4-乙酰胺-2-二乙氨甲基苯酚 | 121-78-8
中文名称
4-乙酰胺-2-二乙氨甲基苯酚
中文别名
3-二乙氨基对乙酰氨基酚
英文名称
N-{3-[(diethylamino)methyl]-4-hydroxyphenyl}acetamide
英文别名
4-acetamido-2-(diethylaminomethyl)phenol;4-acetamido-α-(diethylamino)-o-cresol;4-Acetamido-2-Diethylaminomethylphenol;N-[3-(diethylaminomethyl)-4-hydroxyphenyl]acetamide
CAS
121-78-8
化学式
C13H20N2O2
mdl
MFCD00026732
分子量
236.314
InChiKey
BOUCRWJEKAGKKG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:135 °C
-
沸点:406.2±40.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.122±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1
-
重原子数:17
-
可旋转键数:5
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.46
-
拓扑面积:52.6
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:3
安全信息
-
海关编码:2924299090
SDS
1.1 产品标识符
: 4-Acetamido-2-diethylaminomethylphenol
产品名称
1.2 鉴别的其他方法
无数据资料
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途
仅供科研用途,不作为药物、家庭备用药或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述
2.1 GHS分类
急性毒性, 经口 (类别4)
皮肤刺激 (类别2)
严重的眼损伤 (类别1)
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触) (类别3)
2.2 GHS 标记要素,包括预防性的陈述
象形图
警示词 危险
危险申明
H302 吞咽有害。
H315 造成皮肤刺激。
H318 造成严重眼损伤。
H335 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
警告申明
预防
P261 避免吸入粉尘/烟/气体/烟雾/蒸气/喷雾.
P264 操作后彻底清洁皮肤。
P270 使用本产品时不要进食、饮水或吸烟。
P271 只能在室外或通风良好之处使用。
P280 穿戴防护手套/ 眼保护罩/ 面部保护罩。
措施
P301 + P312 如果吞下去了: 如感觉不适,呼救解毒中心或看医生。
P302 + P352 如与皮肤接触,用大量肥皂和水冲洗受感染部位.
P304 + P340 如吸入,将患者移至新鲜空气处并保持呼吸顺畅的姿势休息.
P305 + P351 + P338 如与眼睛接触,用水缓慢温和地冲洗几分钟。如戴隐形眼镜并可方便地取
出,取出隐形眼镜,然后继续冲洗.
P310 立即呼叫中毒控制中心或医生.
P321 具体治疗(见本标签上提供的急救指导)。
P330 漱口。
P332 + P313 如发生皮肤刺激:求医/ 就诊。
P362 脱掉沾染的衣服,清洗后方可重新使用。
储存
P403 + P233 存放于通风良的地方。 保持容器密闭。
P405 存放处须加锁。
处理
P501 将内容物/ 容器处理到得到批准的废物处理厂。
2.3 其它危害物 - 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
3.1 物 质
: C13H20N2O2
分子式
: 236.31 g/mol
分子量
组分 浓度或浓度范围
4-Acetamido-2-diethylaminomethylphenol
-
CAS 号 121-78-8
模块 4. 急救措施
4.1 必要的急救措施描述
一般的建议
请教医生。 出示此安全技术说明书给到现场的医生看。
吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如果停止了呼吸,给于人工呼吸。 请教医生。
皮肤接触
用肥皂和大量的水冲洗。 请教医生。
眼睛接触
用大量水彻底冲洗至少15分钟并请教医生。
食入
切勿给失去知觉者从嘴里喂食任何东西。 用水漱口。 请教医生。
4.2 主要症状和影响,急性和迟发效应
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示
无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施
5.1 灭火介质
灭火方法及灭火剂
用水雾,耐醇泡沫,干粉或二氧化碳灭火。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害
碳氧化物, 氮氧化物
5.3 给消防员的建议
如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步信息
无数据资料
模块 6. 泄露应急处理
6.1 人员的预防,防护设备和紧急处理程序
使用个人防护设备。 防止粉尘的生成。 防止吸入蒸汽、气雾或气体。 保证充分的通风。
将人员撤离到安全区域。 避免吸入粉尘。
6.2 环境保护措施
不要让产物进入下水道。
6.3 抑制和清除溢出物的方法和材料
收集、处理泄漏物,不要产生灰尘。 扫掉和铲掉。 存放进适当的闭口容器中待处理。
6.4 参考其他部分
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
7.1 安全操作的注意事项
避免接触皮肤和眼睛。 防止粉尘和气溶胶生成。
在有粉尘生成的地方,提供合适的排风设备。一般性的防火保护措施。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性
贮存在阴凉处。 容器保持紧闭,储存在干燥通风处。
7.3 特定用途
无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
8.1 容许浓度
最高容许浓度
没有已知的国家规定的暴露极限。
8.2 暴露控制
适当的技术控制
按照良好工业和安全规范操作。 休息前和工作结束时洗手。
个体防护设备
眼/面保护
面罩與安全眼鏡请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟) 检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/EEC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
身体保护
全套防化学试剂工作服, 防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和含量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
如危险性评测显示需要使用空气净化的防毒面具,请使用全面罩式多功能微粒防毒面具N100型(US
)或P3型(EN
143)防毒面具筒作为工程控制的候补。如果防毒面具是保护的唯一方式,则使用全面罩式送风防毒
面具。 呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息
a) 外观与性状
形状: 固体
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味阈值
无数据资料
d) pH值
无数据资料
e) 熔点/凝固点
无数据资料
f) 起始沸点和沸程
无数据资料
g) 闪点
无数据资料
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 易燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 无数据资料
k) 蒸汽压
无数据资料
l) 蒸汽密度
无数据资料
m) 相对密度
无数据资料
n) 水溶性
无数据资料
o) n-辛醇/水分配系数
辛醇--水的分配系数的对数值: 1.869
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性
10.1 反应性
无数据资料
10.2 稳定性
无数据资料
10.3 危险反应的可能性
无数据资料
10.4 应避免的条件
无数据资料
10.5 不兼容的材料
氧化剂
10.6 危险的分解产物
其它分解产物 - 无数据资料
模块 11. 毒理学资料
11.1 毒理学影响的信息
急性毒性
无数据资料
皮肤刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
眼睛刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
无数据资料
生殖细胞突变性
无数据资料
致癌性
IARC:
此产品中没有大于或等于 0。1%含量的组分被 IARC鉴别为可能的或肯定的人类致癌物。
生殖毒性
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
吸入 - 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入可能有害。 引起呼吸道刺激。
摄入 误吞对人体有害。
皮肤 如果通过皮肤吸收可能是有害的。 造成皮肤刺激。
眼睛 引起眼睛烧伤。
接触后的征兆和症状
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: 无数据资料
模块 12. 生态学资料
12.1 生态毒性
无数据资料
12.2 持久存留性和降解性
无数据资料
12.3 潜在的生物蓄积性
无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移性
无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价
无数据资料
12.6 其它不利的影响
无数据资料
模块 13. 废弃处置
13.1 废物处理方法
产品
将剩余的和未回收的溶液交给处理公司。 联系专业的拥有废弃物处理执照的机构来处理此物质。
与易燃溶剂相溶或者相混合,在备有燃烧后处理和洗刷作用的化学焚化炉中燃烧
受污染的容器和包装
作为未用过的产品弃置。
模块 14. 运输信息
14.1 联合国危险货物编号
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.2 联合国(UN)规定的名称
欧洲陆运危规: 非危险货物
国际海运危规: 非危险货物
国际空运危规: 非危险货物
14.3 运输危险类别
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.4 包裹组
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.5 环境危险
欧洲陆运危规: 否 国际海运危规 海运污染物: 否 国际空运危规: 否
14.6 对使用者的特别提醒
无数据资料
模块 15 - 法规信息
N/A
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
: 4-Acetamido-2-diethylaminomethylphenol
产品名称
1.2 鉴别的其他方法
无数据资料
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途
仅供科研用途,不作为药物、家庭备用药或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述
2.1 GHS分类
急性毒性, 经口 (类别4)
皮肤刺激 (类别2)
严重的眼损伤 (类别1)
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触) (类别3)
2.2 GHS 标记要素,包括预防性的陈述
象形图
警示词 危险
危险申明
H302 吞咽有害。
H315 造成皮肤刺激。
H318 造成严重眼损伤。
H335 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
警告申明
预防
P261 避免吸入粉尘/烟/气体/烟雾/蒸气/喷雾.
P264 操作后彻底清洁皮肤。
P270 使用本产品时不要进食、饮水或吸烟。
P271 只能在室外或通风良好之处使用。
P280 穿戴防护手套/ 眼保护罩/ 面部保护罩。
措施
P301 + P312 如果吞下去了: 如感觉不适,呼救解毒中心或看医生。
P302 + P352 如与皮肤接触,用大量肥皂和水冲洗受感染部位.
P304 + P340 如吸入,将患者移至新鲜空气处并保持呼吸顺畅的姿势休息.
P305 + P351 + P338 如与眼睛接触,用水缓慢温和地冲洗几分钟。如戴隐形眼镜并可方便地取
出,取出隐形眼镜,然后继续冲洗.
P310 立即呼叫中毒控制中心或医生.
P321 具体治疗(见本标签上提供的急救指导)。
P330 漱口。
P332 + P313 如发生皮肤刺激:求医/ 就诊。
P362 脱掉沾染的衣服,清洗后方可重新使用。
储存
P403 + P233 存放于通风良的地方。 保持容器密闭。
P405 存放处须加锁。
处理
P501 将内容物/ 容器处理到得到批准的废物处理厂。
2.3 其它危害物 - 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
3.1 物 质
: C13H20N2O2
分子式
: 236.31 g/mol
分子量
组分 浓度或浓度范围
4-Acetamido-2-diethylaminomethylphenol
-
CAS 号 121-78-8
模块 4. 急救措施
4.1 必要的急救措施描述
一般的建议
请教医生。 出示此安全技术说明书给到现场的医生看。
吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如果停止了呼吸,给于人工呼吸。 请教医生。
皮肤接触
用肥皂和大量的水冲洗。 请教医生。
眼睛接触
用大量水彻底冲洗至少15分钟并请教医生。
食入
切勿给失去知觉者从嘴里喂食任何东西。 用水漱口。 请教医生。
4.2 主要症状和影响,急性和迟发效应
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示
无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施
5.1 灭火介质
灭火方法及灭火剂
用水雾,耐醇泡沫,干粉或二氧化碳灭火。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害
碳氧化物, 氮氧化物
5.3 给消防员的建议
如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步信息
无数据资料
模块 6. 泄露应急处理
6.1 人员的预防,防护设备和紧急处理程序
使用个人防护设备。 防止粉尘的生成。 防止吸入蒸汽、气雾或气体。 保证充分的通风。
将人员撤离到安全区域。 避免吸入粉尘。
6.2 环境保护措施
不要让产物进入下水道。
6.3 抑制和清除溢出物的方法和材料
收集、处理泄漏物,不要产生灰尘。 扫掉和铲掉。 存放进适当的闭口容器中待处理。
6.4 参考其他部分
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
7.1 安全操作的注意事项
避免接触皮肤和眼睛。 防止粉尘和气溶胶生成。
在有粉尘生成的地方,提供合适的排风设备。一般性的防火保护措施。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性
贮存在阴凉处。 容器保持紧闭,储存在干燥通风处。
7.3 特定用途
无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
8.1 容许浓度
最高容许浓度
没有已知的国家规定的暴露极限。
8.2 暴露控制
适当的技术控制
按照良好工业和安全规范操作。 休息前和工作结束时洗手。
个体防护设备
眼/面保护
面罩與安全眼鏡请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟) 检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/EEC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
身体保护
全套防化学试剂工作服, 防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和含量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
如危险性评测显示需要使用空气净化的防毒面具,请使用全面罩式多功能微粒防毒面具N100型(US
)或P3型(EN
143)防毒面具筒作为工程控制的候补。如果防毒面具是保护的唯一方式,则使用全面罩式送风防毒
面具。 呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息
a) 外观与性状
形状: 固体
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味阈值
无数据资料
d) pH值
无数据资料
e) 熔点/凝固点
无数据资料
f) 起始沸点和沸程
无数据资料
g) 闪点
无数据资料
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 易燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 无数据资料
k) 蒸汽压
无数据资料
l) 蒸汽密度
无数据资料
m) 相对密度
无数据资料
n) 水溶性
无数据资料
o) n-辛醇/水分配系数
辛醇--水的分配系数的对数值: 1.869
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性
10.1 反应性
无数据资料
10.2 稳定性
无数据资料
10.3 危险反应的可能性
无数据资料
10.4 应避免的条件
无数据资料
10.5 不兼容的材料
氧化剂
10.6 危险的分解产物
其它分解产物 - 无数据资料
模块 11. 毒理学资料
11.1 毒理学影响的信息
急性毒性
无数据资料
皮肤刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
眼睛刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
无数据资料
生殖细胞突变性
无数据资料
致癌性
IARC:
此产品中没有大于或等于 0。1%含量的组分被 IARC鉴别为可能的或肯定的人类致癌物。
生殖毒性
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
吸入 - 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入可能有害。 引起呼吸道刺激。
摄入 误吞对人体有害。
皮肤 如果通过皮肤吸收可能是有害的。 造成皮肤刺激。
眼睛 引起眼睛烧伤。
接触后的征兆和症状
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: 无数据资料
模块 12. 生态学资料
12.1 生态毒性
无数据资料
12.2 持久存留性和降解性
无数据资料
12.3 潜在的生物蓄积性
无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移性
无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价
无数据资料
12.6 其它不利的影响
无数据资料
模块 13. 废弃处置
13.1 废物处理方法
产品
将剩余的和未回收的溶液交给处理公司。 联系专业的拥有废弃物处理执照的机构来处理此物质。
与易燃溶剂相溶或者相混合,在备有燃烧后处理和洗刷作用的化学焚化炉中燃烧
受污染的容器和包装
作为未用过的产品弃置。
模块 14. 运输信息
14.1 联合国危险货物编号
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.2 联合国(UN)规定的名称
欧洲陆运危规: 非危险货物
国际海运危规: 非危险货物
国际空运危规: 非危险货物
14.3 运输危险类别
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.4 包裹组
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.5 环境危险
欧洲陆运危规: 否 国际海运危规 海运污染物: 否 国际空运危规: 否
14.6 对使用者的特别提醒
无数据资料
模块 15 - 法规信息
N/A
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
上下游信息
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 N-[3,5-二[(二乙基氨基)甲基]-4-羟基苯基]乙酰胺 3',5'-Bis(diethylaminomethyl)-4'-hydroxy-acetanilid 81080-09-3 C18H31N3O2 321.463 4-氨基-Alpha-二乙胺基-O-甲苯酚 4-amino-2-((diethylamino)methyl)phenol 51387-92-9 C11H18N2O 194.277 —— 4-amino-2,6-bis(diethylaminomethyl)phenol 51388-09-1 C16H29N3O 279.426 —— N-(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-5-yl)acetamide 81926-25-2 C10H11NO2 177.203
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:氟取代对阿莫地喹的代谢和抗疟活性的影响。摘要:阿莫地喹(AQ)(2)是一种4-氨基喹啉抗疟药,可引起不良副作用,例如粒细胞缺乏症和肝损害。据信,观察到的药物毒性与亲电子代谢物氨二喹醌亚胺(AQQI)的形成有关,后者可以与细胞大分子结合并引发超敏反应。5'-氟氨二喹(5'-FAQ,3),5',6'-二氟氨二喹(5',6'-DIFAQ,4),2',6'-二氟氨二喹(2',6'-DIFAQ,5) ,2',5',6'-三氟嘧啶(2',5',6'-TRIFAQ,6)和4'-dehydroxy-4'-氟嘧啶(4'-deOH-4'-FAQ,7)合成以评估氟取代对阿莫地喹的氧化潜能,代谢和体外抗疟活性的影响。通过循环伏安法测量氧化电位,观察到在2',6'-和4'-位置的取代(2',6'-DIFAQ和4'-deOH-4'-FAQ)产生了类似物具有比母体药物明显更高的氧化电位。在2',6'-位和4'-位的氟取代也产生了对生物活化更具抗性的类似物。因此2'DOI:10.1021/jm00035a017
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:氨基烷基酚作为抗疟药(杂环氨基)-α-氨基-邻甲酚;迷彩的合成。摘要:DOI:10.1021/ja01184a023
文献信息
-
Discovery of a potent non-oxime reactivator of nerve agent inhibited human acetylcholinesterase作者:Martijn Constantijn de Koning、Gabriele Horn、Franz Worek、Marco van GrolDOI:10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.08.016日期:2018.9compounds that could reactivate OP-inhibited AChE. Recently, a number of non-oxime compounds was discovered in which the 4-amino-2-((diethylamino)methyl)phenol (ADOC) motif proved to be able to reactivate OP-inhibited AChE to some extent. In this paper several structural derivatives of ADOC were synthesized and screened for their ability to reactivate human AChE (hAChE) inhibited by the nerve agents有机磷(OP)化合物(例如神经毒剂)通过在酶活性部位的关键丝氨酸残基进行共价磷酸化来抑制乙酰胆碱酯酶(AChE),从而导致严重的症状并最终导致死亡。目前通过给予某些肟化合物来治疗OP中毒。目前获得的肟通过释放磷酸化的丝氨酸来重新激活OP抑制的AChE。最近对新型活化剂的研究主要致力于设计,合成和评估基于肟的新型化合物,这些化合物致力于克服一些主要局限性,例如其固有毒性,阻碍大脑组织渗透的永久电荷以及无法有效活化所有活性物质。类型的神经毒剂抑制了AChEs。然而,在超过六十年的研究中,仅取得了有限的成功,这表明需要能够重新激活OP抑制的AChE的其他类别的化合物。最近,发现了许多非肟化合物,其中4-氨基-2-((二乙基氨基)甲基)苯酚(ADOC)母题被证明能够在一定程度上重新激活OP抑制的AChE。在本文中,合成了ADOC的几种结构衍生物,并筛选了它们重新激活被神经毒剂VX,沙林,塔宾,环沙
-
Design, synthesis and structure–activity relationships of (1H-pyridin-4-ylidene)amines as potential antimalarials作者:Tiago Rodrigues、Rita C. Guedes、Daniel J.V.A. dos Santos、Marta Carrasco、Jiri Gut、Philip J. Rosenthal、Rui Moreira、Francisca LopesDOI:10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.05.017日期:2009.7(1H-Pyridin-4-ylidene)amines containing lipophilic side chains at the imine nitrogen atom were prepared as potential clopidol isosteres in the development of antimalarials. Their antiplasmodial activity was evaluated in vitro against the Plasmodium falciparum W2 (chloroquine-resistant) and FCR3 (atovaquone-resistant) strains. The most active of these derivatives, 4m, had an IC50 of 1 mu M against W2 and 3 mu M against FCR3. Molecular modeling studies suggest that (1H-pyridin-4-ylidene) amines may bind to the ubiquinol oxidation Q(o) site of cytochrome bc(1). (C) 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
-
Antiplasmodial imidazopyridazines: structure–activity relationship studies lead to the identification of analogues with improved solubility and hERG profiles作者:Peter Mubanga Cheuka、Nina Lawrence、Dale Taylor、Sergio Wittlin、Kelly ChibaleDOI:10.1039/c8md00382c日期:——shown to possess good in vitro antiplasmodial and in vivo antimalarial activity. However, frontrunner compounds have been associated with poor solubility and a hERG (human ether-a-go-go-related gene) inhibition liability raising concerns for potential cardiotoxicity risks. Herein, we report the synthesis and structure–activity relationship studies of new imidazopyridazines aimed at improving aqueous solubility3,6-二芳基化咪唑并哒嗪最近被证明具有良好的体外抗疟原虫和体内抗疟活性。然而,领先化合物的溶解度差和 hERG(人醚-a-go-go相关基因)抑制倾向引起人们对潜在心脏毒性风险的担忧。在此,我们报告了新型咪唑并哒嗪的合成和构效关系研究,旨在提高水溶性并对抗 hERG 抑制,同时保持抗疟原虫效力。虽然我们发现了具有有效抗疟原虫活性的新类似物(针对 NF54 药物敏感菌株的IC 50 = 0.031 μM,针对 K1 多重耐药菌株的IC 50 = 0.0246 μM),但 hERG 抑制仍然是一个问题。另一方面,令人兴奋的是,我们鉴定出了具有显着改善的 hERG 抑制谱(IC 50 = 7.83–32.3 μM)和亚微摩尔抗疟原虫活性(NF54,IC 50 = 0.151–0.922 μM)的新类似物。同样,引入的分子特征也产生了具有中等到高溶解度(60-200 μM)的类似物,同时还显示出亚微摩尔抗疟原虫效力(NF54,IC
-
Antimalarial Benzimidazole Derivatives Incorporating Phenolic Mannich Base Side Chains Inhibit Microtubule and Hemozoin Formation: Structure–Activity Relationship and <i>In Vivo</i> Oral Efficacy Studies作者:Godwin Akpeko Dziwornu、Dina Coertzen、Meta Leshabane、Constance M. Korkor、Cleavon K. Cloete、Mathew Njoroge、Liezl Gibhard、Nina Lawrence、Janette Reader、Mariëtte van der Watt、Sergio Wittlin、Lyn-Marie Birkholtz、Kelly ChibaleDOI:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00354日期:2021.4.22A novel series of antimalarial benzimidazole derivatives incorporating phenolic Mannich base side chains at the C2 position, which possess dual asexual blood and sexual stage activities, is presented. Structure–activity relationship studies revealed that the 1-benzylbenzimidazole analogues possessed submicromolar asexual blood and sexual stage activities in contrast to the 1H-benzimidazole analogues提出了一系列新的抗疟疾苯并咪唑衍生物,该衍生物在C2位上结合了酚类曼尼希碱侧链,具有无性血液和有性的双重活动。结构与活性之间的关系研究表明,与1 H-苯并咪唑类似物相比,1-苄基苯并咪唑类似物具有亚微摩尔无性血液和性阶段活动,而1 H-苯并咪唑类似物仅对无性血液阶段(ABS)寄生虫具有活性。此外,前者在ABS寄生虫中表现出微管抑制活性,但在II / III期配子细胞中表现出更显着的抑制作用。1 H-苯并咪唑类似物除了是血红蛋白形成的真正抑制剂外,还显示出对微管的抑制作用。体内对伯氏疟原虫感染的小鼠进行的功效研究表明,当以4×50 mg / kg口服给药时,领先的化合物41表现出很高的功效(寄生虫血症减少98%)。通常,该化合物对哺乳动物细胞无细胞毒性。
-
Aromatic amino analogues of artemisinin: synthesis and in vivo antimalarial activity作者:Dharmarajan Sriram、Ruth Vandana Devakaram、Murugesan Dinakaran、Perumal YogeeswariDOI:10.1007/s00044-009-9209-5日期:2010.7Nine orally active novel artemisinin derivatives were prepared from artemisinin by four-step synthesis, and the compounds were evaluated in the rodent model using multidrug resistant Plasmodium yoelii nigeriensis. All of the compounds exhibited antimalarial activities with the ED50 ranging from 5.41 mg/kg–12.4 mg/kg. Among them, artemisinin derivative bearing N-(4-hydroxy-3-((4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl)phenyl)
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
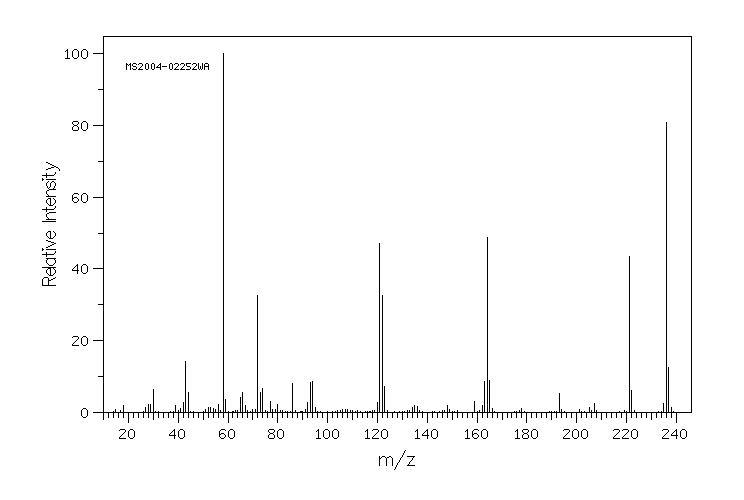
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
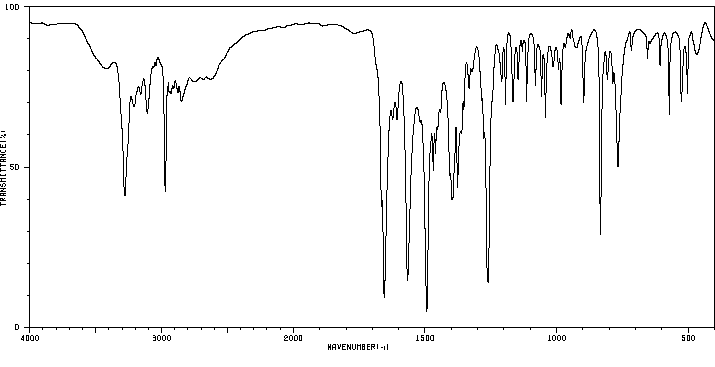
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(βS)-β-氨基-4-(4-羟基苯氧基)-3,5-二碘苯甲丙醇
(S,S)-邻甲苯基-DIPAMP
(S)-(-)-7'-〔4(S)-(苄基)恶唑-2-基]-7-二(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-2,2',3,3'-四氢-1,1-螺二氢茚
(S)-盐酸沙丁胺醇
(S)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧磷杂环戊二烯
(S)-2,2'-双[双(3,5-三氟甲基苯基)膦基]-4,4',6,6'-四甲氧基联苯
(S)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(R)富马酸托特罗定
(R)-(-)-盐酸尼古地平
(R)-(-)-4,12-双(二苯基膦基)[2.2]对环芳烷(1,5环辛二烯)铑(I)四氟硼酸盐
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[((6-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(4-叔丁基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(3-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-4,7-双(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-7“-[(吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2”,3,3'-四氢1,1'-螺二茚满
(R)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二苯氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂环戊烯
(R)-2-[((二苯基膦基)甲基]吡咯烷
(R)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(N-(4-甲氧基苯基)-N-甲基-3-(1-哌啶基)丙-2-烯酰胺)
(5-溴-2-羟基苯基)-4-氯苯甲酮
(5-溴-2-氯苯基)(4-羟基苯基)甲酮
(5-氧代-3-苯基-2,5-二氢-1,2,3,4-oxatriazol-3-鎓)
(4S,5R)-4-甲基-5-苯基-1,2,3-氧代噻唑烷-2,2-二氧化物-3-羧酸叔丁酯
(4S,4''S)-2,2''-亚环戊基双[4,5-二氢-4-(苯甲基)恶唑]
(4-溴苯基)-[2-氟-4-[6-[甲基(丙-2-烯基)氨基]己氧基]苯基]甲酮
(4-丁氧基苯甲基)三苯基溴化磷
(3aR,8aR)-(-)-4,4,8,8-四(3,5-二甲基苯基)四氢-2,2-二甲基-6-苯基-1,3-二氧戊环[4,5-e]二恶唑磷
(3aR,6aS)-5-氧代六氢环戊基[c]吡咯-2(1H)-羧酸酯
(2Z)-3-[[(4-氯苯基)氨基]-2-氰基丙烯酸乙酯
(2S,3S,5S)-5-(叔丁氧基甲酰氨基)-2-(N-5-噻唑基-甲氧羰基)氨基-1,6-二苯基-3-羟基己烷
(2S,2''S,3S,3''S)-3,3''-二叔丁基-4,4''-双(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-2,2''-联苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂戊环
(2S)-(-)-2-{[[[[3,5-双(氟代甲基)苯基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基}-N-(二苯基甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[((1S,2S)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[[((1R,2R)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2-硝基苯基)磷酸三酰胺
(2,6-二氯苯基)乙酰氯
(2,3-二甲氧基-5-甲基苯基)硼酸
(1S,2S,3S,5S)-5-叠氮基-3-(苯基甲氧基)-2-[(苯基甲氧基)甲基]环戊醇
(1S,2S,3R,5R)-2-(苄氧基)甲基-6-氧杂双环[3.1.0]己-3-醇
(1-(4-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(3-溴苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氯苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2,6-二氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(-)-去甲基西布曲明
龙蒿油
龙胆酸钠
龙胆酸叔丁酯
龙胆酸
龙胆紫-d6
龙胆紫