(Z)-Styrylthioacetic acid | 1914-61-0
中文名称
——
中文别名
——
英文名称
(Z)-Styrylthioacetic acid
英文别名
cis-styrylthioacetic acid;Z-styrylthioacetic acid;2-[(Z)-2-phenylethenyl]sulfanylacetic acid
CAS
1914-61-0
化学式
C10H10O2S
mdl
——
分子量
194.254
InChiKey
IUEVBKDVPSQVLM-SREVYHEPSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2.5
-
重原子数:13
-
可旋转键数:4
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.1
-
拓扑面积:62.6
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:3
安全信息
-
海关编码:2930909090
SDS
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Reddy, M. V. Ramana; Reddy, S.; Reddy, D. Bhaskar, Synthetic Communications, 1989, vol. 19, # 5and6, p. 1101 - 1108摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:描述:methyl styrylthioacetate 在 氢氧化钾 作用下, 反应 1.0h, 以86%的产率得到(Z)-Styrylthioacetic acid参考文献:名称:Reddy, M. V. Ramana; Reddy, S.; Reddy, D. Bhaskar, Synthetic Communications, 1989, vol. 19, # 5and6, p. 1101 - 1108摘要:DOI:
文献信息
-
Synthesis, Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Activities of 5-((styrylsulfonyl) methyl)-1,3,4-Oxadiazol / Thiadiazol-2-amine Derivatives作者:Gundala Sravya、Ummadi Nagarjuna、Venkatapuram Padmavathi、Galla Rajitha、Sakuri Chandi priya、Adivireddy PadmajaDOI:10.2174/1570180816666181102114529日期:2019.10.23class of 5-(styrylsulfonylmethyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-amine and 5- (styrylsulfonylmethyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-amine derivatives were prepared by derivatization of amino function. Methods: All the synthesized compounds were tested for antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Results: The 2-amino-3-chloro-N-(5-(4-methylstyrylsulfonylmethyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)-propanamide (12b) and 3-chloro-N-(5-(4-m
-
Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of styryl/pyrrolyl/pyrazolyl sulfonylmethyl-1,3,4-oxadiazolyl amines and styryl/pyrrolyl/pyrazolyl sulfonylmethyl-1,3,4-thiadiazolyl amines作者:G. Sravya、G. Yamini、V. Padmavathi、A. PadmajaDOI:10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.06.014日期:2016.104-oxadiazolyl/1,3,4-thiadiazolyl amines and pyrazolyl sulfonylmethyl-1,3,4-oxadiazolyl/1,3,4-thiadiazolyl amines were prepared from the synthetic intermediate Z-styrylsulfonylacetic acid adopting simple and well versed synthetic methodologies and studied their antimicrobial activity. Amongst all the tested compounds styryl thiadiazole 5c exhibited promising antimicrobial activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa
-
Synthesis, Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities of Sulfone Linked Bis Heterocycles-Pyrazolyl Oxadiazoles and Pyrazolyl Thiadiazole作者:Venkatapuram Padmavathi、Sanapalli Nagi Reddy、Konda MaheshDOI:10.1248/cpb.57.1376日期:——A new class of bis heterocycles-sulfone linked pyrazolyl oxadiazoles and thiadiazoles were developed from Z-styrylsulfonylacetic acid. The pyrazolyl thiadiazoles exhibited excellent antimicrobial activity whereas pyrazolyl oxadiazoles displayed good antioxidant activity.
-
Unsaturated thioacetic acids as novel mechanism-based inhibitors of peptidylglycine α-hydroxylating monooxygenase作者:P. Casara、A. Ganzhorn、C. Philippo、M-C. Chanal、C. DanzinDOI:10.1016/0960-894x(96)00041-8日期:1996.2Several unsaturated thioacetic acids were synthesized as potential mechanism-based inhibitors of peptidylglycine alpha-hydroxylating monooxygenase (PHM) prepared from horse serum. Trans-styrylthioacetic acid produced potent time-dependent inhibition of PHM. Potential mechanisms are proposed to explain PHM inactivation by unsaturated thioacetic acids.
-
Larsson, Erik, Journal fur praktische Chemie (Leipzig 1954), 1981, vol. 323, # 6, p. 985 - 988作者:Larsson, ErikDOI:——日期:——
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
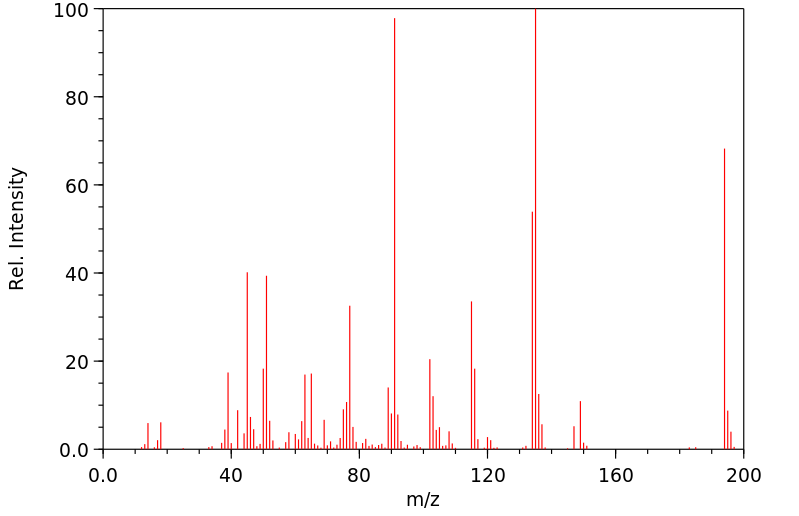
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
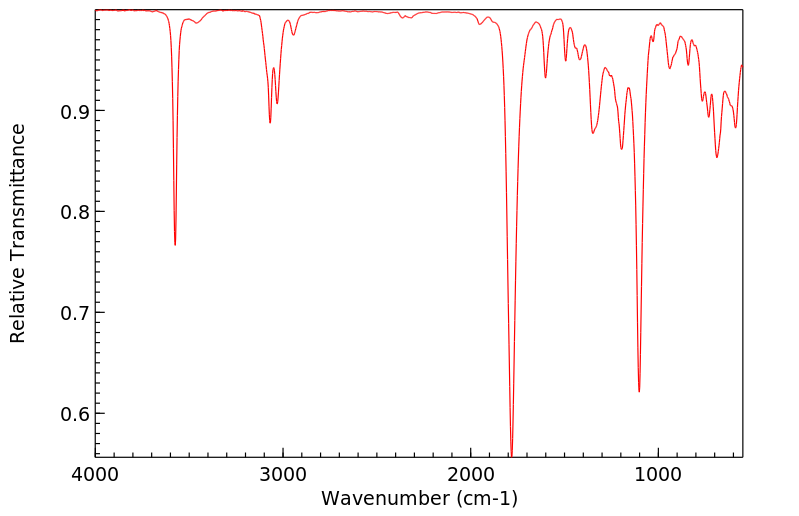
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(βS)-β-氨基-4-(4-羟基苯氧基)-3,5-二碘苯甲丙醇
(S,S)-邻甲苯基-DIPAMP
(S)-(-)-7'-〔4(S)-(苄基)恶唑-2-基]-7-二(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-2,2',3,3'-四氢-1,1-螺二氢茚
(S)-盐酸沙丁胺醇
(S)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧磷杂环戊二烯
(S)-2,2'-双[双(3,5-三氟甲基苯基)膦基]-4,4',6,6'-四甲氧基联苯
(S)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(R)富马酸托特罗定
(R)-(-)-盐酸尼古地平
(R)-(-)-4,12-双(二苯基膦基)[2.2]对环芳烷(1,5环辛二烯)铑(I)四氟硼酸盐
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[((6-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(4-叔丁基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(3-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-4,7-双(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-7“-[(吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2”,3,3'-四氢1,1'-螺二茚满
(R)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二苯氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂环戊烯
(R)-2-[((二苯基膦基)甲基]吡咯烷
(R)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(N-(4-甲氧基苯基)-N-甲基-3-(1-哌啶基)丙-2-烯酰胺)
(5-溴-2-羟基苯基)-4-氯苯甲酮
(5-溴-2-氯苯基)(4-羟基苯基)甲酮
(5-氧代-3-苯基-2,5-二氢-1,2,3,4-oxatriazol-3-鎓)
(4S,5R)-4-甲基-5-苯基-1,2,3-氧代噻唑烷-2,2-二氧化物-3-羧酸叔丁酯
(4S,4''S)-2,2''-亚环戊基双[4,5-二氢-4-(苯甲基)恶唑]
(4-溴苯基)-[2-氟-4-[6-[甲基(丙-2-烯基)氨基]己氧基]苯基]甲酮
(4-丁氧基苯甲基)三苯基溴化磷
(3aR,8aR)-(-)-4,4,8,8-四(3,5-二甲基苯基)四氢-2,2-二甲基-6-苯基-1,3-二氧戊环[4,5-e]二恶唑磷
(3aR,6aS)-5-氧代六氢环戊基[c]吡咯-2(1H)-羧酸酯
(2Z)-3-[[(4-氯苯基)氨基]-2-氰基丙烯酸乙酯
(2S,3S,5S)-5-(叔丁氧基甲酰氨基)-2-(N-5-噻唑基-甲氧羰基)氨基-1,6-二苯基-3-羟基己烷
(2S,2''S,3S,3''S)-3,3''-二叔丁基-4,4''-双(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-2,2''-联苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂戊环
(2S)-(-)-2-{[[[[3,5-双(氟代甲基)苯基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基}-N-(二苯基甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[((1S,2S)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[[((1R,2R)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2-硝基苯基)磷酸三酰胺
(2,6-二氯苯基)乙酰氯
(2,3-二甲氧基-5-甲基苯基)硼酸
(1S,2S,3S,5S)-5-叠氮基-3-(苯基甲氧基)-2-[(苯基甲氧基)甲基]环戊醇
(1S,2S,3R,5R)-2-(苄氧基)甲基-6-氧杂双环[3.1.0]己-3-醇
(1-(4-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(3-溴苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氯苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2,6-二氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(-)-去甲基西布曲明
龙蒿油
龙胆酸钠
龙胆酸叔丁酯
龙胆酸
龙胆紫-d6
龙胆紫