N-甲基呋喃异羟肟酸 | 109531-96-6
中文名称
N-甲基呋喃异羟肟酸
中文别名
N-(2-糠酰)-N-甲基羟胺;N-甲基糠酰羟肟酸;N-(2-呋喃甲酰基)-N-甲基羟胺;N-甲基糠酰羟肟酸[用于高效液相色谱的螯合试剂]
英文名称
N-hydroxy-N-methyl-2-furancarboxamide
英文别名
N-methyl-N-(2-furanoyl)hydroxylamine;N-hydroxy-N-methyl-2-furamide;N-methylfurohydroxamic acid;N-hydroxy-N-methylfuran-2-carboxamide
CAS
109531-96-6
化学式
C6H7NO3
mdl
MFCD00144939
分子量
141.126
InChiKey
KCAHIEOWHDMBKM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:101 °C
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-0.1
-
重原子数:10
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.166
-
拓扑面积:53.7
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:3
安全信息
-
海关编码:2932190090
-
储存条件:室温且干燥环境中保存。
SDS
N-甲基糠酰羟肟酸[用于高效液相色谱的螯合试剂] 修改号码:5
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: N-Methylfurohydroxamic Acid [Chelating ReageNT for HPLC]
修改号码: 5
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害 未分类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志 无
信号词 无信号词
危险描述 无
防范说明 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): N-甲基糠酰羟肟酸[用于高效液相色谱的螯合试剂]
百分比: >99.0%(LC)
CAS编码: 109531-96-6
俗名: N-(2-Furoyl)-N-methylhydroxylamine , N-MFHA
分子式: C6H7NO3
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用水清洗皮肤/淋浴。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,雾状水,二氧化碳
特殊危险性: 小心,燃烧或高温下可能分解产生毒烟。
修改号码:5
模块 5. 消防措施
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 清扫收集粉尘,封入密闭容器。注意切勿分散。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的
法律法规处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止粉尘扩散。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果粉尘或浮质产生,使用局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防尘面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
固体
外形(20°C):
外观: 晶体-粉末
颜色: 白色类白色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点:
101°C
沸点/沸程 无资料
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 无资料
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂] 无资料
修改号码:5
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳, 氮氧化物 (NOx)
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在可燃溶剂中溶解混合,在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中
焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
修改号码:5
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: N-Methylfurohydroxamic Acid [Chelating ReageNT for HPLC]
修改号码: 5
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害 未分类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志 无
信号词 无信号词
危险描述 无
防范说明 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): N-甲基糠酰羟肟酸[用于高效液相色谱的螯合试剂]
百分比: >99.0%(LC)
CAS编码: 109531-96-6
俗名: N-(2-Furoyl)-N-methylhydroxylamine , N-MFHA
分子式: C6H7NO3
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用水清洗皮肤/淋浴。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,雾状水,二氧化碳
特殊危险性: 小心,燃烧或高温下可能分解产生毒烟。
修改号码:5
模块 5. 消防措施
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 清扫收集粉尘,封入密闭容器。注意切勿分散。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的
法律法规处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止粉尘扩散。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果粉尘或浮质产生,使用局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防尘面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
固体
外形(20°C):
外观: 晶体-粉末
颜色: 白色类白色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点:
101°C
沸点/沸程 无资料
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 无资料
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂] 无资料
修改号码:5
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳, 氮氧化物 (NOx)
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在可燃溶剂中溶解混合,在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中
焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
修改号码:5
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
光谱试剂
上下游信息
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— N-(triflyloxy)-N-methylfurancarboxamide 156025-78-4 C7H6F3NO5S 273.19
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:N-甲基呋喃异羟肟酸 在 2,6-二甲基吡啶 、 sodium hydride 作用下, 以 二氯甲烷 、 N,N-二甲基甲酰胺 为溶剂, 反应 3.25h, 生成 N-isopropoxymethyl-N-benzyl-2-furancarboxamide参考文献:名称:A Facile Preparation of N-(Isopropoxyalkyl) Amides by Generation and Trapping of N-Acyliminium Ions from Ionization-Rearrangement Reactions of N-Triflyloxy Amides摘要:A series of hydroxamic acids were converted to N-triflyloxy amides which were heated in 2-propanol to give N-(1-isopropoxyalkyl) amides in high yields. The method is simple, direct, and extremely tolerant of structural diversity both in the N-acyl group, as well as in the 1-isopropoxyalkyl group. N-Alkylation of secondary N-(1-isopropoxyalkyl) amides can be used for converting them to tertiary N-(1-isopropoxyalkyl) amides. N-Acyliminium ions of wide structural diversity can be generated easily from N-(1-isopropoxyalkyl) amides available by this methodology.DOI:10.1021/jo00092a007
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Efficient Conversions of Carboxylic Acids intoO-Alkyl,N-Alkyl andO,N-Dialkylhydroxamic Acids摘要:羧酸可以通过酰基苯并三唑中间体方便地转化为未取代的、N-烷基-、O-烷基-以及O,N-二烷基异羟肟酸。这些试剂的容易获得、温和的条件以及中间体的易于处理是其优势所在。DOI:10.1055/s-2003-42488
文献信息
-
Late-Stage Photoredox C–H Amidation of N-Unprotected Indole Derivatives: Access to <i>N</i>-(Indol-2-yl)amides作者:Yue Weng、Bo Ding、Yunqing Liu、Chunlan Song、Lo-Ying Chan、Chien-Wei ChiangDOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.1c00609日期:2021.4.2carboxamides are valuable in pharmaceutical applications, the preparation N-(indol-2-yl)amides with similar structures continues to be challenging. Herein we report on visible-light-induced late-stage photoredox C–H amidation with N-unprotected indoles and tryptophan-containing peptides, leading to the formation of N-(indol-2-yl)amide derivatives. N-Unprotected indoles and aryloxyamides that contain an electron-withdrawing
-
TARGETED NITROXIDE AGENTS申请人:Wipf Peter公开号:US20100035869A1公开(公告)日:2010-02-11Provided herein are compositions and related methods useful for free radical scavenging, with particular selectivity for mitochondria. The compounds comprise a nitroxide-containing group attached to a mitochondria-targeting group. The compounds can be cross-linked into dimers without loss of activity. Also provided herein are methods, for preventing, mitigating and treating damage caused by radiation. The method comprises delivering a compound, as described herein, to a patient in an amount and dosage regimen effective to prevent, mitigate or treat damage caused by radiation.本文提供了一种对自由基清除有用的组合物和相关方法,具有特定选择性作用于线粒体。这些化合物包括一个连接到线粒体靶向基团的亚硝基含有基团。这些化合物可以交联成二聚体而不丧失活性。本文还提供了一种用于预防、缓解和治疗辐射引起的损伤的方法。该方法包括向患者输送一种如本文所述的化合物,以有效地预防、缓解或治疗辐射引起的损伤。
-
INTRAESOPHAGEAL ADMINISTRATION OF TARGETED NITROXIDE AGENTS FOR PROTECTION AGAINST IONIZING IRRADIATION-INDUCED ESOPHAGITIS申请人:University of Pittsburgh - Of the Commonwealth System of Higher Education公开号:US20190210969A1公开(公告)日:2019-07-11Provided herein are compositions and related methods useful for prevention or mitigation of ionizing radiation-induced esophagitis. The compositions comprise compounds comprising a nitroxide-containing group attached to a mitochondria-targeting group. The compounds can be cross-linked into dimers without loss of activity. The method comprises delivering a compound, as described herein, to a patient in an amount and dosage regimen effective to prevent or mitigate esophageal damage caused by radiation.本文提供了一种用于预防或缓解电离辐射诱导的食管炎的组合物和相关方法。这些组合物包括含有与线粒体靶向基团相连的亚硝基含有基团的化合物。这些化合物可以交联成二聚体而不丧失活性。该方法包括向患者输送本文所述的化合物,以有效预防或缓解由辐射引起的食道损伤。
-
Synthesis and structural characterisation of bismuth(<scp>iii</scp>) hydroxamates and their activity against Helicobacter pylori
-
一种含吡啶羟胺类化合物、制备方法及其用途
表征谱图
-
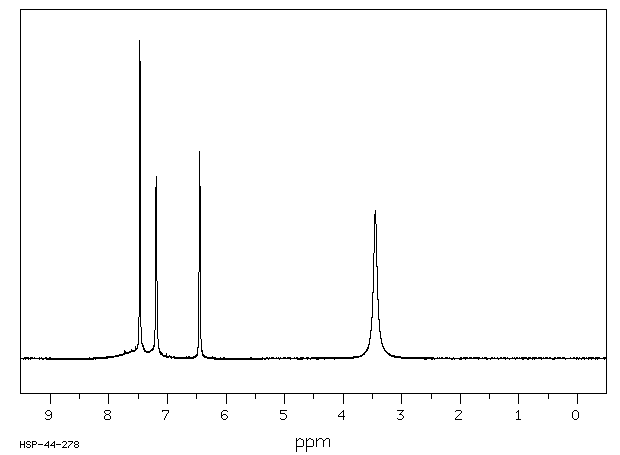
氢谱1HNMR
-
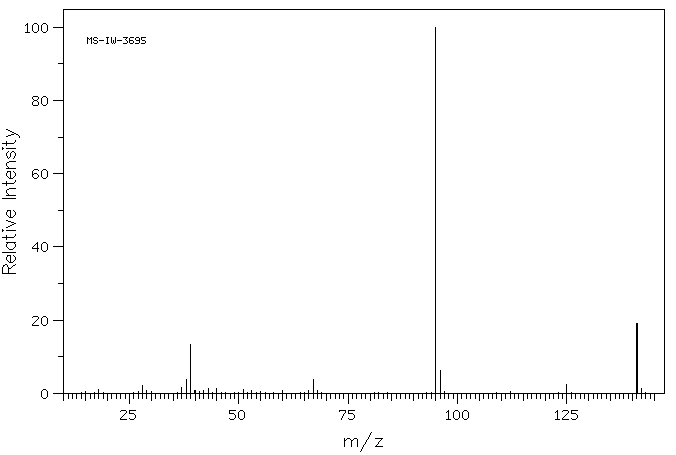
质谱MS
-
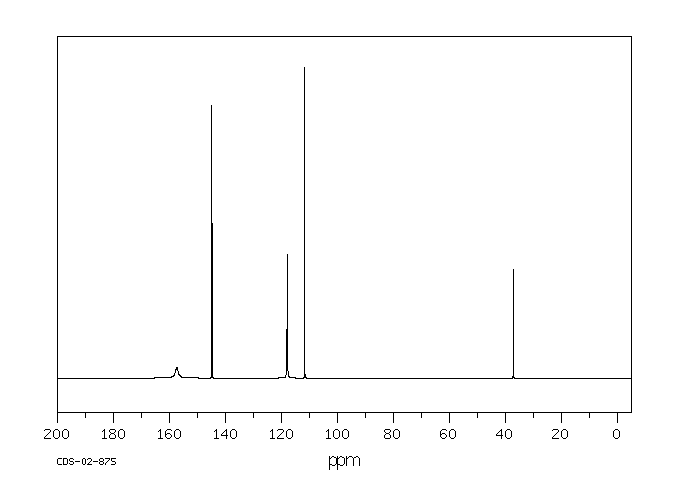
碳谱13CNMR
-
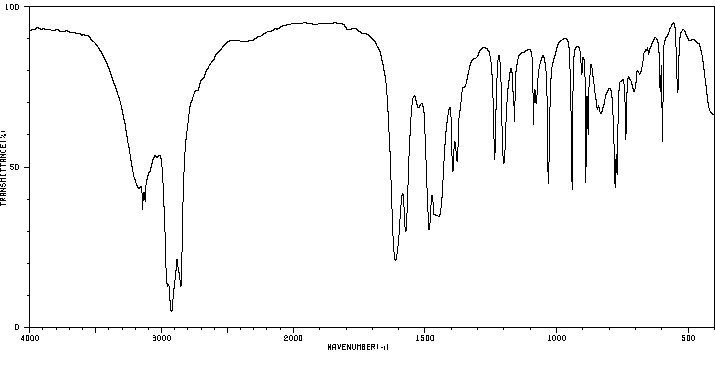
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
除草醚
锡烷,三丁基[(2-呋喃基羰基)氧代]-
醋糠硫胺
醋呋三嗪
酪氨酰-甘氨酰-色氨酰-蛋氨酰-门冬氨酰-苯基丙氨酰-甘氨酸
苯胺,N-[6-乙氧基-2,3-二(4-甲氧苯基)-4H-吡喃-4-亚基]-4-甲基-
糠酸(呋喃甲酸)
糠酸異戊酯
糠酸烯丙酯
碘化溴刚
硫代糠酸甲酯
硝基呋喃杂质
硝呋隆
硝呋醛肟标准品
硝呋达齐
硝呋美隆
硝呋维啶
硝呋立宗
硝呋甲醚
硝呋烯腙盐酸盐
硝呋烯腙
硝呋替莫
硝呋拉定
硝呋拉嗪
硝呋太尔杂质B
硝呋太尔杂质33
硝呋噻唑
硝呋吡醇
硝呋乙宗
盐酸呋喃它酮
盐酸呋喃他酮
疏呋那登
甲基7-[5-乙酰氨基-4-[(2-溴-4,6-二硝基苯基)偶氮]-2-甲氧苯基]-3-羰基-2,4,10-三氧杂-7-氮杂十一烷-11-酸酯
甲基5-溴-3-甲基-2-糠酸酯
甲基5-乙酰氨基-2-糠酸酯
甲基5-{[(氯乙酰基)氨基]甲基}-2-糠酸酯
甲基5-(甲氧基甲基)-2-甲基呋喃-3-羧酸酯
甲基5-(溴甲基)-4-(氯甲基)-2-糠酸酯
甲基5-(乙氧基甲基)-2-甲基-3-糠酸酯
甲基5-({[5-(三氟甲基)-2-吡啶基]硫代}甲基)-2-糠酸
甲基5-(4-甲酰基苯基)-2-糠酸酯
甲基5-(3-甲酰基苯基)-2-糠酸酯
甲基4-甲基-3-糠酸酯
甲基4-溴-5-甲基-2-糠酸酯
甲基4-乙酰基-5-甲基-2-糠酸酯
甲基4,6-二氯-3-(二乙基氨基)呋喃并[3,4-c]吡啶-1-羧酸酯
甲基3-羟基呋喃并[3,2-b]吡啶-2-羧酸酯
甲基3-甲酰基-2-糠酸酯
甲基3-氨基呋喃并[2,3-b]吡啶-2-羧酸酯
甲基3-氨基-5-(2-甲基-2-丙基)-2-糠酸酯