磺草灵 | 3337-71-1
中文名称
磺草灵
中文别名
N-(4-氨基苯基磺酰基)氨基甲酸甲酯;O-甲基-N-(4-氨基苯磺酰基)氨酸甲酸酯;黄草灵;4-氨基苯磺基氨基甲酸甲酯;对氨基苯磺酰基氨基甲酸甲酯;甲基N-(4-氨基苯磺酰)氨基甲酸酯;对氨基苯磺酰胺甲酸甲酯;0-甲基-N-(4-氨基苯磺酰基)氨酸甲酸酯
英文名称
Asulam
英文别名
methyl N-(4-aminophenyl)sulfonylcarbamate
CAS
3337-71-1
化学式
C8H10N2O4S
mdl
MFCD00055534
分子量
230.244
InChiKey
VGPYEHKOIGNJKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:142-144°C (dec.)
-
密度:1.4655 (rough estimate)
-
溶解度:可溶于DMSO(少许)、甲醇(少许)
-
LogP:-0.270
-
颜色/状态:White crystals
-
蒸汽压力:1.39X10-6 mm Hg at 25 °C (est)
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of /nitrogen oxides and sulfur oxides/.
-
解离常数:pKa = 4.82
-
稳定性/保质期:
在常温常压下,这是一种稳定、无色的结晶物质。
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-0.3
-
重原子数:15
-
可旋转键数:3
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.125
-
拓扑面积:107
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:5
ADMET
代谢
两只山羊连续7天通过饲料摄入了标记有放射性碳14的环状阿苏拉姆,剂量为20 ppm。在脂肪和肌肉中未检测到总放射性残留物(小于0.005 ppm),在肾脏中为0.162 ppm,在肝脏中为0.090 ppm,在牛奶中最高为0.021 ppm。母化合物阿苏拉姆在牛奶(占总活性残留物(TRR)的81%)和肾脏(占TRR的100%)中构成残留物的大部分,而其代谢物N4-乙酰磺胺在肝脏(占TRR的58%)中构成残留物的大部分。母化合物在肝脏样本中未被发现。在之前的研究中,磺胺在反刍动物肝脏和肌肉中发现,N4-乙酰阿苏拉姆在肝脏、肾脏、牛奶、肌肉和脂肪中发现。
... Two goats were dosed with ring-labeled (14)C-asulam at 20 ppm in the diet for 7 consecutive days. The total radioactive residues were nondetectable (<0.005 ppm) in fat and muscle, 0.162 ppm in kidneys, 0.090 ppm in liver, and up to 0.021 ppm in milk. The parent compound, asulam, constituted the majority of the residues in milk (81% of total reactive reside (TRR)) and kidneys (100% of TRR) and its metabolite N4-acetylsulfanilamide constitutes the majority of residues in liver (58% of TRR). The parent was not identified in liver samples. In a previous study, sulfanilamide was found in ruminant liver and muscle, and N4-acetylasulam was found in liver, kidney, milk, muscle, and fat.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
母鸡连续7天在饲料中摄入了标记有放射性碳14的阿苏拉姆,剂量为22.5 ppm。蛋中的最大总放射性残留量为蛋黄中0.027 ppm,蛋白中0.062 ppm,脂肪中0.011 ppm,肌肉中0.074 ppm,肾脏中0.444 ppm,肝脏中0.086 ppm。母化合物阿苏拉姆及其代谢物N4-乙酰磺胺占到家禽体内残留物的大部分,分别占蛋黄中总反应性残留物(TRR)的63%和44%,蛋白中的21%和52%,肌肉中的35%和51%,肾脏中的83%和14%。在肝脏样本中未检测到母化合物;N4-乙酰磺胺在肝脏样本中占到TRR的81%。
... Laying hens were dosed with ring-labeled (14)C-asulam at 22.5 ppm in the diet for 7 consecutive days. The maximum total radioactive residues were 0.027 ppm in egg yolks, 0.062 ppm in egg whites, 0.011 ppm in fat, 0.074 ppm in muscle, 0.444 ppm in kidneys, and 0.086 ppm in liver. The parent compound asulam, and its metabolite N4-acetylsulfanilamide constituted the majority of the residues in poultry, comprising 63 and 44% of the total reactive reside (TRR), respectively, in egg yolks, 21 and 52% of the TRR, respectively, in egg whites, 35 and 51% of the TRR, respectively, in muscle, and 83 and 14% of the TRR, respectively, in kidney. The parent was not identified in liver samples; N4-acetyl sulfanilamide represented 81% of the TRR in liver samples.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
Metabolism studies were conducted in male and female Sprague-Dawley rats. The tests used a single oral or iv dose, or repeated i.v. doses for 14 days. The pharmacokinetics of asulam were similar after all dose regimens in both sexes. Peak blood levels were attained at 0.5 hours. No unusual localization of asulam occurred in tissues and all tissue levels were low at 72 hours. Asulam was rapidly eliminated, mostly within 24 hours. 76.5% to 101.5% of the administered dose was eliminated in the urine, and 1.4% to 25.3% of the dose in feces. The major excretory product was unchanged parent compound (70% to 80%), with acetylasulam (3% to 8%) and acetylsulphanilamide (<3%) being the two major metabolites.
Metabolism studies were conducted in male and female Sprague- Dawley rats. The tests used a single oral or iv dose, or repeated i.v. doses for 14 days. The pharmacokinetics of asulam were similar after all dose regimens in both sexes. Peak blood levels were attained at 0.5 hours. No unusual localization of asulam occurred in tissues and all tissue levels were low at 72 hours. Asulam was rapidly eliminated, mostly within 24 hours. 76.5% to 101.5% of the administered dose was eliminated in the urine, and 1.4% to 25.3% of the dose in feces. The major excretory product was unchanged parent compound (70% to 80%), with acetylasulam (3% to 8%) and acetylsulphanilamide (<3%) being the two major metabolites.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
[ring-(14)C]asulam是一种对欧洲蕨类植物具有高度活性的系统性除草剂,在大鼠体内的代谢已经得到了研究。口服或静脉注射的大部分放射性物质(76-100%剂量)在24小时内以原药asulam(61-74%剂量)、N4-乙酰化asulam(8-14%)和N4-乙酰化磺胺苯胺(0.1-2.6%)的形式通过尿液排出。少量放射性物质(0.3-7.4%剂量)出现在粪便中,只有微量的(0.2-0.3%)通过胆汁排出,没有检测到显著的(14)CO2。用(14)C-asulam灌注大鼠肝脏导致更广泛的代谢。灌注液(81%总量)、胆汁(1%)加上肝脏(14%)中的总量分别为:未改变的asulam占23.1%,乙酰化asulam占25.7%,乙酰化磺胺苯胺占不到1%,asulam和乙酰化asulam的结合物占4.5%,以及几个其他未识别的代谢物。与磺胺苯胺相比,asulam更容易被大鼠肝脏匀浆乙酰化,最高的酶活性与线粒体部分相关(2.4 pmol/mg蛋白质/分钟)。尽管在大鼠体内不被羟基化,但有证据表明,asulam可以通过大鼠肝脏微粒体制剂在体外发生羟基化。
The metabolism of [ring-(14)C]asulam, a systemic herbicide highly effective against bracken, has been studied in rats. Most of the radioactivity (76-100% dose) administered orally or intravenously is excreted in the urine in 24 hr as unchanged asulam (61-74% dose), N4-acetylasulam (8-14%) and N4-acetylsulphanilamide (0.1-2.6%). Small amounts of radioactivity (0.3-7.4% dose) were present in the feces, only traces (0.2-0.3%) were excreted in the bile, and no significant (14)CO2 was detected. Perfusion of rat liver with (14)C-asulam resulted in more extensive metabolism. Total amounts present in perfusate (81% total), bile (1%) plus liver (14%) were 23.1% for unchanged asulam, 25.7% for acetylasulam, less than 1% for acetylsulphanilamide, and 4.5% as conjugates of asulam and acetylasulam, together with several other unidentified metabolites. Asulam is acetylated more readily than sulphanilamide, by rat-liver homogenate, and the highest enzyme activity was associated with the mitochondrial fraction (2.4 pmol/mg protein per min). Although not hydroxylated by rats in vivo, evidence was obtained for the hydroxylation of asulam by rat-liver microsomal preparations in vitro.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
The carbamates are hydrolyzed enzymatically by the liver; degradation products are excreted by the kidneys and the liver. (L793)
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
识别和使用:阿苏拉姆是一种用于除草的除草剂。阿苏拉姆被配制成阿苏拉姆钠盐形式并施用。人体研究:在人类淋巴细胞的体外细胞遗传学分析中,阿苏拉姆呈阴性。动物研究:将技术级阿苏拉姆应用于兔眼,产生了轻微的水肿、刺激和发红,这些症状在治疗后第七天清除。在兔子的初级皮肤刺激研究中,阿苏拉姆不是刺激物。它没有在豚鼠身上引起皮肤致敏。在比格犬上进行为期六个月的阿苏拉姆喂养研究中,每天300毫克/千克和1500毫克/千克的阿苏拉姆剂量与食物消耗量减少、体重增加减少、呕吐、腹泻以及红细胞、血红蛋白和压积细胞的减少有关。甲状腺和肾脏重量升高,而睾丸重量降低。在为期两年的小鼠致癌性研究中,阿苏拉姆以0、500、5000或50000 ppm的剂量掺入饮食中。任何肿瘤的发生率都没有增加。使用大鼠进行了为期两年的慢性喂养/致癌性联合研究。在雄性大鼠的肾上腺髓质和甲状腺滤泡细胞中,观察到剂量为180和953毫克/千克/天时的增生性变化。在低剂量和中剂量雄性中,甲状腺C细胞癌和腺瘤及癌的组合有统计学上的显著增加。在高剂量雄性中,良性肾上腺髓质嗜铬细胞瘤有统计学上的显著增加。阿苏拉姆在大鼠或兔子上没有产生致畸作用。用于检测沙门氏菌突变基因的艾姆斯试验呈阴性。检测结构染色体畸变的致突变性试验包括小鼠的显性致死试验,阿苏拉姆呈阴性。生态毒性研究:在鹌鹑(Colinus virginianus)的饮食研究中,阿苏拉姆对食物消耗量、体重或累积死亡率没有影响,在28天的喂养期间没有观察到毒性迹象。同样,该化学物质对F1代的产蛋量、生育力或受精蛋的孵化能力,或对异常没有影响。
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Asulam is a herbicide used for weed control. Asulam is formulated into and applied as the asulam sodium salt. HUMAN STUDIES: In vitro cytogenetics assay in human lymphocytes were negative for asulam. ANIMAL STUDIES: Application of technical asulam to rabbit eyes produced mild chemosis, irritation, and redness which cleared by day seven posttreatment. Asulam was not an irritant in a primary skin irritation study in rabbits. It did not cause dermal sensitization in guinea pigs. In a six-month feeding study of asulam in beagle dogs doses of asulam at 300 mg/kg/day and 1,500 mg/kg/day were associated with reductions in food consumption, body weight gain, emesis, diarrhea, and reductions in red blood cells, hemoglobin and packed cell volume. There were also elevated thyroid and kidney weights and reduced testicular weights. In a two-year carcinogenicity study mice, asulam was administered in the diet at 0, 500, 5,000 or 50,000 ppm. There was no increase in the incidence of any tumors. A two-year combined chronic feeding/carcinogenicity study was conducted using rats. Hyperplastic changes were observed in the adrenal medulla and in thyroid follicular cells of males at the doses of 180 and 953 mg/kg/day. There was a statistically significant increase in thyroid gland c-cell carcinomas and in adenomas and carcinomas combined in both the low- and mid-dose males. There was a statistically-significant increase in benign adrenal medullary pheochromocytomas at the high dose in males. No teratogenic effects were produced by asulam in either rats or rabbits. The Ames Assay which is used to detect gene mutation with Salmonella typhimurium was negative. Mutagenicity assays which detect structural chromosome aberrations included the dominant lethal test in mice and were negative for asulam. ECOTOXICITY STUDIES: When tested in bobwhite quail (Colinus virginianus) dietary study, asulam had no effect on food consumption, body weight, or cumulative mortality, and no signs of toxicity were seen during the 28-day feeding period. Similarly, the chemical had no effect on egg production, fertility, or hatchability of fertile eggs, or on abnormalities in the F1 generation.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
阿舒兰是一种胆碱酯酶或乙酰胆碱酯酶(AChE)抑制剂。胆碱酯酶抑制剂(或“抗胆碱酯酶”)抑制乙酰胆碱酯酶的作用。由于其基本功能,干扰乙酰胆碱酯酶作用的化学物质是强大的神经毒素,在低剂量时会导致过度流涎和眼泪,随后是肌肉痉挛,最终导致死亡。神经气体和许多用于杀虫剂的物质已被证明通过结合乙酰胆碱酯酶活性位点的丝氨酸,完全抑制该酶。乙酰胆碱酯酶分解神经递质乙酰胆碱,后者在神经和肌肉接点处释放,以使肌肉或器官放松。乙酰胆碱酯酶抑制的结果是乙酰胆碱积聚并继续发挥作用,使得任何神经冲动不断传递,肌肉收缩不会停止。最常见的乙酰胆碱酯酶抑制剂之一是基于磷的化合物,它们被设计用来结合到酶的活性位点上。结构要求是一个带有两个亲脂性基团的磷原子,一个离去基团(如卤素或硫氰酸盐),以及一个末端的氧。
Asulam is a cholinesterase or acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor. A cholinesterase inhibitor (or 'anticholinesterase') suppresses the action of acetylcholinesterase. Because of its essential function, chemicals that interfere with the action of acetylcholinesterase are potent neurotoxins, causing excessive salivation and eye-watering in low doses, followed by muscle spasms and ultimately death. Nerve gases and many substances used in insecticides have been shown to act by binding a serine in the active site of acetylcholine esterase, inhibiting the enzyme completely. Acetylcholine esterase breaks down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which is released at nerve and muscle junctions, in order to allow the muscle or organ to relax. The result of acetylcholine esterase inhibition is that acetylcholine builds up and continues to act so that any nerve impulses are continually transmitted and muscle contractions do not stop. Among the most common acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are phosphorus-based compounds, which are designed to bind to the active site of the enzyme. The structural requirements are a phosphorus atom bearing two lipophilic groups, a leaving group (such as a halide or thiocyanate), and a terminal oxygen.
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
对人类无致癌性(未列入国际癌症研究机构IARC清单)。
No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC).
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
急性接触胆碱酯酶抑制剂可能会导致胆碱能危象,表现为严重的恶心/呕吐、流涎、出汗、心动过缓、低血压、昏厥和抽搐。肌肉无力可能性增加,如果涉及呼吸肌,可能会导致死亡。在运动神经积累的乙酰胆碱会导致神经肌肉接头处烟碱表达的过度刺激。当这种情况发生时,可以看到如肌肉无力、疲劳、肌肉痉挛、肌纤维颤动和麻痹等症状。当自主神经节积累乙酰胆碱时,这会导致交感神经系统中烟碱表达的过度刺激。与此相关的症状包括高血压和低血糖。由于乙酰胆碱积累,中枢神经系统中烟碱乙酰胆碱受体的过度刺激会导致焦虑、头痛、抽搐、共济失调、呼吸和循环抑制、震颤、全身无力,甚至可能昏迷。当由于副交感神经乙酰胆碱受体处乙酰胆碱过多而导致毒蕈碱过度刺激时,可能会出现视力障碍、胸部紧绷、由于支气管收缩引起的喘息、支气管分泌物增加、唾液分泌增加、流泪、出汗、肠蠕动和排尿等症状。对于男性和女性的生育、生长和发育,某些生殖效应已特定与有机磷农药暴露有关。关于生殖效应的大部分研究都是在农村地区使用农药和杀虫剂的农民中进行的。在女性中,月经周期紊乱、怀孕时间延长、自然流产、死产以及后代的一些发育效应已与有机磷农药暴露有关。产前暴露与胎儿生长和发育受损有关。神经毒性效应也与人因有机磷农药中毒导致的四种神经毒性效应有关:胆碱能综合征、中间综合征、有机磷诱导的迟发性多发性神经病(OPIDP)和慢性有机磷诱导的神经精神障碍(COPIND)。这些综合征在急性暴露和慢性暴露于有机磷农药后发生。
Acute exposure to cholinesterase inhibitors can cause a cholinergic crisis characterized by severe nausea/vomiting, salivation, sweating, bradycardia, hypotension, collapse, and convulsions. Increasing muscle weakness is a possibility and may result in death if respiratory muscles are involved. Accumulation of ACh at motor nerves causes overstimulation of nicotinic expression at the neuromuscular junction. When this occurs symptoms such as muscle weakness, fatigue, muscle cramps, fasciculation, and paralysis can be seen. When there is an accumulation of ACh at autonomic ganglia this causes overstimulation of nicotinic expression in the sympathetic system. Symptoms associated with this are hypertension, and hypoglycemia. Overstimulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the central nervous system, due to accumulation of ACh, results in anxiety, headache, convulsions, ataxia, depression of respiration and circulation, tremor, general weakness, and potentially coma. When there is expression of muscarinic overstimulation due to excess acetylcholine at muscarinic acetylcholine receptors symptoms of visual disturbances, tightness in chest, wheezing due to bronchoconstriction, increased bronchial secretions, increased salivation, lacrimation, sweating, peristalsis, and urination can occur. Certain reproductive effects in fertility, growth, and development for males and females have been linked specifically to organophosphate pesticide exposure. Most of the research on reproductive effects has been conducted on farmers working with pesticides and insecticdes in rural areas. In females menstrual cycle disturbances, longer pregnancies, spontaneous abortions, stillbirths, and some developmental effects in offspring have been linked to organophosphate pesticide exposure. Prenatal exposure has been linked to impaired fetal growth and development. Neurotoxic effects have also been linked to poisoning with OP pesticides causing four neurotoxic effects in humans: cholinergic syndrome, intermediate syndrome, organophosphate-induced delayed polyneuropathy (OPIDP), and chronic organophosphate-induced neuropsychiatric disorder (COPIND). These syndromes result after acute and chronic exposure to OP pesticides.
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
吸入(L793);口服(L793);皮肤给药(L793)
Inhalation (L793) ; oral (L793); dermal (L793)
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
吸收、分配和排泄
两只山羊连续7天通过饲料摄入了标记有放射性碳14的环状阿苏拉姆,浓度为20 ppm。总放射性残留物在脂肪和肌肉中无法检测到(小于0.005 ppm),在肾脏中为0.162 ppm,在肝脏中为0.090 ppm,在牛奶中高达0.021 ppm。母化合物阿苏拉姆构成了牛奶(占总活性残留物(TRR)的81%)和肾脏(占TRR的100%)中残留物的大部分,其代谢物N4-乙酰磺胺构成了肝脏(占TRR的58%)中残留物的大部分。母化合物在肝脏样本中未被发现。在之前的一项研究中,磺胺酰胺在反刍动物肝脏和肌肉中被发现,N4-乙酰阿苏拉姆在肝脏、肾脏、牛奶、肌肉和脂肪中被发现。
... Two goats were dosed with ring-labeled (14)C-asulam at 20 ppm in the diet for 7 consecutive days. The total radioactive residues were nondetectable (<0.005 ppm) in fat and muscle, 0.162 ppm in kidneys, 0.090 ppm in liver, and up to 0.021 ppm in milk. The parent compound, asulam, constituted the majority of the residues in milk (81% of total reactive reside (TRR)) and kidneys (100% of TRR) and its metabolite N4-acetylsulfanilamide constitutes the majority of residues in liver (58% of TRR). The parent was not identified in liver samples. In a previous study, sulfanilamide was found in ruminant liver and muscle, and N4-acetylasulam was found in liver, kidney, milk, muscle, and fat.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
... 在连续7天内,蛋鸡被喂食含有环标(14)C-阿苏拉姆的饲料,剂量为22.5 ppm。蛋黄中的最大总放射性残留量为0.027 ppm,蛋白中为0.062 ppm,脂肪中为0.011 ppm,肌肉中为0.074 ppm,肾脏中为0.444 ppm,肝脏中为0.086 ppm。原始化合物阿苏拉姆及其代谢物N4-乙酰磺胺嘧啶在家禽中构成了大部分残留物,分别占蛋黄中总活性残留物(TRR)的63%和44%,蛋白中的TRR分别为21%和52%,肌肉中的TRR分别为35%和51%,肾脏中的TRR分别为83%和14%。在肝脏样本中没有检测到原始化合物;N4-乙酰磺胺嘧啶在肝脏样本中占TRR的81%。
... Laying hens were dosed with ring-labeled (14)C-asulam at 22.5 ppm in the diet for 7 consecutive days. The maximum total radioactive residues were 0.027 ppm in egg yolks, 0.062 ppm in egg whites, 0.011 ppm in fat, 0.074 ppm in muscle, 0.444 ppm in kidneys, and 0.086 ppm in liver. The parent compound asulam, and its metabolite N4-acetylsulfanilamide constituted the majority of the residues in poultry, comprising 63 and 44% of the total reactive reside (TRR), respectively, in egg yolks, 21 and 52% of the TRR, respectively, in egg whites, 35 and 51% of the TRR, respectively, in muscle, and 83 and 14% of the TRR, respectively, in kidney. The parent was not identified in liver samples; N4-acetyl sulfanilamide represented 81% of the TRR in liver samples.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
Metabolism studies were conducted in male and female Sprague-Dawley rats. The tests used a single oral or iv dose, or repeated i.v. doses for 14 days. The pharmacokinetics of asulam were similar after all dose regimens in both sexes. Peak blood levels were attained at 0.5 hours. No unusual localization of asulam occurred in tissues and all tissue levels were low at 72 hours. Asulam was rapidly eliminated, mostly within 24 hours. 76.5% to 101.5% of the administered dose was eliminated in the urine, and 1.4% to 25.3% of the dose in feces. The major excretory product was unchanged parent compound (70% to 80%), with acetylasulam (3% to 8%) and acetylsulphanilamide (<3%) being the two major metabolites.
Metabolism studies were conducted in male and female Sprague- Dawley rats. The tests used a single oral or iv dose, or repeated i.v. doses for 14 days. The pharmacokinetics of asulam were similar after all dose regimens in both sexes. Peak blood levels were attained at 0.5 hours. No unusual localization of asulam occurred in tissues and all tissue levels were low at 72 hours. Asulam was rapidly eliminated, mostly within 24 hours. 76.5% to 101.5% of the administered dose was eliminated in the urine, and 1.4% to 25.3% of the dose in feces. The major excretory product was unchanged parent compound (70% to 80%), with acetylasulam (3% to 8%) and acetylsulphanilamide (<3%) being the two major metabolites.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
[ring-(14)C]asulam是一种对欧洲蕨类植物具有高度活性的系统性除草剂,在大鼠体内的代谢已经得到了研究。口服或静脉注射的大部分放射性物质(76-100%剂量)在24小时内以原药asulam(61-74%剂量)、N4-乙酰化asulam(8-14%)和N4-乙酰化磺胺苯胺(0.1-2.6%)的形式通过尿液排出。少量放射性物质(0.3-7.4%剂量)出现在粪便中,只有微量(0.2-0.3%)通过胆汁排出,没有检测到显著的(14)CO2。用(14)C-asulam灌注大鼠肝脏会导致更广泛的代谢。灌注液(81%总量)、胆汁(1%)加上肝脏(14%)中的总量分别为:未改变的asulam占23.1%,乙酰化asulam占25.7%,乙酰化磺胺苯胺不到1%,以及asulam和乙酰化asulam的共轭物占4.5%,还有几个其他未识别的代谢物。在大鼠肝脏匀浆中,asulam比磺胺苯胺更容易被乙酰化,最高的酶活性与线粒体部分相关(2.4 pmol/mg蛋白质/分钟)。尽管在大鼠体内没有被羟基化,但有证据表明,asulam可以通过大鼠肝脏微粒体体外制剂进行羟基化。
The metabolism of [ring-(14)C]asulam, a systemic herbicide highly effective against bracken, has been studied in rats. Most of the radioactivity (76-100% dose) administered orally or intravenously is excreted in the urine in 24 hr as unchanged asulam (61-74% dose), N4-acetylasulam (8-14%) and N4-acetylsulphanilamide (0.1-2.6%). Small amounts of radioactivity (0.3-7.4% dose) were present in the feces, only traces (0.2-0.3%) were excreted in the bile, and no significant (14)CO2 was detected. Perfusion of rat liver with (14)C-asulam resulted in more extensive metabolism. Total amounts present in perfusate (81% total), bile (1%) plus liver (14%) were 23.1% for unchanged asulam, 25.7% for acetylasulam, less than 1% for acetylsulphanilamide, and 4.5% as conjugates of asulam and acetylasulam, together with several other unidentified metabolites. Asulam is acetylated more readily than sulphanilamide, by rat-liver homogenate, and the highest enzyme activity was associated with the mitochondrial fraction (2.4 pmol/mg protein per min). Although not hydroxylated by rats in vivo, evidence was obtained for the hydroxylation of asulam by rat-liver microsomal preparations in vitro.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
危险品标志:Xn
-
危险类别码:R22
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:2935009016
-
危险品运输编号:NONH for all modes of transport
SDS
1.1 产品标识符
: 磺草灵
产品名称
1.2 鉴别的其他方法
无数据资料
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途
仅供科研用途,不作为药物、家庭备用药或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述
2.1 GHS分类
急性毒性, 经口 (类别4)
急性水生毒性 (类别3)
2.2 GHS 标记要素,包括预防性的陈述
象形图
警示词 警告
危险申明
H302 吞咽有害。
H402 对水生生物有害。
警告申明
预防
P264 操作后彻底清洁皮肤。
P270 使用本产品时不要进食、饮水或吸烟。
P273 避免释放到环境中。
措施
P301 + P312 如果吞下去了: 如感觉不适,呼救解毒中心或看医生。
P330 漱口。
处理
P501 将内容物/ 容器处理到得到批准的废物处理厂。
2.3 其它危害物 - 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
3.1 物 质
: C8H10N2O4S
分子式
: 230.24 g/mol
分子量
组分 浓度或浓度范围
Asulam
-
CAS 号 3337-71-1
EC-编号 222-077-1
模块 4. 急救措施
4.1 必要的急救措施描述
一般的建议
请教医生。 出示此安全技术说明书给到现场的医生看。
吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如果停止了呼吸,给于人工呼吸。 请教医生。
皮肤接触
用肥皂和大量的水冲洗。 请教医生。
眼睛接触
用水冲洗眼睛作为预防措施。
食入
切勿给失去知觉者从嘴里喂食任何东西。 用水漱口。 请教医生。
4.2 主要症状和影响,急性和迟发效应
4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示
无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施
5.1 灭火介质
灭火方法及灭火剂
用水雾,耐醇泡沫,干粉或二氧化碳灭火。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害
碳氧化物, 氮氧化物, 硫氧化物
产品分解后性质不明
碳氧化物, 氮氧化物, 硫氧化物
5.3 给消防员的建议
如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步信息
无数据资料
模块 6. 泄露应急处理
6.1 人员的预防,防护设备和紧急处理程序
使用个人防护设备。 防止粉尘的生成。 防止吸入蒸汽、气雾或气体。 保证充分的通风。 避免吸入粉尘。
6.2 环境保护措施
在确保安全的前提下,采取措施防止进一步的泄漏或溢出。 不要让产物进入下水道。
防止排放到周围环境中。
6.3 抑制和清除溢出物的方法和材料
收集、处理泄漏物,不要产生灰尘。 扫掉和铲掉。 存放进适当的闭口容器中待处理。
6.4 参考其他部分
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
7.1 安全操作的注意事项
避免接触皮肤和眼睛。 防止粉尘和气溶胶生成。
在有粉尘生成的地方,提供合适的排风设备。一般性的防火保护措施。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性
贮存在阴凉处。 容器保持紧闭,储存在干燥通风处。
7.3 特定用途
无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
8.1 容许浓度
最高容许浓度
没有已知的国家规定的暴露极限。
8.2 暴露控制
适当的技术控制
按照良好工业和安全规范操作。 休息前和工作结束时洗手。
个体防护设备
眼/面保护
带有防护边罩的安全眼镜符合 EN166要求请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟)
检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/EEC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
身体保护
全套防化学试剂工作服, 防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和含量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
如须暴露于有害环境中,请使用P95型(美国)或P1型(欧盟 英国
143)防微粒呼吸器。如需更高级别防护,请使用OV/AG/P99型(美国)或ABEK-P2型 (欧盟 英国 143)
防毒罐。
呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息
a) 外观与性状
形状: 固体
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味阈值
无数据资料
d) pH值
无数据资料
e) 熔点/凝固点
无数据资料
f) 起始沸点和沸程
无数据资料
g) 闪点
无数据资料
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 易燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 无数据资料
k) 蒸汽压
无数据资料
l) 蒸汽密度
无数据资料
m) 相对密度
无数据资料
n) 水溶性
无数据资料
o) n-辛醇/水分配系数
无数据资料
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性
10.1 反应性
无数据资料
10.2 稳定性
无数据资料
10.3 危险反应的可能性
无数据资料
10.4 应避免的条件
无数据资料
10.5 不兼容的材料
强氧化剂
10.6 危险的分解产物
其它分解产物 - 无数据资料
模块 11. 毒理学资料
11.1 毒理学影响的信息
急性毒性
半数致死剂量 (LD50) 经口 - 大鼠 - 2,000 mg/kg
半数致死浓度(LC50) 吸入 - 大鼠 - > 18,900 mg/m3
半数致死剂量 (LD50) 经皮 - 大鼠 - > 10,000 mg/kg
皮肤刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
眼睛刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
无数据资料
生殖细胞突变性
无数据资料
致癌性
IARC:
此产品中没有大于或等于 0。1%含量的组分被 IARC鉴别为可能的或肯定的人类致癌物。
生殖毒性
致畸性 - 兔子 - 经口
母体效应:其他影响。
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入可能有害。 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
摄入 误吞对人体有害。
皮肤 如果通过皮肤吸收可能是有害的。 可能引起皮肤刺激。
眼睛 可能引起眼睛刺激。
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: FD1190000
模块 12. 生态学资料
12.1 生态毒性
对鱼类的毒性 半数致死浓度(LC50) - Oncorhynchus mykiss (红鳟) - > 175 mg/l - 96 h
对水蚤和其他水生无脊 半致死有效浓度(EC50) - Daphnia magna (大型蚤) - 29.5 mg/l - 48 h
椎动物的毒性
12.2 持久存留性和降解性
无数据资料
12.3 潜在的生物蓄积性
无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移性
无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价
无数据资料
12.6 其它不利的影响
对水生生物有害。
无数据资料
模块 13. 废弃处置
13.1 废物处理方法
产品
将剩余的和未回收的溶液交给处理公司。 联系专业的拥有废弃物处理执照的机构来处理此物质。
与易燃溶剂相溶或者相混合,在备有燃烧后处理和洗刷作用的化学焚化炉中燃烧
受污染的容器和包装
作为未用过的产品弃置。
模块 14. 运输信息
14.1 联合国危险货物编号
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.2 联合国(UN)规定的名称
欧洲陆运危规: 非危险货物
国际海运危规: 非危险货物
国际空运危规: 非危险货物
14.3 运输危险类别
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.4 包裹组
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.5 环境危险
欧洲陆运危规: 否 国际海运危规 海运污染物: 否 国际空运危规: 否
14.6 对使用者的特别提醒
无数据资料
模块 15 - 法规信息
N/A
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
: 磺草灵
产品名称
1.2 鉴别的其他方法
无数据资料
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途
仅供科研用途,不作为药物、家庭备用药或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述
2.1 GHS分类
急性毒性, 经口 (类别4)
急性水生毒性 (类别3)
2.2 GHS 标记要素,包括预防性的陈述
象形图
警示词 警告
危险申明
H302 吞咽有害。
H402 对水生生物有害。
警告申明
预防
P264 操作后彻底清洁皮肤。
P270 使用本产品时不要进食、饮水或吸烟。
P273 避免释放到环境中。
措施
P301 + P312 如果吞下去了: 如感觉不适,呼救解毒中心或看医生。
P330 漱口。
处理
P501 将内容物/ 容器处理到得到批准的废物处理厂。
2.3 其它危害物 - 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
3.1 物 质
: C8H10N2O4S
分子式
: 230.24 g/mol
分子量
组分 浓度或浓度范围
Asulam
-
CAS 号 3337-71-1
EC-编号 222-077-1
模块 4. 急救措施
4.1 必要的急救措施描述
一般的建议
请教医生。 出示此安全技术说明书给到现场的医生看。
吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如果停止了呼吸,给于人工呼吸。 请教医生。
皮肤接触
用肥皂和大量的水冲洗。 请教医生。
眼睛接触
用水冲洗眼睛作为预防措施。
食入
切勿给失去知觉者从嘴里喂食任何东西。 用水漱口。 请教医生。
4.2 主要症状和影响,急性和迟发效应
4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示
无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施
5.1 灭火介质
灭火方法及灭火剂
用水雾,耐醇泡沫,干粉或二氧化碳灭火。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害
碳氧化物, 氮氧化物, 硫氧化物
产品分解后性质不明
碳氧化物, 氮氧化物, 硫氧化物
5.3 给消防员的建议
如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步信息
无数据资料
模块 6. 泄露应急处理
6.1 人员的预防,防护设备和紧急处理程序
使用个人防护设备。 防止粉尘的生成。 防止吸入蒸汽、气雾或气体。 保证充分的通风。 避免吸入粉尘。
6.2 环境保护措施
在确保安全的前提下,采取措施防止进一步的泄漏或溢出。 不要让产物进入下水道。
防止排放到周围环境中。
6.3 抑制和清除溢出物的方法和材料
收集、处理泄漏物,不要产生灰尘。 扫掉和铲掉。 存放进适当的闭口容器中待处理。
6.4 参考其他部分
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
7.1 安全操作的注意事项
避免接触皮肤和眼睛。 防止粉尘和气溶胶生成。
在有粉尘生成的地方,提供合适的排风设备。一般性的防火保护措施。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性
贮存在阴凉处。 容器保持紧闭,储存在干燥通风处。
7.3 特定用途
无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
8.1 容许浓度
最高容许浓度
没有已知的国家规定的暴露极限。
8.2 暴露控制
适当的技术控制
按照良好工业和安全规范操作。 休息前和工作结束时洗手。
个体防护设备
眼/面保护
带有防护边罩的安全眼镜符合 EN166要求请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟)
检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/EEC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
身体保护
全套防化学试剂工作服, 防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和含量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
如须暴露于有害环境中,请使用P95型(美国)或P1型(欧盟 英国
143)防微粒呼吸器。如需更高级别防护,请使用OV/AG/P99型(美国)或ABEK-P2型 (欧盟 英国 143)
防毒罐。
呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息
a) 外观与性状
形状: 固体
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味阈值
无数据资料
d) pH值
无数据资料
e) 熔点/凝固点
无数据资料
f) 起始沸点和沸程
无数据资料
g) 闪点
无数据资料
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 易燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 无数据资料
k) 蒸汽压
无数据资料
l) 蒸汽密度
无数据资料
m) 相对密度
无数据资料
n) 水溶性
无数据资料
o) n-辛醇/水分配系数
无数据资料
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性
10.1 反应性
无数据资料
10.2 稳定性
无数据资料
10.3 危险反应的可能性
无数据资料
10.4 应避免的条件
无数据资料
10.5 不兼容的材料
强氧化剂
10.6 危险的分解产物
其它分解产物 - 无数据资料
模块 11. 毒理学资料
11.1 毒理学影响的信息
急性毒性
半数致死剂量 (LD50) 经口 - 大鼠 - 2,000 mg/kg
半数致死浓度(LC50) 吸入 - 大鼠 - > 18,900 mg/m3
半数致死剂量 (LD50) 经皮 - 大鼠 - > 10,000 mg/kg
皮肤刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
眼睛刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
无数据资料
生殖细胞突变性
无数据资料
致癌性
IARC:
此产品中没有大于或等于 0。1%含量的组分被 IARC鉴别为可能的或肯定的人类致癌物。
生殖毒性
致畸性 - 兔子 - 经口
母体效应:其他影响。
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入可能有害。 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
摄入 误吞对人体有害。
皮肤 如果通过皮肤吸收可能是有害的。 可能引起皮肤刺激。
眼睛 可能引起眼睛刺激。
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: FD1190000
模块 12. 生态学资料
12.1 生态毒性
对鱼类的毒性 半数致死浓度(LC50) - Oncorhynchus mykiss (红鳟) - > 175 mg/l - 96 h
对水蚤和其他水生无脊 半致死有效浓度(EC50) - Daphnia magna (大型蚤) - 29.5 mg/l - 48 h
椎动物的毒性
12.2 持久存留性和降解性
无数据资料
12.3 潜在的生物蓄积性
无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移性
无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价
无数据资料
12.6 其它不利的影响
对水生生物有害。
无数据资料
模块 13. 废弃处置
13.1 废物处理方法
产品
将剩余的和未回收的溶液交给处理公司。 联系专业的拥有废弃物处理执照的机构来处理此物质。
与易燃溶剂相溶或者相混合,在备有燃烧后处理和洗刷作用的化学焚化炉中燃烧
受污染的容器和包装
作为未用过的产品弃置。
模块 14. 运输信息
14.1 联合国危险货物编号
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.2 联合国(UN)规定的名称
欧洲陆运危规: 非危险货物
国际海运危规: 非危险货物
国际空运危规: 非危险货物
14.3 运输危险类别
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.4 包裹组
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.5 环境危险
欧洲陆运危规: 否 国际海运危规 海运污染物: 否 国际空运危规: 否
14.6 对使用者的特别提醒
无数据资料
模块 15 - 法规信息
N/A
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
除草剂磺草灵
产品信息 磺草灵(商品名称:Asilan,其他名称:Asulox、MB9057)属于氨基甲酸酯类选择性内吸传导型苗期除草剂。它是细胞生长抑制剂。于1965年由H. J. Cottrell & B. J. Heywood首次报道,并由May和Baker公司(现属拜耳)上市。主要应用于甘蔗、冷杉、草皮、观赏性作物及非作物领域,剂型为水剂。
**2022年6月28日,农业农村部农药检定所公示了2022年第5批拟批准登记农药产品名单。其中包含南通泰禾化工股份有限公司的97%磺草灵原药(仅限出口到澳大利亚),这是国内首个磺草灵原药。
作用机理 磺草灵是一种内吸传导型氨基甲酸酯类除草剂,易被植物茎、叶、根吸收后迅速传导至地下根茎生长点,使地下根茎呼吸受抑制并丧失繁殖能力,阻碍细胞分裂而致植株枯死。其作用机制在于妨碍叶酸合成,减少核酸合成。
毒性 大鼠急性经口LD50 > 8000 mg/kg,急性经皮LD50 > 1200 mg/kg;小鼠急性经口LD50 17540 mg/kg(雄),急性经皮LD50 15000 mg/kg;钾盐小鼠急性经口LD50 9386 mg/kg。该农药毒性分级为中毒。
物理化学性质 磺草灵可燃性危险特性为燃烧产生有毒氮氧化物、硫氧化物气体,储运时应库房通风低温干燥,并与食品原料分开存储运输;灭火剂建议使用干粉、泡沫或砂土。
生产方法制备方法一
- 先将对氨基苯磺酰胺与乙酰氯反应生成对乙酰氨基苯磺酰胺,将其保护为氨基。
- 之后将2.14kg (10.0mol) 4-乙酰氨基苯磺酰胺、1.75g (12.7mol)无水碳酸钾和16L丙酮混合物在搅拌下缓慢添加1.14kg (12.1mol)氯甲酸甲酯。
- 加毕,加热回流18h,冷至室温后过滤。滤饼悬浮在水中并用盐酸酸化至酸性得到粗品。再溶解于碳酸氢钠溶液中,过滤得精制品。
制备方法二 将氯甲酸甲酯与甲醇回流反应脱去一分子氯化氢生成碳酸二甲酯;然后在甲醇钠存在下与对氨基苯磺酰胺作用生成磺草灵。
分类- 农药
- 毒性分级:中毒
- 急性毒性:
- 口服-大鼠 LD50: 2000 毫克/公斤;
- 口服-小鼠 LD50: 5000 毫克/公斤
在阔叶杂草发生密度较大的甘蔗田,可与莠去津混用。茎叶处理时加入中性洗衣粉等湿润剂3~4.5g可以提高防除效果。
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:A Convenient Method of Protection and Mild Deprotection of α-Aminoacids摘要:Functionalisation of beta or gamma carboxyl group of aspartic and glutamic acids with labile substituents was performed via the use of N-trichloroethoxycarbonyl-5-oxazolidinone as protective group.DOI:10.1080/00397919308018603
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:CH222077摘要:公开号:
文献信息
-
[EN] ACC INHIBITORS AND USES THEREOF<br/>[FR] INHIBITEURS DE L'ACC ET UTILISATIONS ASSOCIÉES
-
[EN] 3-[(HYDRAZONO)METHYL]-N-(TETRAZOL-5-YL)-BENZAMIDE AND 3-[(HYDRAZONO)METHYL]-N-(1,3,4-OXADIAZOL-2-YL)-BENZAMIDE DERIVATIVES AS HERBICIDES<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS DE 3-[(HYDRAZONO))MÉTHYL]-N-(TÉTRAZOL-5-YL)-BENZAMIDE ET DE 3-[(HYDRAZONO)MÉTHYL]-N-(1,3,4-OXADIAZOL-2-YL)-BENZAMIDE UTILISÉS EN TANT QU'HERBICIDES申请人:SYNGENTA CROP PROTECTION AG公开号:WO2021013969A1公开(公告)日:2021-01-28The present invention related to compounds of Formula (I): or an agronomically acceptable salt thereof, wherein Q, R2, R3, R4, R5 and R6 are as described herein. The invention further relates to compositions comprising said compounds, to methods of controlling weeds using said compositions, and to the use of compounds of Formula (I) as a herbicide.本发明涉及以下式(I)的化合物或其农业上可接受的盐,其中Q、R2、R3、R4、R5和R6如本文所述。该发明还涉及包含所述化合物的组合物,使用这些组合物控制杂草的方法,以及将式(I)的化合物用作除草剂的用途。
-
[EN] INSECTICIDAL TRIAZINONE DERIVATIVES<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS DE TRIAZINONE INSECTICIDES申请人:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG公开号:WO2013079350A1公开(公告)日:2013-06-06Compounds of the formula (I) or (I'), wherein the substituents are as defined in claim 1, are useful as pesticides.式(I)或(I')的化合物,其中取代基如权利要求1所定义的那样,可用作杀虫剂。
-
[EN] HERBICIDALLY ACTIVE HETEROARYL-S?BSTIT?TED CYCLIC DIONES OR DERIVATIVES THEREOF<br/>[FR] DIONES CYCLIQUES SUBSTITUÉES PAR HÉTÉROARYLE À ACTIVITÉ HERBICIDE OU DÉRIVÉS DE CELLES-CI申请人:SYNGENTA LTD公开号:WO2011012862A1公开(公告)日:2011-02-03The invention relates to a compound of formula (I), which is suitable for use as a herbicide wherein G is hydrogen or an agriculturally acceptable metal, sulfonium, ammonium or latentiating group; Q is a unsubstituted or substituted C3-C8 saturated or mono-unsaturated heterocyclyl containing at least one heteroatom selected from O, N and S, or Q is heteroaryl or substituted heteroaryl; m is 1, 2 or 3; and Het is an optionally substituted monocyclic or bicyclic heteroaromatic ring; and wherein the compound is optionally an agronomically acceptable salt thereof.
-
TRIAZOLE ACC INHIBITORS AND USES THEREOF
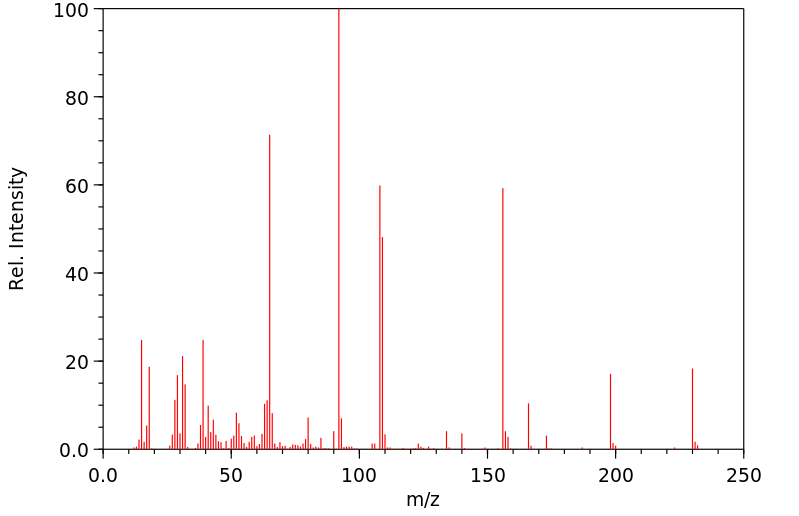
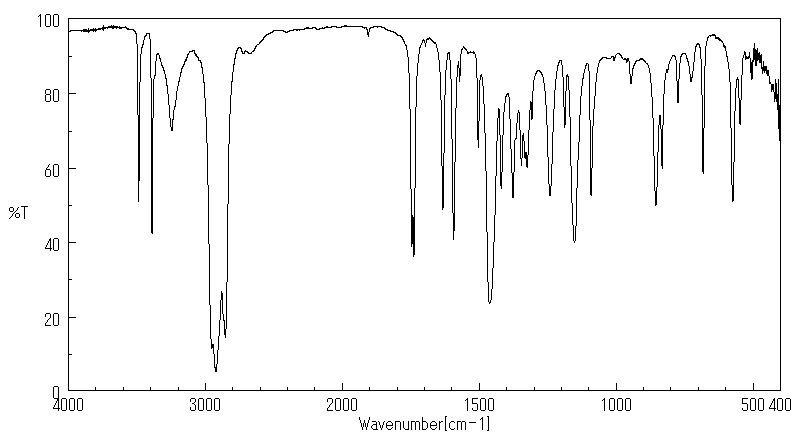
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(βS)-β-氨基-4-(4-羟基苯氧基)-3,5-二碘苯甲丙醇
(S,S)-邻甲苯基-DIPAMP
(S)-(-)-7'-〔4(S)-(苄基)恶唑-2-基]-7-二(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-2,2',3,3'-四氢-1,1-螺二氢茚
(S)-盐酸沙丁胺醇
(S)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧磷杂环戊二烯
(S)-2,2'-双[双(3,5-三氟甲基苯基)膦基]-4,4',6,6'-四甲氧基联苯
(S)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(R)富马酸托特罗定
(R)-(-)-盐酸尼古地平
(R)-(-)-4,12-双(二苯基膦基)[2.2]对环芳烷(1,5环辛二烯)铑(I)四氟硼酸盐
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[((6-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(4-叔丁基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(3-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-4,7-双(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-7“-[(吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2”,3,3'-四氢1,1'-螺二茚满
(R)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二苯氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂环戊烯
(R)-2-[((二苯基膦基)甲基]吡咯烷
(R)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(N-(4-甲氧基苯基)-N-甲基-3-(1-哌啶基)丙-2-烯酰胺)
(5-溴-2-羟基苯基)-4-氯苯甲酮
(5-溴-2-氯苯基)(4-羟基苯基)甲酮
(5-氧代-3-苯基-2,5-二氢-1,2,3,4-oxatriazol-3-鎓)
(4S,5R)-4-甲基-5-苯基-1,2,3-氧代噻唑烷-2,2-二氧化物-3-羧酸叔丁酯
(4S,4''S)-2,2''-亚环戊基双[4,5-二氢-4-(苯甲基)恶唑]
(4-溴苯基)-[2-氟-4-[6-[甲基(丙-2-烯基)氨基]己氧基]苯基]甲酮
(4-丁氧基苯甲基)三苯基溴化磷
(3aR,8aR)-(-)-4,4,8,8-四(3,5-二甲基苯基)四氢-2,2-二甲基-6-苯基-1,3-二氧戊环[4,5-e]二恶唑磷
(3aR,6aS)-5-氧代六氢环戊基[c]吡咯-2(1H)-羧酸酯
(2Z)-3-[[(4-氯苯基)氨基]-2-氰基丙烯酸乙酯
(2S,3S,5S)-5-(叔丁氧基甲酰氨基)-2-(N-5-噻唑基-甲氧羰基)氨基-1,6-二苯基-3-羟基己烷
(2S,2''S,3S,3''S)-3,3''-二叔丁基-4,4''-双(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-2,2''-联苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂戊环
(2S)-(-)-2-{[[[[3,5-双(氟代甲基)苯基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基}-N-(二苯基甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[((1S,2S)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[[((1R,2R)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2-硝基苯基)磷酸三酰胺
(2,6-二氯苯基)乙酰氯
(2,3-二甲氧基-5-甲基苯基)硼酸
(1S,2S,3S,5S)-5-叠氮基-3-(苯基甲氧基)-2-[(苯基甲氧基)甲基]环戊醇
(1S,2S,3R,5R)-2-(苄氧基)甲基-6-氧杂双环[3.1.0]己-3-醇
(1-(4-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(3-溴苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氯苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2,6-二氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(-)-去甲基西布曲明
龙蒿油
龙胆酸钠
龙胆酸叔丁酯
龙胆酸
龙胆紫-d6
龙胆紫