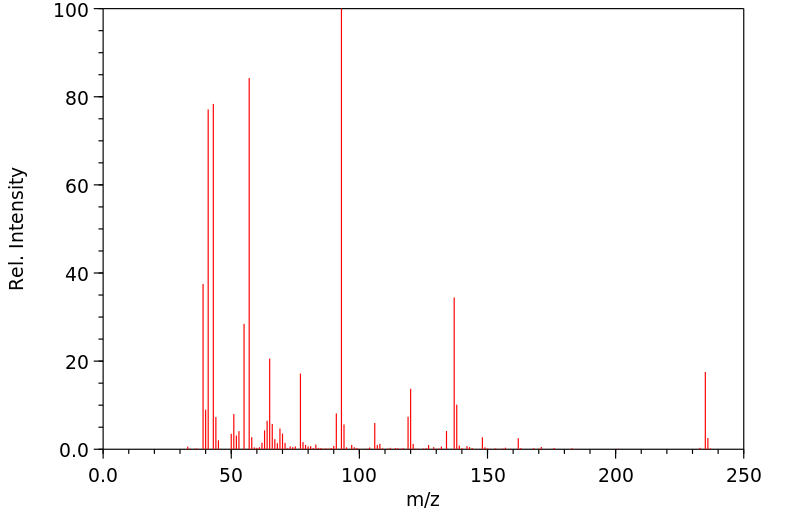
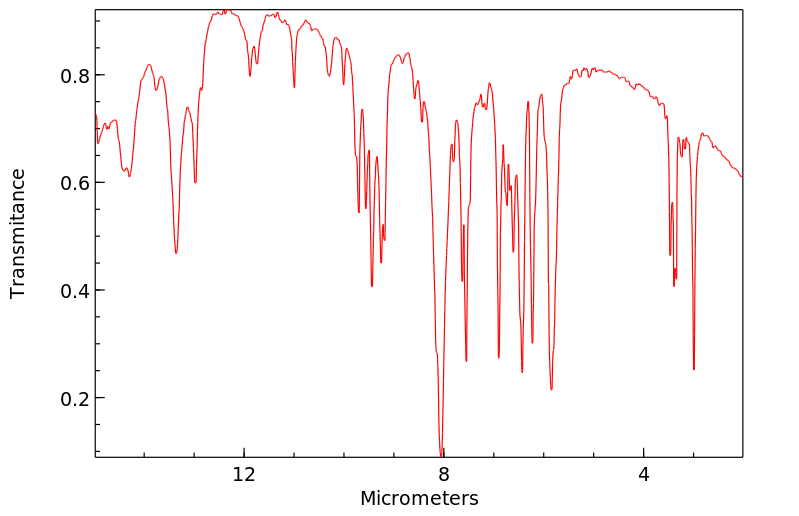
N-phenyl heptyl carbamate | 109562-39-2
中文名称
——
中文别名
——
英文名称
N-phenyl heptyl carbamate
英文别名
heptyl phenylcarbamate;Heptanol-(1), Phenyl-carbamoyl-Derivat;1-Phenylcarbamoyl-heptanol-(1);phenyl-carbamic acid heptyl ester;N-phenyl carbamic acid (1-heptyl) ester;Phenyl-carbamidsaeure-heptylester;Carbanilsaeure-n-heptylester;Carbanilic acid, n-heptyl ester;heptyl N-phenylcarbamate
CAS
109562-39-2
化学式
C14H21NO2
mdl
——
分子量
235.326
InChiKey
OJXUXLGVKNOXFM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:58-58.5 °C
-
沸点:300.8±11.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.032±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):4.9
-
重原子数:17
-
可旋转键数:8
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.5
-
拓扑面积:38.3
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:2
安全信息
-
海关编码:2924299090
SDS
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:N-phenyl heptyl carbamate 在 二月桂酸二丁基锡 硫酸 作用下, 以 硝基苯 为溶剂, 100.0~250.0 ℃ 、20.0 kPa 条件下, 生成 N,N'-(4,4'-methanediyl-diphenyl)-biscarbamic acid bis(2,4-di-tert-amylphenyl) ester参考文献:名称:PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF N-SUBSTITUTED CARBAMIC ACID ESTER AND PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF ISOCYANATE USING THE N-SUBSTITUTED CARBAMIC ACID ESTER摘要:公开号:EP2322504B9
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:使用三苯基膦/三氯异氰尿酸体系高产、快速、多组分合成尿素和氨基甲酸酯衍生物摘要:图形摘要摘要描述了使用三苯基膦(PPh3)/三氯异氰尿酸系统从胺和醇合成脲和氨基甲酸酯衍生物的有效方法。该协议允许制备对称、不对称的二、三和四取代脲和氨基甲酸酯,并且可以容忍广泛的官能团。为了优化反应条件,研究了温度、胺和醇的浓度、溶剂和反应时间等实验变量。在优化的条件下获得了令人满意的产量。本方法在实验上简单、温和,是现有方法的一种有价值的替代方法。DOI:10.1080/10426507.2015.1085038
文献信息
-
(4-Arylsulfamoyl)phenylcarbamic acid esters: I. Synthesis and activity against herpes viruses作者:V. I. Krutikov、A. V. Erkin、V. V. Tets、A. A. ShmarovDOI:10.1134/s1070363216070069日期:2016.7Aiming to modify the biological activity of sulfonamides, a number of alkyl (4-arylsulfamoyl)- phenylcarbamates were prepared in 50–70% yield. Biological screening showed that the target compounds possessed a high activity against herpes viruses as well as a traditional antibiotic one.
-
Direct Catalytic Synthesis of <i>N</i> ‐Arylcarbamates from CO <sub>2</sub> , Anilines and Alcohols作者:Masazumi Tamura、Ayaka Miura、Masayoshi Honda、Yu Gu、Yoshinao Nakagawa、Keiichi TomishigeDOI:10.1002/cctc.201801443日期:2018.11.7The direct catalytic synthesis of carbamates from CO2, amines and methanol was achieved by controlling both the reaction equilibrium and the reactivity of the three components. The combination of CeO2 and 2‐cyanopyridine was an effective catalyst, providing various carbamates including N‐arylcarbamates in high selectivities.
-
An Efficient, One-Pot Synthesis of Carbamates from the Corresponding Alcohols Using Mitsunobu’s Reagent作者:Devdutt Chaturvedi、Nisha Mishra、Virendra MishraDOI:10.1007/s00706-006-0557-2日期:2007.1A novel Mitsunobu -based protocol was developed for the synthesis of carbamates from the corresponding alcohols using carbon dioxide and amines in good to excellent yields. This protocol is mild, chemoselective, and efficient compared to other reported methods.
-
Selenium-Catalyzed Oxidative Carbonylation of Aniline and Alcohols to <i>N</i>-Phenylcarbamates作者:Xiaopeng Zhang、Huanzhi Jing、Guisheng ZhangDOI:10.1080/00397910903134626日期:2010.5.11A facile one-pot, phosgene-free synthesis of N-phenylcarbamates is demonstrated. Catalyzed by selenium, oxidative carbonylation of aniline with alcohols in the presence of carbon monoxide and oxygen affords the corresponding N-phenylcarbamates, mostly in fair to good yields. Selenium can be easily recovered because of its phase-transfer catalysis function.
-
Discovery and Mechanistic Understanding of a Lipase from <i>Rhizorhabdus dicambivorans</i> for Efficient Ester Aminolysis in Aromatic Amines作者:Jialing Wang、Zhuangzhuang Huang、Haodong Xu、Yong Nian、Bin Wu、Bingfang He、Gerhard SchenkDOI:10.1002/cssc.202301735日期:——A new lipase, Ndbn, capable of efficiently catalyzing the amidation between esters and aromatic amines which are weak nucleophilic reagents was discovered. Furthermore, Ndbn exhibits the capability to catalyze the aminolysis of carboxylic acids without the need for preparing ester substrate or a strictly anhydrous reaction environment. Additionally, an unusual preference of Ndbn for aromatic amines
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(βS)-β-氨基-4-(4-羟基苯氧基)-3,5-二碘苯甲丙醇
(S,S)-邻甲苯基-DIPAMP
(S)-(-)-7'-〔4(S)-(苄基)恶唑-2-基]-7-二(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-2,2',3,3'-四氢-1,1-螺二氢茚
(S)-盐酸沙丁胺醇
(S)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧磷杂环戊二烯
(S)-2,2'-双[双(3,5-三氟甲基苯基)膦基]-4,4',6,6'-四甲氧基联苯
(S)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(R)富马酸托特罗定
(R)-(-)-盐酸尼古地平
(R)-(-)-4,12-双(二苯基膦基)[2.2]对环芳烷(1,5环辛二烯)铑(I)四氟硼酸盐
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[((6-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(4-叔丁基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(3-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-4,7-双(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-7“-[(吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2”,3,3'-四氢1,1'-螺二茚满
(R)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二苯氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂环戊烯
(R)-2-[((二苯基膦基)甲基]吡咯烷
(R)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(N-(4-甲氧基苯基)-N-甲基-3-(1-哌啶基)丙-2-烯酰胺)
(5-溴-2-羟基苯基)-4-氯苯甲酮
(5-溴-2-氯苯基)(4-羟基苯基)甲酮
(5-氧代-3-苯基-2,5-二氢-1,2,3,4-oxatriazol-3-鎓)
(4S,5R)-4-甲基-5-苯基-1,2,3-氧代噻唑烷-2,2-二氧化物-3-羧酸叔丁酯
(4S,4''S)-2,2''-亚环戊基双[4,5-二氢-4-(苯甲基)恶唑]
(4-溴苯基)-[2-氟-4-[6-[甲基(丙-2-烯基)氨基]己氧基]苯基]甲酮
(4-丁氧基苯甲基)三苯基溴化磷
(3aR,8aR)-(-)-4,4,8,8-四(3,5-二甲基苯基)四氢-2,2-二甲基-6-苯基-1,3-二氧戊环[4,5-e]二恶唑磷
(3aR,6aS)-5-氧代六氢环戊基[c]吡咯-2(1H)-羧酸酯
(2Z)-3-[[(4-氯苯基)氨基]-2-氰基丙烯酸乙酯
(2S,3S,5S)-5-(叔丁氧基甲酰氨基)-2-(N-5-噻唑基-甲氧羰基)氨基-1,6-二苯基-3-羟基己烷
(2S,2''S,3S,3''S)-3,3''-二叔丁基-4,4''-双(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-2,2''-联苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂戊环
(2S)-(-)-2-{[[[[3,5-双(氟代甲基)苯基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基}-N-(二苯基甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[((1S,2S)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[[((1R,2R)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2-硝基苯基)磷酸三酰胺
(2,6-二氯苯基)乙酰氯
(2,3-二甲氧基-5-甲基苯基)硼酸
(1S,2S,3S,5S)-5-叠氮基-3-(苯基甲氧基)-2-[(苯基甲氧基)甲基]环戊醇
(1S,2S,3R,5R)-2-(苄氧基)甲基-6-氧杂双环[3.1.0]己-3-醇
(1-(4-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(3-溴苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氯苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2,6-二氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(-)-去甲基西布曲明
龙蒿油
龙胆酸钠
龙胆酸叔丁酯
龙胆酸
龙胆紫-d6
龙胆紫