肌酸酐 | 60-27-5
中文名称
肌酸酐
中文别名
肌氨基酐;2-氨基-1-甲基-2-咪唑啉-4-酮;1-甲基乙内酰脲-2-酰亚胺;普卡比利;肌(氨)酸酐;缩水肌肉素;2-氨基-1,5-二氢-1-甲基-4H-咪唑啉-4-酮;2-亚氨基-N-甲基乙内酰脲;2-亚氨基-1-甲基咪唑啉-4-酮;肌酐;2-氨基-1-甲基咪唑啉-4-酮
英文名称
creatinine
英文别名
2-amino-1-methyl-2-imidazolin-4-one;2-imino-1-methylimidazolidine-4-one;2-imino-1-methylimidazolidin-4-one;4H-Imidazol-4-one, 2-amino-1,5-dihydro-1-methyl-
CAS
60-27-5
化学式
C4H7N3O
mdl
MFCD00059730
分子量
113.119
InChiKey
DDRJAANPRJIHGJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:295 °C (dec.) (lit.)
-
沸点:211.83°C (rough estimate)
-
密度:1.2526 (rough estimate)
-
闪点:290 °C
-
溶解度:1MHCl:0.1 g/mLat 20 °C,澄清溶液
-
LogP:-1.760
-
物理描述:Solid
-
碰撞截面:119.1 Ų [M-H]-; 119.8 Ų [M-H]-; 123.3 Ų [M+H]+; 123.4 Ų [M+H]+; 132.8 Ų [M+Na]+; 132.9 Ų [M+Na]+
-
稳定性/保质期:
稳定存在,但不与强氧化剂相容。
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-1.8
-
重原子数:8
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.5
-
拓扑面积:58.7
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:1
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险品标志:Xi
-
安全说明:S24/25,S26,S36/37/39,S45
-
危险类别码:R34
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:2933290090
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1789 8/PG 3
-
危险性防范说明:P280,P305+P351+P338
-
危险性描述:H302
-
储存条件:本品应密封存放在干燥处。
SDS
肌酸酐 修改号码:5
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: Creatinine
修改号码: 5
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害 未分类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志 无
信号词 无信号词
危险描述 无
防范说明 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 肌酸酐
百分比: >99.0%(LC)(T)
CAS编码: 60-27-5
分子式: C4H7N3O
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用水清洗皮肤/淋浴。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,雾状水,二氧化碳
特殊危险性: 小心,燃烧或高温下可能分解产生毒烟。
肌酸酐 修改号码:5
模块 5. 消防措施
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 清扫收集粉尘,封入密闭容器。注意切勿分散。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的
法律法规处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止粉尘扩散。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果粉尘或浮质产生,使用局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防尘面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
固体
外形(20°C):
外观: 晶体-粉末
颜色: 白色类白色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点: 255°C (分解)
沸点/沸程 无资料
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 无资料
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂] 无资料
肌酸酐 修改号码:5
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳, 氮氧化物 (NOx)
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在可燃溶剂中溶解混合,在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中
焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
肌酸酐 修改号码:5
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: Creatinine
修改号码: 5
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害 未分类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志 无
信号词 无信号词
危险描述 无
防范说明 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 肌酸酐
百分比: >99.0%(LC)(T)
CAS编码: 60-27-5
分子式: C4H7N3O
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用水清洗皮肤/淋浴。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,雾状水,二氧化碳
特殊危险性: 小心,燃烧或高温下可能分解产生毒烟。
肌酸酐 修改号码:5
模块 5. 消防措施
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 清扫收集粉尘,封入密闭容器。注意切勿分散。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的
法律法规处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止粉尘扩散。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果粉尘或浮质产生,使用局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防尘面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
固体
外形(20°C):
外观: 晶体-粉末
颜色: 白色类白色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点: 255°C (分解)
沸点/沸程 无资料
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 无资料
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂] 无资料
肌酸酐 修改号码:5
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳, 氮氧化物 (NOx)
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在可燃溶剂中溶解混合,在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中
焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
肌酸酐 修改号码:5
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Liebig, Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie, 1858, vol. 108, p. 355摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:BSTFA对肌酐和肌酸衍生化的GC-MS研究及其在人体尿液中的测定摘要:考虑到其相对恒定的尿排泄率,肌酐(2-氨基-1-甲基-5 H尿中的-imidazol-4-one,MW 113.1)是有用的内源性生化参数,可校正多种内源性和外源性物质的尿排泄率。通过基于气相色谱(GC)的方法可靠地测量肌酐需要对其胺基和酮基进行衍生化。肌酐与其开放式肌酸(甲基胍基乙酸,MW 131.1)处于平衡状态,肌酸具有胍基和羧基。肌酸酐和肌酸的三甲基甲硅烷基化和三氟乙酰化是人类血清中使用火焰或电子电离进行GC-质谱(MS)分析的最古老的衍生化方法。我们对肌酸酐的衍生化(d进行GC-MS研究0 -creatinine),[ methylo - 2 ħ 3]肌酐(d 3 -creatinine,内标),肌酸(d 0 -肌酸)与Ñ,ö -双在没有(三甲基硅烷基)三氟乙酰胺使用标准衍生化条件(BSTFA)(60分钟,60℃),但任何基础。反应产物的特征在于负离子化学电离(NICI)和正离子DOI:10.3390/molecules26113206
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:Synthesis, in-vitro α-glucosidase inhibition, antioxidant, in-vivo antidiabetic and molecular docking studies of pyrrolidine-2,5-dione and thiazolidine-2,4-dione derivatives摘要:alpha-Glucosidase is considered as a therapeutic target for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM2). In current study, we synthesized pyrrolidine-2,5-dione (succinimide) and thiazolidine-2,4-dione derivatives and evaluated for their ability to inhibit alpha-Glucosidase. Pyrrolidine-2,5-dione derivatives (11a-o) showed moderate to poor alpha-glucosidase inhibition. Compound 11o with the IC50 value of 28.3 +/- 0.28 mu M emerged as a good inhibitor of alpha-glucosidase. Thiazolidine-2,4-dione and dihydropyrimidine (TZD-DHPM) hybrids (22a-c) showed excellent inhibitory activities. The most active compound 22a displayed IC50 value of 0.98 +/- 0.008 mu M. Other two compounds of this series also showed activity in low micromolar range. The in-vivo antidiabetic study of three compounds 11n, 11o and 22a were also determined using alloxan induced diabetes mice model. Compounds 11o and 22a showed significant hypoglycemic effect compared to the reference drug. In-vivo acute toxicity study showed the safety of these selected compounds. In-silico docking studies were carried out to rationalize the in-vitro results. The binding modes and bioassay results of TZD-DHPM hybrids showed that interactions with important residues appeared significant for high potency.DOI:10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.103128
文献信息
-
Spontaneous Biomimetic Formation of (±)‐Dictazole B under Irradiation with Artificial Sunlight作者:Adam Skiredj、Mehdi A. Beniddir、Delphine Joseph、Karine Leblanc、Guillaume Bernadat、Laurent Evanno、Erwan PouponDOI:10.1002/anie.201403454日期:2014.6.16Guided by biosynthetic considerations, the total synthesis of dictazole B is reported for the first time. Experimental evidence for an easy access to challenging cyclobutane alkaloids of marine origin, which are often postulated to be biosynthetic precursors of more complex structures, is provided.
-
Optical Supramolecular Sensing of Creatinine作者:Andrés F. Sierra、Daniel Hernández-Alonso、Miguel A. Romero、José A. González-Delgado、Uwe Pischel、Pablo BallesterDOI:10.1021/jacs.9b12071日期:2020.3.4dye or a black-hole quencher from the receptor's cavity by means of competition with the creatinine analytes. The systems were thermodynamically and kinetically characterized regarding their 1:1 binding properties by means of nu-clear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H and 31P NMR), isothermal titration calorimetry, and optical spectroscopies (UV/vis absorption and fluorescence). For the use of the杯[4]吡咯膦酸酯-空腔酸被用作受体,用于设计肌酐及其亲脂性衍生物己基肌酐的超分子传感器。传感原理基于通过与肌酐分析物的竞争,对来自受体腔的固有荧光客体染料或黑洞猝灭剂的指示剂置换分析。通过核磁共振波谱(1H 和 31P NMR)、等温滴定量热法和光谱学(UV/vis 吸收和荧光)对系统的 1:1 结合特性进行热力学和动力学表征。对于黑洞指示染料的使用,杯[4]吡咯用丹磺酰基发色团作为信号单元进行了修饰,该发色团与指示染料进行福斯特共振能量转移。1:1 指示染料的结合常数在 107 M-1 的范围内,而己基肌酐显示的值约为 (2-4) × 105 M-1。己基肌酸酐对指示剂的竞争性置换产生了超分子荧光开启传感器,其在微摩尔分析物浓度下工作,与对健康和患病患者观察到的浓度相容。其中一个系统的检测限达到亚微摩尔范围 (110 nM)。
-
Molecular mechanism of action of 5,6-dihydroxytryptamine. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 4-methyl-, 7-methyl- and 4,7-dimethyl-5,6-dihydroxytryptamines作者:Achintya K. Sinhababu、Anil K. Ghosh、Ronald T. BorchardtDOI:10.1021/jm00147a027日期:1985.9The major mechanism by which the serotonin neurotoxin 5,6-dihydroxytryptamine (5,6-DHT) expresses its neurodegenerative action may involve alkylation of biological nucleophiles by the electrophilic quinoid autoxidation products. To determine the relative importance of various sites on these autoxidation products toward alkylation we have rationally designed and synthesized 4-Me-5,6-DHT (16a), 7-Me-5血清素神经毒素5,6-二羟基色胺(5,6-DHT)表达其神经退行性作用的主要机制可能涉及通过亲电性醌类自氧化产物对生物亲核试剂进行烷基化。为了确定这些自氧化产物上各个部位对烷基化的相对重要性,我们合理设计并合成了4-Me-5,6-DHT(16a),7-Me-5,6-DHT(16b)和4,7 -Me2-5,6-DHT(16c)。这些类似物的吲哚核是通过相应的2,β-二硝基苯乙烯的还原环化作用而构建的,而氨基乙基侧链则是通过氨基甲硫氨酸引入的。氧化还原数据显示,与5,6-DHT相比,所有类似物都更容易被氧化。在培养的分化的神经母细胞瘤N-2a细胞中评估生物学活性。抑制效力的顺序,通过测量对[3 H]胸苷掺入DNA的抑制作用确定的C 16远大于16 a,大于5 a,6-DHT约等于16 b。通过测量其对[3H] -5-HT吸收的抑制作用确定的对血清素能摄取的亲和力顺序(以microM表示,以IC50值表示)为5
-
Posaconazole derivative, pharmaceutical composition and use thereof申请人:WUHAN LL SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT CO., LTD.公开号:US10517867B2公开(公告)日:2019-12-31The present disclosure provides a posaconazole derivative, a pharmaceutical composition and use thereof, which specifically include a compound represented by the following formula (I), a racemate, stereoisomer, tautomer, oxynitride, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof: The compounds of the present disclosure have strong antifungal activity, high safety, and good water solubility, without the need for the addition of a cosolvent (such as hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin, sulfobutyl ether-β-cyclodextrin, and the like) with potential safety risks. Furthermore, the formulation process of the compound could have less difficulty and less cost, and therefore can be used to prepare improved antifungal drugs.
-
4-Oxo-2-imidazolidinylidene ureas申请人:McNeil Laboratories, Incorporated公开号:US03983135A1公开(公告)日:1976-09-28Compounds of the class of 4-oxo-2-imidazolidinylidene ureas and 4-oxo-2-hexahydropyrimidinylidene ureas, useful as anti-secretory agents and central nervous system (CNS) depressants.
表征谱图
-
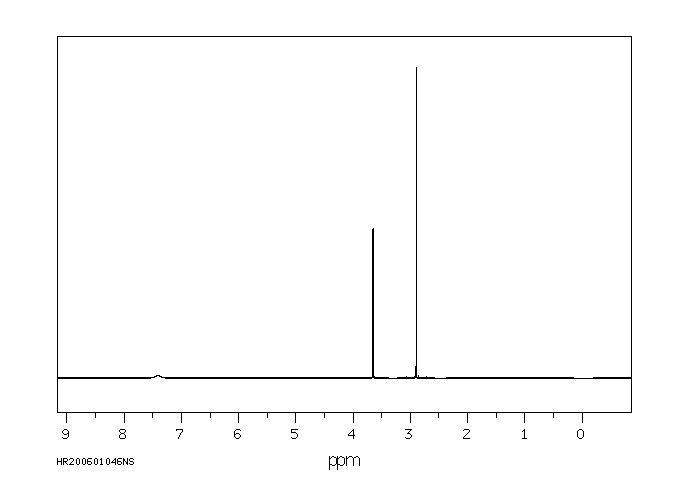
氢谱1HNMR
-
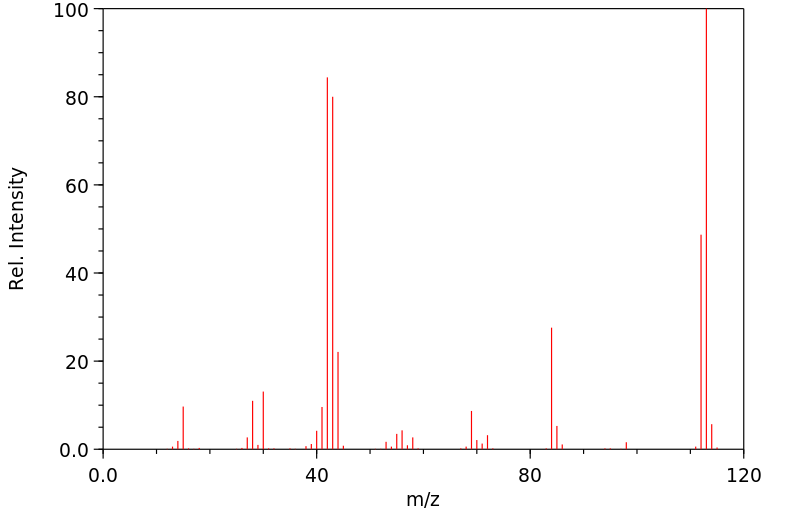
质谱MS
-
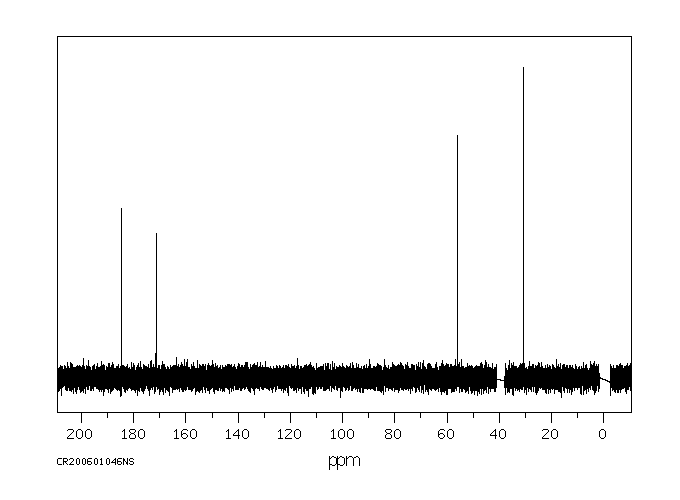
碳谱13CNMR
-
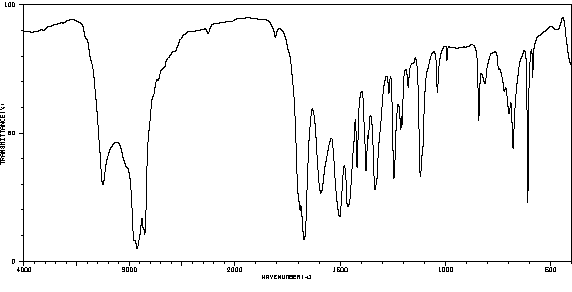
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(甲基3-(二甲基氨基)-2-苯基-2H-azirene-2-羧酸乙酯)
(±)-盐酸氯吡格雷
(±)-丙酰肉碱氯化物
(d(CH2)51,Tyr(Me)2,Arg8)-血管加压素
(S)-(+)-α-氨基-4-羧基-2-甲基苯乙酸
(S)-阿拉考特盐酸盐
(S)-赖诺普利-d5钠
(S)-2-氨基-5-氧代己酸,氢溴酸盐
(S)-2-[[[(1R,2R)-2-[[[3,5-双(叔丁基)-2-羟基苯基]亚甲基]氨基]环己基]硫脲基]-N-苄基-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(S)-2-[3-[(1R,2R)-2-(二丙基氨基)环己基]硫脲基]-N-异丙基-3,3-二甲基丁酰胺
(S)-1-(4-氨基氧基乙酰胺基苄基)乙二胺四乙酸
(S)-1-[N-[3-苯基-1-[(苯基甲氧基)羰基]丙基]-L-丙氨酰基]-L-脯氨酸
(R)-乙基N-甲酰基-N-(1-苯乙基)甘氨酸
(R)-丙酰肉碱-d3氯化物
(R)-4-N-Cbz-哌嗪-2-甲酸甲酯
(R)-3-氨基-2-苄基丙酸盐酸盐
(R)-1-(3-溴-2-甲基-1-氧丙基)-L-脯氨酸
(N-[(苄氧基)羰基]丙氨酰-N〜5〜-(diaminomethylidene)鸟氨酸)
(6-氯-2-吲哚基甲基)乙酰氨基丙二酸二乙酯
(4R)-N-亚硝基噻唑烷-4-羧酸
(3R)-1-噻-4-氮杂螺[4.4]壬烷-3-羧酸
(3-硝基-1H-1,2,4-三唑-1-基)乙酸乙酯
(2S,4R)-Boc-4-环己基-吡咯烷-2-羧酸
(2S,3S,5S)-2-氨基-3-羟基-1,6-二苯己烷-5-N-氨基甲酰基-L-缬氨酸
(2S,3S)-3-((S)-1-((1-(4-氟苯基)-1H-1,2,3-三唑-4-基)-甲基氨基)-1-氧-3-(噻唑-4-基)丙-2-基氨基甲酰基)-环氧乙烷-2-羧酸
(2S)-2,6-二氨基-N-[4-(5-氟-1,3-苯并噻唑-2-基)-2-甲基苯基]己酰胺二盐酸盐
(2S)-2-氨基-N,3,3-三甲基-N-(苯甲基)丁酰胺
(2S)-2-氨基-3-甲基-N-2-吡啶基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-(苯基甲基)丁酰胺,
(2S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-2-吡啶基丁酰胺
(2S,4R)-1-((S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基丁酰基)-4-羟基-N-(4-(4-甲基噻唑-5-基)苄基)吡咯烷-2-甲酰胺盐酸盐
(2R,3'S)苯那普利叔丁基酯d5
(2R)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-(苯甲基)丁酰胺
(2-氯丙烯基)草酰氯
(1S,3S,5S)-2-Boc-2-氮杂双环[3.1.0]己烷-3-羧酸
(1R,5R,6R)-5-(1-乙基丙氧基)-7-氧杂双环[4.1.0]庚-3-烯-3-羧酸乙基酯
(1R,4R,5S,6R)-4-氨基-2-氧杂双环[3.1.0]己烷-4,6-二羧酸
齐特巴坦
齐德巴坦钠盐
齐墩果-12-烯-28-酸,2,3-二羟基-,苯基甲基酯,(2a,3a)-
齐墩果-12-烯-28-酸,2,3-二羟基-,羧基甲基酯,(2a,3b)-(9CI)
黄酮-8-乙酸二甲氨基乙基酯
黄荧菌素
黄体生成激素释放激素(1-6)
黄体生成激素释放激素 (1-5) 酰肼
黄体瑞林
麦醇溶蛋白
麦角硫因
麦芽聚糖六乙酸酯
麦根酸