代谢
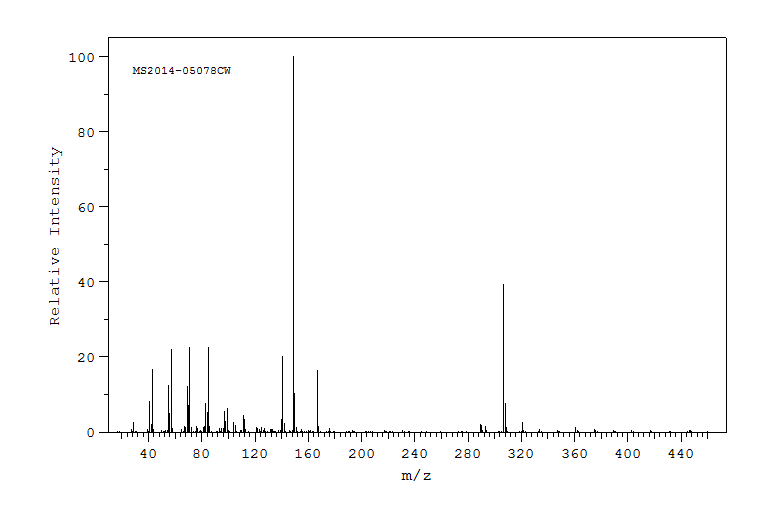
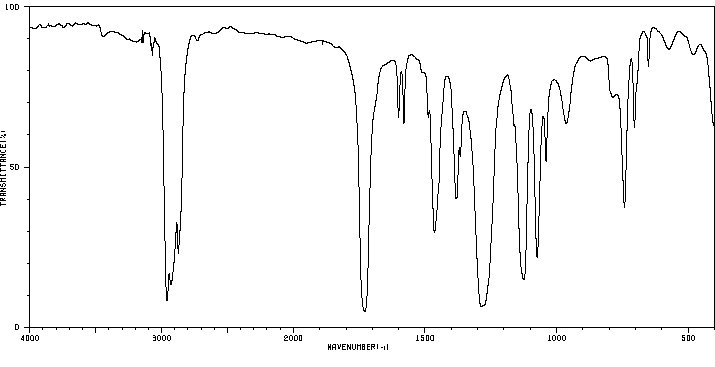
邻苯二甲酸二异癸酯(DiDP)是一种主要含有10个碳原子的支链二烷基链的邻苯二甲酸酯同分异构体混合物,广泛用作聚氯乙烯的塑化剂。人类对DiDP的暴露程度尚不明确,部分原因是缺乏足够的DiDP暴露生物标志物。我们在成年雌性Sprague-Dawley大鼠单次口服DiDP(300 mg/kg)后,在尿液中鉴定出了DiDP的几个主要代谢物。这些代谢物可能被用作DiDP暴露的生物标志物。尿液中的代谢物通过色谱法分离并经色谱行为和全扫描负离子电喷雾电离质谱鉴定。对于具有相似分子量的代谢物,我们进一步在精确质量模式下进行了鉴定。对于一些代谢物,我们使用真实标准进行了明确的鉴定。其中一个是DiDP的水解单酯,单异癸基邻苯二甲酸酯(MiDP),检测为次要代谢物,以及MiDP的一个omega氧化产物,单(羧基-异壬基)邻苯二甲酸酯(MCiNP),它是尿液中含量最丰富的代谢物。我们还暂时鉴定了MiDP的其他次要代谢物,包括单(羟基-异癸基)邻苯二甲酸酯、单(氧代-异癸基)邻苯二甲酸酯、单(羧基-异庚基)邻苯二甲酸酯、单(羧基-异己基)邻苯二甲酸酯、单(羧基-异戊基)邻苯二甲酸酯、单(羧基-异丁基)邻苯二甲酸酯和单(羧基-乙基)邻苯二甲酸酯。还检测到了二异十一烷基邻苯二甲酸酯(DiUdP)和二异壬基邻苯二甲酸酯(DiNP)的氧化代谢物,这表明DiDP配方中存在DiUdP和DiNP。在DiDP给药后的4天内,所有这些代谢物的尿浓度逐渐降低。MCiNP和其他DiDP次要代谢物在尿液中的含量比MiDP更丰富,这表明这些氧化产物作为DiDP暴露评估的生物标志物比MiDP更好。为了了解人类通过尿液中MCiNP和其他DiDP次要代谢物的浓度对DiDP的暴露程度,需要对这些代谢物的毒代动力学进行进一步研究。
Diisodecyl phthalate (DiDP) is an isomeric mixture of phthalates with predominantly 10-carbon branched-dialkyl chains, widely used as a plasticizer for polyvinyl chloride. The extent of human exposure to DiDP is unknown in part because adequate biomarkers of exposure to DiDP are not available. We identified several major metabolites of DiDP in urine of adult female Sprague-Dawley rats after a single oral administration of DiDP (300 mg/kg). These metabolites can potentially be used as biomarkers of exposure to DiDP. The metabolites extracted from urine were chromatographically resolved and identified by their chromatographic behavior and full scan negative ion electrospray ionization mass spectrum. The identity of metabolites with similar molecular weights was further examined in accurate mass mode. For some metabolites, unequivocal identification was done using authentic standards. Among these were the hydrolytic monoester of DiDP, monoisodecyl phthalate (MiDP), detected as a minor metabolite, and one omega oxidation product of MiDP, mono(carboxy-isononyl) phthalate (MCiNP), which was the most abundant urinary metabolite. We also tentatively identified other secondary metabolites of MiDP, mono(hydroxy-isodecyl) phthalate, mono(oxo-isodecyl) phthalate, mono(carboxy-isoheptyl) phthalate, mono(carboxy-isohexyl) phthalate, mono(carboxy-isopentyl) phthalate, mono(carboxy-isobutyl) phthalate, and mono(carboxy-ethyl) phthalate. Oxidative metabolites of diisoundecyl phthalate (DiUdP) and diisononyl phthalate(DiNP) were also detected suggesting the presence of DiUdP and DiNP in the DiDP formulation. The urinary concentrations of all these metabolites gradually decreased in the 4 days following the administration of DiDP. MCiNP and other DiDP secondary metabolites are more abundant in urine than MiDP, suggesting that these oxidative products are better biomarkers for DiDP exposure assessment than MiDP. Additional research on the toxicokinetics of these metabolites is needed to understand the extent of human exposure to DiDP from the urinary concentrations of MCiNP and other DiDP secondary metabolites.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)