1,1':3',1''-三联环戊烷 | 6051-40-7
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
沸点:280.24°C (rough estimate)
-
密度:0.8438 (estimate)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):6.5
-
重原子数:15
-
可旋转键数:2
-
环数:3.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
安全信息
-
海关编码:2902199090
反应信息
-
作为产物:描述:alkaline earth salt of/the/ methylsulfuric acid 在 2-甲基戊烷 、 镍 作用下, 135.0~140.0 ℃ 、15.69 MPa 条件下, 生成 1,1':3',1''-三联环戊烷参考文献:名称:The Synthesis of Multicyclopentyls1摘要:DOI:10.1021/ja01848a028
文献信息
-
The synergistic effect of Cu<sup>0</sup> and Cu<sup>+</sup> for one-step synthesis of aviation biofuel from biomass-derived ketones作者:Tan Li、Jing Su、Linjia Yin、Xiangkun Zhang、Cong Wang、Xinbao Li、Jing Zhang、Kaige WangDOI:10.1039/d3gc02671j日期:——A Cu-based catalyst was developed for one-step solvent-free synthesis of aviation biofuel from biomass-derived ketones, including acetone, cyclopentanone, cyclohexanone, and 2-pentanone. Under the optimal working conditions, the conversion rate of acetone, cyclopentanone, cyclohexanone and 2-pentanone of 100% can be achieved by using Cu/Al2O3. 79.7 c% maximum carbon yield of liquid hydrocarbons with开发了一种铜基催化剂,用于从生物质衍生的酮(包括丙酮、环戊酮、环己酮和2-戊酮)一步无溶剂合成航空生物燃料。在最佳工况下,采用Cu/Al 2 O 3 ,丙酮、环戊酮、环己酮、2-戊酮的转化率均可达到100% 。在1.0 MPa H 2、280 ℃、2 h -1 WHSV条件下,液态烃最大碳收率为79.7 c%,航空生物燃料选择性为89.5% 。研究了焙烧温度对催化剂酸碱度以及Cu物种价态和分散度的影响。基于DFT计算和原位DRIFTS结果,Cu +上羰基的优先吸附和氢的有效解离增加了催化剂表面上H和原料的局部浓度,加速了Cu 0上占主导地位的速率决定步骤。Cu 0和Cu +的协同作用促进了航空生物燃料的形成。
-
T‐shaped Ni<sup>0</sup> Systems Featuring Cationic Tetrylenes: Direct Observation of L/Z‐type Ligand Duality, and Alkene Hydrogenation Catalysis作者:Annika Schulz、Till L. Kalkuhl、Philip M. Keil、Terrance J. HadlingtonDOI:10.1002/anie.202305996日期:2023.8.7
Abstract We report a facile synthetic method for accessing rare T‐shaped Ni0 species, stabilised by low‐coordinate cationic germylene and stannylene ligands which behave as Z‐type ligands toward Ni0. An in‐depth computational analysis indicates significant Ni
d →Ep donation (E=Ge, Sn), with essentially no E→Ni donation. The tetrylene ligand's Lewis acidity can be modulated in situ through the addition of a donor ligand, which selectively binds at the Lewis acidic tetrylene site. This switches this binding centre from a Z‐type to a classical L‐type ligand, with a concomitant geometry switch at Ni0 from T‐shaped to trigonal planar. Exploring the effects of this geometry switch in catalysis, isolated T‐shaped complexes3 a –c and4 a –c are capable of the hydrogenation of alkenes under mild conditions, whilst the closely related trigonal planar and tetrahedral Ni0 complexes5 ,D , andE , which feature L‐type chloro‐ or cationic‐tetrylene ligands, are inactive under these conditions. Further, addition of small amounts of N‐bases to the catalytic systems involving T‐shaped complexes significantly reduces turnover rates, giving evidence for the in situ modulation of ligand electronics for catalytic switching.摘要 我们报告了一种获得稀有 T 型 Ni0 物种的简便合成方法,该物种由低配位阳离子锗烯和锡烯配体稳定,这些配体对 Ni0 来说是 Z 型配体。 深入的计算分析表明,存在大量的 Nid→Ep 捐献(E=Ge、Sn),基本上没有 E→Ni 捐献。通过添加供体配体,可以在原位调节四亚甲基配体的路易斯酸度,供体配体会选择性地与路易斯酸性的四亚甲基位点结合。这就将该结合中心从 Z 型配体转换为经典的 L 型配体,同时在 Ni0 处的几何形状也从 T 型转换为三棱锥平面。为了探索这种几何转换在催化作用中的影响,分离出的 T 型配合物 3 a-c 和 4 a-c 能够在温和的条件下对烯烃进行氢化反应,而与之密切相关的三叉平面和四面体 Ni0 配合物 5、D 和 E(具有 L 型氯或阳离子-三甲苯配体)则在这些条件下不起作用。此外,在涉及 T 型配合物的催化体系中加入少量 N-碱会显著降低周转率,从而证明了原位调节配体电子元件以实现催化转换。 -
v. Braun; Reitz-Kopp, Chemische Berichte, 1941, vol. 74, p. 1105,1109作者:v. Braun、Reitz-KoppDOI:——日期:——
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
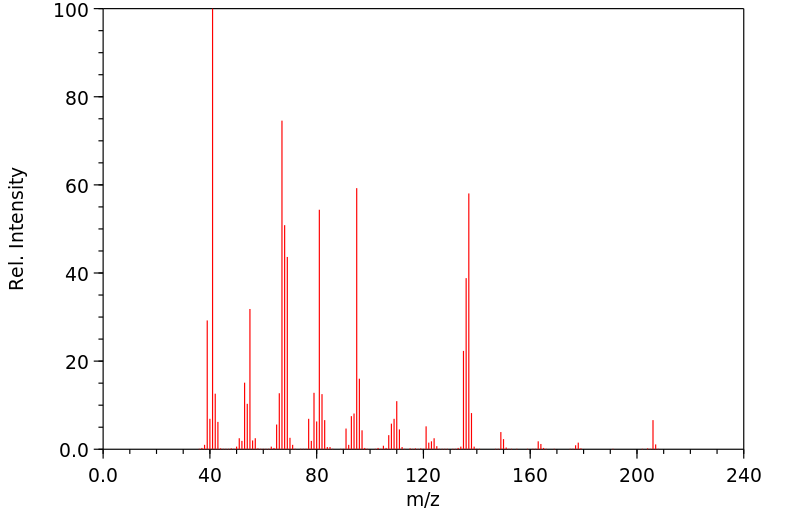
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息