聚维酮碘(PVP-I) | 25655-41-8
中文名称
聚维酮碘(PVP-I)
中文别名
聚乙烯吡咯烷酮碘络合物;聚乙烯吡咯烷酮碘;碘络酮;吡咯烷酮碘;聚维酮碘;聚乙烯吡咯烷酮与碘的混合物;PVP碘;PVP-I
英文名称
Povidone-Iodine
英文别名
PVP-I;Povidone iodine;1-ethenylpyrrolidin-2-one;molecular iodine
CAS
25655-41-8
化学式
C6H9NO*I2
mdl
——
分子量
364.953
InChiKey
CPKVUHPKYQGHMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:300 °C
-
溶解度:H2O:可溶,100mg/mL
-
物理描述:DryPowder
-
颜色/状态:Yellowish-brown amorphous hygroscopic powder
-
气味:A slight characteristic odor
-
稳定性/保质期:
遵照规定使用和储存,则不会分解。
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2.52
-
重原子数:10
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.5
-
拓扑面积:20.3
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:1
ADMET
毒理性
识别和使用:1-乙烯基-2-吡咯烷酮聚合物,碘复合物(聚维酮碘)是一种淡黄棕色的无定形吸湿性粉末。聚维酮碘是一种碘载体,主要用于消毒和防腐,主要用于治疗污染的伤口和手术前皮肤和粘膜的准备,也用于设备的消毒。人类暴露和毒性:在对413名接触性皮炎患者进行的贴片测试中,有1人对聚维酮碘过敏。在一例双手背部一度和二度烧伤使用聚维酮碘治疗的第二周,出现了可逆性甲状腺功能亢进;延迟碘排泄可能涉及其中。另一份病例报告显示,一名二度烧伤的患者在使用聚维酮碘外用治疗后出现了严重的钠过多和酸中毒。此外,在新生儿局部应用聚维酮碘软膏于手术伤口后,还描述了甲状腺功能减退症。烧伤是聚维酮碘使用的罕见但潜在的严重并发症。急性肾衰竭是聚维酮碘管理的可能副作用,尤其是通过粘膜表面。此外,即使是稀释的聚维酮碘溶液对人类成纤维细胞也有毒性。临床上使用的浓度(0.1%至20%)对中性粒细胞和单核细胞有毒。聚维酮碘对SH-SY5Y(神经)和RSC96(施万)细胞具有细胞毒性。动物研究:聚维酮碘制剂在豚鼠中具有耳毒性。当聚维酮碘直接放置在前眼房中时,兔子的角膜出现水肿。在雌性大鼠的膀胱内灌注时,尿路上皮受到损伤。尚未在动物中进行长期研究,以评估聚维酮碘的致癌或致突变潜力。一份关于聚维酮碘致突变潜力的报告表明,它在 Ames S. typhimurium模型的修改中呈阳性,但这些结果无法被另一研究人员复制。另一项使用小鼠淋巴瘤和Balb/3T3细胞进行的测试显示,聚维酮碘没有显著的致突变或转化能力。其他数据表明,根据显性致死试验、微核试验和染色体分析,它不会在小鼠或仓鼠中产生致突变效应。
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: 1-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidinone polymers, iodine complex (povidone-iodine) is a yellowish-brown amorphous hygroscopic powder. Povidone-iodine is an iodophore that is used as a disinfectant and antiseptic mainly for the treatment of contaminated wounds and pre-operative preparation of the skin and mucous membranes, as well as for disinfection of equipment. HUMAN EXPOSURE AND TOXICITY: From patch tests carried out in 413 patients with contact dermatoses, 1 was found to be allergic to povidone-iodine. Reversible hyperthyroidism has been reported during the second week of treatment of first- and second-degree burns to the dorsa of both hands with povidone-iodine; delayed iodine excretion might have been involved. In another case report severe hypernatremia and acidosis occurred in a patient with second-degree burns who was treated topically with povidone-iodine. In addition, hypothyroidism in a neonate following topical administration to a surgical wound of a providone-iodine ointment has been described. Burns are a rare but potentially serious complication of povidone-iodine use. Acute renal failure secondary to povidone iodine administration is possible, especially through mucosal surfaces. In addition, even dilute solutions of povidone-iodine are toxic to human fibroblasts. The concentrations used clinically (0.1 to 20%) are toxic for granulocytes and monocytes. Povidone-iodine was cytotoxic to SH-SY5Y (neuronal) and RSC96 (Schwann) cells. ANIMAL STUDIES: Povidone-Iodine preparation was ototoxic in guinea pigs. Corneal edema developed in rabbits when povidone-iodine was placed directly in the anterior eye chamber. Injury to the urothelium occurred from intravesical instillation in female rats. No long-term studies in animals have been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic or mutagenic potential of povidone-iodine. One report of the mutagenic potential of povidone-iodine indicated that it was positive in a modification of the Ames S. typhimurium model, but these results could not be reproduced by another researcher. Another test using mouse lymphoma and Balb/3T3 cells showed that povidone-iodine has no significant mutagenic or transformation capabilities. Other data indicated that it does not produce mutagenic effects in mice or hamsters according to the dominant lethal test, micronucleus test, and chromosome analysis.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
◉ 母乳喂养期间使用总结:母亲在分娩前后和母乳喂养期间使用聚维酮碘,会增加母乳中碘含量,可能导致母乳喂养的婴儿出现暂时性甲状腺功能减退,特别是在碘缺乏地区。母亲在分娩前后接触聚维酮碘有时会干扰新生儿的甲状腺研究作为新生儿筛查测试的一部分。尽管聚维酮碘通过完整成人皮肤的最小吸收,但应通过使用较低浓度的聚维酮碘、将其涂抹在身体最小可能的表面积、缩短接触时间以及避免重复涂抹,尽量减少将母乳喂养的母亲接触聚维酮碘。如果剖宫产分娩后立即用酒精从腹部去除聚维酮碘,它会被吸收到血液中并通过母乳排出,但在围产期可能不会影响新生儿尿碘、TSH或FT4。阴道使用时碘吸收可能很广泛;避免在母乳喂养期间使用聚维酮碘进行灌洗或使用含碘的卫生棉条。
◉ 对母乳喂养婴儿的影响:在比利时的一项研究中,母乳喂养的婴儿在出生后5天进行了甲状腺功能测试。暴露于接受分娩期间局部使用聚维酮碘的母亲的母乳的婴儿,其基础和促甲状腺激素释放激素刺激的促甲状腺激素(TSH)水平较高。所有组的血清甲状腺素(T4)和三碘甲状腺原氨酸(T3)水平均正常。
一名妇女在怀孕期间和分娩后6周内几乎每天用1%聚维酮碘(含1%碘)洗澡,并每天将1%聚维酮碘软膏涂抹在皮肤上,用于治疗疖病。在6周大时,她的母乳喂养的婴儿(喂养程度未说明)血清甲状腺素水平低至4 ng/L(正常7至20 ng/L),血清促甲状腺激素水平显著升高至99单位/L(正常0.8至5单位/L)。婴儿接受口服左甲状腺素治疗,直到7个月大时甲状腺功能测试和发育正常。
一名妇女在分娩后开始每天两次使用聚维酮碘作为阴道灌洗剂。她的母乳喂养的婴儿在出生后前3周内出现了甲状腺功能减退(血清甲状腺素降低和高促甲状腺激素)。在开始给婴儿补充口服左甲状腺素并停止母亲使用聚维酮碘后,婴儿的甲状腺功能测试在一周内恢复正常。
比利时的一组研究人员回顾了在他们医院分娩的4745名新生儿在出生后第5天的促甲状腺激素水平的结果。婴儿被分为两组,一组是母亲在分娩期间接受10%聚维酮碘溶液局部使用而有碘超负荷的婴儿(n = 3086),另一组是母亲没有碘超负荷的婴儿(n = 1659)。母亲接受聚维酮碘涂抹作为硬脊膜外麻醉的单次涂抹至900平方厘米或作为剖宫产的整个腹部壁的3次涂抹。与没有碘超负荷的母亲相比,母乳喂养的婴儿如果有碘超负荷,则有更大的风险出现促甲状腺激素水平升高并需要召回重新测试(3.2%的剖宫产和2.7%的硬脊膜外麻醉)。与母乳喂养的婴儿相比,用奶瓶喂养的婴儿受影响较小。在用0.5%氯己定和70%异丙醇代替聚维酮碘进行消毒6个月后,在这家医院分娩的1178名婴儿没有增加甲状腺功能测试升高的风险,并且减少了召回母乳喂养婴儿的比例。
在一项针对西班牙母亲的研究中,21名接受10%聚维酮碘(n = 21)或氯己定(n = 13)局部涂抹至会阴,从产程的最后阶段开始直到分娩后每天涂抹至会阴切开,发现他们的母乳喂养的婴儿在出生后第5至7天的促甲状腺激素、甲状腺素或游离甲状腺素没有差异。
一名在怀孕期间和分娩后前几周使用聚维酮碘作为灌洗剂的母乳喂养的婴儿,在10天大时出现窦性心动过速和血液总甲状腺素和游离甲状腺素浓度增加的症状,在1个月大时促甲状腺激素升高。停止使用聚维酮碘后,婴儿的总甲状腺素在1个月内恢复正常,游离甲状腺素在1.5个月内恢复正常,促甲状腺激素水平在2.5个月内恢复正常。除了母亲使用聚维酮碘外,没有发现其他解释甲状腺功能异常的原因,但没有测量血液和牛奶中的碘含量。聚维酮碘很可能是婴儿不良反应的原因。
在日本的一项研究中,将80名连续足月患者随机分为4组,他们在分娩前接受聚维酮碘或苯扎氯铵作为皮肤消毒剂,其中一组在分娩后接受这些消毒剂用于产后阴道撕裂。产前剂量约为7毫升,产后剂量约为0.5毫升溶液。与没有接受聚维酮碘的母亲相比,接受产前和产后局部使用聚维酮碘的母亲的婴儿的促甲状腺激素水平
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation:The use of povidone-iodine in the mother near term and during breastfeeding increases breastmilk iodine levels and can cause transient hypothyroidism in breastfed infants, especially in geographic areas that are iodine deficient. Maternal exposure to povidone-iodine near term can sometimes interfere with thyroid studies done as a part of newborn screening tests. Although iodine from povidone-iodine is minimally absorbed through intact adult skin, exposure of mothers who are or will be breastfeeding to povidone-iodine should be minimized by using lower concentrations of povidone-iodine, applying it to the smallest possible surface areas of the body, shortening contact time, and avoiding repeated applications. If povidone iodine is removed from the abdomen with alcohol within several minutes after its application for cesarean section delivery, it is absorbed into the bloodstream and excreted in breastmilk, but may not affect neonatal urinary iodine, TSH or FT4 during the perinatal period. Iodine absorption can be extensive with vaginal use; avoid douching with povidone iodine or use of iodine-containing tampons during breastfeeding.
◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants:In a study in Belgium, breastfed infants had thyroid function tests measured at 5 days of age. Both basal and thyrotropin-releasing hormone-stimulated thyrotropin (TSH) levels were higher in infants exposed to the breastmilk from mothers who received topical povidone-iodine during delivery. Serum thyroxine (T4) and liothyronine (T3) levels were normal in all groups.
A woman began bathing almost daily with povidone-iodine (1% iodine) and applying povidone-iodine 1% ointment to her skin daily during pregnancy and for 6 weeks postpartum for furunculosis. At 6 weeks of age, her breastfed (extent not stated) infant had a low serum thyroxine level of 4 ng/L (normal 7 to 20 ng/L), a greatly elevated serum thyrotropin level of 99 units/L (normal 0.8 to 5 units/L). The infant was treated with oral levothyroxine until the age of 7 months at which time thyroid function tests and development were normal.
A woman began using povidone-iodine as a vaginal douche twice daily after delivery. Her breastfed infant developed hypothyroidism (low serum thyroxine and high thyrotropin) over the first 3 weeks of life. After oral levothyroxine supplementation of the infant was begun and maternal povidone-iodine was discontinued, the infant's thyroid function tests normalized within a week.
A group of investigators in Belgium reviewed the results of infant thyrotropin levels on day 5 postpartum in 4745 newborn infants delivered over a 2-year period at their hospital. Infants were divided among those whose mothers had iodine overload (n = 3086) from topical povidone-iodine 10% solution during labor and delivery and those whose mothers had no iodine overload (n = 1659). Mothers had povidone-iodine applied either as a single application to 900 square cm for epidural anesthesia or 3 applications to the entire abdominal wall for cesarean section. Breastfed infants whose mothers had iodine overload had a greater risk for having elevated thyrotropin levels and requiring recall for retesting (3.2% with cesarean section and 2.7% with epidural anesthesia) compared to those who did not (0.1%). Bottle-fed infants were affected much less than breastfed infants. After replacing povidone-iodine with chlorhexidine 0.5% in 70% isopropanol for disinfection for 6 months, 1178 infants that were delivered at this institution had no increased rate of elevations in thyroid function tests and a reduced rate of recalls in breastfed infants.
In a study of mothers in Spain who received 10% povidone-iodine (n = 21) or chlorhexidine (n = 13) topically to the perineum starting immediately before the final stage of labor and daily postpartum to the episiotomy, no differences in thyrotropin, thyroxine or free thyroxine was found among their breastfed infants at day 5 to 7 postpartum.
A breastfed infant whose mother was using povidone-iodine as a douche during pregnancy and during the first few weeks after delivery had symptoms of sinus tachycardia and increased concentrations of blood total and free thyroxine at 10 days of age and elevated thyrotropin at 1 month of age. The povidone-iodine was discontinued and the infant's total thyroxine normalized by 1 month of age, free thyroxine normalized by 1.5 months of age and the thyrotropin level normalized by 2.5 months of age. No other explanation for the thyroid function abnormalities could be found except maternal povidone-iodine use, but blood and milk iodine levels were not measured. Povidone-iodine was the probable cause of the adverse reaction in the infant.
A study in Japan randomized 80 consecutive term patients into 4 groups who received either povidone-iodine or benzalkonium chloride as a skin disinfectant before delivery and one of these for postpartum vaginal lacerations. Prepartum doses were about 7 mL and postpartum doses were about 0.5 mL of solution. Infant thyrotropin levels were elevated in the infants whose mothers received topical povidone-iodine pre- and postpartum compared to infants whose mothers received no povidone-iodine. After discontinuing the use of peripartum povidone-iodine, the rate of recall of infants for abnormal thyroid function tests dropped from 4.47% to 0.74%.
In Switzerland, a girl born at 29 weeks of gestation with adequate size for gestational age showed negative TSH screening on day 5. Her mother had developed an abscess of the abdominal wall 1 week after her cesarian section and was treated with povidone-iodine tampons. The baby's TSH was elevated to 23 milliunits/L on day 23, and 288 milliunits/L on day 29. Free thyroxine (T4) levels were decreased to 2.8 ng/L and free liothyronine (T3) with 1.52 ng/L, without signs or symptoms of hypothyroidism. Iodine contents of maternal milk and of infant urine were 4.4 mg/L and 3.9 mg/L, respectively. Treatment with levothyroxine was started, breastfeeding was discontinued and disinfection with povidone-iodine was stopped. The infant's thyroid function tests normalized after 6 days. The infant's abnormal thyroid function tests were probably caused by maternal iodine use.
◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk:Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
来源:Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed)
毒理性
乙醇、甘油、十二烷基硫酸钠、苯扎氯铵(I)和聚山梨酯80对碘伏-碘配方中碘释放的影响在体外和大鼠体内进行了研究。乙醇和苯扎氯铵(I)增加了口服剂量后24小时内碘的吸收。体外实验中碘释放的结果各不相同,苯扎氯铵(I)产生了最大的效果。注意到了可能对实验室测试的干扰。在大鼠的肝脏、血液和甲状腺水平有所报告。
The effect of ethyl alcohol, glycerin, sodium lauryl sulfate, benzalkonium chloride (I) and polysorbate 80, on iodine release from povidone-iodine formulations, was studied in vitro and in rats. Ethyl alcohol and I increased the absorption of iodine 24 h after oral doses. In vitro results on iodine release were variable, with I producing the greatest effect. Possible interferences with laboratory tests were noted. Liver, blood and thyroid levels in rats were reported.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
/SRP:/ 立即急救:确保已经进行了充分的中和。如果患者停止呼吸,请开始人工呼吸,最好使用需阀复苏器、袋阀面罩装置或口袋面罩,按训练操作。如有必要,执行心肺复苏。立即用缓慢流动的水冲洗受污染的眼睛。不要催吐。如果发生呕吐,让患者前倾或置于左侧(如果可能,头部向下)以保持呼吸道畅通,防止吸入。保持患者安静,维持正常体温。寻求医疗救助。 /碘及其相关化合物/
/SRP:/ Immediate first aid: Ensure that adequate decontamination has been carried out. If patient is not breathing, start artificial respiration, preferably with a demand-valve resuscitator, bag-valve-mask device, or pocket mask, as trained. Perform CPR as necessary. Immediately flush contaminated eyes with gently flowing water. Do not induce vomiting. If vomiting occurs, lean patient forward or place on left side (head-down position, if possible) to maintain an open airway and prevent aspiration. Keep patient quiet and maintain normal body temperature. Obtain medical attention. /Iodine and related compounds/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
/SRP:/ 基本治疗:建立专利气道(如有需要,使用口咽或鼻咽气道)。如有必要,进行吸痰。观察呼吸不足的迹象,如有必要,进行辅助通气。通过非重复呼吸面罩以10至15升/分钟的速度给予氧气。监测肺水肿,如有必要,进行治疗……。监测休克,如有必要,进行治疗……。对于眼睛污染,立即用水冲洗眼睛。在运输过程中,用0.9%的生理盐水(NS)连续冲洗每只眼睛……。不要使用催吐剂。对于摄入,如果患者能够吞咽、有强烈的呕吐反射且不流口水,则用水冲洗口腔,并给予5毫升/千克,最多200毫升的水进行稀释。给予活性炭……。在去污染后,用干燥的无菌敷料覆盖皮肤烧伤……。/碘及其相关化合物/
/SRP:/ Basic treatment: Establish a patent airway (oropharyngeal or nasopharyngeal airway, if needed). Suction if necessary. Watch for signs of respiratory insufficiency and assist ventilations if necessary. Administer oxygen by nonrebreather mask at 10 to 15 L/min. Monitor for pulmonary edema and treat if necessary ... . Monitor for shock and treat if necessary ... . For eye contamination, flush eyes immediately with water. Irrigate each eye continuously with 0.9% saline (NS) during transport ... . Do not use emetics. For ingestion, rinse mouth and administer 5 mL/kg up to 200 mL of water for dilution if the patent can swallow, has a strong gag reflex, and does not drool. Administer activated charcoal ... . Cover skin burns with dry sterile dressings after decontamination ... . /Iodine and related compounds/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
聚维酮碘是用于局部应用的,不会被吸收。
Povidone-Iodine is intended for topical application and is not absorbed.
来源:DrugBank
吸收、分配和排泄
聚维酮碘是用于局部应用的,不会被消除。
Povidone-Iodine is intended for topical application and is not eliminated.
来源:DrugBank
吸收、分配和排泄
碘伏适用于局部应用,没有分布容积。
Povidone-Iodine is intended for topical application and has no volume of distribution.
来源:DrugBank
吸收、分配和排泄
碘伏适用于局部涂抹,不会被消除。
Povidone-Iodine is intended for topical application and is not eliminated.
来源:DrugBank
吸收、分配和排泄
Topical application of povidone iodine on the umbilical cord and normal intact skin of newborn infants resulted in significantly elevated plasma iodine levels. High iodine levels were also found in two neonates who had povidone iodine applied to denuded skin. No significant alteration in thyroid function was seen. The possible toxic manifestations of high plasma iodine levels are discussed.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
安全说明:S24/25
-
WGK Germany:2
-
海关编码:3808940010,29339900
-
危险品运输编号:NONH for all modes of transport
-
RTECS号:TR1579600
SDS
模块 1. 化学品
1.1 产品标识符
: Poly(vinylpyrrolidone)–Iodine complex
产品名称
1.2 鉴别的其他方法
Povadyne® antiseptic
PVP-I
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途
仅用于研发。不作为药品、家庭或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述
2.1 GHS-分类
皮肤刺激 (类别 3)
2.2 GHS 标记要素,包括预防性的陈述
象形图 无
警示词 警告
危险申明
H316 引起轻微皮肤刺激。
警告申明 无
2.3 其它危害物 - 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
3.1 物 质
: Povadyne® antiseptic
别名
PVP-I
组分 浓度或浓度范围
Poly(vinylpyrrolidone)-Iodine complex
<=100%
化学文摘登记号(CAS 25655-41-8
No.)
模块 4. 急救措施
4.1 必要的急救措施描述
一般的建议
请教医生。 向到现场的医生出示此安全技术说明书。
吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如呼吸停止,进行人工呼吸。 请教医生。
皮肤接触
用肥皂和大量的水冲洗。 请教医生。
眼睛接触
用水冲洗眼睛作为预防措施。
食入
切勿给失去知觉者通过口喂任何东西。 用水漱口。 请教医生。
4.2 主要症状和影响,急性和迟发效应
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示
无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施
5.1 灭火介质
灭火方法及灭火剂
用水雾,抗乙醇泡沫,干粉或二氧化碳灭火。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害
产品分解后性质不明
5.3 给消防员的建议
如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步信息
无数据资料
模块 6. 泄露应急处理
6.1 作业人员防护措施、防护装备和应急处置程序
使用个人防护用品。 避免粉尘生成。 避免吸入蒸气、烟雾或气体。 保证充分的通风。 避免吸入粉尘。
6.2 环境保护措施
不要让产品进入下水道。
6.3 泄漏化学品的收容、清除方法及所使用的处置材料
收集和处置时不要产生粉尘。 扫掉和铲掉。 放入合适的封闭的容器中待处理。
6.4 参考其他部分
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
7.1 安全操作的注意事项
在有粉尘生成的地方,提供合适的排风设备。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性
贮存在阴凉处。 使容器保持密闭,储存在干燥通风处。
7.3 特定用途
无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
8.1 容许浓度
最高容许浓度
没有已知的国家规定的暴露极限。
8.2 暴露控制
适当的技术控制
根据良好的工业卫生和安全规范进行操作。 休息前和工作结束时洗手。
个体防护设备
眼/面保护
带有防护边罩的安全眼镜符合 EN166要求请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟)
检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/EEC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
身体保护
根据危险物质的类型,浓度和量,以及特定的工作场所选择身体保护措施。,
防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和数量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
不需要保护呼吸。如需防护粉尘损害,请使用N95型(US)或P1型(EN 143)防尘面具。
呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息
a) 外观与性状
形状: 固体
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味阈值
无数据资料
d) pH值
无数据资料
e) 熔点/凝固点
熔点/凝固点: 300 °C
f) 沸点、初沸点和沸程
无数据资料
g) 闪点
无数据资料
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 易燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 无数据资料
k) 蒸气压
无数据资料
l) 蒸汽密度
无数据资料
m) 密度/相对密度
无数据资料
n) 水溶性
无数据资料
o) n-辛醇/水分配系数
无数据资料
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性
10.1 反应性
无数据资料
10.2 稳定性
无数据资料
10.3 危险反应
无数据资料
10.4 应避免的条件
无数据资料
10.5 不相容的物质
氧化剂
10.6 危险的分解产物
其它分解产物 - 无数据资料
模块 11. 毒理学资料
11.1 毒理学影响的信息
急性毒性
半数致死剂量 (LD50) 经口 - 大鼠 - > 8,000 mg/kg
皮肤刺激或腐蚀
皮肤 - 兔子 - 轻度的皮肤刺激
眼睛刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
无数据资料
生殖细胞致突变性
无数据资料
致癌性
IARC:
此产品中没有大于或等于 0。1%含量的组分被 IARC鉴别为可能的或肯定的人类致癌物。
生殖毒性
婴儿可能出现先天性畸形和畸形的危险
孕期大量接触碘可能引起胎儿甲状腺机能减退。含碘药物可引发胎儿甲状腺肿。
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入可能有害。 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
摄入 如服入是有害的。
皮肤 通过皮肤吸收可能有害。 可能引起皮肤刺激。
眼睛 可能引起眼睛刺激。
接触后的征兆和症状
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: TR1579600
模块 12. 生态学资料
12.1 生态毒性
对鱼类的毒性 半数致死浓度(LC50) - 虹鳟 (红鳟鱼) - 1,050 mg/l - 1 h
12.2 持久性和降解性
无数据资料
12.3 潜在的生物累积性
无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移性
无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价
无数据资料
12.6 其它不良影响
无数据资料
模块 13. 废弃处置
13.1 废物处理方法
产品
将剩余的和不可回收的溶液交给有许可证的公司处理。
与易燃溶剂相溶或者相混合,在备有燃烧后处理和洗刷作用的化学焚化炉中燃烧
受污染的容器和包装
按未用产品处置。
模块 14. 运输信息
14.1 联合国危险货物编号
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.2 联合国运输名称
欧洲陆运危规: 非危险货物
国际海运危规: 非危险货物
国际空运危规: 非危险货物
14.3 运输危险类别
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.4 包裹组
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.5 环境危险
欧洲陆运危规: 否 国际海运危规 国际空运危规: 否
海洋污染物(是/否): 否
14.6 对使用者的特别提醒
无数据资料
若适用,该化学品满足《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月9号国务院通过)的要求。
模块 16. 其他信息
进一步信息
上述信息视为正确,但不包含所有的信息,仅作为指引使用。本文件中的信息是基于我们目前所知,就正
确的安全提示来说适用于本品。该信息不代表对此产品性质的保证。
参见发票或包装条的反面。
模块 15 - 法规信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
外用消毒剂:聚维酮碘
产品概述
聚维酮碘是一种由表面活性剂与碘络合而成的不稳定络合物,属碘伏类外用消毒剂。在常温下表现为黄棕色至红棕色无定形粉末,易溶于水或乙醇中而不溶于乙醚或氯仿。
成分及其作用机制- 表面活性剂(1-乙烯基-2-砒咯烷酮均聚物):这种物质有助于溶液对物体的润湿和穿透,从而加强碘的杀菌作用。
- 结合碘: 约80~90% 的结合碘可解聚成游离碘。高浓度使得其具有强大的杀菌力,无味、无刺激且无致敏性,毒性低。
该消毒剂为广谱杀菌剂,能杀死病毒、细菌、芽孢、真菌和原虫。在15ppm的浓度下,一分钟内可杀灭金黄色葡萄球菌、大肠杆菌和绿脓杆菌;结核杆菌则需更长时间,而真菌如枯草杆菌则需要1.5小时;杀黑色变种芽胞和蜡样杆菌芽胞需要较高浓度和较长时间。在150ppm的浓度下,十分钟内能破坏乙肝表面抗原(HBsAg)。
适用范围聚维酮碘不仅可用于皮肤消毒,还可用于金属医疗器械、食具等的消毒。在消毒用浓度下通常为红色或琥珀色,可以直接用于手术病人切口部位的皮肤和脑膜,也可供妇产科、泌尿科体外冲洗之用。当其浓度下降至10ppm以下时,变为白色或淡黄色,失去杀菌活性。
理化性质聚维酮碘是元素碘与聚合物载体结合而成的疏松复合物,其中聚维酮起载体和助溶作用。常温下为黄棕色至棕红色无定形粉末,微臭,易溶于水或乙醇中,水溶液呈酸性,不溶于乙醚、氯仿、丙酮、乙烷及四氯化碳。
药效学聚维酮碘能直接使菌体内的蛋白质变性、沉淀,致使病原微生物死亡。它对金黄色葡萄球菌、淋球菌、绿脓杆菌、梅毒螺旋体、乙肝病毒、艾滋病毒、阴道毛滴虫等均有强大药理活性。
产品类型 凝胶剂聚维酮碘凝胶剂是聚维酮碘与亲水性基质制成的妇科外用半流动胶体剂,保持缓释效果。由于不断释放出游离碘,使皮肤和黏膜保持一定的碘浓度以抑杀细菌。
适应症- 化脓性皮炎、皮肤真菌感染、小面积轻度烧烫伤。
- 口腔、妇科、外科、皮肤科预防感染。
- 家庭食具、器具等杀菌消毒。
- 食品工业、养殖业用于杀菌消毒及动物疾病防治。
- 对本品或碘过敏者禁用。
- 烧伤面积大于20%者不宜局部或长期使用。肝功能不良或烧伤患者不宜用。
- 孕妇和儿童(特别是新生儿)慎用。
聚维酮碘在药剂中作杀菌消毒剂、抑菌剂,用于滴眼剂、滴鼻剂、乳膏剂等防腐,并可制成消毒液。主要用于医院手术、注射等皮肤消毒和器材消毒,以及口腔、妇科、外科、皮肤科等预防感染;家庭食具、器具等杀菌消毒;食品工业、养殖业用于杀菌消毒及动物疾病防治。
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:盐酸 、 1-羟基苯并三唑 、 1-羟基苯并三唑一水物 、 、 nembutal 、 聚维酮碘(PVP-I) 、 、 以 cellulose 、 乙醇 、 水 为溶剂, 生成 1-(3-二甲基氨基丙基)-3-乙基碳二亚胺参考文献:名称:CELLULOSE DERIVATIVE摘要:一种纤维素衍生物,在水中溶解时具有适当的弹性模量和粘度,可用作粘附障碍剂。该纤维素衍生物的分子量为5×103至5×106,由以下式(1)所表示的重复单元组成: 其中,R1、R2和R3分别独立地选择以下化学式(a)、(b)、(c)和(d)中的预定量的基团:(式(c)中的X是碱金属,式(d)中的R4和R5是各自独立的具有10至28个碳原子的烷基或烯基基团)。公开号:US20100279982A1
文献信息
-
AQUEOUS COMPOSITION BASED ON POLYOXYMETHYLENE DIALKYL ETHERS (POM) AND THEIR USE FOR THE PRESERVATION AND/OR EMBALMING OF THE HUMAN OR ANIMAL BODY申请人:ARKEMA FRANCE公开号:US20200305414A1公开(公告)日:2020-10-01The invention relates to a composition comprising: a) a mixture of polyoxymethylene dialkyl ethers (POM) having a restricted specific molecular distribution b) at least one biocidal agent c) at least one pro-penetrating agent d) at least one dye e) optionally, another additive and water as diluent. It also relates to a non-therapeutic method of preserving and/or embalming a dead human or animal body using the composition, such as the use of this composition for anatomopathological purposes.
-
COMPOSITION AQUEUSE A BASE DE POLYOXYMETHYLENES DIALKYL ETHERS (POM) ET SON UTILISATION POUR LA CONSERVATION ET/OU L'EMBAUMEMENT DU CORPS HUMAIN OU ANIMAL申请人:ARKEMA FRANCE公开号:EP3714691A1公开(公告)日:2020-09-30L'invention concerne un mélange de polyoxyméthylène dialkyl éthers (POM) ayant une distribution moléculaire spécifique restreinte ainsi que son procédé de préparation. L'invention concerne également une composition comprenant : a) un mélange de polyoxyméthylène dialkyl éthers (POM) ayant une distribution moléculaire spécifique restreinte b) au moins un agent biocide c) au moins un agent pro-pénétrant d) au moins un colorant e) en option, un autre additif et de l'eau comme diluant. Elle concerne également un procédé non thérapeutique de conservation et/ou d'embaumement d'un corps humain ou animal mort en utilisant ladite composition, comme l'utilisation de cette composition pour des besoins d'anatomopathologie.
-
Hand sanitizer holster申请人:Russo Paula公开号:US10653232B1公开(公告)日:2020-05-19The hand sanitizer holster is a garment. The hand sanitizer holster comprises a belt, a fastening structure, and a plurality of primary holsters. The fastening structure secures the belt to a healthcare worker. The plurality of primary holsters attach to the belt. Each of the plurality of primary holsters contains a chemical container filled with a sanitizer. The sanitizer is an anti-microbial chemical used for cleaning the hands of the healthcare worker. Each holster contained within the plurality of primary holsters is configured such that the sanitizer dispenses from the chemical container without removing the chemical container from the holster. In a second potential embodiment of the disclosure, the hand sanitizer holster further comprises a shoulder harness. The shoulder harness further comprises one or more straps and one or more secondary holsters.
-
Sanitary wipe glove申请人:Brooks La Veda公开号:US11006683B1公开(公告)日:2021-05-18The sanitary wipe glove is a pre-moistened wipe. The sanitary wipe glove is configured for use with a patient. The sanitary wipe glove is worn on the patient. The patient uses the sanitary wipe glove for personal cleansing and hygiene. The sanitary wipe glove comprises a glove, an elastic band, and a cleansing agent. The elastic band attaches to the glove. The cleansing agent is a liquid phase solution that is absorbed into the glove. The glove is worn on the hand of the patient.卫生擦拭手套是一种预湿润擦拭布。卫生擦拭手套用于病人。卫生巾手套戴在病人身上。病人使用卫生巾手套进行个人清洁卫生。卫生擦拭手套由手套、松紧带和清洁剂组成。松紧带与手套相连。清洁剂是一种液相溶液,可被手套吸收。手套戴在病人的手上。
-
HOLE INJECTION/TRANSPORT LAYER COMPOSITIONS AND DEVICES申请人:Plextronics, Inc.公开号:EP1851048A2公开(公告)日:2007-11-07
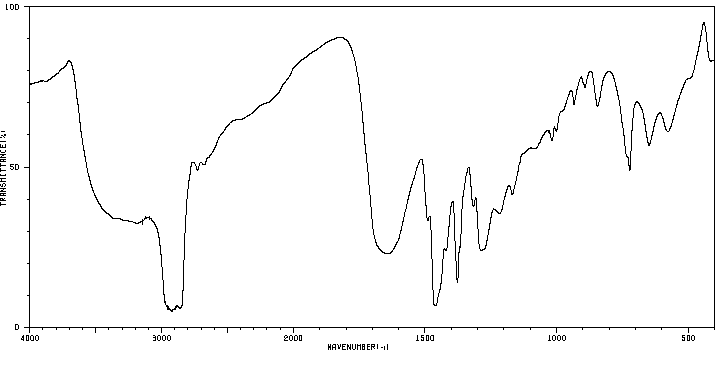
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(5R,Z)-3-(羟基((1R,2S,6S,8aS)-1,3,6-三甲基-2-((E)-prop-1-en-1-yl)-1,2,4a,5,6,7,8,8a-八氢萘-1-基)亚甲基)-5-(羟甲基)-1-甲基吡咯烷-2,4-二酮
(2R,2''R)-(-)-2,2''-联吡咯烷
麦角甾-7,22-二烯-3-基亚油酸酯
马来酰亚胺霉素
马来酰亚胺基酰肼盐酸盐
马来酰亚胺基甲基-3-马来酰亚胺基丙酸酯
马来酰亚胺丙酰基-dPEG4-NHS
马来酰亚胺-酰胺-PEG6-琥珀酰亚胺酯
马来酰亚胺-酰胺-PEG6-丙酸
马来酰亚胺-酰胺-PEG24-丙酸
马来酰亚胺-酰胺-PEG12-丙酸
马来酰亚胺-四聚乙二醇-羧酸
马来酰亚胺-四聚乙二醇-丙酸叔丁酯
马来酰亚胺-四聚乙二醇-丙烯酸琥珀酰亚胺酯
马来酰亚胺-六聚乙二醇-羧酸
马来酰亚胺-六聚乙二醇-丙酸叔丁酯
马来酰亚胺-八聚乙二醇-丙酸叔丁酯
马来酰亚胺-二聚乙二醇-丙酸叔丁酯
马来酰亚胺-三(乙烯乙二醇)-丙酸
马来酰亚胺-一聚乙二醇-羧酸
马来酰亚胺-一聚乙二醇-丙烯酸琥珀酰亚胺酯
马来酰亚胺-PEG3-羟基
马来酰亚胺-PEG2-胺三氟醋酸盐
马来酰亚胺-PEG2-琥珀酰亚胺酯
马来酰亚胺
频哪醇硼酸酯
顺式草酸双(-3,8-二氮杂双环[4.2.0]辛烷-8-羧酸叔丁酯)
顺式4-甲基吡咯烷酮-3-醇盐酸盐
顺式4-氟吡咯烷酮-3-醇盐酸盐
顺式3,4-二羟基吡咯烷盐酸盐
顺式3,4-二氨基吡咯烷-1-羧酸叔丁酯
顺式-二甲基 1-苄基吡咯烷-3,4-二羧酸
顺式-N-[2-(2,6-二甲基-1-哌啶基)乙基]-2-氧代-4-苯基-1-吡咯烷乙酰胺
顺式-N-Boc-吡咯烷-3,4-二羧酸
顺式-5-苄基-2-叔丁氧羰基六氢吡咯并[3,4-c]吡咯
顺式-5-甲基-1H-六氢吡咯并[3,4-b]吡咯二盐酸盐
顺式-5-氧代六氢环戊二烯并[c]吡咯-2(1H)-羧酸叔丁酯
顺式-5-乙氧羰基-1H-六氢吡咯并[3,4-B]吡咯盐酸盐
顺式-5-(碘甲基)-4-苯基-2-吡咯烷酮
顺式-5-(碘甲基)-4-甲基-2-吡咯烷酮
顺式-4-氧代-六氢-吡咯并[3,4-C]吡咯-2-甲酸叔丁酯
顺式-3-氟-4-羟基吡咯烷-1-羧酸叔丁酯
顺式-3-氟-4-甲基吡咯烷盐酸盐
顺式-2-甲基六氢吡咯并[3,4-c]吡咯
顺式-2,5-二甲基吡咯烷
顺式-1-苄基-3,4-吡咯烷二甲酸二乙酯
顺式-1-甲基六氢吡咯并[3,4-b]吡咯
顺式-(9CI)-3,4-二乙烯-1-(三氟乙酰基)-吡咯烷
顺-八氢环戊[c]吡咯-5-酮盐酸盐
非星匹宁