N-乙基二苄胺 | 10479-25-1
中文名称
N-乙基二苄胺
中文别名
——
英文名称
N,N-dibenzylethanamine
英文别名
N,N-dibenzylethylamine;N,N-dibenzyl-N-ethylamine;N-ethyldi(benzyl)amine;N-Ethyldibenzylamine
CAS
10479-25-1
化学式
C16H19N
mdl
MFCD00014435
分子量
225.334
InChiKey
WBGPDYJIPNTOIB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:93-94 °C
-
沸点:101-106 °C(Press: 0.35 Torr)
-
密度:1.009±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.6
-
重原子数:17
-
可旋转键数:5
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.25
-
拓扑面积:3.2
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:1
安全信息
-
海关编码:2921499090
SDS
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 三苄胺 tribenzylamine 620-40-6 C21H21N 287.404 N,N-二苄基-乙酰胺 N,N-dibenzylacetamide 10479-30-8 C16H17NO 239.317 —— N,N-Dibenzyl-thioformamid 25576-20-9 C15H15NS 241.357 N-乙基苄胺 N-ethylbenzylamine 14321-27-8 C9H13N 135.209 二苄胺 dibenzylamine 103-49-1 C14H15N 197.28 N-苄基-N-乙基苯甲酰胺 N-benzyl-N-ethylbenzamide 71398-55-5 C16H17NO 239.317 N-苄基乙酰胺 N-(phenylmethyl)acetamide 588-46-5 C9H11NO 149.192 N,N-二苄基羟胺 N,N-dibenzylhydroxylamine 621-07-8 C14H15NO 213.279
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:巴西五省孢子粉中以五硫平为基础的抑制剂的合成与鉴定。摘要:巴西Sporothrix brasiliensis是巴西人畜共患孢子菌病的病原体,目前被认为是该属中具有临床重要性的最强毒种。孢子丝虫病是一种新兴疾病,在过去的二十年中一直处于最前沿,最近在里约热内卢州出现了孢子丝虫病感染的热点地区。自1998年以来,仅在巴西里约热内卢就报告了4000多例此类感染的传染源。我们开发了一个稀有的pentathiepin环系统的重点文库,并确定了产生化合物21和22的有效替代模式。这些化合物比伊曲康唑更有效,伊曲康唑是目前治疗孢子体病的标准。DOI:10.3390/antibiotics8040249
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:WCl6/LiAlH4 Promoted transformation of imines into secondary and tertiary amines摘要:DOI:10.1016/0022-328x(85)80125-x
文献信息
-
The titanocene-catalyzed reduction of acetamides to tertiary amines by PhMeSiH<sub>2</sub>作者:Kumaravel Selvakumar、Kesamreddy Rangareddy、John F HarrodDOI:10.1139/v04-063日期:2004.8.1
A variety of acetamide derivatives are reduced in excellent yields to tertiary amines by PhMeSiH2 in the presence of Cp2TiX2 (X = F or Me) catalysts. The reactions are very clean at 80 °C. At room temperature a secondary reaction, hydrogenolysis of the C(O)N bond, intervenes and reduces the chemoselectivity. Nevertheless, this chemistry provides a simple methodology for the amide/alkylamine transformation using inexpensive, commercially available reagents.Key words: amides, reduction, secondary amides, methylphenylsilane, titanocene, catalysis.
-
Homogeneous Catalytic Hydrogenation of Amides to Amines作者:Jacorien Coetzee、Deborah L. Dodds、Jürgen Klankermayer、Sandra Brosinski、Walter Leitner、Alexandra M. Z. Slawin、David J. Cole-HamiltonDOI:10.1002/chem.201204270日期:2013.8.12Hydrogenation of amides in the presence of [Ru(acac)3] (acacH=2,4‐pentanedione), triphos [1,1,1‐tris‐ (diphenylphosphinomethyl)ethane] and methanesulfonic acid (MSA) produces secondary and tertiary amines with selectivities as high as 93 % provided that there is at least one aromatic ring on N. The system is also active for the synthesis of primary amines. In an attempt to probe the role of MSA and在[Ru(acac)3 ](acacH = 2,4-戊二酮),三[[1,1,1-三(二苯基膦甲基)乙烷]]和甲磺酸(MSA)的存在下进行酰胺加氢生成仲胺和叔胺如果在N上至少有一个芳环,则其选择性高达93%。该系统对伯胺的合成也具有活性。为了探索MSA的作用和反应机理,已经从[Ru(acac)3 ],三醇和MSA或[RuX(OAc)(triphos)]的反应中制备了一系列甲磺酸钠络合物。 (X = H或OAc)或[RuH 2(CO)(triphos )]与MSA。晶体学表征复合物包括:[茹(OAC-κ 1 O)2(H 2O)(triphos)],[Ru(OAc‐κ 2 O,O')(CH 3 SO 3 ‐κ 1 O)(triphos )],[Ru(CH 3 SO 3‐ κ 1 O)2(H 2 O)(三膦)]和[孺2(μ-CH 3 SO 3)3(三磷酸)2 ] [CH 3 SO 3 ],而其他复合物,例如[茹(OAC-κ
-
PROCESS FOR PREPARING FORMIC ACID申请人:Fachinetti Giuseppe公开号:US20130006015A1公开(公告)日:2013-01-03A process for preparing formic acid by hydrogenation of carbon dioxide in the presence of a tertiary amine (I) and a catalyst at a pressure of from 0.2 to 30 MPa abs and a temperature of from 20 to 200° C., wherein the catalyst is a heterogeneous catalyst comprising gold.
-
Bench-Stable Cobalt Pre-Catalysts for Mild Hydrosilative Reduction of Tertiary Amides to Amines and Beyond作者:Alibek Nurseiit、Jaysan Janabel、Kristina A. Gudun、Aishabibi Kassymbek、Medet Segizbayev、Tulegen M. Seilkhanov、Andrey Y. KhalimonDOI:10.1002/cctc.201801605日期:2019.1.23unsaturated organic molecules, including the normally challenging reduction of amides to amines. With regard to hydrosilative reduction of amides even more effective and activator free catalytic systems can be generated from the bench‐stable, commercially available Co(acac)2 and Co(OAc)2 with dpephos and PPh3 ligands. These systems operate under mild conditions (<100 °C), with many examples of room temperature
-
HETEROCYCLIC UREA DERIVATIVES AND METHODS OF USE THEREOF申请人:CHOY Allison Laura公开号:US20100317624A1公开(公告)日:2010-12-16Compounds of formula (IA) and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts are described. Processes for their preparation, pharmaceutical compositions containing them, their use as medicaments and their use in the treatment of bacterial infections are also described.公式(IA)的化合物及其药用可接受的盐被描述。还描述了它们的制备过程、含有它们的药物组合物、它们作为药物的使用以及它们在治疗细菌感染中的用途。
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
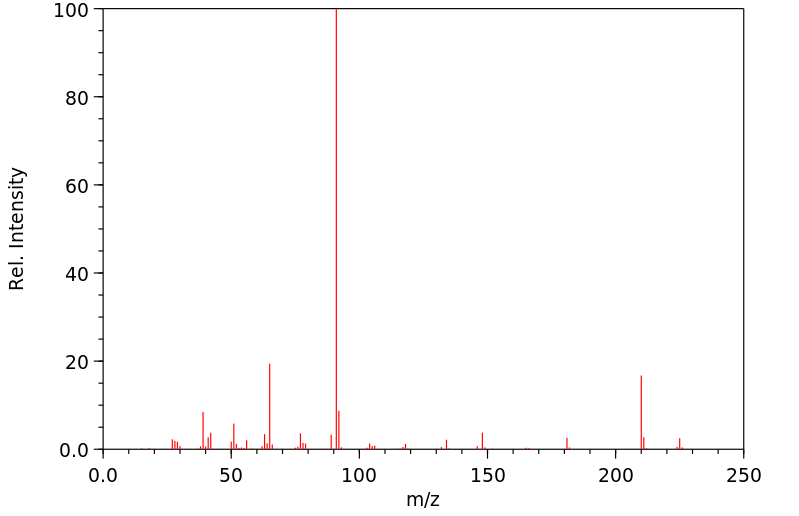
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
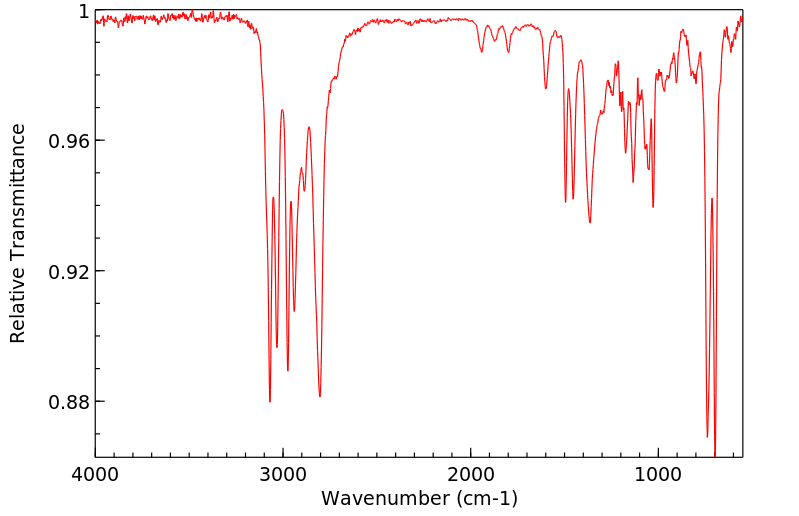
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(βS)-β-氨基-4-(4-羟基苯氧基)-3,5-二碘苯甲丙醇
(S,S)-邻甲苯基-DIPAMP
(S)-(-)-7'-〔4(S)-(苄基)恶唑-2-基]-7-二(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-2,2',3,3'-四氢-1,1-螺二氢茚
(S)-盐酸沙丁胺醇
(S)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧磷杂环戊二烯
(S)-2,2'-双[双(3,5-三氟甲基苯基)膦基]-4,4',6,6'-四甲氧基联苯
(S)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(R)富马酸托特罗定
(R)-(-)-盐酸尼古地平
(R)-(-)-4,12-双(二苯基膦基)[2.2]对环芳烷(1,5环辛二烯)铑(I)四氟硼酸盐
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[((6-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(4-叔丁基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(3-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-4,7-双(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-7“-[(吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2”,3,3'-四氢1,1'-螺二茚满
(R)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二苯氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂环戊烯
(R)-2-[((二苯基膦基)甲基]吡咯烷
(R)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(N-(4-甲氧基苯基)-N-甲基-3-(1-哌啶基)丙-2-烯酰胺)
(5-溴-2-羟基苯基)-4-氯苯甲酮
(5-溴-2-氯苯基)(4-羟基苯基)甲酮
(5-氧代-3-苯基-2,5-二氢-1,2,3,4-oxatriazol-3-鎓)
(4S,5R)-4-甲基-5-苯基-1,2,3-氧代噻唑烷-2,2-二氧化物-3-羧酸叔丁酯
(4S,4''S)-2,2''-亚环戊基双[4,5-二氢-4-(苯甲基)恶唑]
(4-溴苯基)-[2-氟-4-[6-[甲基(丙-2-烯基)氨基]己氧基]苯基]甲酮
(4-丁氧基苯甲基)三苯基溴化磷
(3aR,8aR)-(-)-4,4,8,8-四(3,5-二甲基苯基)四氢-2,2-二甲基-6-苯基-1,3-二氧戊环[4,5-e]二恶唑磷
(3aR,6aS)-5-氧代六氢环戊基[c]吡咯-2(1H)-羧酸酯
(2Z)-3-[[(4-氯苯基)氨基]-2-氰基丙烯酸乙酯
(2S,3S,5S)-5-(叔丁氧基甲酰氨基)-2-(N-5-噻唑基-甲氧羰基)氨基-1,6-二苯基-3-羟基己烷
(2S,2''S,3S,3''S)-3,3''-二叔丁基-4,4''-双(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-2,2''-联苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂戊环
(2S)-(-)-2-{[[[[3,5-双(氟代甲基)苯基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基}-N-(二苯基甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[((1S,2S)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[[((1R,2R)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2-硝基苯基)磷酸三酰胺
(2,6-二氯苯基)乙酰氯
(2,3-二甲氧基-5-甲基苯基)硼酸
(1S,2S,3S,5S)-5-叠氮基-3-(苯基甲氧基)-2-[(苯基甲氧基)甲基]环戊醇
(1S,2S,3R,5R)-2-(苄氧基)甲基-6-氧杂双环[3.1.0]己-3-醇
(1-(4-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(3-溴苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氯苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2,6-二氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(-)-去甲基西布曲明
龙蒿油
龙胆酸钠
龙胆酸叔丁酯
龙胆酸
龙胆紫-d6
龙胆紫