Cis-1,4-Cyclohexanedicarboxylic Acid | 619-81-8
中文名称
——
中文别名
——
英文名称
Cis-1,4-Cyclohexanedicarboxylic Acid
英文别名
cis-cyclohexane-1,4-dicarboxylic acid;(1s,4s)-cyclohexane-1,4-dicarboxylic acid;meso-cis-1,4-cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid;cis-e,a-1,4-cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid;e,a-cis-1,4-cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid;1,4-cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid
CAS
619-81-8
化学式
C8H12O4
mdl
——
分子量
172.181
InChiKey
PXGZQGDTEZPERC-OLQVQODUSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:168 °C
-
沸点:384.1±35.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.3200
-
溶解度:溶于乙醇、乙醚、氯仿、甲醇
-
稳定性/保质期:
远离氧化物和强碱。
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0.96
-
重原子数:12.0
-
可旋转键数:2.0
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.75
-
拓扑面积:74.6
-
氢给体数:2.0
-
氢受体数:2.0
安全信息
-
海关编码:2917209090
-
危险性防范说明:P261,P305+P351+P338
-
危险性描述:H302,H315,H319,H335
-
储存条件:存放在密封容器内,并放置在阴凉、干燥处。储存地点须远离氧化剂和火源。
SDS
顺-1,4-环己烷二甲酸 修改号码:5
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: cis-1,4-Cyclohexanedicarboxylic Acid
修改号码: 5
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害
皮肤腐蚀/刺激 第2级
严重损伤/刺激眼睛 2A类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志
信号词 警告
危险描述 造成皮肤刺激
造成严重眼刺激
防范说明
[预防] 处理后要彻底清洗双手。
穿戴防护手套/护目镜/防护面具。
[急救措施] 眼睛接触:用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续冲洗。
眼睛接触:求医/就诊
皮肤接触:用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激:求医/就诊。
脱掉被污染的衣物,清洗后方可重新使用。
其他没有分类的危险 粉末或颗粒状与空气混合可能引起粉尘爆炸
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 顺-1,4-环己烷二甲酸
百分比: >90.0%(GC)
CAS编码: 619-81-8
顺-1,4-环己烷二甲酸 修改号码:5
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
分子式: C8H12O4
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,雾状水,二氧化碳
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 清扫收集粉尘,封入密闭容器。注意切勿分散。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的
法律法规处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止粉尘扩散。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果粉尘或浮质产生,使用局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防尘面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
外形(20°C): 固体
外观: 晶体-粉末
颜色: 白色类白色
顺-1,4-环己烷二甲酸 修改号码:5
模块 9. 理化特性
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点:
168°C
沸点/沸程 无资料
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 无资料
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂]
溶于: 甲醇, 醚, 氯仿, 乙醇
log水分配系数 = 1.32
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 粉末或颗粒状与空气混合可能引起粉尘爆炸。
避免接触的条件: 静电
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂, 强碱
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 1.32
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在可燃溶剂中溶解混合,在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中
焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
顺-1,4-环己烷二甲酸 修改号码:5
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: cis-1,4-Cyclohexanedicarboxylic Acid
修改号码: 5
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害
皮肤腐蚀/刺激 第2级
严重损伤/刺激眼睛 2A类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志
信号词 警告
危险描述 造成皮肤刺激
造成严重眼刺激
防范说明
[预防] 处理后要彻底清洗双手。
穿戴防护手套/护目镜/防护面具。
[急救措施] 眼睛接触:用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续冲洗。
眼睛接触:求医/就诊
皮肤接触:用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激:求医/就诊。
脱掉被污染的衣物,清洗后方可重新使用。
其他没有分类的危险 粉末或颗粒状与空气混合可能引起粉尘爆炸
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 顺-1,4-环己烷二甲酸
百分比: >90.0%(GC)
CAS编码: 619-81-8
顺-1,4-环己烷二甲酸 修改号码:5
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
分子式: C8H12O4
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,雾状水,二氧化碳
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 清扫收集粉尘,封入密闭容器。注意切勿分散。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的
法律法规处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止粉尘扩散。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果粉尘或浮质产生,使用局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防尘面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
外形(20°C): 固体
外观: 晶体-粉末
颜色: 白色类白色
顺-1,4-环己烷二甲酸 修改号码:5
模块 9. 理化特性
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点:
168°C
沸点/沸程 无资料
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 无资料
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂]
溶于: 甲醇, 醚, 氯仿, 乙醇
log水分配系数 = 1.32
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 粉末或颗粒状与空气混合可能引起粉尘爆炸。
避免接触的条件: 静电
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂, 强碱
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 1.32
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在可燃溶剂中溶解混合,在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中
焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
顺-1,4-环己烷二甲酸 修改号码:5
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 (1R,4r)-4-(乙氧基羰基)环己烷羧酸 cyclohexane-1,4-dicarboxylic acid monoethyl ester 15177-66-9 C10H16O4 200.235 —— 1,1,4,4-Cyclohexanetetracarboxylic acid 153032-61-2 C10H12O8 260.2 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— trans-1,4-Cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid 619-82-9 C8H12O4 172.181 —— (1s,4s)-Dimethyl cyclohexane-1,4-dicarboxylate 3399-21-1 C10H16O4 200.235 —— cis-CHDM 3236-47-3 C8H16O2 144.214 3-氧杂二环[3.2.2]壬烷-2,4-二酮 3-Oxa-bicyclo<3.2.2>nonan-2,4-dion 4355-32-2 C8H10O3 154.166
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:Cis-1,4-Cyclohexanedicarboxylic Acid 在 dimethyl sulfide borane 作用下, 以 四氢呋喃 为溶剂, 反应 2.0h, 以100%的产率得到cis-CHDM参考文献:名称:XL01126 的发现:一种有效、快速、协同、选择性、口服生物可利用且血脑屏障渗透性的富含亮氨酸重复激酶 2 的 PROTAC 降解剂摘要:富含亮氨酸重复激酶 2 (LRRK2) 是帕金森病最有希望的靶点之一。 LRRK2 靶向策略主要集中于 1 型激酶抑制剂,但其具有局限性,因为受抑制的蛋白质会干扰自然机制,从而可能导致不良副作用。在此,我们报告了 LRRK2 蛋白水解靶向嵌合体 (PROTAC) 的开发,最终发现了降解剂 XL01126,作为替代 LRRK2 靶向策略。基于 E3 连接酶 von Hippel-Lindau (VHL)、Cereblon (CRBN) 和细胞凋亡抑制剂 (cIAP) 配体的 PROTAC 的初步设计和筛选确定了含有硫醚缀合的 VHL 配体 VH101 的最佳降解剂。第二轮药物化学探索使 XL01126 成为多种细胞系中 LRRK2 的快速有效降解剂,其 DC 50值在 15-72 nM 范围内, D最大值范围在 82% 至 90% 之间,降解半衰期跨越0.6 至 2.4 小时。 XL01126DOI:10.1021/jacs.2c05499
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Baeyer, Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie, 1888, vol. 245, p. 156摘要:DOI:
文献信息
-
Compositions for Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis and Other Chronic Diseases申请人:Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated公开号:US20150231142A1公开(公告)日:2015-08-20The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising an inhibitor of epithelial sodium channel activity in combination with at least one ABC Transporter modulator compound of Formula A, Formula B, Formula C, or Formula D. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical formulations thereof, and to methods of using such compositions in the treatment of CFTR mediated diseases, particularly cystic fibrosis using the pharmaceutical combination compositions.
-
COMPOSITIONS FOR TREATMENT OF CYSTIC FIBROSIS AND OTHER CHRONIC DISEASES申请人:Van Goor Fredrick F.公开号:US20110098311A1公开(公告)日:2011-04-28The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising an inhibitor of epithelial sodium channel activity in combination with at least one ABC Transporter modulator compound of Formula A, Formula B, Formula C, or Formula D. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical formulations thereof, and to methods of using such compositions in the treatment of CFTR mediated diseases, particularly cystic fibrosis using the pharmaceutical combination compositions.
-
Epimerization of Tertiary Carbon Centers via Reversible Radical Cleavage of Unactivated C(sp<sup>3</sup>)–H Bonds作者:Yaxin Wang、Xiafei Hu、Cristian A. Morales-Rivera、Guo-Xing Li、Xin Huang、Gang He、Peng Liu、Gong ChenDOI:10.1021/jacs.8b05753日期:2018.8.1cleavage of C(sp3)-H bonds can enable racemization or epimerization, offering a valuable tool to edit the stereochemistry of organic compounds. While epimerization reactions operating via cleavage of acidic C(sp3)-H bonds, such as the Cα-H of carbonyl compounds, have been widely used in organic synthesis and enzyme-catalyzed biosynthesis, epimerization of tertiary carbons bearing a nonacidic C(sp3)-H bondC(sp3)-H 键的可逆断裂可以实现外消旋化或差向异构化,为编辑有机化合物的立体化学提供了宝贵的工具。虽然通过裂解酸性 C(sp3)-H 键(例如羰基化合物的 Cα-H)进行的差向异构化反应已广泛用于有机合成和酶催化生物合成,但带有非酸性 C(sp3) 的叔碳的差向异构化-H 键更具挑战性,可用的实用方法很少。在这里,我们报告了第一个合成有用的协议,用于在温和条件下通过未活化的 C(sp3)-H 键与高价碘试剂苯并恶唑叠氮化物和 H2O 的可逆自由基裂解来进行叔碳差向异构化。这些反应对各种环烷烃的未活化 3° CH 键表现出优异的反应性和选择性,并为编辑传统方法难以处理的碳支架的立体化学构型提供了强大的策略。机理研究表明,N3• 作为催化氢原子穿梭的独特能力对于以高效率和选择性可逆地破坏和重组 3° CH 键至关重要。
-
METHOD FOR PRODUCING TRANS-BIS(AMINOMETHYL)CYCLOHEXANE, METHOD FOR PRODUCING BIS(ISOCYANATOMETHYL)CYCLOHEXANE, BIS(ISOCYANATOMETHYL)CYCLOHEXANE, POLYISOCYANATE COMPOSITION, AND POLYURETHANE RESIN申请人:MITSUI CHEMICALS, INC.公开号:US20160207875A1公开(公告)日:2016-07-21A method for producing trans-bis(aminomethyl)cyclohexane includes a trans-isomerization step in which cis-dicyanocyclohexane is isomerized into trans-dicyanocyclohexane by heating dicyanocyclohexane containing cis-dicyanocyclohexane in the presence of a tar component produced by distillation of dicyanocyclohexane; and an aminomethylation step in which trans-dicyanocyclohexane produced by the trans-isomerization step is allowed to contact with hydrogen to produce trans-bis(aminomethyl)cyclohexane.
-
Heterocyclic Compounds申请人:Yen Chi-Feng公开号:US20090264339A1公开(公告)日:2009-10-22This invention relates to heterocyclic compounds of the formulas shown in the specification. It also relates to methods for treating inflammatory diseases or immune diseases, developmental or degenerative diseases, and tissue injuries with one of the heterocyclic compounds.这项发明涉及规范中所示的异环化合物。它还涉及使用其中一种异环化合物治疗炎症性疾病或免疫性疾病、发育性或退行性疾病以及组织损伤的方法。
表征谱图
-
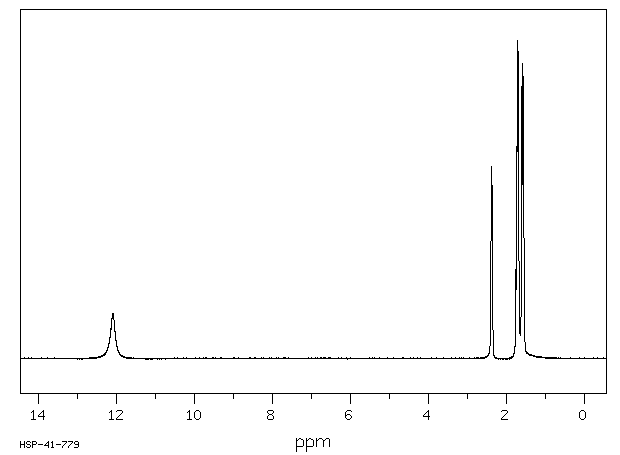
氢谱1HNMR
-
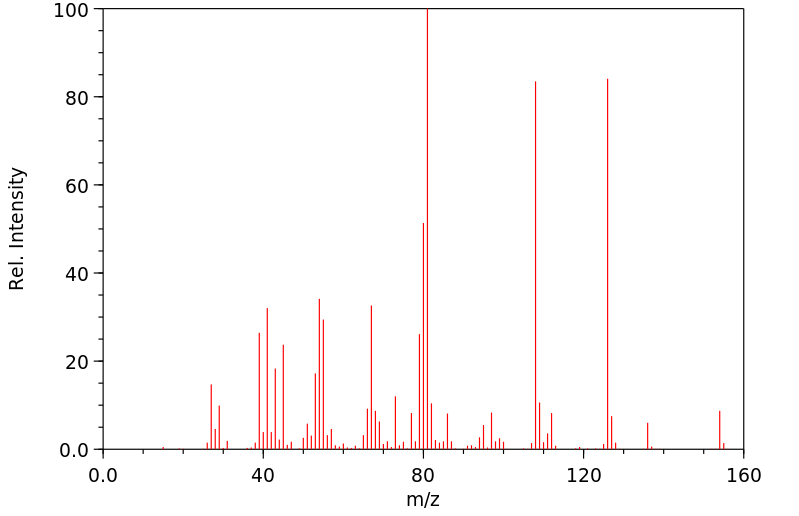
质谱MS
-
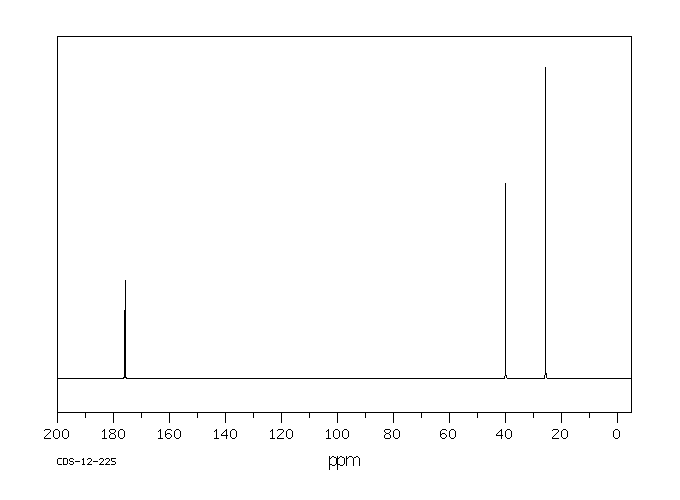
碳谱13CNMR
-
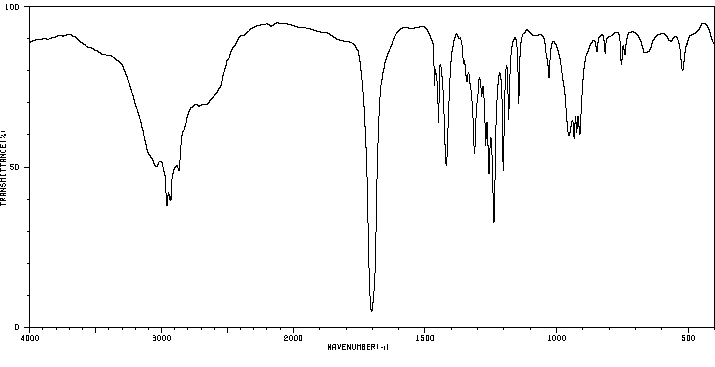
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(甲基3-(二甲基氨基)-2-苯基-2H-azirene-2-羧酸乙酯)
(±)-盐酸氯吡格雷
(±)-丙酰肉碱氯化物
(d(CH2)51,Tyr(Me)2,Arg8)-血管加压素
(S)-(+)-α-氨基-4-羧基-2-甲基苯乙酸
(S)-阿拉考特盐酸盐
(S)-赖诺普利-d5钠
(S)-2-氨基-5-氧代己酸,氢溴酸盐
(S)-2-[[[(1R,2R)-2-[[[3,5-双(叔丁基)-2-羟基苯基]亚甲基]氨基]环己基]硫脲基]-N-苄基-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(S)-2-[3-[(1R,2R)-2-(二丙基氨基)环己基]硫脲基]-N-异丙基-3,3-二甲基丁酰胺
(S)-1-(4-氨基氧基乙酰胺基苄基)乙二胺四乙酸
(S)-1-[N-[3-苯基-1-[(苯基甲氧基)羰基]丙基]-L-丙氨酰基]-L-脯氨酸
(R)-乙基N-甲酰基-N-(1-苯乙基)甘氨酸
(R)-丙酰肉碱-d3氯化物
(R)-4-N-Cbz-哌嗪-2-甲酸甲酯
(R)-3-氨基-2-苄基丙酸盐酸盐
(R)-1-(3-溴-2-甲基-1-氧丙基)-L-脯氨酸
(N-[(苄氧基)羰基]丙氨酰-N〜5〜-(diaminomethylidene)鸟氨酸)
(6-氯-2-吲哚基甲基)乙酰氨基丙二酸二乙酯
(4R)-N-亚硝基噻唑烷-4-羧酸
(3R)-1-噻-4-氮杂螺[4.4]壬烷-3-羧酸
(3-硝基-1H-1,2,4-三唑-1-基)乙酸乙酯
(2S,4R)-Boc-4-环己基-吡咯烷-2-羧酸
(2S,3S,5S)-2-氨基-3-羟基-1,6-二苯己烷-5-N-氨基甲酰基-L-缬氨酸
(2S,3S)-3-((S)-1-((1-(4-氟苯基)-1H-1,2,3-三唑-4-基)-甲基氨基)-1-氧-3-(噻唑-4-基)丙-2-基氨基甲酰基)-环氧乙烷-2-羧酸
(2S)-2,6-二氨基-N-[4-(5-氟-1,3-苯并噻唑-2-基)-2-甲基苯基]己酰胺二盐酸盐
(2S)-2-氨基-N,3,3-三甲基-N-(苯甲基)丁酰胺
(2S)-2-氨基-3-甲基-N-2-吡啶基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-(苯基甲基)丁酰胺,
(2S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-2-吡啶基丁酰胺
(2S,4R)-1-((S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基丁酰基)-4-羟基-N-(4-(4-甲基噻唑-5-基)苄基)吡咯烷-2-甲酰胺盐酸盐
(2R,3'S)苯那普利叔丁基酯d5
(2R)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-(苯甲基)丁酰胺
(2-氯丙烯基)草酰氯
(1S,3S,5S)-2-Boc-2-氮杂双环[3.1.0]己烷-3-羧酸
(1R,5R,6R)-5-(1-乙基丙氧基)-7-氧杂双环[4.1.0]庚-3-烯-3-羧酸乙基酯
(1R,4R,5S,6R)-4-氨基-2-氧杂双环[3.1.0]己烷-4,6-二羧酸
齐特巴坦
齐德巴坦钠盐
齐墩果-12-烯-28-酸,2,3-二羟基-,苯基甲基酯,(2a,3a)-
齐墩果-12-烯-28-酸,2,3-二羟基-,羧基甲基酯,(2a,3b)-(9CI)
黄酮-8-乙酸二甲氨基乙基酯
黄荧菌素
黄体生成激素释放激素(1-6)
黄体生成激素释放激素 (1-5) 酰肼
黄体瑞林
麦醇溶蛋白
麦角硫因
麦芽聚糖六乙酸酯
麦根酸