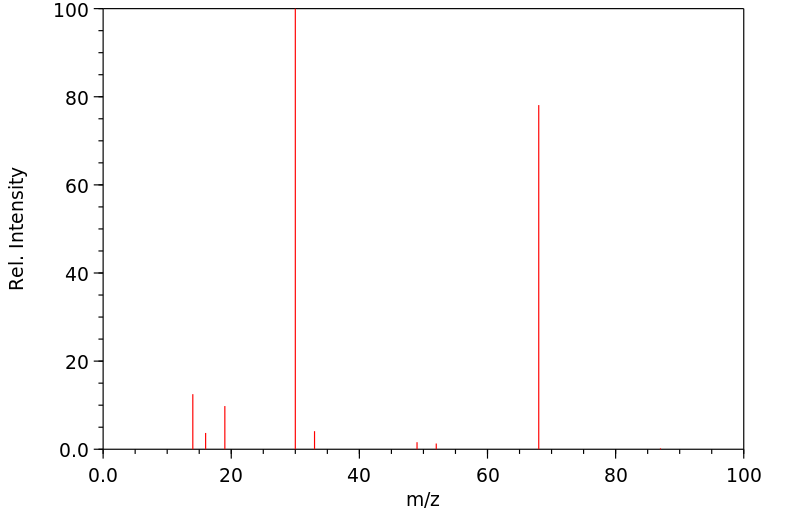
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
高碘酸
氟化氘
过氯酰氟
过氧二硫酰氯
肼二氢溴酸盐
肼二氟化物
联氨-d4氯化氘
联氨-15N2二盐酸盐
羟铵氟化物
羟胺二氢氟酸盐
羟基胺氢碘酸盐
磺酰氯
磷酰胺叠氮化亚胺氯化(9CI)
磷酰氟
碘叠氮化物
碘化氮
碘化氢(~121~I)
碘化氘
碘123
硫酰碘
硫酰氟
硫光气
硝酰氟
硝基溴
盐酸肼
盐酸羟胺-D3
盐酸羟胺-15N
盐酸羟胺
盐酸
焦硫酰氟
溴叠氮化物
溴化铵-15N
溴化氧硒
溴化氢(~80~Br)
溴化氢(~75~Br)
溴化氘
氯磺酸
氯磷酰腈
氯氧基氟化物
氯氟磺酰
氯叠氮化物
氯化铵-d4
氯化硫杂氮
氯化硫
氯化氮
氯化亚砜
氯化二硫酰
氯二氟氧膦
氨磺酰碘化(9CI)
氨基磺酰氯