敌菌丹 | 2425-06-1
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:160-161°
-
沸点:365.7±52.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.4682 (rough estimate)
-
闪点:>100 °C
-
溶解度:氯仿(少量溶解)、二氯甲烷(极少量)、甲醇(少量溶解)
-
物理描述:Captafol is a white crystalline solid with a slight, but pungent odor. Mp: 162°C. Practically insoluble in water. Only slightly soluble in organic solvents. Technical captafol is a wettable light tan powder that is used as a fungicide. Inhaled dust irritates the respiratory tract. Irritates skin and damages eyes. Acute oral toxicity in humans is low. Not persistent in the environment (decomposes with a half-life of 11 days in the soil). Highly toxic to fish and other aquatic organisms.
-
颜色/状态:White, solid
-
气味:Slight, characteristic pungent odor.
-
蒸汽密度:Relative vapor density (air = 1): 12
-
蒸汽压力:8.27X10-9 mm Hg @ 20 °C
-
稳定性/保质期:
在常温常压下稳定,但在酸性和碱性条件下不稳定。它会在熔点温度时缓慢分解。
-
分解:Rapidly hydrolyzed in acidic and alkaline media. At 50 °C, 50% decomposition occurs in about 3 hr at pH 6.
-
保留指数:2337.9;2341.3;2323;2337.4
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.8
-
重原子数:18
-
可旋转键数:3
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.6
-
拓扑面积:62.7
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:3
ADMET
安全信息
-
职业暴露等级:D
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: 0.1 mg/m3 [skin]
-
危险品标志:N,T
-
安全说明:S45,S53,S60,S61
-
危险类别码:R50/53,R43,R45
-
海关编码:29305000
-
危险品运输编号:UN3077 9/PG 3
-
RTECS号:GW4900000
制备方法与用途
外观及物理化学性质
敌菌丹为白色结晶固体,熔点为160~161℃。在室温下几乎不挥发,难溶于水但微溶于大多数有机溶剂。其分解缓慢且在强碱条件下不稳定,在熔点温度时会缓慢分解。工业品呈现亮黄褐色粉末状。
用途与毒性
敌菌丹是一种用于叶面喷施的非内吸性、保护性农业杀菌剂,1961年由美国Chevron化学品公司生产(Chevron Chemical Company)。它可防治多种作物上的霜霉病、疫病、炭疽病等。敌菌丹对大鼠口服的LD50为5,000~6,200 mg/kg,毒性属于低毒级别,但使用时仍需注意安全,防止吸入或接触皮肤,配药和施药人员应穿戴防护装备。
注意事项
- 请勿与碱性药剂及油类物质混用。
- 使用过程中,操作人员应注意个人防护,避免吸入药液或接触皮肤。
- 如有对敌菌丹过敏反应,需及时处理皮疹等症状。
- 施药后清洗各种工具,并妥善处置污水和剩余药液,防止污染环境。
- 运输和储存时应有专门的车皮和仓库,不得与食物及日用品混放。
制备方法
敌菌丹由丁二烯和顺丁烯二酸酐反应生成四氢邻苯二酸酐,然后通过氨与四氢邻苯二酸酐作用形成亚胺,再与1,1,2,2-四氯乙基氯化硫反应而成。图1展示了其合成路线。
作用方式
敌菌丹是一种多作用点的广谱保护性杀菌剂,结构中的二甲酰亚胺基(-CON(H)co-)具有较高的杀菌活性,可用于防治果树、蔬菜和经济作物上的根腐病、立枯病、霜霉病、疫病和炭疽病。不过对白粉病效果较差,除喷雾使用外,也可作为土壤消毒和种子处理用。
毒性
敌菌丹大鼠急性口服LD50为2,500 mg/kg(80%可湿性粉剂水悬液),大白兔经皮毒性LD50大于15,400 mg/kg。长期饲养实验中,每日使用500 mg/kg对大鼠或10 mg/kg剂量对狗均未产生中毒现象。然而,有人对其过敏,并证实具有致癌作用。敌菌丹对野鸭和家鸭的急性口服LD50分别为大于23,070 mg/kg和101,700 mg/kg。此外,对虹鳟鱼、金鱼和青鳃鱼的接触4天半致死浓度(LC50)分别为0.5 mg/L、3.0 mg/L和0.15 mg/L,大翻车鱼为2.8 mg/L。
防治对象
敌菌丹曾广泛用于防治番茄叶和果实的病害、马铃薯枯萎病及咖啡仁果病等。此外,它也可作为木材防腐剂使用。关于敌菌丹的农业杀菌剂、制备方法、作用方式及其毒性等方面的信息由Chemicalbook的玉莲编辑整理(2016-03-04)。
剂型
化学性质黄褐色至类白色粉末状。
类别农药。
毒性分级低毒。
急性毒性- 大鼠口服LD50:2,500毫克/公斤
- 腹腔注射小鼠LDLo:3毫克/公斤
库房需通风干燥,低温保存。与食品原料分开储存运输。
灭火剂干粉、泡沫、砂土。
职业标准时间加权平均容许浓度(TWA):0.1毫克/立方米。
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Fungicidal compositions based on alkyl phosphites摘要:提供了一种杀真菌组合物和用于保护葡萄藤免受疾病侵害的方法。该组合物应用于葡萄藤上,其活性物质含有以下配方的磷酸单酯盐混合物的1份重量:##STR1## 其中R是具有2到4个碳原子的烷基基团,Me是碱金属、碱土金属或铝原子,n是整数,从1到3等于Me的价数,并且从0.05到8份的至少一种接触性杀真菌剂,所述接触性杀真菌剂选自具有铜基础的化合物、金属乙撑二硫代氨基甲酸盐和邻苯二甲酰亚胺衍生物。公开号:US04698334A1
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:Fungicidal compositions based on alkyl phosphites摘要:提供了一种用于保护葡萄藤免受疾病侵害的杀菌剂组合物和方法。该组合物应用于葡萄藤上,其活性物质包含以下成分的混合物:1份重量的磷酸单酯盐,其化学式为##STR1## 其中R是具有2到4个碳原子的烷基基团,Me是碱金属、碱土金属或铝原子,n是1到3的整数,等于Me的价,以及0.05到8份的至少一种接触型杀菌剂,所述接触型杀菌剂选自以铜为基础的化合物、金属乙撑二硫代氨基甲酸盐和邻苯二甲酰亚胺的衍生物。公开号:US05169646A1
文献信息
-
[EN] ACC INHIBITORS AND USES THEREOF<br/>[FR] INHIBITEURS DE L'ACC ET UTILISATIONS ASSOCIÉES
-
[EN] BICYCLYL-SUBSTITUTED ISOTHIAZOLINE COMPOUNDS<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS ISOTHIAZOLINE SUBSTITUÉS PAR UN BICYCLYLE申请人:BASF SE公开号:WO2014206910A1公开(公告)日:2014-12-31The present invention relates to bicyclyl-substituted isothiazoline compounds of formula (I) wherein the variables are as defined in the claims and description. The compounds are useful for combating or controlling invertebrate pests, in particular arthropod pests and nematodes. The invention also relates to a method for controlling invertebrate pests by using these compounds and to plant propagation material and to an agricultural and a veterinary composition comprising said compounds.本发明涉及公式(I)中变量如索权和说明中所定义的自行车基取代异噻唑啉化合物。这些化合物对抗或控制无脊椎动物害虫,特别是节肢动物害虫和线虫方面具有用途。该发明还涉及一种通过使用这些化合物来控制无脊椎动物害虫的方法,以及包含所述化合物的植物繁殖材料、农业和兽医组合物。
-
[EN] AZOLINE COMPOUNDS<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS AZOLINE申请人:BASF SE公开号:WO2015128358A1公开(公告)日:2015-09-03The present invention relates to azoline compounds of formula (I) wherein A, B1, B2, B3, G1, G2, X1, R1, R3a, R3b, Rg1 and Rg2 are as defined in the claims and the description. The compounds are useful for combating or controlling invertebrate pests, in particular arthropod pests and nematodes. The invention also relates to a method for controlling invertebrate pests by using these compounds and to plant propagation material and to an agricultural and a veterinary composition comprising said compounds.本发明涉及式(I)的噁唑啉化合物,其中A、B1、B2、B3、G1、G2、X1、R1、R3a、R3b、Rg1和Rg2如权利要求和描述中所定义。这些化合物对抗或控制无脊椎动物害虫,特别是节肢动物害虫和线虫方面具有用途。该发明还涉及一种利用这些化合物控制无脊椎动物害虫的方法,以及包括所述化合物的植物繁殖材料、农业和兽医组合物。
-
[EN] SUBSTITUTED QUINAZOLINES AS FUNGICIDES<br/>[FR] QUINAZOLINES SUBSTITUÉES, UTILISÉES EN TANT QUE FONGICIDES申请人:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG公开号:WO2010136475A1公开(公告)日:2010-12-02The present invention relates to a compound of formula (I) wherein wherein the substituents have the definitions as defined in claim 1or a salt or a N-oxide thereof, their use and methods for the control and/or prevention of microbial infection, particularly fungal infection, in plants and to processes for the preparation of these compounds.本发明涉及一种具有如下式(I)的化合物,其中取代基具有权利要求1中定义的定义,或其盐或N-氧化物,它们的用途以及用于控制和/或预防植物中微生物感染,特别是真菌感染的方法,以及制备这些化合物的方法。
-
[EN] MICROBIOCIDAL OXADIAZOLE DERIVATIVES<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS D'OXADIAZOLE MICROBIOCIDES申请人:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG公开号:WO2017157962A1公开(公告)日:2017-09-21Compounds of the formula (I) wherein the substituents are as defined in claim 1, useful as a pesticides, especially fungicides.式(I)的化合物,其中取代基如权利要求1所定义,作为杀虫剂特别是杀菌剂有用。
表征谱图
-
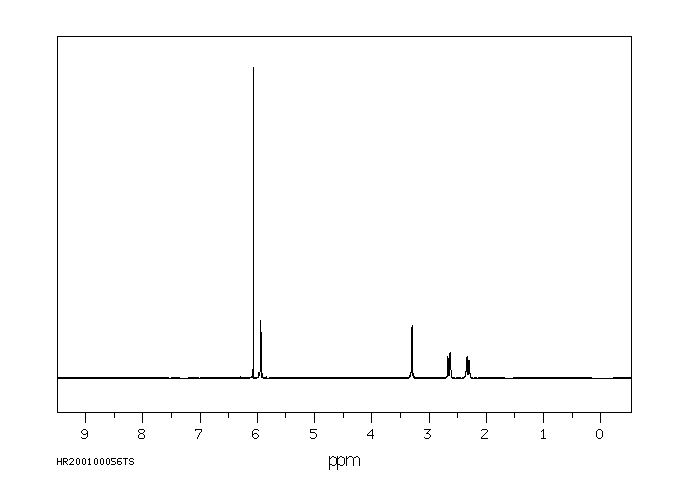
氢谱1HNMR
-
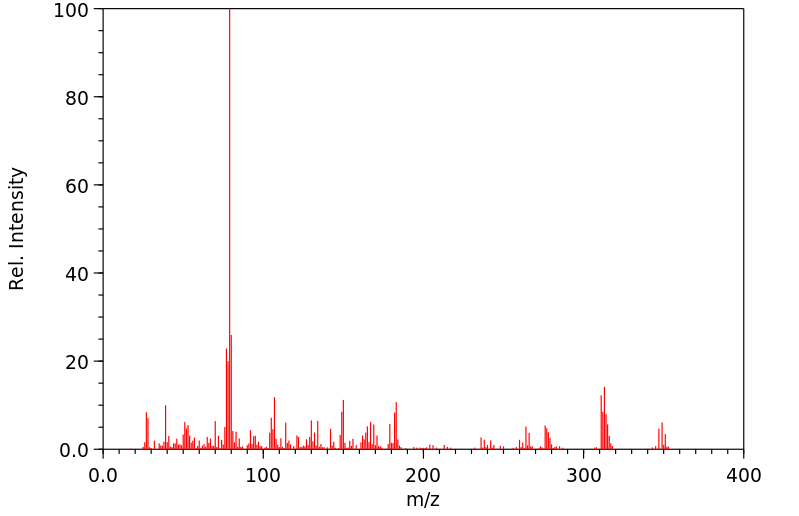
质谱MS
-
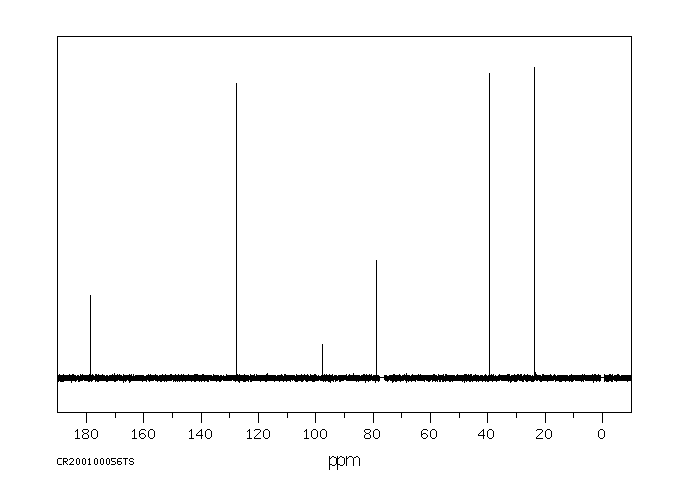
碳谱13CNMR
-
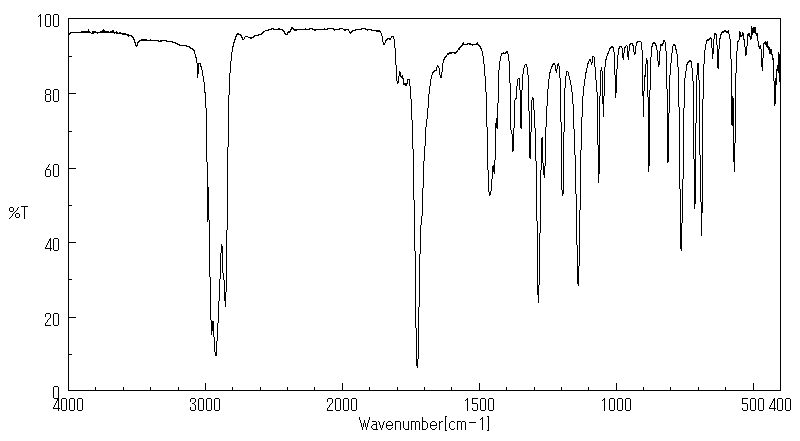
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息