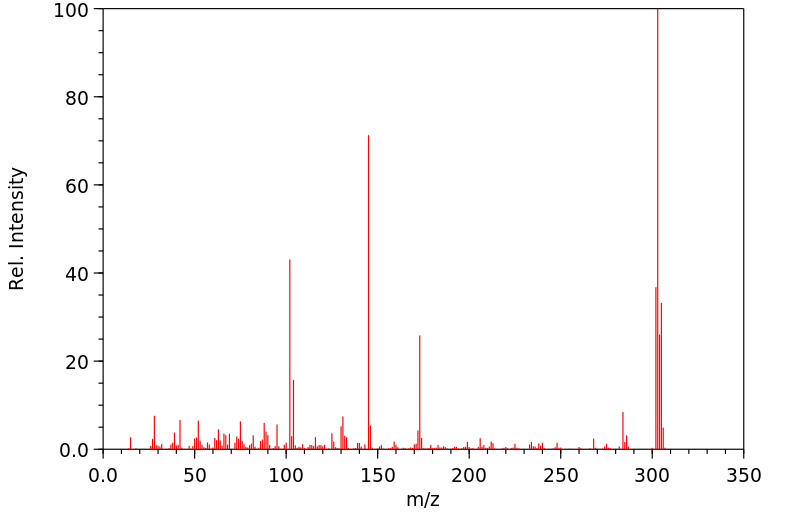
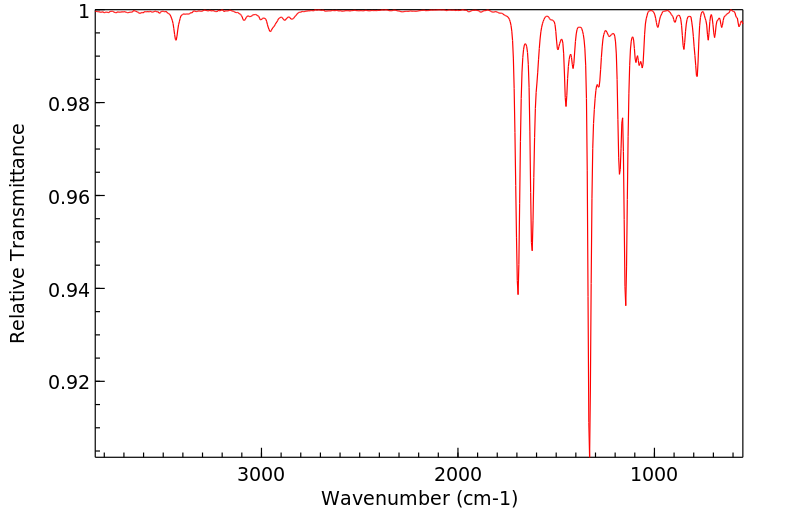
代谢
Norflurazon 以 2 或 110 mg/kg 的单次口服剂量、2 mg/kg 的单次静脉注射剂量,或者在大鼠饮食中添加 2 ppm 并持续 14 天后给予 2 mg/kg 的单次口服剂量给药。在尿液中,96 小时内排除了 18.5-28.4% 的给药剂量,65.3-79.5% 的给药剂量通过粪便排出。分离出了 Norflurazon 的十三个代谢物。Norflurazon 的代谢似乎有四种途径:N-去甲基化;通过谷胱甘肽取代氯原子;谷胱甘肽攻击芳香环;以及氯原子被氢取代...进行了一项额外的代谢研究,以确定在大鼠单次低剂量 1 mg/kg 或单次高剂量 100 mg/kg 口服后,排泄物中是否存在磺酰代谢物。在给予药物的鼠的尿液和粪便中都检测到了磺酰代谢物。在尿液中,低剂量时磺酰代谢物占尿液中放射活性的 0.03%,高剂量时占 0.2%。在粪便中,低剂量时磺酰代谢物占粪便放射活性的 0.3%,高剂量时占 0.1%。
Norflurazon was administered as single oral doses of 2 or 110 mg/kg, a single i.v. dose of 2 mg/kg, or a single oral dose of 2 mg/kg following administration of 2 ppm in animal diet for 14 days to separate groups of rats. In urine, between 18.5-28.4% of the administered dose was eliminated by 96 hours post-dose, and between 65.3-79.5% of the administered dose was eliminated in feces. Thirteen metabolites of norflurazon were isolated. There appear to be 4 pathways for norflurazon metabolism: N-demethylation; displacement of the chlorine atom by glutathione; glutathione attack on the aromatic ring; and replacement of the chlorine atom by hydrogen ... . An additional metabolism study was conducted to determine the presence of the sulfone metabolite in rat excreta after a single low oral dose of 1 mg/kg, or a single high oral dose of 100 mg/kg. The sulfone metabolite was detected in both urine and feces of dosed rats. In urine, the sulfone metabolite accounted for 0.03% of urinary radioactivity at the low dose, and 0.2% of urinary radioactivity at the high dose. The sulfone metabolite accounted for 0.3% of fecal radioactivity at the low dose, and for 0.1% of fecal radioactivity at the high dose.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)