十四烷酰胺,N-羟基- | 17698-03-2
中文名称
十四烷酰胺,N-羟基-
中文别名
——
英文名称
n-dodecylacetohydroxamic acid
英文别名
tetradecanehydroxamic acid;myristohydroxamic acid;Myristohydroxamsaeure;tetradecanoic acid hydroxamide;Dodecylacetohydroxamsaeure;N-hydroxytetradecanamide
CAS
17698-03-2
化学式
C14H29NO2
mdl
——
分子量
243.39
InChiKey
XHKBEIYZVFBVAM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
沸点:386.26°C (rough estimate)
-
密度:0.9475 (rough estimate)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):4.5
-
重原子数:17
-
可旋转键数:12
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.93
-
拓扑面积:49.3
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:2
SDS
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Winternitz,F.; Wlotzka,C., Bulletin de la Societe Chimique de France, 1960, p. 509 - 515摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:由有吸引力的非共价相互作用控制的铱催化的对映选择性 C(sp3)-H 酰胺化摘要:尽管在过去十年中取得了显着进展,但在对映选择性 C(sp3)-H 官能化反应中手性催化剂的新设计策略仍然是非常需要的。特别是,使用有吸引力的非共价相互作用进行速率加速和对映控制的能力将显着扩展不对称金属催化的当前武器库。在此,我们报告了高对映选择性 Ir(III) 催化的二恶唑酮底物的分子内 C(sp3)-H 酰胺化反应的开发,该反应用于使用新设计的基于 α-氨基酸的手性配体合成光学富集的 γ-内酰胺。这种 Ir 催化的反应在非常温和的条件下以优异的效率进行,并对活化和未活化的烷基 C(sp3)-H 键具有出色的对映选择性。它为γ-烷基γ-内酰胺的不对称合成提供了第一条通用路线。发现水是一种独特的共溶剂,可在 γ-芳基内酰胺生产中实现出色的对映选择性。机理研究表明,配体在 Ir 中心周围形成了一个明确的凹槽型手性袋。该口袋的疏水作用允许在极性或水性介质中轻松立体控制底物结合。这种新的 IrDOI:10.1021/jacs.9b02811
文献信息
-
Studies of Collectors. IX. The Flotation of a Trace Amount of Uranium by Using 2-(Alkylamino)propionohydroxamic Acid and Cotelomer-Type Surfactants Bearing Hydroxyaminocarbonyl and Pyridyl Groups作者:Yoshifumi Koide、Masazumi Uchino、Kimiho YamadaDOI:10.1246/bcsj.60.3477日期:1987.10Chelating surfactants bearing hydroxyaminocarbonyl and amino groups (RnAHx) and cotelomer-type surfactants bearing hydroxyaminocarbonyl and pyridyl groups (Ls–VP–Q–Hx) were prepared and applied as flotation collectors for a trace amount of uranium. The uranium in an aqueous solution of pH 4–8 and in seawater was floated more effectively by ion flotation using RnAHx or by foam fractionation using Ls–VP–Q–Hx, compared with alkylhydroxamic acid (RnHx) and telomers bearing hydroxyaminocarbonyl groups (Lo–Hx). The effective flotation was concluded to be due to the chelate effects between the two groups on the complex formation and to the HLB of the resulting complex. Furthermore, the uranium recoveries were examined by using a hydroxamic acid polymer (62Hx), a N-methylhydroxamic acid telomer (Ls5.6MHx), and its cotelomer (Ls3.2VP4.5MHx).
-
Fatty acid analogs and their use in the treatment of conditions related to metabolic syndrome申请人:Epitracker, Inc.公开号:US10792266B2公开(公告)日:2020-10-06Compositions comprising fatty acid analogs are provided for treating metabolic syndrome, anemia, cancer, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, dyslipidemia, hypertension, inflammation, insulin resistance, prediabetes, fatty liver disease, steatohepatitis, iron overload, neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia, and other related conditions. Methods for the diagnosis and monitoring of metabolic syndrome and other conditions are also provided.
-
Inoue; Yukawa, Nippon Nogeikagaku Kaishi, 1940, vol. 16, p. 504作者:Inoue、YukawaDOI:——日期:——
-
KOIDE, YOSHIFUMI;UCHINO, MASAZUMI;YAMADA, KIMIHO, BULL. CHEM. SOC. JAP., 60,(1987) N 10, 3477-3483作者:KOIDE, YOSHIFUMI、UCHINO, MASAZUMI、YAMADA, KIMIHODOI:——日期:——
-
HAMILTON R. J.; MITCHELL S. F.; SEWELL P. A., J. CHROMATOGR., 395,(1987) 33-46作者:HAMILTON R. J.、 MITCHELL S. F.、 SEWELL P. A.DOI:——日期:——
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
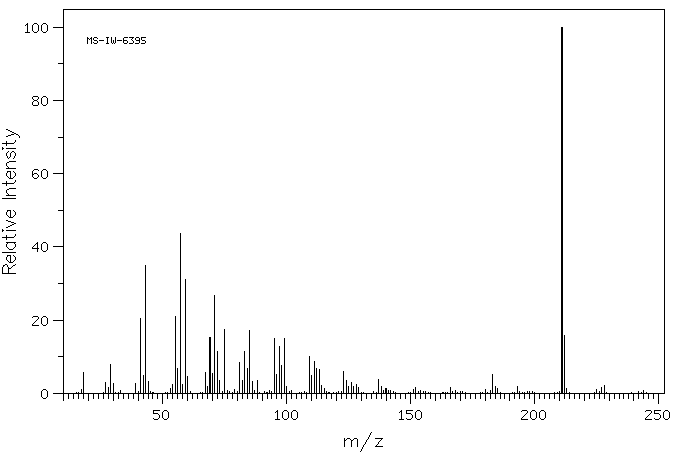
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
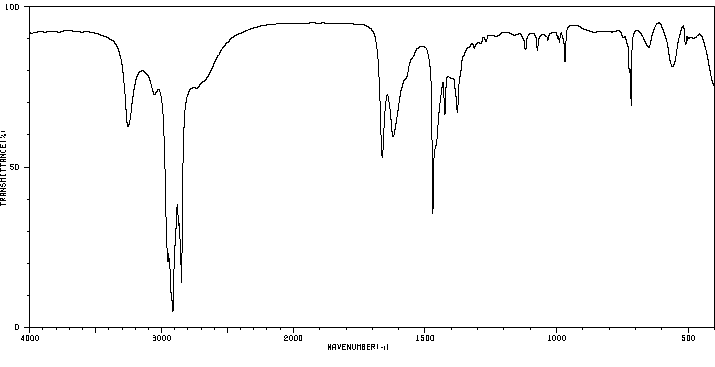
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(甲基3-(二甲基氨基)-2-苯基-2H-azirene-2-羧酸乙酯)
(±)-盐酸氯吡格雷
(±)-丙酰肉碱氯化物
(d(CH2)51,Tyr(Me)2,Arg8)-血管加压素
(S)-(+)-α-氨基-4-羧基-2-甲基苯乙酸
(S)-阿拉考特盐酸盐
(S)-赖诺普利-d5钠
(S)-2-氨基-5-氧代己酸,氢溴酸盐
(S)-2-[[[(1R,2R)-2-[[[3,5-双(叔丁基)-2-羟基苯基]亚甲基]氨基]环己基]硫脲基]-N-苄基-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(S)-2-[3-[(1R,2R)-2-(二丙基氨基)环己基]硫脲基]-N-异丙基-3,3-二甲基丁酰胺
(S)-1-(4-氨基氧基乙酰胺基苄基)乙二胺四乙酸
(S)-1-[N-[3-苯基-1-[(苯基甲氧基)羰基]丙基]-L-丙氨酰基]-L-脯氨酸
(R)-乙基N-甲酰基-N-(1-苯乙基)甘氨酸
(R)-丙酰肉碱-d3氯化物
(R)-4-N-Cbz-哌嗪-2-甲酸甲酯
(R)-3-氨基-2-苄基丙酸盐酸盐
(R)-1-(3-溴-2-甲基-1-氧丙基)-L-脯氨酸
(N-[(苄氧基)羰基]丙氨酰-N〜5〜-(diaminomethylidene)鸟氨酸)
(6-氯-2-吲哚基甲基)乙酰氨基丙二酸二乙酯
(4R)-N-亚硝基噻唑烷-4-羧酸
(3R)-1-噻-4-氮杂螺[4.4]壬烷-3-羧酸
(3-硝基-1H-1,2,4-三唑-1-基)乙酸乙酯
(2S,4R)-Boc-4-环己基-吡咯烷-2-羧酸
(2S,3S,5S)-2-氨基-3-羟基-1,6-二苯己烷-5-N-氨基甲酰基-L-缬氨酸
(2S,3S)-3-((S)-1-((1-(4-氟苯基)-1H-1,2,3-三唑-4-基)-甲基氨基)-1-氧-3-(噻唑-4-基)丙-2-基氨基甲酰基)-环氧乙烷-2-羧酸
(2S)-2,6-二氨基-N-[4-(5-氟-1,3-苯并噻唑-2-基)-2-甲基苯基]己酰胺二盐酸盐
(2S)-2-氨基-N,3,3-三甲基-N-(苯甲基)丁酰胺
(2S)-2-氨基-3-甲基-N-2-吡啶基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-(苯基甲基)丁酰胺,
(2S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-2-吡啶基丁酰胺
(2S,4R)-1-((S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基丁酰基)-4-羟基-N-(4-(4-甲基噻唑-5-基)苄基)吡咯烷-2-甲酰胺盐酸盐
(2R,3'S)苯那普利叔丁基酯d5
(2R)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-(苯甲基)丁酰胺
(2-氯丙烯基)草酰氯
(1S,3S,5S)-2-Boc-2-氮杂双环[3.1.0]己烷-3-羧酸
(1R,5R,6R)-5-(1-乙基丙氧基)-7-氧杂双环[4.1.0]庚-3-烯-3-羧酸乙基酯
(1R,4R,5S,6R)-4-氨基-2-氧杂双环[3.1.0]己烷-4,6-二羧酸
齐特巴坦
齐德巴坦钠盐
齐墩果-12-烯-28-酸,2,3-二羟基-,苯基甲基酯,(2a,3a)-
齐墩果-12-烯-28-酸,2,3-二羟基-,羧基甲基酯,(2a,3b)-(9CI)
黄酮-8-乙酸二甲氨基乙基酯
黄荧菌素
黄体生成激素释放激素(1-6)
黄体生成激素释放激素 (1-5) 酰肼
黄体瑞林
麦醇溶蛋白
麦角硫因
麦芽聚糖六乙酸酯
麦根酸